Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Os Isotopic Characteristics of Middle Silurian Volcanic Rocks in Northwest of the Xiemisitai Mountains, West Junggar and Its Tectonic Implications
-
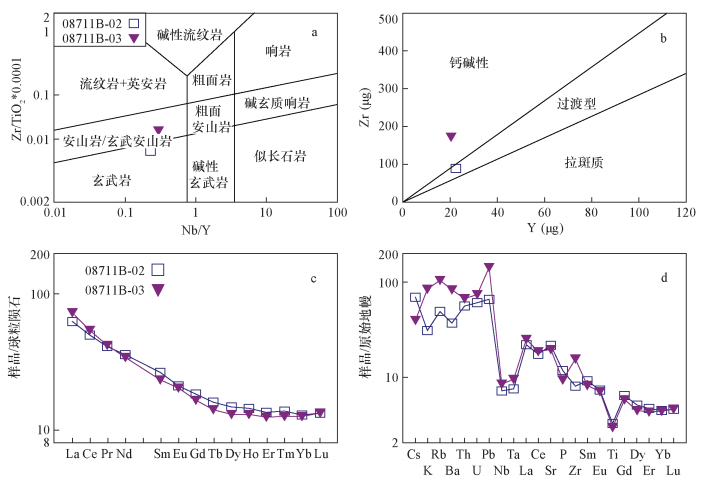
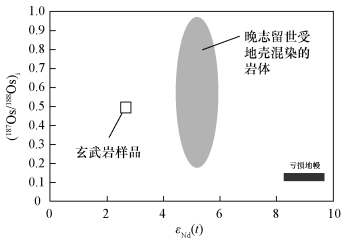
摘要: 西准噶尔谢米斯台山火山岩近期报道形成于志留纪而非之前认为的中泥盆世,但有关中志留世火山岩特征及构造意义研究较弱。本文对西准噶尔谢米斯台山西北段乌兰浩特中志留世玄武岩、玄武安山岩样品进行了系统的地球化学主量、微量元素与Sr-Nd-Os同位素特征分析。火山岩样品表现出高MgO(5.15%~7.81%)、镁值(56.0~60.7)和低CaO(4.56%~5.09%)、FeOT/MgO(1.15~1.40)的特征,属于高镁火山岩类。玄武岩的εNd(t)值为+2.65,87Sr/86Sr和187Os/188Os初始比值分别为0.70439和0.4901。略显富集的同位素比值与高Th/Yb值(2.2~2.7)、低Ba/La值(17.4~33.4)表明其可能是受洋底沉积物熔体交代地幔部分熔融的产物,并遭受了一定程度地壳混染。火山岩样品为钙碱性,具有轻稀土和大离子亲石元素富集、Nb和Ta亏损等弧岩浆特征,推测乌兰浩特中志留世火山岩形成于与准噶尔洋板片由南向北俯冲有关的弧后环境。
-
关键词:
- 中志留世 /
- 火山岩 /
- Sr-Nd-Os同位素 /
- 弧后 /
- 西准噶尔
Abstract: Volcanic rocks in the Xiemisitai Mountains, in Northwest Junggar were recently considered to form in the Silurian rather than the Devonian period. However, the characteristic and tectonic setting of Middle Silurian volcanic rocks in this area are poorly constrained. In this study, major and trace elements and Sr-Nd-Os isotopic composition analyses were synthetically conducted on the Middle Silurian basalt and basaltic andesite in northwest of the Xiemisitai Mountains, West Junggar. These volcanic samples are characterized by high MgO (5.15%-7.81%) with Mg of 56.0-60.7, low CaO (4.56%-5.09%) and FeOT/MgO (1.15-1.40), similar to those of high-Mg volcanic rocks. Basalts have εNd(t) of 2.65, (87Sr/86Sr)i of 0.70439, and (187Os/188Os)i of 0.4901. The slightly enriched isotopic signatures, high Th/Yb (2.2-2.7) and low Ba/La (17.4-33.4) indicate that they originated from depleted mantle metasomatized by melts from subducted sediments and suffered from crustal contamination. The volcanic rocks are calc-alkaline and exhibit arc-like geochemistry with the enrichment of light REE and large ion lithophile elements. It is suggested that these rocks were probably formed in a back-arc setting due to northward subduction of the Junggar Oceanic slab.-
Key words:
- Middle Silurian /
- volcanic rocks /
- Sr-Nd-Os isotopes /
- back-arc /
- West Junggar
-

-
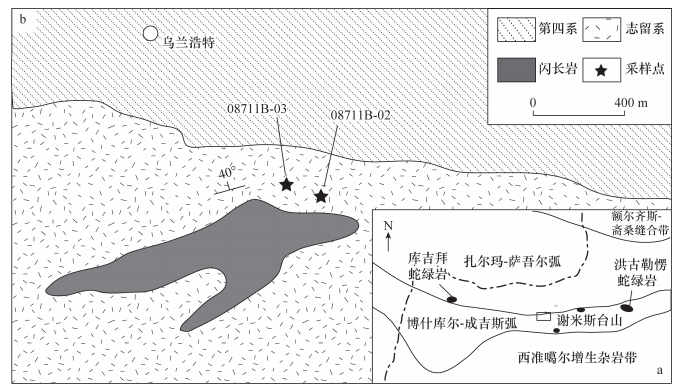
图 1 谢米斯台山西北段地质简图与采样点位置(修改自Chen等[5])
Figure 1.
图 4 玄武岩样品的Nd-Os同位素比值图(晚志留世受地壳混染的岩体数据据Chen等[5])
Figure 4.
表 1 火山岩的主要氧化物测试结果(单位为%)
Table 1. Major oxides compositions (%) of volcanic rocks
元素 玄武岩
(08711B-02)玄武安山岩
(08711B-03)SiO2 50.83 56.23 TiO2 0.704 0.634 Al2O3 16.49 15.43 Fe2O3T 10.00 8.00 MnO 0.135 0.148 MgO 7.81 5.15 CaO 4.56 5.09 Na2O 3.75 3.78 K2O 0.94 2.55 P2O5 0.255 0.203 LOI 4.41 2.65 总计 99.88 99.86 表 2 火山岩的微量元素和稀土元素含量(单位为μg/g)测试结果
Table 2. Compositions of trace elements and rare earth elements (μg/g) of volcanic rocks
元素 玄武岩
08711B-02)玄武安山岩
(08711B-03)Li 28.9 12.9 Be 1.1 1.33 Sc 24.1 22 V 218 168 Cr 8.93 36.1 Co 26 20.3 Ni 9.48 18.6 Cu 64.9 75.1 Zn 79.7 81.5 Ga 18 16.3 Ge 1.25 1.18 Rb 31.2 67 Sr 455 411 Y 22.3 20.4 Zr 89.4 173 Nb 5.09 6.02 Cs 2.24 1.27 Ba 261 578 La 15 17.3 Ce 30.7 33.2 Pr 3.92 4.01 Nd 16.7 16 Sm 4.06 3.59 Eu 1.22 1.18 Gd 3.77 3.42 Tb 0.6 0.53 Dy 3.74 3.29 Ho 0.82 0.74 Er 2.23 2.06 Tm 0.35 0.32 Yb 2.18 2.14 Lu 0.34 0.34 Hf 2.25 3.72 Ta 0.31 0.39 Pb 12.3 26.7 Th 4.78 5.72 U 1.28 1.56 表 3 火山岩样品08711B-02的同位素比值测试结果
Table 3. The isotopic data of the volcanic rock sample No.08711B-02
-
[1] Chen J F, Han B F, Ji J Q, et al.Zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications of paleozoic plutons in northern West Junggar, north Xinjiang, China[J].Lithos, 2010, 115:137-152. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.11.014
[2] 孟磊, 申萍, 沈远超, 等.新疆谢米斯台中段火山岩岩石地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(10):3047-3056. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201010016.htm
Meng L, Shen P, Shen Y C, et al.Igneous rocks geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and its geological significance in the central section of Xiemisitai area, Xinjiang[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(10):3047-3056. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201010016.htm
[3] Shen P, Shen Y C, Li X H, et al.Northwestern Junggar basin, Xiemisitai mountains, China:A geochemical and geochronological approach[J].Lithos, 2012, 140-141:103-108. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.004
[4] Yang G X, Li Y J, Xiao W J, et al.Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the middle silurian volcanic rocks in northern West Junggar, NW China[J].International Geology Review, 2014, 56:869-884. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.905214
[5] Chen J F, Han B F, Zhang L, et al.Middle paleozoic initial amalgamation and crustal growth in the West Junggar (NW China):Constraints from geochronology, geochem-istry and Sr-Nd-Hf-Os isotopes of calc-alkaline and alkaline intrusions in the Xiemisitai-Saier Mountains[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113:90-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.028
[6] Han B F, Wang S G, Jahn B M.Depleted-mantle source for the Ulungur River A-type granites from north Xinjiang, China:Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence, and implications for phanerozoic crustal growth[J].Chemical Geology, 1997, 138:135-159. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00003-X
[7] Chen B, Jahn B M.Genesis of post-collisional granitoids and basement nature of the Junggar terrane, NW China:Nd-Sr isotope and trace element evidence[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23:691-703. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00118-4
[8] 史仁灯, 支霞臣, 陈雷, 等.Re-Os同位素体系在蛇绿岩应用研究中的进展[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(6):1685-1695. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200606025.htm
Shi R D, Zhi X C, Chen L, et al.Comments on the progress on the applications of Re-Os isotopic study on the ophiolites[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(6):1685-1695. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200606025.htm
[9] Chen B, Jahn B M, Suzuki K.Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os isotopic constraints on the origin of high-Mg adakitic rocks from the North China Craton:Tectonic implications[J].Geology, 2013, 41:91-94. doi: 10.1130/G33472.1
[10] Han B F, Guo Z J, Zhang Z C, et al.Age, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of a late paleozoic stitching pluton in the north Tian Shan suture zone, Western China[J].Geological Society of American Bulletin, 2010, 122:627-640. doi: 10.1130/B26491.1
[11] Xiao W J, Huang B C, Han C M, et al.A review of the western part of the Altaids:A key to understanding the architecture of accretionary orogens[J].Gondwana Research, 2010, 18:253-273. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.01.007
[12] Zhu Y F, Chen B, Xu X, et al.A new geological map of the western Junggar, north Xinjiang (NW China):Implications for paleoenvironmental reconstruction[J].Episodes, 2013, 36:205-220. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279621962_A_new_geological_map_of_the_western_Junggar_north_Xinjiang_NW_China_Implications_for_Paleoenvironmental_reconstruction
[13] Yin J, Chen W, Xiao W J, et al.Late silurian-early devonian adakitic granodiorite, A-type and Ⅰ-type granites in NW Junggar, NW China:Partial melting of mafic lower crust and implications for slab roll-back[J].Gondwana Research, 2015, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.016. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.016
[14] 孙勇, 李永军, 杨高学, 等.西准噶尔谢米斯台山西缘中志留世火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及构造意义[J].新疆地质, 2015, 33(1):27-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201501006.htm
Sun Y, Li Y J, Yang G X, et al.Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and tectonic settings implication of the middle silurian volcanic rocks in the west of Xiemisitai mountain, west Junggar[J].Xinjiang Geology, 2015, 33(1):27-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201501006.htm
[15] Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C.Determination of trace elem-ents in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2000, 51:507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
[16] 贾双琳, 赵平, 杨刚, 等.混合酸敞开或高压密闭溶样-ICPMS测定地质样品中稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(2):186-191. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201402006.htm
Jia S L, Zhao P, Yang G, et al.Quick determination of rare earth elements in geological samples with open acid digestion or high-pressure closed digestion by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(2):186-191. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201402006.htm
[17] 何学贤, 唐索寒, 朱祥坤, 等.多接收器等离子体质谱(MC-ICPMS)高精度测定Nd同位素方法[J].地球学报, 2007, 28(4):405-410. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200704012.htm
He X X, Tang S H, Zhu X K, et al.Precise measurement of Nd isotopic ratios by means of multi-collector magnetic sector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2007, 28(4):405-410. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200704012.htm
[18] 唐索寒, 李津, 梁细荣, 等.钕同位素比值143Nd/144Nd标准溶液研制[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(2):176-183. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170211&flag=1
Tang S H, Li J, Liang X R, et al.Reference material preparation of 143Nd/144Nd isotope ratio[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(2):176-183. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170211&flag=1
[19] 李超, 杨雪, 赵鸿, 等.pg-ng级Os同位素热表明电离质谱高精度分析测试技术[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(4):392-398. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150403&flag=1
Li C, Yang X, Zhao H, et al.High precise isotopic measurements of pg-ng Os by negative ion thermal ionization mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(4):392-398. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150403&flag=1
[20] Kelemen P B.Genesis of high Mg# andesites and the continental crust[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 120:1-19. doi: 10.1007/BF00311004
[21] Tatsumi Y.Geochemical modeling of patial melting of subducting sediments and subsequent melt-mantle interaction:Generation of high-Mg andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, Southwest Japan[J].Geology, 2001, 29:323-326. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0323:GMOPMO>2.0.CO;2
[22] Ma X H, Cao R, Zhou Z H, et al.Early cretaceous high-Mg diorites in the Yanji area, Northeastern China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97:393-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.010
[23] 王明梁, 唐红峰.英云闪长质熔体与地幔橄榄石反应的实验研究——对克拉通内部高镁安山岩成因的约束[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2014, 44:405-413. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201403002.htm
Wang M L, Tang H F.Reaction experiments between tonalitic melt and mantle olivine and their implications for genesis of high-Mg andesites within cratons[J].Science China:Earth Sciences, 2014, 44:405-413. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201403002.htm
[24] Kamei A, Owada M, Nagao T, et al.High-Mg diorites derived from Sanukitic HMA magmas, Kyushu Island, Southwest Japan Arc:Evidence from clinopyroxene and whole rock compositions[J].Lithosphere, 2004, 75:359-371. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449370400057X
[25] Ma X, Chen B, Chen J F, et al.Petrogenesis and geodynamic significance of the late palaeozoic Dongwanzi complex, North China Craton:Constraints from petrological, geochemical, and Os-Nd-Sr isotopic data[J].International Geology Review, 2014, 56:1521-1540. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.948082
[26] Chesley J, Righter K, Ruiz J.Large scale mantle metaso-matism:A Re-Os perspective[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219:49-60. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00698-8
[27] Ren R, Han B F, Guan S W, et al.Linking the southern West Junggar terrane to the Yili block:Insights from the oldest accretionary complexes in West Junggar, NW China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences (2017), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.03.011.
[28] Liu B, Han B F, Xu Z, et al.The cambrian initiation of intra-oceanic subduction in the southern Paleo-Asian Ocean:Further evidence from the Barleik subduction-related metamorphic complex in the West Junggar region, NW China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 123:1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.03.015
[29] 杨刚, 肖龙, 王国灿, 等.西准噶尔谢米斯台西段花岗岩年代学、地球化学、锆石Lu-Hf同位素特征及大地构造意义[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(3):548-562. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201503014.htm
Yang G, Xiao L, Wang G C, et al.Geochronology, geochemistry and zircon Lu-Hf study of granites in western section of Xiemisitai area, western Junggar[J].Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(3):548-562. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201503014.htm
[30] 纵瑞文, 龚一鸣, 韩非.新疆额敏东部志留纪化石的发现及其地质意义[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(3):563-572. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201503015.htm
Zong R W, Gong Y M, Han F.Discovery of silurian fossils and its geological significance in eastern Ermin, Xinjiang of NW China[J].Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(3):563-572. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201503015.htm
-



 下载:
下载: