Determination of 8 Metallogenic Elements in Tibetan Skarn-type Copper-polymetallic Rich Ore from Tibet by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry
-
摘要: 矽卡岩型铜多金属富矿石是西藏特有矿产,具有成矿元素多样且含量普遍较高的特点,矿物类型主要为硫化物型,成矿元素有Cu、Pb、Zn、Fe、Ag、Bi、Cd、Co等。采用湿法处理此类样品时常因银、铅等元素含量较高出现难溶解、易沉淀现象,导致测定结果偏低。本文采用盐酸预处理、硝酸-氢氟酸-高氯酸溶矿体系,能有效除去样品中的硫,样品分解效果好,选择稀释倍数为1000、溶液介质为10%盐酸,样品溶液不会产生沉淀,采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定各待测元素均可获得较好的准确度、精密度。方法测定范围为:Cu 0.0056%~20.0%,Pb 0.0087%~20.0%,Zn 0.0031%~20.0%,Fe 0.0090%~20.0%,Ag 5.40~3000 μg/g,Bi 10.8~5000 μg/g,Cd 0.69~5000 μg/g,Co 2.09~5000 μg/g。用国家标准物质进行验证,方法准确度小于5.40%,精密度(RSD,n=11)小于4.41%。该方法具有前处理流程简单、分析速度快、同时测定元素多、线性范围宽等优点,经实际样品测试与不同方法分析数据吻合。
-
关键词:
- 铜多金属富矿石 /
- 酸溶 /
- 除硫 /
- 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法
Abstract: Skarn-type copper-polymetallic rich ore is a unique mineral resource in Tibet and is characterized by numerous diverse elements with high content. The mineral type is mainly sulfide, while the metallogenic ore elements are typically Cu, Pb, Zn, Fe, Ag, Bi, Cd and Co. The use of wet methods to analyze the samples will result in low measurement results due to the high content of silver, lead and other elements, which are difficult to dissolve and precipitate. The analytical results of these samples tend to be on the low side, due to the insoluble and easy-to-precipitate state during the wet pre-treatment caused by the relatively high amount of certain elements. In this study, hydrochloric acid was introduced to pre-desulfurize the ore, followed by dissolution with a mixed acid of nitric, hydrofluoric, and perchloric acid. As a result, the samples can be decomposed completely with effective desulphurization. When the dilution factor was optimized to 1000 and 10% hydrochloric acid was chosen as the solution medium, the sample solution did not precipitate and the multi-element analysis by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) yielded good accuracy and precision. The method measurement ranges are 0.0056% to 20.0% for Cu, 0.0087% to 20.0% for Pb, 0.0031% to 20.0% for Zn, 0.0090% to 20.0% for Fe, 5.40 μg/g to 3000 μg/g for Ag, 10.8 μg/g to 5000 μg/g for Bi, 0.69 μg/g to 5000 μg/g for Cd, 2.09 μg/g to 5000 μg/g for Co, respectively. The method accuracy was less than 5.40% and the precision (RSD, n=11) was less than 4.41%, which was verified by the national standard reference materials. This method has distinct advantages of simple preliminary treatment, efficient analysis, simultaneous detection of multiple elements, and a wide linear range. The results are in agreement with other methods according to actual sample test analysis. -

-
表 1 各元素标准曲线浓度及组合
Table 1. Concentration and combination of the elements in calibration standard solution
标准溶液系列 元素 元素浓度(mg/L) 溶液介质 标准溶液1 Cu、Pb、Zn、Fe 0.00 5.00 10.0 20.0 50.0 100 150 200 10%王水 标准溶液2 Ag 0.00 0.10 0.20 0.50 1.00 2.00 5.00 10%硝酸 标准溶液3 Bi、Cd、Co 0.00 0.10 0.20 0.50 1.00 2.00 5.00 10%王水 表 2 4种除硫方式对比
Table 2. A comparison of four different desulfurizing methods
预处理方式 硫去除率(%) GBW07169 GBW07170 GBW07171 GBW07172 四酸溶矿 22.9 25.5 28.0 25.3 硝酸预处理 11.0 9.80 9.10 11.9 王水预处理 5.30 4.20 5.40 5.10 盐酸预处理 49.0 49.2 89.8 85.1 表 3 元素检出限及测定范围
Table 3. Detection limits and measured ranges of elements
分析元素 标准偏差(%) 检出限(μg/g) 测定范围(μg/g) 分析元素 标准偏差(%) 检出限(%) 测定范围(%) Ag 0.54 1.62 5.40~3000 Cu 0.00056 0.0017 0.0056~20.0 Bi 1.08 3.25 10.8~5000 Pb 0.00087 0.0026 0.0087~20.0 Cd 0.069 0.21 0.69~5000 Zn 0.00031 0.00094 0.0031~20.0 Co 0.209 0.63 2.09~5000 Fe 0.00090 0.0027 0.0090~20.0 表 4 方法精密度和准确度
Table 4. Precision and accuracy tests of method
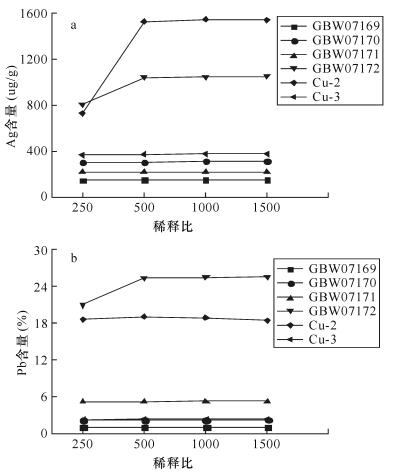
标准物质编号 元素 测定值(μg/g) 标准值(μg/g) RSD (%) 相对误差(%) GBW07169 (铜矿石) Ag 161 154 4.41 4.41 Bi 1615 1533 1.08 5.34 Cd 38.8 38.3 1.22 1.42 Co 123 118 2.58 3.83 Cu 5.46 5.49 0.55 -0.50 Pb 1.12 1.12 1.04 -0.10 Zn 0.61 0.61 1.31 0.41 Fe 9.07 9.12 0.47 -0.50 GBW07170 (铜矿石) Ag 324 319 3.22 1.45 Bi 3645 3622 1.40 0.64 Cd 64.5 61.9 0.69 4.22 Co 233 221 2.19 5.40 Cu 12.54 12.59 0.47 -0.40 Pb 2.26 2.24 1.24 0.97 Zn 1.22 1.21 1.36 0.96 Fe 8.88 8.92 0.55 -0.43 GBW07171 (铅矿石) Ag 219 228 2.55 -3.83 Bi 605 607 1.47 -0.38 Cd 322 - 1.93 - Co 72.7 67.4 1.88 4.72 Cu 0.47 0.47 1.24 -0.31 Pb 5.27 5.27 0.83 -0.090 Zn 8.94 8.71 0.92 2.68 Fe 9.74 9.77 0.73 -0.33 GBW07172 (铅矿石) Ag 1087 113 0.44 -4.18 Bi 3129 3239 2.15 -3.40 Cd 315 - 2.45 - Co 75.7 72.3 2.35 4.68 Cu 1.00 1.00 2.78 0.10 Pb 25.61 25.58 0.43 0.13 Zn 8.92 8.73 1.31 2.16 Fe 7.64 7.61 1.55 0.33 注:Cu、Pb、Zn、Fe元素的质量分数为10-2。 表 5 ICP-OES与其他方法测定结果比较
Table 5. A comparison of analytical results by ICP-OES and other methods
样品编号 测定方法 测定值(%) 测定值(μg/g) Cu Pb Zn Fe Ag Bi Cd Co 样品1 ICP-OES 6.37 17.96 9.23 12.36 1594 9884 473 420 其他方法 6.41 18.13 9.58 12.18 1599 10803 473 404 样品2 ICP-OES 7.55 2.36 3.70 15.05 400 4961 181 398 其他方法 7.67 2.28 3.93 14.74 408 5015 181 415 样品3 ICP-OES 12.36 46.88 0.38 11.98 3970 16056 52 165 其他方法 12.54 46.33 0.36 11.76 3956 17243 59 168 样品4 ICP-OES 2.06 58.58 8.34 4.24 2786 8946 404 71.1 其他方法 1.96 60.40 7.99 4.19 2813 8612 386 65.2 -
[1] 唐菊兴, 多吉, 刘鸿飞, 等.冈底斯成矿带东段矿床成矿系列及找矿突破的关键问题研究[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(4):393-410. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201204003.htm
Tang J X, Duo J, Liu H F, et al.Minerogenetic series of ore deposits in the east part of the Gangdise metallogenic belt[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(4):393-410. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201204003.htm
[2] Zuo R G.Identifying geochemical anomalies associated with Cu and Pb-Zn skarn mineralization using principal component analysis and spectrum-area fractal modeling in the Gangdese Belt, Tibet (China)[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 11(1-2):13-22. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0375674211001051
[3] 李光明, 刘波, 屈文俊, 等.西藏冈底斯成矿带的斑岩-矽卡岩成矿系统——来自斑岩矿床和矽卡岩型铜多金属矿床的Re-Os同位素年龄证据[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(4):482-490. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx200504008
Li G M, Liu B, Qu W J, et al.The porphyry-skarn ore-forming system in Gangdese metallogenic belt, Southern Xizang:Evidence from molybdenite Re-Os age of porphyry-type copper deposits and skarn-type copper polymetallic deposits[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2005, 29(4):482-490. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx200504008
[4] 徐进力, 邢夏, 张勤, 等.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法直接测定铜矿石中银铜铅锌[J].岩矿测试, 2010, 29(4):377-382. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100411
Xu J L, Xing X, Zhang Q, et al.Direct determination of silver, copper, lead and zinc in copper ores by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2010, 29(4):377-382. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100411
[5] 王小强, 侯晓磊, 杨惠玲.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法同时测定铅锌矿中银铜铅锌[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(5):576-579. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110510
Wang X Q, Hou X L, Yang H L.Simultaneous quantification of silver, copper, lead and zinc in lead-zinc ores by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(5):576-579. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110510
[6] 熊英, 王晓雁, 胡建平.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法同时测定铜铅锌矿石中铜铅锌钴镍等元素方法确认[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(3):209-304. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110310
Xiong Y, Wang X Y, Hu J P.Affirmation of the method that simultaneous determination of copper, lead, zinc, cobalt and nickel in copper, lead and zinc ores by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(3):209-304. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110310
[7] 王蕾, 温宏利, 马新荣, 等.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定硫化物矿中的高含量铅[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(3):305-309. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110311
Wang L, Wen H L, Ma X R, et al.Determination of high content of lead in sulfide ores by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(3):305-309. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110311
[8] 宋晓红, 冯旭, 段伟亚, 等.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-AES)测定硫化物矿石中的14种常微量元素[J].中国无机分析化学, 2014, 4(2):36-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201402010.htm
Song X H, Feng X, Duan W Y, et al.Determination of 14 kinds of major and minor elements in sulfide ore by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 4(2):36-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201402010.htm
[9] 马生凤, 温宏利, 马新荣, 等.四酸溶样-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定铁、铜、锌、铅等硫化物矿石中22个元素[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(1):65-72. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/3b86c674f242336c1eb95eb0-3.html
Ma S F, Wen H L, Ma X R, et al.Determination of 22 elements in iron, copper, zinc, and lead sulphide ores by ICP-AES with four acids digestion[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2011, 30(1):65-72. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/3b86c674f242336c1eb95eb0-3.html
[10] 宋召霞, 高云, 张志刚.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱(ICP-AES)法测定硫化物矿石中的铜铅锌[J].中国无机分析化学, 2017, 7(1):35-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX2013S1002.htm
Song Z X, Gao Y, Zhang Z G.Determination of copper, lead and zinc in sulphide ores by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 7(1):35-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX2013S1002.htm
[11] Balaram V, Anjaia K V, Reddy M R P.Comparative study on the trace and rare earth element analysis of an Indian polymetallic nodule reference sample by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Analyst, 1995, 120(5):1401-1406. doi: 10.1039/an9952001401
[12] 李清彩, 赵庆令, 荀红梅.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定多金属矿石中砷镉铟硫锑[J].冶金分析, 2015, 35(2):61-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yjfx201502013
Li Q C, Zhao Q L, Xun H M.Determination of arsenic, cadmium, indium, sulfur and antimony in polymetallic ore by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(2):61-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yjfx201502013
[13] 张世龙, 吴周丁, 刘小玲, 等.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定多金属矿石中铁、铜、铅、锌、砷、锑、钼和镉的含量[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2015, 51(7):930-933. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lhjy-hx201507009
Zhang S L, Wu Z D, Liu X L, et al.ICP-AES determination of Fe, Cu, Pb, Zn, As, Sb, Mo and Cd in multi-metal ores[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2015, 51(7):930-933. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lhjy-hx201507009
[14] 付桂花, 杨旭, 邱宏喜.硫脲介质ICP-OES测定多金属矿石中的银铝铋钴铜铁锰镍铅锑钛锌[J].黄金, 2015, 36(6):73-77. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/hk/Magazine?magazineId=huangj&yearIssue=2015_6
Fu G H, Yang X, Qiu H X.Determination of Ag, Al, Bi, Cu, Co, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Sb, Ti and Zn in poly-metallic ores by ICP-AES in thiourea medium[J].Gold, 2015, 36(6):73-77. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/hk/Magazine?magazineId=huangj&yearIssue=2015_6
[15] 刘高令, 姜贞贞, 吴文清, 等.盐酸介质下火焰原子吸收光谱法测定铅精粉中的高含量银[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(6):621-625. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.06.008
Liu G L, Jiang Z Z, Wu W Q, et al.Determination of high content silver in lead powder by flame atomic absorption spectrometry under hydrochloric acid medium[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(6):621-625. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.06.008
[16] 王俊桃, 毛云, 刘锦梅, 等.硫化矿物中无机盐及重金属离子溶出的影响因素探讨[J].安全与环境工程, 2007, 14(1):4-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KTAQ200701001.htm
Wang J T, Mao Y, Liu J M, et al.Study on aquatic environmental influence of mining solid waste material in the metal sulfide deposit area[J].Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2007, 14(1):4-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KTAQ200701001.htm
[17] Chao T T, Sanzolone R F, 李生郁.硫化矿物的化学溶解[J].国外地质勘探技术, 1981(9):28-32.
Chao T T, Sanzolone R F, Li S Y.Chemical dissolution of sulfide minerals[J].Foreign Geoexploration Technology, 1981(9):28-32.
-



 下载:
下载: