Effects of Anions and pH on the Determination of Diclofenac in Water Solutions by High Performance Liquid Chromatography
-
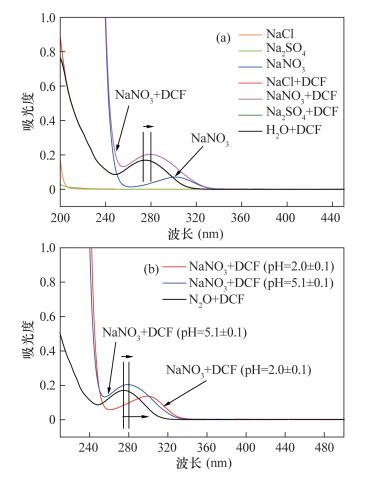
摘要: 双氯芬酸(DCF)是一种常用的非甾体消炎药,随着生产量和使用量的不断增大,其在环境中被频繁检出。DCF能在生物体内富集,对生物具有潜在毒性,已经引起了广大学者的关注。DCF的准确定量是开展其相关研究的基础,在应用液相色谱测试DCF的过程中,通常通过前处理消除样品基质干扰,但关于基质如何干扰DCF测量并没有详细研究。为了满足野外及实验室测试需要,本文针对高效液相色谱-紫外检测DCF过程中,水体中常见的阴离子SO42-、Cl-和NO3-,液相色谱流动相组成和水样pH对DCF准确定量的影响展开研究。结果表明:① SO42-和Cl-对DCF的最大吸收波长(277 nm)没有影响,但是NO3-的存在会使DCF的最大吸收峰发生偏移,产生红移现象,并且使吸光度略微增大;②同等条件下,在酸性介质(pH < 5)中DCF的定量结果比在碱性介质中的低。与碱性介质(pH=7.26)中DCF的峰面积相比,样品在pH=2.01的酸性介质中测得的峰面积减少73.14%,因此在碱性条件下DCF定量更为准确。Abstract: Diclofenac (DCF) is one of the widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. With the increased production and consumption, DCF is frequently detected in the environment. DCF can be enriched in organisms and has potential toxicity to several organisms, causing much concern. The accuracy determination of DCF is the basis for other studies. In a previous study, pretreatment methods were always used to eliminate matrix effects during the measurement of DCF, but how the sample matrix influences DCF measurement was not studied in details. In order to meet the need of field sample measurement and laboratory research, the effects of common anions SO42-, Cl- and NO3-, solution pH, and mobile phase constitutions on the determination of DCF using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with the UV-Vis detector (HPLC-UV) were investigated. The results show that SO42- and Cl- had no effect on the maximum absorption wavelength of DCF (277 nm), but NO3- changed the maximum absorption wavelength of DCF (277 nm) and resulted in the red shift phenomenon. Under the same condition, the measured concentration of DCF by HPLC in acidic medium (pH < 5) was lower than that in an alkaline medium. Comparing with the peak area of DCF in alkaline medium (pH=7.26), the peak area of DCF in acidic medium (pH=2.01) decreased by 73.14%. Therefore, determination of DCF under alkaline conditions has greater accuracy.
-
Key words:
- water environments /
- diclofenac /
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography /
- anions /
- pH /
- mobile phase
-

-
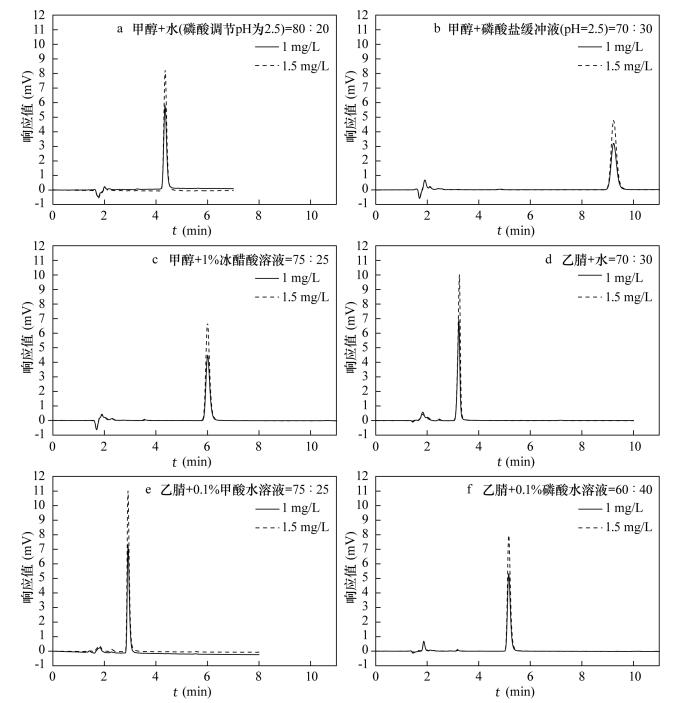
表 1 不同流动相体系下DCF的色谱峰的特点
Table 1. Characteristics of chromatographic peak of DCF in different mobile phases
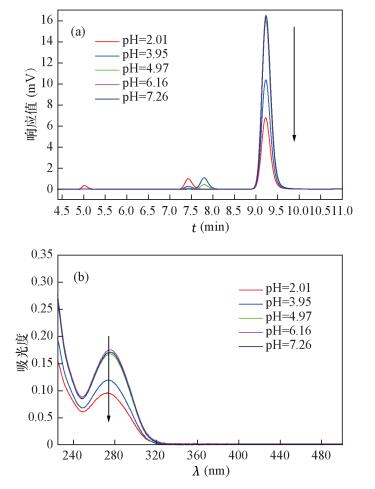
流动相体系 1.0 mg/L 1.5 mg/L 出峰时间 峰面积 峰高 容量因子(k’) 出峰时间 峰面积 峰高 容量因子(k’) 甲醇+水(磷酸调节pH=2.5)=80:20 4.348 45895 5681 1.898 4.352 67706 8309 1.685 甲醇+磷酸盐缓冲液(pH =2.5)=70:30 9.227 47942 3178 4.901 9.229 71853 4769 4.824 甲醇+1%冰醋酸水溶液=75:25 6.004 48223 4475 2.153 5.999 72287 6711 2.152 乙腈+水=70:30 3.223 45100 6885 1.061 3.243 67807 10012 1.064 乙腈+0.1%甲酸水=75:25 2.915 44858 7327 0.594 2.912 67669 11044 0.594 乙腈+0.1%磷酸水溶液=60:40 5.158 44227 5306 1.774 5.159 66662 7966 2.125 表 2 不同pH条件下DCF峰面积和吸光度
Table 2. The peak area and absorbance of DCF in different pH condition
测量参数 pH=2.01 pH=3.95 pH=4.97 pH=6.16 pH=7.26 峰面积 66478 156485 240641 249095 247508 吸光度(277 nm) 0.096 0.09 0.174 0.174 0.173 -
[1] Vieno N, Sillanpää M.Fate of diclofenac in municipal wastewater treatment plant-A review[J].Environment International, 2014, 69:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.03.021
[2] Scheurell M, Franke S, Shah R M, et al.Occurrence of diclofenac and its metabolites in surface water and effluent samples from Karachi, Pakistan[J].Chemosphere, 2009, 77(6):870-876. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.066
[3] Balakrishna K, Rath A, Praveenkumarreddy Y, et al.A review of the occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Indian water bodies[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 137:113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.014
[4] López-Serna R, Jurado A, Vázquez-Suňé E, et al.Occurrence of 95 pharmaceuticals and transformation products in urban groundwaters underlying the metropolis of Barcelona, Spain[J].Environmental Pollution, 2013, 174:305-315. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.022
[5] Carmona E, Andreu V, Picó Y.Occurrence of acidic pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Turia River Basin:From waste to drinking water[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 484:53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.085
[6] 温智皓, 段艳平, 孟祥周, 等.城市污水处理厂及其受纳水体中5种典型PPCPs的赋存特征和生态风险[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(3):927-932. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hjkz201303016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Wen Z H, Duan Y P, Meng X Z, et al.Occurrence and risk assessment of five selected PPCPs in municipal wastewater treatment plant and the receiving water[J].Environmental Science, 2013, 34(3):927-932. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hjkz201303016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[7] Ma R, Wang B, Lu S, et al.Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Dongting Lake, China:Occurrence, chiral profiling and environmental risk[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 557:268-275. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969716304788
[8] Ma R, Wang B, Yin L, et al.Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Beijing, China:Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and its environmental implication[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 323:147-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.030
[9] Vulliet E, Cren-Olivé C.Screening of pharmaceuticals and hormones at the regional scale, in surface and groundwaters intended to human consumption[J].Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(10):2929-2934. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.04.033
[10] Feito R, Valcárcel Y, Catalá M.Biomarker assessment of toxicity with miniaturised bioassays:Diclofenac as a case study[J].Ecotoxicology, 2012, 21(1):289-296. doi: 10.1007/s10646-011-0790-2
[11] Poirier-Larabie S, Segura P A, Gagnon C.Degradation of the pharmaceuticals diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole and their transformation products under controlled environmental conditions[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 557:257-267. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004896971630482X
[12] Schmitt-Jansen M, Bartels P, Adler N, et al.Phytotoxicity assessment of diclofenac and its phototransformation products[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, 387(4):1389-1396. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0825-3
[13] Vedenyapina M D, Borisova D A, Simakova A P, et al.Adsorption of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solutions on expanded graphite[J].Solid Fuel Chemistry, 2013, 47(1):59-63. doi: 10.3103/S0361521912060134
[14] Bajpai M, Rai N, Bajpai S K.Equilibrium adsorption studies on removal of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solution using sawdust-polyaniline (SD-PAn) composites[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 125(2):1382-1390. doi: 10.1002/app.v125.2
[15] 朱小红, 李涛, 马鹏飞, 等.气相色谱-质谱检测方法快速筛查保健食品及中成药中8种非甾体抗炎[J].药物分析杂志, 2012, 32(10):1847-1852. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YWFX201210034.htm
Zhu X H, Li T, Ma P F, et al.GC-MS rapid screening of eight non-steroidal anti-inflammatorydrugs in health foods and traditional Chinese medicines[J].Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2012, 32(10):1847-1852. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YWFX201210034.htm
[16] Kaynak M S, Buyutuncel E, Cagler H J, et al.Determination of regional intestinal permeability of diclofenac and metoprolol using a newly-developed and validated high performance liquid chromatographic method[J].Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 14(1):163-170. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v14i1.23
[17] Sotelo J L, Ovejero G, Rodríguez A, et al.Competitive adsorption studies of caffeine and diclofenac aqueous solutions by activated carbon[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 240:443-453. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.11.094
[18] Sotelo J L, Rodríguez A R, Mateos M M, et al.Adsorption of pharmaceutical compounds and an endocrine disruptor from aqueous solutions by carbon materials[J].Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part B, Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 2012, 47(7):640-652. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2012.668462
[19] 张璟, 陈阳, 李沛, 等.基于微透析技术及HPLC-ESI-MS测定大鼠关节腔透析液中双氯芬酸钠浓度及其应用[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2012, 17(11):1233-1239. http://lib.cqvip.com/qk/85070X/201211
Zhang J, Chen Y, Li P, et al.Determination of diclofenac sodium in dialysate of joint cavity in rats based on microdialysis and HPLC-ESI-MS and its application[J].Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2012, 17(11):1233-1239. http://lib.cqvip.com/qk/85070X/201211
[20] 卢红选, 刘卫国.HPLC-MS/MS测定城市废水中的10种药物与个人护理用品[J].地球环境学报, 2016, 7(4):425-430. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHJ201604010.htm
Lu H X, Liu W G.Determination of 10 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waste water by HPLC-MS/MS[J].Journal of Earth Environment, 2016, 7(4):425-430. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHJ201604010.htm
[21] Krajišnik D, Daković A, Milojević M, et al.Properties of diclofenac sodium sorption onto natural zeolite modified with cetylpyridinium chloride[J].Colloids Surfaces B:Biointerfaces, 2011, 83(1):165-172. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.11.024
[22] 石建稳, 艾慧颖, 王旭, 等.TiO2/粉煤灰光催化降解双氯芬酸钠研究[J].环境科学学报, 2014, 34(2):370-376. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hjxx201402014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Shi J W, Ai H Y, Wang X, et al.Photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac sodium over the photocatalyst of TiO2/CFA[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(2):370-376. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hjxx201402014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[23] 张楠, 刘国光, 刘海津, 等.双氯芬酸在水环境中光降解的初步研究[J].环境化学, 2013, 32(1):42-47. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.01.007
Zhang N, Liu G G, Liu H J, et al.Photodegration mechanism of diclofenac in aqueous environment[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(1):42-47. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.01.007
[24] 于万禄, 熊振湖, 马华继.Photo-Fenton法降解水中新型污染物双氯芬酸及降解产物的毒性评价[J].环境科学学报, 2009, 29(10):2070-2075. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.10.008
Yu W L, Xiong Z H, Ma H J.Degradation of the emergent pollutant diclofenac in water by photo-Fenton and toxicity evaluation of its degradation products[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(10):2070-2075. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.10.008
[25] Huguet M, Deborde M, Papot S, et al.Oxidative decarboxylation of diclofenac by manganese oxide bed filter[J].Water Research, 2013, 47(14):5400-5408. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.016
[26] 童新, 王军辉.纳米TiO2光催化氧化去除水中痕量双氯芬酸的研究[J].环境污染与防治, 2012, 34(8):53-57. http://www.whxb.pku.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract29507.shtml
Tong X, Wang J H.Photocatalytic oxidation of trace diclofenac in water by nanosized TiO2[J].Environmental Pollution & Control, 2012, 34(8):53-57. http://www.whxb.pku.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract29507.shtml
[27] 张楠. 双氯芬酸在水环境中光解行为的研究[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10476-1012421584.htm Zhang N. Study on Photolytic Behavior of Diclofenac in Aqueous Environment[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Normal University, 2012.
[28] 李璐, 刘菲, 陈鸿汉, 等.高效液相色谱法同时测定水体中的环丙沙星和氟甲喹[J].色谱, 2013, 31(6):567-571. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_sp201306013.aspx
Li L, Liu F, Chen H H, et al.Simultaneous determination of ciprofloxacin and flumequine in water samples by high performance liquid chromatography[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2013, 31(6):567-571. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_sp201306013.aspx
[29] 冯奇奇, 卜龙利, 高波, 等.ZnIn2S4可见光催化降解水中的双氯芬酸[J].环境工程学报, 2017, 11(2):739-747. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509051
Feng Q Q, Bu L L, Gao B, et al.Photocatalytic degradation of aqueous diclofenac by ZnIn2S4 under visible light[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(2):739-747. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509051
[30] Chefetz B, Mualem T, Ben-Ari J.Sorption and mobility of pharmaceutical compounds in soil irrigated with reclaimed wastewater[J].Chemosphere, 2008, 73(8):1335-1343. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.06.070
[31] Wang Y, Liu H, Liu G, et al.Oxidation of diclofenac by potassium ferrate(Ⅵ):Reaction kinetics and toxicity evaluation[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 506:252-258. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969714015769
[32] Wang X, Li J R, Fu M L, et al.Fabrication and evaluation of Au-Pd core-shell nanocomposites for dechlorination of diclofenac in water[J].Environmental Technology, 2015, 36(12):1510-1518. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2014.994044
[33] Wang Y, Liu H, Liu G, et al.Oxidation of diclofenac by aqueous chlorine dioxide:Identification of major disinfection by products and toxicity evaluation[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 473:437-445. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969713015295
[34] Kovala-Demertzi D.Transition metal complexes of di-clofenac with potentially interesting anti-inflammatory activity[J].Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 2000, 79(1):153-157. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0162013499001750
-



 下载:
下载: