40Ar/39Ar Dating of Muscovite from the Zhelande Au Deposit, Irtysh Tectonic Zone, Xinjiang and Its Geological Implications
-
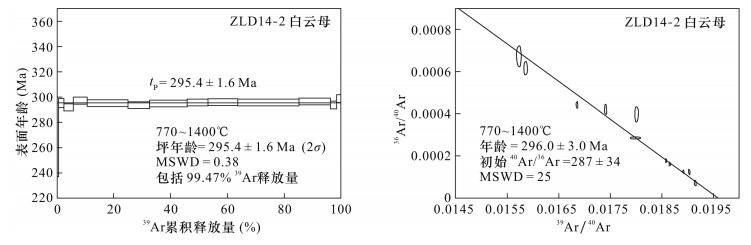
摘要: 哲兰德金矿是额尔齐斯构造带上重要的造山型金矿,产出于韧性剪切带中,金矿化赋存于黄铁矿化闪长岩脉、含金石英脉和黄铁矿化千枚岩中,矿化与韧脆性剪切变形有关。沿剪切面理发育的白云母、绿泥石等新生矿物,为测定金矿形成时代提供了依据。本研究利用白云母40Ar/39Ar年代学手段,确定了韧性剪切带的形成时代和金成矿时代。结果表明白云母坪年龄为295.4±1.6 Ma,韧性剪切变形和金成矿作用发生在295 Ma,略早于多拉纳萨依金矿形成时间。结合前人资料认为,新疆额尔齐斯构造带造山型金矿形成于295~270 Ma。
-
关键词:
- 地质特征 /
- 40Ar/39Ar年龄 /
- 造山型金矿 /
- 哲兰德 /
- 额尔齐斯构造带
Abstract:BACKGROUNDThe Zhelande gold deposit is an important orogenic gold deposit in the Irtysh tectonic belt. This deposit is hosted in the ductile shear zone. Mineralization occurs as gold-bearing pyritized diorite veins, gold-bearing quartz veins, and gold-bearing pyritized phyllite. The mineralization is related to the brittle-ductile shear deformation. Muscovite, chlorite and other new minerals occurred in the shear surface. OBJECTIVESTo determine the metallogenic age by 40Ar/39Ar method. METHODSMuscovite 40Ar/39Ar dating was used to constrain the timing of ductile shear deformation and gold mineralization. RESULTSResults show that the plateau age of the muscovite is 295.4±1.6 Ma, suggesting that the ductile shear deformation and gold mineralization occurred at about 295 Ma, slightly earlier than the formation of the Duolanasayi gold deposit. CONCLUSIONSCombined with previous data, the orogenic gold deposits in the Irtysh tectonic belt of Xinjiang possibly formed at 295-270 Ma. -
Key words:
- geological characteristics /
- Ar-Ar age /
- orogenic gold deposit /
- Zhelande /
- Irtysh tectonic zone
-

-
图 1 哲兰德金矿区地质略图[15]
Figure 1.
表 1 哲兰德金矿中白云母40Ar/39Ar阶段升温加热分析
Table 1. Results of 40Ar/39Ar stepwise heating dating for muscovite from the Zhelande Au deposit
ZLD14-2白云母;样品质量(W)=10.68 mg;J=0.003493 T(℃) (40Ar/ 39Ar)m (36Ar/39Ar)m (37Ar/ 39Ar)m (38Ar/39Ar)m 40Ar(%) F 39Ar(×10-14 mol) 39Ar累积(%) 年龄±1σ(Ma) 700 75.1437 0.1149 0.0000 0.0347 54.81 41.1860 0.09 0.53 242.5±5.5 770 63.5889 0.0428 0.0000 0.0210 80.09 50.9296 0.34 2.48 295.4±3.5 820 57.4390 0.0242 0.1561 0.0176 87.55 50.2933 0.57 5.77 292.0±2.8 860 58.9824 0.0260 0.0000 0.0175 86.94 51.2802 0.84 10.58 297.2±2.8 900 55.6024 0.0159 0.0418 0.0155 91.55 50.9075 2.51 24.96 295.3±2.7 930 52.5392 0.0065 0.0962 0.0138 96.35 50.6258 1.33 32.60 293.7±2.7 960 52.8558 0.0067 0.0000 0.0138 96.26 50.8793 2.32 45.90 295.1±2.7 1000 53.8169 0.0096 0.0000 0.0141 94.75 50.9893 1.26 53.14 295.7±2.7 1040 53.6039 0.0086 0.0000 0.0140 95.24 51.0540 1.84 63.67 296.0±2.7 1080 52.2438 0.0041 0.0000 0.0132 97.69 51.0359 3.76 85.24 295.9±2.7 1120 52.2407 0.0036 0.0307 0.0133 97.94 51.1470 1.92 96.26 296.6±2.7 1160 55.5188 0.0166 0.2049 0.0157 91.19 50.6375 0.38 98.46 293.8±3.0 1400 63.0620 0.0388 0.0000 0.0190 81.80 51.5818 0.27 100.00 298.9±3.1 tT=295.3 Ma;tP=295.4±1.6 Ma;ti=296.0±3.0 Ma 注:表中下标m代表质谱测定的同位素比值;F=40Ar*/39Ar,是指放射性成因40Ar和39Ar比值;tT=总气体年龄;tP=坪年龄;ti=反等时线年龄。 -
[1] 袁霞, 陈文, 张斌, 等.西天山望峰金矿床绢云母40Ar/39Ar年龄及矿床成因研究[J].矿床地质, 2017, 36(1):57-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201701004
Yuan X, Chen W, Zhang B, et al.40Ar/39Ar age of sericite and genetic study of Wangfeng gold deposit, West Tianshan Mountains[J].Mineral Deposits, 2017, 36(1):57-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201701004
[2] 杨富全, 秦纪华, 刘锋, 等.新疆准噶尔北缘玉勒肯哈腊苏铜(钼)矿区韧性剪切变形时代——来自白云母和黑云母Ar-Ar年龄的约束[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(1):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2013.01.001
Yang F Q, Qin J H, Liu F, et al.Ar-Ar dating of the ductile shear zones in the Yulekenhalasu Cu-(Mo) ore deposit[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2013, 37(1):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2013.01.001
[3] Yang F Q, Liu F, Li Q, et al.In situ LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of igneous rocks in the Ashele Basin, Altay orogenic belt, Northwest China:Constraints on the timing of polymetallic copper mineralization[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79:477-496. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.10.022
[4] 朱乔乔, 谢桂青, 蒋宗胜, 等.湖北金山店大型矽卡岩型铁矿热液榍石特征和原位微区LA-ICPMS U-Pb定年[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(5):1322-1338. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201405010
Zhu Q Q, Xie G Q, Jiang Z S, et al.Characteristics and in situ U-Pb dating of hydrothermal titanite by LA-ICPMS of the Jingshandian iron skarn deposit, Hubei Province[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(5):1322-1338. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201405010
[5] 杨成栋, 杨富全, 吴玉峰.新疆阿尔泰萨尔朔克金多金属矿区岩浆活动-剪切变形时限——锆石U-Pb和绢云母40Ar/39Ar测年证据[J].地质论评, 2016, 62(3):631-648. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201603008
Yang C D, Yang F Q, Wu Y F.Timing of magmatic activity-shearing deformation from the Sarsuk polymetallic gold depositon the southern margin of Altay, Xinjiang:Constraints from zircon U-Pb and sericite 40Ar/39Ar dating[J].Geological Review, 2016, 62(3):631-648. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201603008
[6] Zhou Q F, Qin K Z, Tang D M, et al.LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon, columbite-tantalite and 40Ar-39Ar muscovite age constraints for the rare-element pegmatite dykes in the Altai orogenic belt, NW China[J].Geological Magazine, 2018, 155(3):707-728. doi: 10.1017/S0016756816001096
[7] 侯淋, 唐菊兴, 林彬, 等.西藏东窝东矿床矿化蚀变过程元素迁移及绢云母40Ar-39Ar年代学及其地质意义[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(4):440-449. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201612050179
Hou L, Tang J X, Lin B, et al.Element migration during alteration and 40Ar/39Ar dating of sericite from the Dongwodong deposit, Tibet and its geological significance[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(4):440-449. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201612050179
[8] 高允, 孙艳, 赵芝, 等.内蒙古武川县赵井沟铌钽多金属矿床白云母40Ar-39Ar同位素年龄及地质意义[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):551-558. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201612290190
Gao Y, Sun Y, Zhao Z, et al.40Ar-39Ar dating of muscovite from the Zhaojinggou Nb-Ta polymetallic depositin Wuchuan county of Inner Mongolia and its geological implications[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):551-558. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201612290190
[9] Golestani M, Karimpour M H, Shafaroudi A M, et al.Geochemistry, U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd isotopes of the Neogene igneous rocks, at the Iju porphyry copper deposit, NW Shahr-e-Babak, Iran[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 93:290-307. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.01.001
[10] Liu L J, Zhou T F, Zhang D Y, et al.S isotopic geochemistry, zircon and cassiterite U-Pb geochronology of the Haobugao Sn polymetallic deposit, Southern Great Xing'an Range, NE China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 93:168-180. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.12.008
[11] 闫升好, 陈文, 王义天, 等.新疆额尔齐斯金成矿带的40Ar/39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2004, 78(8):500-506. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200404009
Yan S H, Chen W, Wang Y T, et al.40Ar/39Ar dating and its significance of the Ertix gold metallogenic belt in the Altay Orogen, Xinjiang[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(8):500-506. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200404009
[12] 闫升好, 滕荣丽, 王义天, 等.新疆布尔根含金剪切带的40Ar/39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(3):648-655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.023
Yan S H, Teng R L, Wang Y T, et al.40Ar/39Ar dating of the Bu'ergen gold-bearing shear zone on the southern margin of the Altay Mountains, Xinjiang, and its significance[J].Geology in China, 2006, 33(3):648-655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.023
[13] 刘协鲁, 王义天, 胡乔青, 等.陕西凤太矿集区柴蚂金矿床成矿时代的40Ar/39Ar年龄证据[J].矿床地质, 2018, 37(1):163-174.
Liu X L, Wang Y T, Hu Q Q, et al.Evidence of 40Ar/39Ar age data for ore-forming time of Chaima gold deposit in Fengtai ore concentration area, Shaanxi Province[J].Mineral Deposits, 2018, 37(1):163-174.
[14] 李光明, 沈远超, 刘铁兵, 等.新疆阿尔泰南缘托库孜巴依金矿成矿演化:石英脉系、同位素地球化学及其Ar-Ar年代学证据[J].矿床地质, 2007, 26(1):15-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.01.002
Li G M, Shen Y C, Liu T B, et al.Metallogenic evolutiong of Tuokuzibayi gold deposit in Southern Altay, North Xinjiang:Evidence from characteristics of quartz vein systems, isotopic geochemistry and Ar-Ar chronology[J].Mineral Deposits, 2007, 26(1):15-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.01.002
[15] 周能武, 郭新成, 何桂林.新疆哈巴河地区托库孜巴依金矿区两类含矿脉岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(5):707-715. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.05.007
Zhou N W, Guo X C, He G L.LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of two types of ore-bearing dykes in the Tuokuzibayi gold ore district in Habahe ares of Xinjiang and their geological significance[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(5):707-715. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.05.007
[16] Groves D I, Goldfarbb R J, Gebre-Mariam M, et al.Orogenic gold deposits:A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13:7-27. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7
[17] 陶世旭, 潘杰, 张彦锋.哈巴河县哲兰德金矿地质特征及成因分析[J].地球, 2016(4):135. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201804081.htm
Tao S X, Pan J, Zhang Y F.Geology and origin of the Zhelande Au deposit in the Habahe county[J].Earth, 2016(4):135. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201804081.htm
[18] 柴凤梅, 欧阳刘进, 董连慧, 等.新疆阿舍勒铜锌矿区英云闪长岩年代学及地球化学[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1):41-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.003
Chai F M, Ouyang L J, Dong L H, et al.Geochronology and genesis of tonalities from the Ashele Cu-Zn deposit on the southern margin of Altay, Xinjiang[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2013, 32(1):41-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.003
[19] Ludwig K R.User's Manual for Isoplot/ex, v2.49:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Geochronological Center Special Publication, 2001:1-58.
[20] 陈文, 张彦, 金贵善, 等.青藏高原东南缘晚新生代幕式抬升作用的Ar-Ar热年代学证据[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(4):867-872. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200604010
Chen W, Zhang Y, Jin G S, et al.Late Cenozoic episodic uplifting in southeastern part of the Tibetan plateau-Evidence from Ar-Ar thermochornology[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 22(4):867-872. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200604010
[21] 陈文, 张彦, 赵海滨, 等.新疆东天山红山金矿成矿时代研究[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(3):632-640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.021
Chen W, Zhang Y, Zhao H B, et al.Mineralization age of the Hongshan gold deposit, East Tianshan, Xinjiang[J].Geology in China, 2006, 33(3):632-640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.021
[22] Zhang C L, Santosh M, Zou H B, et al.Revisiting the 'Irtish tectonic belt':Implications for the Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Altai orogen[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 52:117-133. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.02.016
[23] 吴玉峰, 杨富全, 刘锋, 等.新疆阿舍勒铜锌矿区脆韧性剪切带中绢云母40Ar/39Ar年代学及其地质意义[J].地球学报, 2015, 36(1):121-126. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201501019
Wu Y F, Yang F Q, Liu F, et al.40Ar-39Ar dating of sericite from the brittle ductile shear zone in the Ashele Cu-Zn ore district, Xinjiang[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(1):121-126. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201501019
[24] Laurent-Charvet S, Charvet J, Monie P, et al.Late Paleozoic strike-slip shear zones in eastern central Asia (NW China):New structural and geochronological data[J].Tectonics, 2003, 22(2):1-24. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2001TC901047/full
[25] 刘飞, 王镇远, 林伟, 等.中国阿尔泰造山带南缘额尔齐斯断裂带的构造变形及意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(5):1811-1824. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201305024
Liu F, Wang Z Y, Lin W, et al.Structure deformation and tectonic significance of Erqis fault zone in the southern margin of Chinese Altay[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(5):1811-1824. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201305024
-




 下载:
下载: