Application of the Automated Mineral Identification and Characterization System (AMICS) in the Identification of Rare Earth and Rare Minerals
-
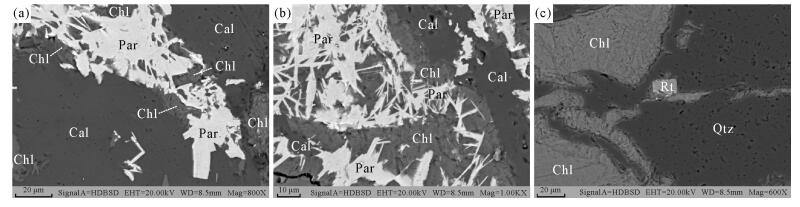
摘要: 云南武定迤纳厂铁-铜-稀土矿床是我国扬子地块西南缘具有代表性的元古代铁-铜-稀土矿床之一,矿床中除Fe、Cu外,还伴生REEs、Nb、Co、Mo、Au、U等元素。由于矿石矿物组成复杂,并且稀土、稀有矿物结晶粒度细小、嵌布特征复杂,使用传统的测试技术很难准确地识别鉴定,因此该矿床中稀土、稀有(铌)矿物的赋存状态研究一直较为薄弱。本文应用目前国际上矿物与地质行业先进的矿物自动分析系统——矿物表征自动定量分析系统(AMICS),结合扫描电镜-能谱仪(SEM-EDS)显微结构原位分析技术,实现了常规岩矿鉴定手段难以完成的矿物定量识别和鉴定,准确地测定了武定迤纳厂铁-铜-稀土矿床脉状矿石中矿物种类及其含量,在脉状矿石发现了含量可观的氟碳钙铈矿(0.82%)和少量的含铌金红石(0.02%)等稀土稀有矿物。研究表明,除了铁氧化物成矿阶段,在铜硫化物成矿阶段也伴随有稀土成矿作用,因此可将主矿化期划分为铁氧化物-稀土矿化阶段(Ⅱ-1)和铜硫化物(-金)-稀土矿化阶段(Ⅱ-2)。研究成果为矿石中稀土、稀有金属等战略矿产资源的综合利用及矿床的进一步研究提供了可靠的数据,同时建立了一套先进、实用的岩石矿物鉴定技术,可望在地质、勘探、资源的有效利用等领域得到更广泛应用。Abstract: The Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit is one of the representative Proterozoic Fe-Cu-REE deposits in central Yunnan, at the southwestern margin of the Yangtze Block, China. Beside Fe and Cu, there are REEs, Nb, Mo, Co, Au, U and other elements in the ores. The study on the occurences of rare earth minerals and rare minerals is very weak. It is difficult to identify precisely using the traditional testing techniques and methods due to the relatively complex mineral composition, the small size and the complex dissemination characteristics of rare earth minerals and rare minerals in ores. In order to explore the occurrences of rare earth minerals and rare minerals, the Automated Mineral Identification and Characterization System (AMICS) was used. This system is the most up-to-date mineral automatic analysis system in mineralogy and geology in the world. Combined with the Scanning Electron Microscope and X-ray Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (SEM-EDS) microstructure in-situ analysis technique, this system was used to determine the species and contents of minerals in vein ores from the Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit. The quantitative mineral identification, which was difficult to achieve by conventional means of rock-mineral identification, have been completed. The results show that there are 0.82% parasites and 0.02% Nb-bearing rutiles in the vein ores. Both of the iron oxides and copper sulfides mineralization stages are associated with REE mineralization in this deposit. Two main mineralization stages are identified, i.e., the Fe-REE mineralization stage (Ⅱ-1) and Cu (-Au)-REE mineralization stage (Ⅱ-2). This study provides accurate and reliable evidence for the comprehensive utilization of rare earth and rare metal resources and the further study of Fe-Cu-REE deposits. An advanced and practical technical method of rock-mineral identification was established, which is expected to be more widely used in fields such as geology, exploration and effective utilization of mineral resources.
-

-
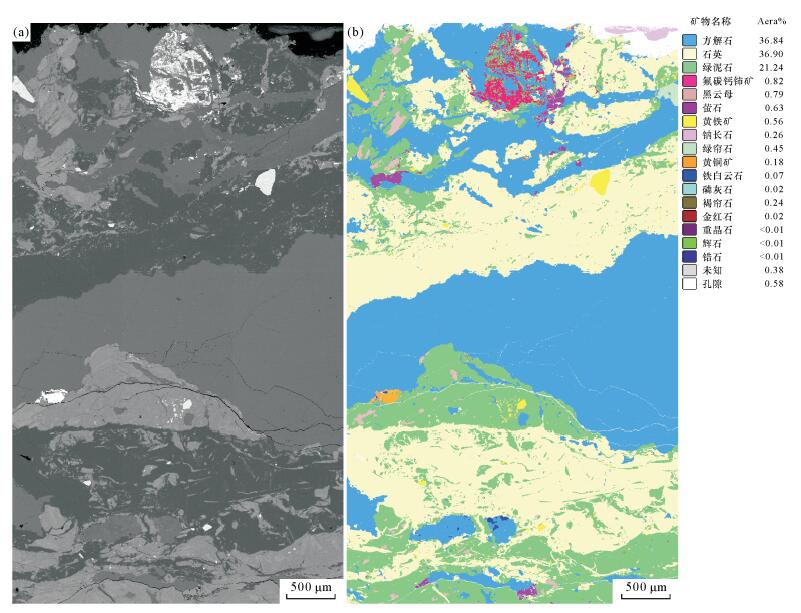
表 1 武定迤纳厂铁-铜-稀土矿床矿石样品AMICS矿物定量检测结果
Table 1. Quantitative composition of the Sample YNC1-1-1 by AMICS from the Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit
矿物名称 质量分数(%) 面积百分比(%) 面积(μm2) 矿物颗粒数 相对误差 矿物标准分子式 石英 34.38 36.90 7500209.93 26069 0.01 SiO2 方解石 35.81 36.84 7487643.98 21315 0.01 CaCO3 绿泥石 24.17 21.24 4317504.81 39607 0.01 Fe32+Mg1.5AlFe0.53+Si3AlO12(OH)6 氟碳钙铈矿 1.28 0.82 167615.90 5255 0.03 CaCe1.1La0.9(CO3)3F2 黑云母 0.87 0.79 160222.11 450 0.09 KMg2.5Fe0.52+AlSi3O10(OH)1.75F0.25 萤石 0.70 0.63 128600.05 2776 0.04 CaF2 黄铁矿 1.00 0.56 114151.95 3593 0.03 FeS2 绿帘石 0.56 0.45 91840.77 3048 0.04 Ca2FeFeAl(Si2O7)(SiO4)O(OH) 钠长石 0.24 0.26 53234.30 468 0.09 Na0.95Ca0.05Al1.05Si2.95O8 褐帘石 0.32 0.24 48501.47 3669 0.03 La0.5Ce0.5Ca0.5Y0.5Al2Fe(SiO4)3(OH) 黄铜矿 0.27 0.18 36844.15 852 0.07 CuFeS2 铁白云石 0.07 0.07 13484.56 133 0.17 CaFe0.62+Mg0.3Mn0.12+(CO3)2 磷灰石 0.02 0.02 4078.82 60 0.26 Ca5(PO4)3(OH)F 金红石 0.02 0.02 3135.25 159 0.16 TiO2 辉石 < 0.01 < 0.01 688.96 15 0.52 Ca0.9Na0.1Mg0.9Fe0.22+Al0.4Ti0.1Si1.9O6 锆石 < 0.01 < 0.01 184.72 10 0.63 Zr(SiO4) 重晶石 < 0.01 < 0.01 44.93 3 1.15 BaSO4 未知 0.27 0.38 76973.31 5780 0.03 - 孔隙 - 0.58 118515.33 6188 0.02 - 合计 99.98 99.98 20323475.30 119450 - - -
[1] 杨时蕙.从磁铁矿内部结构探讨云南迤纳厂铁矿床的成因[J].中国地质科学院成都地质矿产研究所所刊, 1982, 3(1):137-147. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198303001010.htm
Yang S H.An approach to the genesis of magnetite deposit, Yinachang, Yunnan, from the internal structures of magnetite[J].Bulletin of the Chengdu Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1982, 3(1):137-147. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198303001010.htm
[2] 杨耀民, 涂光炽, 胡瑞忠.迤纳厂稀土铁铜矿床稀土元素地球化学[J].矿物学报, 2004, 24(3):301-308. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwxb200403015
Yang Y M, Tu G Z, Hu R Z.REE geochemistry of Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit in Yunnan Province[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2004, 24(3):301-308. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwxb200403015
[3] 杨耀民, 涂光炽, 胡瑞忠, 等.武定迤纳厂Fe-Cu-REE矿床Sm-Nd同位素年代学及其地质意义[J].科学通报, 2005, 50(12):1253-1258. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.12.017
Yang Y M, Tu G Z, Hu R Z, et al.Sm-Nd isotopic geochronology of the Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit at Wuding, Yunnan Province and its geologic significance[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(12):1253-1258. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.12.017
[4] Zhao X F, Zhou M F.Fe-Cu deposits in the Kangdian region, SW China:A Proterozoic IOCG (iron oxide-copper-gold) metallogenic province[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2011, 46(7):731-747. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0342-y
[5] Zhao X F, Zhou M F, Gao J F, et al.In situ Sr isotope analysis of apatite by LA-MC-ICP-MS:Constraints on the evolution of ore fluids of the Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit, Southwest China[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2015, 50(7):871-884. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0578-z
[6] 叶霖, 刘玉平, 李朝阳, 等.云南武定迤纳厂铜矿含矿石英脉40Ar-39Ar年龄及其意义[J].矿物学报, 2004, 24(4):411-414.
Ye L, Liu Y P, Li C Y, et al.Ar-Ar isotopic age Yinachang copper deposit, Wuding, Yunnan Province, China and its implications[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2004, 24(4):411-414.
[7] 侯林, 丁俊, 邓军, 等.云南武定迤纳厂铁铜矿岩浆角砾岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其意义[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(4):580-588. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/86b3a02827284b73f24250f5.html
Hou L, Ding J, Deng J, et al.Zircon LA-ICP-MS dating of the magmatic breccia from the Yinachang iron-copper deposit in Wuding County of Yunnan Province and its geological significance[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(4):580-588. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/86b3a02827284b73f24250f5.html
[8] 叶现韬, 朱维光, 钟宏, 等.云南武定迤纳厂Fe-Cu-REE矿床的锆石U-Pb和黄铜矿Re-Os年代学、稀土元素地球化学及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(4):1167-1186. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_ysxb98201304006
Ye X T, Zhu W G, Zhong H, et al.Zircon U-Pb and chalcopyrite Re-Os geochronology, REE geochemistry of the Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit in Yunnan Province and its geological significance[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(4):1167-1186. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_ysxb98201304006
[9] Hou L, Ding J, Deng J, et al.Geology, geochronology, and geochemistry of the Yinachang Fe-Cu-Au-REE deposit of the Kangdian region of SW China:Evidence for a Paleo-Mesoproterozoic tectono-magmatic event and associated IOCG systems in the Western Yangtze Block[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 103:129-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.016
[10] 丁俊, 侯林.云南武定迤纳厂岩浆热液型铁-铜-金-稀土矿床流体特征研究[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(4):39-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201204004
Ding J, Hou L.Study on ore-forming fluid characteristics of Yinachang Fe-Cu-Au-REE deposit, Wuding, Yunnan Province, China[J].Northwestern Geology, 2012, 45(4):39-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201204004
[11] 侯林, 丁俊, 王长明, 等.云南武定迤纳厂铁-铜-金-稀土矿床成矿流体与成矿作用[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(4):1187-1202. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20130407&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2013
Hou L, Ding J, Wang C M, et al.Ore-forming fluid and metallogenesis of the Yinachang Fe-Cu-Au-REE deposit, Wuding, Yunan Province, China[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(4):1187-1202. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20130407&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2013
[12] 侯林, 彭惠娟, 丁俊.云南武定迤纳厂铁-铜-金-稀土矿床成矿物质来源——来自矿床地质与S、Pb、H、O同位素的制约[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(2):205-218. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_yskwxzz201502006.aspx
Hou L, Peng H J, Ding J.Sources of the ore-forming materials for the Yinachang Fe-Cu-Au-REE deposit, Wuding, Yunnan Province:Constraints from the ore geology and the S, Pb, H, O isotope geochemistry[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2015, 34(2):205-218. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_yskwxzz201502006.aspx
[13] Li X C, Zhou M F.Multiple stages of hydrothermal REE remobilization recorded in fluorapatite in the Paleoproterozoic Yinachang Fe-Cu-(REE) deposit, Southwest China[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 166(1):53-73. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277963492_Fluid_Inclusion_and_Isotopic_Constraints_on_the_Origin_of_the_Paleoproterozoic_Yinachang_Fe-Cu-REE_Deposit_Southwest_China
[14] Creelman R A, Ward C R.A scanning electron micro-scope method for automated, quantitative analysis of mineral matter in coal[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 1996, 30(3):249-269. doi: 10.1016/0166-5162(95)00043-7
[15] Liu Y H, Gupta R, Sharma A, et al.Mineral matter-organic matter association characterisation by QEMSCAN and applications in coal utilisation[J].Fuel, 2005, 84(10):1259-1267. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2004.07.015
[16] Pascoe R D, Power M R, Simpson B.QEMSCAN analysis as a tool for improved understanding of gravity separator performance[J].Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(5):487-495. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2006.12.012
[17] Gu Y.Automated scanning electron microscope based mineral liberation analysis an introduction to JKMRC/FEI Mineral Liberation Analyser[J].Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, 2003, 2(1):33-41. doi: 10.4236/jmmce.2003.21003
[18] Redwan M, Rammlmair D, Meima J A.Application of mineral liberation analysis in studying micro-sedimentological structures within sulfide mine tailings and their effect on hardpan formation[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 414:480-493. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.038
[19] 梁冬云, 邹霓, 李波.MLA自动检测技术在低品位钼矿石工艺矿物学研究中的应用[J].中国钼业, 2010, 34(1):32-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgmy201001006
Liang D Y, Zou N, Li B.Application of MLA automated quantitative mineralogy in process mineralogy research on low-grade molybdenum ore[J].China Molybdenum Industry, 2010, 34(1):32-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgmy201001006
[20] 李波, 梁冬云, 张莉莉.富磷灰石复杂稀土矿石工艺矿物学研究[J].中国稀土学报, 2012, 30(6):761-765. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgxtxb201206020
Li B, Liang D Y, Zhang L L.Process mineralogy of an apatite-rich complex rare earth ore[J].Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2012, 30(6):761-765. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgxtxb201206020
[21] 苟瑞涛. 基于MLA的碳酸岩-碱性杂岩稀土-铌-铁矿矿物学特征研究——以内蒙古白云鄂博矿床为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2016: 1-68.
Gou R T. The Study on Mineralogical Characteristics of REE-Nb-Fe Ore within Carbonatites-Alkaline Complexes Based on MLA-A Case Study for Bayan Obo Deposit in Inner Mongolia, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2016: 1-68.
[22] Zhou M F, Zhao X F, Chen W T, et al.Proterozoic Fe-Cu metallogeny and supercontinental cycles of the Southwestern Yangtze Block, Southern China and Northern Vietnam[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 139:59-82. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.08.013
[23] 杨波, 丁俊, 徐金沙, 等.滇中武定迤纳厂铁铜多金属矿床中稀土、金的赋存状态特征研究[J].矿物岩石, 2014, 34(4):36-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWYS201404005.htm
Yang B, Ding J, Xu J S, et al.Research of occurrence character and REE of associated gold for the Yinachang Fe-Cu-Au-REE deposit in central Yunnan region[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2014, 34(4):36-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWYS201404005.htm
[24] Zhao X F, Zhou M F, Li J W, et al.Sulfide Re-Os and Rb-Sr isotope dating of the Kangdian IOCG metallogenic Province, Southwest China:Implications for regional metallogenesis[J].Economic Geology, 2013, 108(6):1489-1498. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.6.1489
[25] Zhao G C, Cawood P A, Wilde S A, et al.Review of global 2.1-1.8Ga orogens:Implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2002, 59(1-4):125-162. http://www.doc88.com/p-7374577182368.html
[26] Zhao G C, Sun M, Wilde S A, et al.Assembly, accretion and breakup of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Columbia supercontinent:Records in the North China Craton[J].Gondwana Research, 2003, 6(3):417-434. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70996-5
[27] Zhao G C, Sun M, Wilde S A, et al.A Paleo-Mesopro-terozoic supercontinent:Assembly, growth and breakup[J].Earth Science Reviews, 2004, 67(1-2):91-123. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.02.003
[28] 李献华, 周汉文, 李正祥, 等.扬子块体西缘新元古代双峰式火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石化学特征[J].地球化学, 2001, 30(4):315-322. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dqhx200104003.aspx
Li X H, Zhou H W, Li Z X, et al.Zircon U-Pb age and petrochemical characteristics of the Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanics from Western Yangtze Block[J].Geochimica, 2001, 30(4):315-322. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dqhx200104003.aspx
[29] 李献华, 周汉文, 李正祥, 等.川西新元古代双峰式火山岩成因的微量元素和Sm-Nd同位素制约及其大地构造意义[J].地质科学, 2002, 37(3):264-276. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94066X/2002003/6526473.html
Li X H, Zhou H W, Li Z X, et al.Petrogenesis of Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanics in Western Sichuan and its tectonic implications:Geochemical and Sm-Nd isotopic constraints[J].Chinese Journal of Geology, 2002, 37(3):264-276. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94066X/2002003/6526473.html
[30] 江新胜, 王剑, 崔晓庄, 等.滇中新元古代澄江组锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究及其地质意义[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2012, 42(10):1496-1507. http://earth.scichina.com:8080/sciD/CN/Y2012/V42/I10/1496
Jiang X S, Wang J, Cui X Z, et al.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of the Neoproterozoic Chengjiang Formation in Central Yunnan Province (SW China) and its geological significance[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2012, 42(10):1496-1507. http://earth.scichina.com:8080/sciD/CN/Y2012/V42/I10/1496
-



 下载:
下载: