Micro-morphology and Mineral Composition of Different Color Qinghai Nephrites
-
摘要: 青海软玉颜色丰富,近年来对青海软玉矿物学的研究不少,但针对不同颜色青海软玉矿物学特征的研究还存在欠缺。本文利用偏光显微镜、扫描电子显微镜、电子探针及粉晶X射线衍射仪器,从透闪石微形貌特征、微观结构、矿物组成及结晶度四个方面,研究了青海软玉颜色与矿物学特征的对应关系。结果表明:白玉、烟青玉、糖玉中透闪石主要为纤维状,显微纤维变晶结构,结晶度为96.12%~96.88%;青白玉和翠青玉中透闪石主要为叶片状,显微叶片变晶结构,结晶度为97.35%,97.32%;青玉和碧玉中透闪石主要为叶片状,显微叶片-隐晶质变晶结构,结晶度为95.48%,95.29%;黄玉中透闪石主要为柱状,显微柱状变晶结构,结晶度为97.84%。青海软玉主要组成矿物均为透闪石,含量在95%以上,部分次要矿物如翠青玉中的榍石、黄玉中的钙长石、青玉中的菱镁矿、碧玉中的铬铁矿、糖玉中的斜黝帘石只出现在特定颜色的青海软玉样品中。研究认为不同颜色青海软玉矿物学特征确实存在差异,这些特征为研究不同颜色青海软玉成矿环境及成矿条件提供了科学依据。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDQinghai nephrites show different colors. In recent years, there have been a lot of studies on Qinghai nephrite mineralogy, but the studies on the mineral characteristics of Qinghai nephrite with different colors are lacking. OBJECTIVESTo study the relationship between color and mineralogical features of Qinghai nephrites. METHODSPolarizing Microscopy, Scanning Electron Microscopy, Electron Probe Microanalyzer and Powder X-ray Diffraction were used to analyze the microtopography, microstructure, mineral composition and crystallinity of tremolite. RESULTSTremolite in white, blue-violet and brown Qinghai nephrite are mainly fibrous and have micro-fiber blastic texture with crystallinity of 96.12%-96.88%. Tremolite in green-white and viridis Qinghai nephrite are mainly foliated, and has micro-foliated blastic texture with crystallinity of 97.35% and 97.32%, respectively. Tremolite in green and azure-green Qinghai nephrite are mainly foliated, and have microscopic blade-cryptocrystalline blastic texture with crystallinity of 95.48% and 95.29%, respectively. Tremolite in yellow Qinghai nephrite is mainly columnar, and has micro-columnar blastic texture and crystallinity of 97.84%. The main mineral different color Qinghai nephrite is tremolite, with content of more than 95%. Some minor minerals only appear in the specific color Qinghai nephrite, such as titanite in viridis Qinghai nephrite, anorthite in yellow Qinghai nephrite, magnesite in green Qinghai nephrite, chromite in azure-green Qinghai nephrite, and clinozoisite in brown Qinghai nephrite. CONCLUSIONSThere are differences in mineral features of Qinghai nephrite in different colors, which provide a scientific basis for the study of ore-forming environments and conditions of Qinghai nephrites in different colors. -
Key words:
- nephrite /
- color /
- tremolite /
- blastic texture /
- crystallinity
-
青海软玉具有良好的透明度和非常丰富的颜色,除了白色系列外,还包括绿色、棕色、黄色、紫色等颜色,其中特有的品种为翠绿玉和烟青玉。对青海软玉矿物学方面的研究始于2004年。在矿物组成方面,冯晓燕等[1]提出青海软玉透闪石含量多在90%~95%,次要矿物为透辉石、方解石及白云石等。李冉等[2]认为青海软玉的主要矿物成分是透闪石,次要矿物为透辉石、方解石、白云石、硅灰石等。以上研究只是作了客观陈述,未有图片和数据证明资料。汤红云等[3]利用偏光显微镜下矿物的光学特征,说明了青海软玉的主要矿物组成是透闪石,其质量分数多数大于99%,杂质矿物质量分数多数小于1%,主要有磷灰石、白云石、绿帘石、黏土矿物、铁质、黄铁矿、铬铁矿(碧玉)。在软玉微形貌和微观结构研究方面,普遍认为透闪石多呈长柱状、针状、纤维状、微细纤维状;主要结构类型有毛毡状结构、显微纤维-隐晶质结构、显微纤维结构、显微叶片状-隐晶质结构、显微叶片状结构和放射状纤维结构[3-6]。青海软玉中水线的主要矿物为透闪石, 且含量更高、结晶度更好,显微镜和扫描电镜下观察水线与主体部分呈突变接触,水线中的透闪石晶体为细长纤维,具有明显的定向性[7-8]。青海软玉的结晶度普遍较高,平均值为96%[4],主要致色元素为Fe2+、Fe3+、Mn、Cr、Ti[9-10]。前人的研究结果,对青海软玉矿物组成缺乏矿物成分测试数据,对青海软玉的微形貌、微观结构和结晶度研究仅限于共性的研究,而对不同颜色的青海软玉之间矿物学特征的区别并未涉及。 透闪石的形态及排列方式不同,导致了不同颜色青海软玉光泽和透明度不同;其组成矿物的不同,说明了不同的物质来源和成矿环境。本文利用偏光显微镜、扫描电镜、电子探针及X射线衍射仪,从微形貌、微观结构、矿物组成方面,研究不同颜色青海软玉样品的矿物学特征上的差异,尤其是在矿物组成方面的不同进行探究,为宝石鉴定和成矿研究奠定基础。 1. 实验部分
1.1 样品及产地
样品白玉、青白玉、翠青玉和烟青玉采集于纳赤台三岔河玉矿,黄玉和碧玉来自大(小)灶火玉矿,糖玉、糖包青和糖包白玉来自托拉海(野牛沟)玉矿,碧玉来自青海省内门源县祁连山段(图 1)。三岔口矿点样品于2014年在矿点实地采集,托拉海和大灶火矿点样品购买于青海格尔木市场,已通过颜色和质地鉴定,确定样品产地。1.2 样品处理
在宝石显微镜下观察样品,选择颜色纯正,质地纯净的部分,进行切割,磨成光薄片和探针片。剩余产品,通过敲击,形成新鲜断口,在扫描电镜下观察微形貌。根据岩矿薄片鉴定结果,选择透闪石含量在95%以上的样品,将其磨成200目粉末状,并加热到100℃恒温24 h干燥,然后置于干燥器中冷却至室温,进行X射线衍射测试。1.3 分析方法
(1) 微观形貌及微观结构分析:在南京大学内生金属矿床国家重点实验室采用Hitachi公司的S-3500N型扫描电镜进行微观形貌的测试。测试条件:加速电压为3~15 kV,照像分辩率为15 nm,室温20℃,微观形貌的观察放大倍数都为10000X。利用南京大学内生金属矿床国家重点实验室偏光显微镜观察青海样品的结构及构造特征。 (2) 主要矿物及次要矿物分析:在南京大学内生金属矿床国家重点实验室采用JEOL JXA-8100型电子探针对不同颜色青海软玉光薄片样品进行背散射电子成像观察以及矿物成分分析。仪器工作条件:室温20℃,加速电压15 kV,加速电流20 nA,束斑直径 < 1 μm。 (3) 晶胞参数及结晶度分析:在南京大学现代分析中心采用瑞士ARL公司的X′TRA型X射线衍射仪进行测试。测试样品在玛瑙研钵中研磨成200目,样品质量在200 mg以上,扫描角度为5°~75°,扫描步长为0.02°,扫描速度10°/min,测试温度为室温。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 不同颜色青海软玉的微观形貌特征
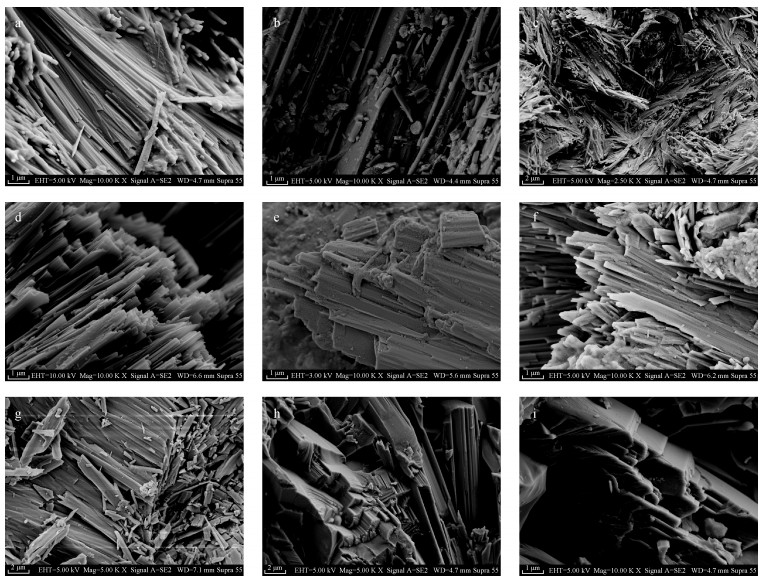
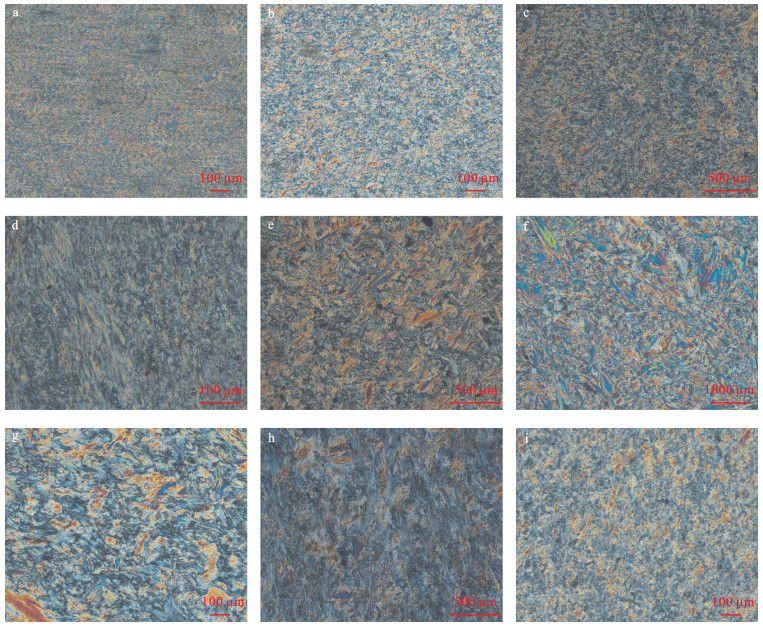
扫描电镜下不同颜色青海软玉的微观形貌观察发现,青海软玉中的透闪石主要呈纤维状、叶片状、柱状,定向性较好,与前人对青海软玉研究成果基本相同[1, 5]。不同之处在于,本次研究发现,不同颜色青海软玉样品中,透闪石的形态及排列方式并不相同,主要体现如下。 (1) 纤维状透闪石:主要出现在白玉、糖玉、烟青玉样品中。白玉的纤维状透闪石直径小于0.1 μm,定向性好,排列比较紧密(图 2a);烟青玉中纤维状透闪石直径在0.2 μm左右,定向性比较好,排列紧密(图 2b);糖玉中纤维状透闪石直径与白玉相差不大(图 2c),但长短不一,大小不等,排列方向杂乱无章,相互穿插且镶嵌紧密。(2) 叶片状透闪石:主要出现在翠青玉、青白玉、青玉、碧玉样品中。叶片状透闪石宽度一般小于0.5 μm,定向性变化较大。翠青玉(图 2d)和青白玉(图 2e)中,叶片状透闪石排列非常紧密,定向性也比较好。青玉(图 2f)和碧玉(图 2g)中,叶片状透闪石排列不够紧密,接近于平行排列,结构不够致密。 (3) 柱状透闪石:只在黄玉样品中发现。柱状透闪石的半径在1 μm左右,排列紧密,定向性较好,柱面解理发育(图 2h,i)。2.2 不同颜色青海软玉的微观结构特征
镜下观察发现,青海软玉基本上属于变晶结构,主要包括纤维交织变晶结构、显微叶片变晶结构、显微纤维变晶结构、显微柱状变晶结构、显微叶片-隐晶质变晶结构,与前人研究成果基本相同[6, 8]。不同之处在于,不同颜色青海软玉样品的微观结构特征存在不同,主要体现如下。 (1) 纤维交织变晶结构 纤维交织变晶结构在青海软玉中非常罕见,仅见于糖包白中白玉、糖包青中青白玉的结构中。偏光显微镜下,透闪石呈短纤维状,长度一般小于10 μm。正交偏光显微镜下,透闪石干涉色为Ⅰ级灰白-黄白(图 3a)。纤维状透闪石排列方向不一致,但相互穿插且镶嵌紧密、结构致密,透明度降低,油脂光泽非常好,接近于籽料。 (2) 显微纤维变晶结构 显微纤维变晶结构在青海白玉、糖玉和烟青玉样品中比较常见。该结构中的透闪石呈长纤维状,长度一般在100~200 μm之间,断口较为平坦。正交偏光显微镜下,透闪石干涉色为Ⅰ级黄白-Ⅱ蓝绿(图 3b,c,d)。透闪石平行排列,排列比较紧密,因而结构比较致密,透明度较高,油脂-蜡状光泽。 (3) 显微叶片状变晶结构 显微叶片状变晶结构在青白玉和翠青玉样品中比较常见。该结构中的透闪石呈叶片状,长度在100 μm左右,断口较为平坦,断面平直。正交偏光显微镜下,透闪石干涉色为Ⅰ级黄白-Ⅱ蓝绿(图 3e,f)。叶片状透闪石排列非常紧密,定向性比较好,导致翠青玉和青白玉的透明度较高,而叶片状的透闪石对光的反射明显强于纤维状透闪石,因而光泽增强,蜡状-半玻璃光泽。 (4) 显微叶片-隐晶质变晶结构 显微叶片-隐晶质变晶结构在青玉和碧玉样品中比较常见。该结构中的透闪石呈叶片状,长度在100 μm左右,断口为参差状。正交偏光显微镜下,透闪石干涉色为Ⅱ蓝绿(图 3g,h)。叶片状透闪石排列比较疏松,接近于平行排列,结构不够致密,透明度比较低,光泽也较暗。 (5) 显微柱状变晶结构 显微柱状变晶结构仅出现在黄玉样品中。该结构中的透闪石呈柱状,长度在100~200 μm之间,断口为平坦状。正交偏光显微镜下,透闪石干涉色为Ⅰ级黄白~Ⅱ蓝绿(图 3i)。柱状透闪石排列不够紧密,定向性较好,柱面解理发育。由于柱状透闪石间存在的空隙较大,因此透射光增强,透明度提高,为微透明-半透明。而柱面积的增大,使得单位面积中反射光的数量增多,光泽变强,呈蜡状-半玻璃光泽。2.3 不同颜色青海软玉中的主要矿物及次要矿物
电子探针测试结果显示,8种颜色的青海软玉主要矿物组成为透闪石,含量在95%以上。次要矿物主要有透辉石、方解石、榍石、斜黝帘石、蛇纹石、磁铁矿、菱镁石、绿泥石、钙长石。与前人研究成果[6, 9-10]不同之处在于黄玉中发现钙长石,糖玉中发现斜黝帘石,翠青玉中发现榍石,未发现硅灰石、磷灰石、黄铁矿。 (1) 透闪石 不同颜色青海软玉的透闪石中,SiO2(55.37%~59.54%)、MgO(20.45%~24.37%)、CaO(13.30%~14.05%),与透闪石的理论值(分别为58.18%、24.16%和13.18%)相比偏低,这与M1、M2、M3、M4位置上的离子置换有关。 (2) 透辉石 透辉石主要出现在青白玉、翠青玉和黄玉样品中,其产出形态主要有两种:一种是早期形成的透辉石,晶粒较大,多为自形晶,通过后期的交代作用,早期形成的透辉石被透闪石交代,如图 4a所示,透闪石穿插在透辉石中;另一种透辉石与透闪石伴生,呈质点状,主要出现在碧玉中,FeO含量(4.64%)明显高于第一种透辉石(表 1),可能与超镁铁岩的组成有密切的关系[11](图 4b)。(3) 方解石 方解石主要出现在白玉、糖玉和烟青玉样品中,一般位于矿体的中央带,主要有两种形式:一种自形程度比较好,粒径小于200 μm,呈独立的矿物形式散布在软玉矿体中,主要为软玉成矿过程中的产物(图 4c);另一种形式为片状自形方解石,呈细脉状产生(图 4d)。这两种方解石与透闪石同时成矿,其中CaO含量在55.20%~55.93%之间(表 1),非常接近方解石的理论值56%,说明成矿温度比较低[12]。 (4) 榍石 榍石仅发现于翠青玉样品中,比较少见,有时与透辉石共生(图 4f)。榍石外形为不规则状,粒径一般都小于200 μm(图 4f)。翠青玉(如图 4e中的透辉石-2)的Cr2O3含量(0.32%)与MgO含量(17.94%)明显高于表 1中透辉石-1的Cr2O3(0.01%)与MgO含量(15.19%)(表 1)。此外,翠青玉中的榍石,高钛无环带结构(图 4f),为典型的热液榍石,说明后期的成矿热液可能与基性岩浆岩有关[13]。 (5) 斜黝帘石 斜黝帘石仅出现在糖玉样品中,比较少见。斜黝帘石边缘比较规则,呈长条形,长轴一般小于200 μm,短轴小于50 μm。斜黝帘石-1上残留有斜黝帘石-2(图 4g),而斜黝帘石-1中FeO含量(5.75%)明显高于斜黝帘石-2中FeO含量(0.28%,表 1),说明蚀变热液富含Fe[14-15]。 (6) 蛇纹石 蛇纹石主要出现在青玉和碧玉样品中,呈现两种形式:一种呈现为晶粒较大,自形程度较好,被透闪石穿插交代(图 4h),说明早于透闪石形成的矿物;另一种呈基质形式与透闪石混杂在一起(图 4i),主要为早期形成的蛇纹石,后期继续被热液交代而形成透闪石。如表 1数据所示,第一种蛇纹石的Al2O3含量(0.14%)明显低于第二种蛇纹石的Al2O3含量(4.56%),说明了不同的成矿来源[16]。 (7) 磁铁矿和菱镁矿 磁铁矿主要出现在青玉样品中,呈质点状散布在矿体中,在局部位置比较集中(图 4i)。菱镁矿仅出现在青玉样品中,晶型不完整。两种矿物的粒径一般都小于200 μm(图 4i),主要为交代过程中的产物。透闪石穿插在磁铁矿中,说明磁铁矿的形成时间早于透闪石。而菱镁矿呈独立晶型存在,说明与透闪石同时成矿。菱镁矿中MgO含量(39.96%)明显低于其理论值(47.81%),FeO含量(5.80%)明显偏高(表 1),说明可能由富铁矿物蚀变而来。磁铁矿中FeO含量(92.43%,表 1)也说明这一点[17]。 (8) 铬铁矿和绿泥石 铬铁矿和绿泥石仅出现在碧玉样品中(表 1,图 4j, k),绿泥石中SiO2含量为33.44%,MgO含量为23.14%,Al2O3含量为19.89%,为叶绿泥石[18]。铬铁矿中Cr2O3含量为59.83%,低于铬铁矿中Cr2O3的标准值,说明铬铁矿形成于富含铁的环境[19]。 (9) 钙长石 钙长石仅出现在黄玉样品中,呈片状,长轴方向小于100 μm,宽度小于20 μm。钙长石在黄玉样品中以两种形式存在:一种为独立的晶型(钙长石-1,图 4l),说明与透闪石同时成矿;另外一种被透闪石穿插(钙长石-2,图 4l),说明早于透闪石成矿。由表 1中的数据,钙长石-1中Si、Ca、Al含量(SiO2 40.08%, CaO 24.04%,Al2O3 34.33%)与钙长石理论值(SiO2 43.20%,CaO 20.10%,Al2O3 36.70%)比较,CaO偏高。而钙长石-2中Si、Ca、Al含量(SiO2 43.79%,CaO 19.58%,Al2O3 35.42%)与理论值非常接近,说明早期形成的钙长石成矿环境为基性岩环境[20]。表 1. 不同颜色青海软玉矿物电子探针数据Table 1. Electron probe data of minerals in different colors Qinghai nephrite by EPMA样品 矿物组成 SiO2
(%)MgO
(%)CaO
(%)Al2O3
(%)FeO
(%)MnO
(%)TiO2
(%)K2O
(%)Na2O
(%)Cr2O3
(%)含量
(%)矿物 白玉 主要矿物 59.19 23.93 13.99 0.61 0.30 0.05 0.01 0.01 0.06 0.00 98.15 透闪石 次要矿物 0.02 0.17 55.93 0.00 0.03 0.12 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.01 56.33 方解石 0.07 0.08 0.00 0.02 92.08 0.02 0.04 0.00 0.03 0.05 92.39 磁铁矿 烟青玉 主要矿物 58.22 23.74 13.67 0.89 0.41 0.09 0.01 0.04 0.02 0.02 97.11 透闪石 次要矿物 0.00 0.09 55.54 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.00 55.73 方解石 糖玉 主要矿物 59.40 23.90 13.85 0.08 0.15 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.00 97.47 透闪石 次要矿物 0.00 0.08 55.20 0.00 0.04 0.08 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 55.43 方解石 38.53 0.45 23.68 28.26 5.75 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.06 0.00 96.82 斜黝帘石-1 39.20 0.47 24.74 32.50 0.28 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 97.21 斜黝帘石-2 青白玉 主要矿物 59.54 24.37 13.50 0.13 0.09 0.00 0.01 0.03 0.06 0.02 97.75 透闪石 次要矿物 54.34 17.54 24.17 2.53 0.43 0.03 0.09 0.00 0.32 0.00 99.46 透辉石 黄玉 主要矿物 58.17 23.92 14.05 1.78 0.40 0.03 0.00 0.07 0.17 0.00 98.59 透闪石 54.94 16.26 24.56 2.74 0.69 0.03 0.00 0.03 0.50 0.02 99.77 透辉石 次要矿物 40.08 0.06 24.04 34.33 0.73 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.00 0.00 99.31 钙长石-1 43.79 0.03 19.58 35.42 0.28 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.01 99.17 钙长石-2 翠青玉 主要矿物 58.64 23.79 13.80 0.26 0.73 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.05 0.02 97.36 透闪石 54.67 15.19 25.63 0.96 2.91 0.08 0.27 0.00 0.14 0.01 99.85 透辉石-1 次要矿物 54.09 17.94 25.27 0.01 1.93 0.05 0.01 0.00 0.07 0.32 99.68 透辉石-2 30.75 0.08 27.32 2.36 1.31 0.04 37.24 0.01 0.01 0.03 99.15 榍石 青玉 主要矿物 55.91 20.45 13.30 0.96 5.45 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 96..27 透闪石 0.05 39.96 0.09 0.04 5.80 0.44 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.00 46.43 菱镁矿 次要矿物 0.46 0.35 0.00 0.00 92.43 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.32 93.63 磁铁矿 45.17 36.71 0.09 0.14 6.88 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.03 89.07 蛇纹石 碧玉 主要矿物 55.37 21.72 13.49 1.33 3.22 0.03 0.01 0.03 0.03 0.09 95..32 透闪石 42.35 35.08 0.05 4.56 5.38 0.01 0.07 0.00 0.02 0.03 87.55 蛇纹石 53.88 13.90 20.98 3.60 4.64 0.12 0.01 0.00 0.44 0.11 97.68 透辉石 次要矿物 33.44 23.14 0.56 19.89 8.76 0.45 0.10 0.14 0.28 0.01 86.77 绿泥石 0.05 1.00 0.00 3.12 33.85 0.83 0.06 0.00 0.04 59.83 98.78 铬铁矿 2.4 晶胞参数及结晶度
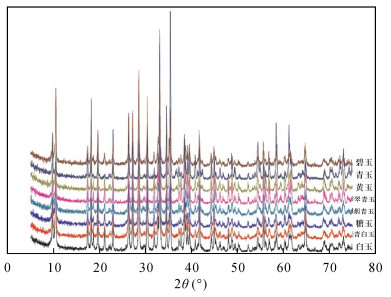
8种颜色青海软玉样品的XRD谱图基本相似(图 5),其主要特征谱线为:8.423~8.451 (110)、3.381~3.388 (131)、3.276~3.281 (240)、3.125~3.130(310)、2.706~2.709 (151)、2.017~2.109 (351),晶胞参数a0为9.499~9.917, b0为18.047~18.506, c0为5.287~5.569, β为103.83~104.98(表 2),与JADE衍射标准谱图库中透闪石(99-0105)的XRD谱图基本一致[21-22],说明了青海软玉的主要矿物组成为透闪石。同时,8种颜色青海软玉的XRD谱图中,除了透闪石特征谱线外,其他次要矿物的谱线几乎没有检出,说明青海软玉中透闪石的含量比较高,这与偏光显微镜和电子探针观察结果相符合。测试结果显示,8种颜色青海软玉的XRD谱图多集中在10°~43°,根据衍射峰强度与背景强度的比值的大小,利用下列公式估算结晶度(C):表 2. 不同颜色青海软玉晶面间距、晶胞参数和结晶度Table 2. Interplanar distance, unite cell parameters and crystallinity of Qinghai nephrites with different colors by XRD样品 d(110) d(131) d(240) d(310) d(151) d(351) a0 b0 c0 β C(%) 白玉 8.423 3.381 3.276 3.125 2.707 2.017 9.879 18.049 5.289 104.97 96.65 糖玉 8.435 3.383 3.278 3.127 2.707 2.017 9.902 18.068 5.387 104.86 96.12 烟青玉 8.436 3.386 3.278 3.127 2.709 2.017 9.808 18.047 5.337 103.83 96.88 青白玉 8.435 3.383 3.276 3.127 2.706 2.017 9.861 18.057 5.287 104.69 97.35 翠青玉 8.451 3.386 3.281 3.130 2.709 2.018 9.809 18.072 5.466 104.51 97.32 黄玉 8.434 3.388 3.276 3.125 2.707 2.017 9.917 18.064 5.366 104.98 97.84 碧玉 8.450 3.386 3.281 3.129 2.709 2.108 9.499 18.506 5.569 104.43 95.29 青玉 8.449 3.388 3.281 3.129 2.709 2.019 9.654 18.495 5.428 104.76 95.48 数据平均值 8.436 3.471 3.277 3.128 2.772 2.028 9.814 18.096 5.397 104.60 96.81 透闪石 8.377 3.373 3.268 3.119 2.700 2.013 9.818 18.047 5.275 104.79 - 式中:Pi为第i个衍射峰的强度;Bi为第i个衍射峰的背景强度。 计算结果显示, 青海软玉结晶度平均值为96.81%(表 2),结晶度比较高。其中显微柱状变晶结构的黄玉结晶度最高为97.84%,显微纤维变晶结构的青白玉和翠青玉结晶度次高,为97.35%~97.32%;显微纤维变晶结构的白玉、烟青玉和糖玉结晶度较高,为96.12%~96.88%;显微叶片-隐晶质变晶结构的青玉和碧玉结晶度最低,为95.48%~95.29%。C=∑Pi/(∑Pi+∑Bi) 3. 结论
不同颜色的青海软玉成矿作用及来源不同,导致其矿物学特征存在不同。本研究表明,不同颜色青海软玉中透闪石形态主要为叶片状(青白玉、翠青玉、青玉、碧玉);柱状(黄玉);纤维状(白玉、糖玉、烟青玉)。在黄玉(柱状)和翠青玉(片状)中发现高温矿物钙长石和榍石[23]; 在青玉(片状)、碧玉(片状)、白玉(纤维状)、糖玉(纤维状)、烟青玉(纤维状)中发现中~低温矿物菱镁矿、绿泥石和方解石[23],说明青海软玉中透闪石的形态与成矿温度关系不是正相关关系。 青海软玉主要为变晶结构,是原岩在流体影响下重结晶而成。矿物的结晶度与成矿温度、压力和次要元素的含量有关,一般随着温度的升高、压力的降低、杂质离子的减少而升高[24]。不同颜色青海软玉结晶度由黄玉→翠青玉→青白玉→烟青玉→白玉→糖玉依次降低,次要矿物组成表明结晶度的变化与成矿温度降低有关。而青玉(Fe:5.45%)和碧玉(Fe:3.32%)较低的结晶度与Fe含量增加有关。白玉、烟青玉和糖玉中自形程度较好、成分较纯的方解石,翠青玉和黄玉中穿插交代的透辉石,青玉样品中Al2O3含量(0.14%)很低的蛇纹石,碧玉中粒状分布的铬铁矿,说明了不同颜色的青海软玉对应着不同的成矿过程。致谢
- 本工作得到了本人博士生导师南京大学王汝成教授的帮助,桂林理工大学张良钜教授给予的指导和建议,在此一并表示衷心的感谢!
要点
- (1) 对比了不同颜色青海软玉微观形貌和矿物组成。
- (2) 揭示了不同颜色青海软玉微观结构在结晶度上的差异。
- (3) 发现不同颜色青海软玉矿物学特征的差异与成矿条件及成矿来源有关。
HIGHLIGHTS
- (1) Micromorphology and mineral compositions of different color Qinghai nephrites were compared.
- (2) Differences in crystallinity of microstructure and for different color Qinghai nephrites were revealed.
- (3) It was found that the differences in mineral features of different color Qinghai nephrites were related to the ore-forming conditions and sources.
-
表 1 不同颜色青海软玉矿物电子探针数据
Table 1. Electron probe data of minerals in different colors Qinghai nephrite by EPMA
样品 矿物组成 SiO2
(%)MgO
(%)CaO
(%)Al2O3
(%)FeO
(%)MnO
(%)TiO2
(%)K2O
(%)Na2O
(%)Cr2O3
(%)含量
(%)矿物 白玉 主要矿物 59.19 23.93 13.99 0.61 0.30 0.05 0.01 0.01 0.06 0.00 98.15 透闪石 次要矿物 0.02 0.17 55.93 0.00 0.03 0.12 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.01 56.33 方解石 0.07 0.08 0.00 0.02 92.08 0.02 0.04 0.00 0.03 0.05 92.39 磁铁矿 烟青玉 主要矿物 58.22 23.74 13.67 0.89 0.41 0.09 0.01 0.04 0.02 0.02 97.11 透闪石 次要矿物 0.00 0.09 55.54 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.00 55.73 方解石 糖玉 主要矿物 59.40 23.90 13.85 0.08 0.15 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.00 97.47 透闪石 次要矿物 0.00 0.08 55.20 0.00 0.04 0.08 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 55.43 方解石 38.53 0.45 23.68 28.26 5.75 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.06 0.00 96.82 斜黝帘石-1 39.20 0.47 24.74 32.50 0.28 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 97.21 斜黝帘石-2 青白玉 主要矿物 59.54 24.37 13.50 0.13 0.09 0.00 0.01 0.03 0.06 0.02 97.75 透闪石 次要矿物 54.34 17.54 24.17 2.53 0.43 0.03 0.09 0.00 0.32 0.00 99.46 透辉石 黄玉 主要矿物 58.17 23.92 14.05 1.78 0.40 0.03 0.00 0.07 0.17 0.00 98.59 透闪石 54.94 16.26 24.56 2.74 0.69 0.03 0.00 0.03 0.50 0.02 99.77 透辉石 次要矿物 40.08 0.06 24.04 34.33 0.73 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.00 0.00 99.31 钙长石-1 43.79 0.03 19.58 35.42 0.28 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.01 99.17 钙长石-2 翠青玉 主要矿物 58.64 23.79 13.80 0.26 0.73 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.05 0.02 97.36 透闪石 54.67 15.19 25.63 0.96 2.91 0.08 0.27 0.00 0.14 0.01 99.85 透辉石-1 次要矿物 54.09 17.94 25.27 0.01 1.93 0.05 0.01 0.00 0.07 0.32 99.68 透辉石-2 30.75 0.08 27.32 2.36 1.31 0.04 37.24 0.01 0.01 0.03 99.15 榍石 青玉 主要矿物 55.91 20.45 13.30 0.96 5.45 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 96..27 透闪石 0.05 39.96 0.09 0.04 5.80 0.44 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.00 46.43 菱镁矿 次要矿物 0.46 0.35 0.00 0.00 92.43 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.32 93.63 磁铁矿 45.17 36.71 0.09 0.14 6.88 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.03 89.07 蛇纹石 碧玉 主要矿物 55.37 21.72 13.49 1.33 3.22 0.03 0.01 0.03 0.03 0.09 95..32 透闪石 42.35 35.08 0.05 4.56 5.38 0.01 0.07 0.00 0.02 0.03 87.55 蛇纹石 53.88 13.90 20.98 3.60 4.64 0.12 0.01 0.00 0.44 0.11 97.68 透辉石 次要矿物 33.44 23.14 0.56 19.89 8.76 0.45 0.10 0.14 0.28 0.01 86.77 绿泥石 0.05 1.00 0.00 3.12 33.85 0.83 0.06 0.00 0.04 59.83 98.78 铬铁矿 表 2 不同颜色青海软玉晶面间距、晶胞参数和结晶度
Table 2. Interplanar distance, unite cell parameters and crystallinity of Qinghai nephrites with different colors by XRD
样品 d(110) d(131) d(240) d(310) d(151) d(351) a0 b0 c0 β C(%) 白玉 8.423 3.381 3.276 3.125 2.707 2.017 9.879 18.049 5.289 104.97 96.65 糖玉 8.435 3.383 3.278 3.127 2.707 2.017 9.902 18.068 5.387 104.86 96.12 烟青玉 8.436 3.386 3.278 3.127 2.709 2.017 9.808 18.047 5.337 103.83 96.88 青白玉 8.435 3.383 3.276 3.127 2.706 2.017 9.861 18.057 5.287 104.69 97.35 翠青玉 8.451 3.386 3.281 3.130 2.709 2.018 9.809 18.072 5.466 104.51 97.32 黄玉 8.434 3.388 3.276 3.125 2.707 2.017 9.917 18.064 5.366 104.98 97.84 碧玉 8.450 3.386 3.281 3.129 2.709 2.108 9.499 18.506 5.569 104.43 95.29 青玉 8.449 3.388 3.281 3.129 2.709 2.019 9.654 18.495 5.428 104.76 95.48 数据平均值 8.436 3.471 3.277 3.128 2.772 2.028 9.814 18.096 5.397 104.60 96.81 透闪石 8.377 3.373 3.268 3.119 2.700 2.013 9.818 18.047 5.275 104.79 - -
[1] 冯晓燕, 张蓓莉.青海软玉的成分及结构特征[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2004, 6(4):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2004.04.002
Feng X Y, Zhang B L.Study on compositions and texture characteristics of nephrite from Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2004, 6(4):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2004.04.002
[2] 李冉, 廖宗廷, 李玉加, 等.青海软玉中硅灰石的确定及其意义[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2004, 6(1):17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2004.01.005
Li R, Liao Z T, Li Y J, et al. Wollastonite in Qinghai nephrite jade and its significance[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2004, 6(1):17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2004.01.005
[3] 汤红云, 钱伟吉, 陆晓颖, 等.青海软玉产出的地质特征及物质成分特征[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2012, 14(1):24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2012.01.006
Tang H Y, Qian W J, Lu X Y, et al.Geological and composition feature of nephrite from Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2012, 14(1):24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2012.01.006
[4] 周征宇, 廖宗廷, 陈盈, 等.青海软玉的岩石矿物学特征[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(1):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.01.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080108
Zhou Z Y, Liao Z T, Chen Y, et al.Petrological and mineralogical characteristics of Qinghai nephrite[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(1):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.01.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080108
[5] 李云峰, 高敏, 王悠然.青海软玉的宝玉石学特征及成因分析[J].现代矿业, 2014, 28(3):54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2014.03.016
Li Y F, Gao M, Wang Y R.The characteristics and genetic analysis of nephrite in Qinghai Province[J]. Modern Mining, 2014, 28(3):54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2014.03.016
[6] Yu H Y, Wang R C, Guo J C, et al.Study of the minerogenetic mechanism and origin of Qinghai nephrite from Golmud, Qinghai, Northwest China[J]. Science in China(Earth Sciences), 2016, 59(8):1597-1609. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-0231-8
[7] 周征宇, 廖宗廷, 袁媛, 等.青海软玉中"水线"的特征及其成因探讨[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2005, 7(3):10-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2005.03.003
Zhou Z Y, Liao Z T, Yuan Y, et al.Study on characteristics and genesis of 'water line' in Qinghai nephrite jade[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2005, 7(3):10-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2005.03.003
[8] 袁媛, 廖宗廷, 周征宇.青海软玉水线的物相分析和微观形貌研究[J].上海地质, 2005(4):68-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2005.04.019
Yuan Y, Liao Z T, Zhou Z Y.Study on compositions and micro-textures of water-line in nephrite from Qinghai Province[J]. Shanghai Geology, 2005(4):68-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2005.04.019
[9] 刘虹靓, 杨明星, 杨天翔, 等.青海翠青玉的宝石学特征及颜色研究[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2013, 15(1):7-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2013.01.002
Liu H L, Yang M X, Yang T X, et al.Study on colour and gemmological characteristics of viridis nephrite from Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2013, 15(1):7-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2013.01.002
[10] Yu H Y, Wang R C, Guo J C, et al.Color-inducing elements and mechanisms in nephrites from Golmud, Qinghai, NW China:Insights from spectroscopic and compositional analyses[J]. Journal of Mineralogical & Petrological Sciences, 2016, 59:1597-1609. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016JMPeS.111..313Y
[11] Chen J B, Zeng Z G.Metasomatism of the peridotites from Southern Mariana fore-arc:Trace element characteristics of clinopyroxene and amphibole[J]. Science in China(Earth Sciences), 2007, 50(7):1005-1012. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0023-y
[12] Liu Y, Deng J, Shi G H, et al.Geochemistry and petrology of nephrite from Alamas, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42(3):440-451. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.05.012
[13] 王汝成, 谢磊, 陈骏, 等.南岭中段花岗岩中榍石对锡成矿能力的指示意义[J].高校地质学报, 2011, 17(3):368-380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2011.03.002
Wang R C, Xie L, Chen J, et al.Titanite as an indicator mineral of tin mineralizing potential of granites in the Middle Nanling Range[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2011, 17(3):368-380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2011.03.002
[14] 赵文俞, 牟善斌, 秦麟卿, 等.木兰山蓝片岩中斜黝帘石-低铁绿帘石连生体的确定[J].岩矿测试, 2002, 21(1):29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2002.01.006 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/c5c3f106-7b20-4a88-a49e-eb06454da6bb
Zhao W Y, Mou S B, Qin L Q, et al.Determination of fine intergrowth of low-Fe epidote and clinoepidote in the glaucophane schist from Mulan mountain by electron probe microanalysis and optical microscopy[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2002, 21(1):29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2002.01.006 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/c5c3f106-7b20-4a88-a49e-eb06454da6bb
[15] Bocchio R, Diella V, Adamo I, et al.Mineralogical characterization of the gem-variety pink clinozoisite from Val Malenco, Central Alps, Italy[J]. Rendiconti Lincei, 2017, 28:1-9.
[16] 王永亚, 干福熹.广西陆川蛇纹石玉的岩相结构及成矿机理[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(5):788-793. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.05.006 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/c5c3f106-7b20-4a88-a49e-eb06454da6bb
Wang Y Y, Gan F X.Mineral structure and mineralization mechanism of serpentine jade from Luchuan, Guangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(5):788-793. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.05.006 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/c5c3f106-7b20-4a88-a49e-eb06454da6bb
[17] 吕书君, 杨富全, 柴凤梅, 等.新疆准噶尔北缘托斯巴斯套铁铜金矿床矽卡岩和磁铁矿矿物学特征及其地质意义[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(3):510-521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.03.027 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/91a4e16f-fcdd-41db-bbbf-a88e5fe3a88c
Lü S J, Yang F Q, Chai F M, et al.Mineralogical characteristics of skarn in Tuosibasitao iron-copper-gold deposits of the northern margin of Junggar, Xinjiang, and their geological significance[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(3):510-521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.03.027 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/91a4e16f-fcdd-41db-bbbf-a88e5fe3a88c
[18] Lacroix B, Charpentier D, Buatier M, et al.Formation of chlorite during thrust fault reactivation.Record of fluid origin and P-T conditions in the Monte Perdido thrust fault (Southern Pyrenees)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2012, 163(6):1083-1102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=db1a5d67097f4ea047ad3fdf805a3541
[19] 李立兴, 朱明玉, 方同明, 等.应用电子探针技术研究北京密云放马峪铬铁矿床成因-来自含铬尖晶石矿物化学的证据[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5):600-608. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.05.017
Li L X, Zhu M Y, Fang T M, et al.Origin of the Fangmayu chromite deposit, Miyun, Beijing:Constraints from electron microprobe analyses of Cr-spinel[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5):600-608. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.05.017
[20] 包鲁明, 谭劲, 池召坤, 等.透辉石-钙长石体系熔体在不同过冷条件下晶体生长研究[J].矿物岩石, 2009, 29(3):17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2009.03.004
Bao L M, Tan J, Chi Z K, et al.Crystal growth of diopside-anorthite melting system under different undercooking condition[J]. Acta Petrological and Mineralogical, 2009, 29(3):17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2009.03.004
[21] Gottschalk M, Andrut M, Melzer S.The determination of the cummingtonite content of synthetic tremolite[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 1999, 11(11):967-982. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0023&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F09603123.2018.1453051&key=10.1127%2Fejm%2F11%2F6%2F0967
[22] Paolo B, Giovanni B A, Girolamo B.Crystal chemical and structural characterization of fibrous tremolite from Susa Valley, Italy, with comments on potential harmful effects on human health[J]. American Mineralogist, 2008, 93(8-9):1349-1355. doi: 10.2138/am.2008.2869
[23] 梁祥济.中国矽卡岩和矽卡岩矿床形成机理的实验研究[M].北京:学苑出版社, 2000:152-186.
Liang X J.Experimntal Studies on the Mechanism of the Formation of Skarns and Skarn Ore Deposits in China[M]. Beijing:Academy Press, 2000:152-186.
[24] 何明跃, 王濮.石英的结晶度指数及其标型意义[J].矿物岩石, 1994, 14(3):22-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400670508
He M Y, Wang P.The crystallinity of quartz and its typomorphic significance[J]. Minerals and Rocks, 1994, 14(3):22-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400670508
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 陶隆凤,郝楠楠,金翠玲,史淼,韩秀丽. 青海野牛沟软玉的宝石矿物学及谱学特征. 光谱学与光谱分析. 2024(11): 3165-3171 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蓝叶,于海燕,阮青锋,沙鑫,易泽邦,杨育富. 透闪石玉成矿研究现状与展望. 桂林理工大学学报. 2022(01): 55-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 崔中良,黄怡祯,郭心雨. 闪石玉研究进展的文献计量学分析. 宝石和宝石学杂志(中英文). 2022(05): 155-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郝楠楠,陶隆凤,王宁,张凯成. 青海野牛沟透闪石玉的谱学特征及颜色成因分析. 河北地质大学学报. 2021(06): 11-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱亚杰. 不同产地碧玉的鉴别特征. 中国宝玉石. 2020(03): 73-79+54 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 于海燕,贾宗勇,雷威. 中国软玉的稀土元素地球化学特征及影响因素研究. 现代矿业. 2019(03): 13-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘喜锋,贾玉衡,刘琰. 新疆若羌—且末戈壁料软玉的地球化学特征及成因类型研究. 岩矿测试. 2019(03): 316-325 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)
-






 下载:
下载: