Surface Modification of Natural Mordenite and Its Application in Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution
-
摘要: 天然丝光沸石作为一种绿色廉价多孔材料广泛应用于环境治理中去除重金属,目前报道的天然沸石对重金属的去除率多在60%~90%,提升其去除效率已成为研究热点。本文采用正硅酸乙酯对天然丝光沸石进行表面重构改性,通过TEM、XRD、BET等手段表征其形貌和结构。结果表明:正硅酸乙酯水解生成的SiO2可与天然丝光沸石复合形成新颖的"SiO2/丝光沸石",原沸石表面包覆了新生纳米SiO2孔结构,同时没有损坏原始沸石的多孔结构,使改性沸石材料兼具了天然丝光沸石和纳米SiO2孔结构优点,增强了对重金属离子的吸附能力。该改性材料对水中Pb2+、Cd2+、Zn2+和Mn2+的最高吸附率为99.3%、97.1%、98.3%和97.0%,且极少解吸,性能稳定。考虑经济成本并保证合适吸附率的情况下选择吸附效率最佳的投加量,得到改性材料对初始浓度10 mg/L的Pb2+、Cd2+、Zn2+、Mn2+溶液的最佳投加量分别为0.5 g/L、2 g/L、2 g/L、5 g/L,可为中试和规模应用提供参考。较之焙烧、酸、碱、盐和有机改性,本改性方式对多种重金属均有高的吸附率,并显现出操作简便、成本低和环境友好等优势,具有较好应用前景。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDNatural mordenite is widely used as a green and cheap porous material to remove heavy metals in environmental treatment. Currently, the removal rate of heavy metals by natural zeolites is from 60% to 90%, and improving its removal efficiency has been a hot topic. OBJECTIVESTo reconstruct and modify natural mordenite by tetraethyl orthosilicate, and determine its effect on the removal of heavy metals in water. METHODSThe morphology and structure of the modified mordenites were characterized by TEM, XRD and BET. RESULTSThe SiO2 hydrolyzed by tetraethyl orthosilicate can be combined with natural mordenite to form a new 'SiO2/mordenite'. The surface of the original mordenite is coated with the pore structure of the new nano-SiO2 without damaging the porous structure of the original mordenite. The modified mordenite combines the advantages of natural mordenite and nano-SiO2 pore structure, enhancing the adsorption of heavy metal ions. The highest adsorption rate of modified mordenite for Pb2+, Cd2+, Zn2+, and Mn2+ was 99.3%, 97.1%, 98.3%, and 97.0%, respectively. The modified mordenites were minimally desorbed during the entire process and have stable performance. Considering the cost and the appropriate adsorption rate, the best dosage of adsorption efficiency is selected. The optimal dosage of Pb2+, Cd2+, Zn2+ and Mn2+ solutions for the initial concentration of 10 mg/L is 0.5, 2, 2 and 5 g/L, respectively. It can provide a reference for a pilot experiment and scale applications. CONCLUSIONSCompared with roasting, acid, alkali, salt and organic modification, this modification method has a high adsorption rate for a variety of heavy metals, and shows the advantages of simple operation, low cost and environmental friendliness, making it a good application prospect. -
Key words:
- natural mordenites /
- silica /
- surface modification /
- heavy metals /
- adsorption
-
水体中重金属因其高毒性和累积性伤害备受国内外学者关注[1-2]。目前我国多个河流发现重金属存在轻度到中等污染,尤以Cd、Pb、Cr和Hg最为严重[3-4];非洲Lagos地区发现93%的地下水样品存在重金属污染[5];欧洲Trepca和Sitnica河流域也发现水体和沉积物样品中Cd、As、Pb和Zn超标[6];北美地区则存在酸性矿山废水污染周边环境的问题[7]。因此,开发高效稳定、低廉环保和操作简便的治理方法意义重大。多种方法或技术已被开发用于去除重金属,包括化学沉淀、离子交换、电沉积、膜过滤、光化学过程和吸附法[8]。在这些方法中,吸附法因其简便高效和成本低廉得到最广泛的应用,其中吸附材料的选择对于吸附法去除重金属至关重要,已报道的吸附材料主要有生物质炭[9]、活性炭[10]、粉煤灰[11]、坡缕石[12]、海泡石[13]、天然沸石[14]等。 天然沸石因其独特的多孔和架状结构,自身带有丰富的孔道且比表面积大,具较强的吸附和离子交换能力,作为吸附剂具备应用效果显著且稳定、成本低、绿色环保的特点,被广泛应用于重金属废水处理[15]。目前报道的天然沸石对重金属的去除率多在60%~90%左右,这是由于天然沸石本身晶体结构的孔径较小,孔道狭窄,不易快速“抓取”重金属离子,且反应过程中窄小的孔道易被堵塞,后续的重金属离子难以进入沸石结构中,使吸附反应受阻,影响了沸石对重金属的快速吸附,总去除率偏低[16]。 对天然沸石的表面进行改性或修饰,如焙烧改性、盐酸改性、碱改性、复合改性和硅烷化改性[17-19],都是提高其去除重金属能力的可行的改性方法。焙烧改性、酸改性、碱改性主要是将沸石孔道增大或者孔容增大来扩大沸石的比表面积;复合改性是通过增大孔隙度来提高沸石的有效吸附表面;硅烷化改性则是在沸石表面接枝一定的有机物质,如氨基(—NH2)等,这些官能团可与重金属离子通过配位反应结合成稳定络合物[16]。然而,这些改性方法都是以扩大沸石本身的孔径、孔容为基础,或者只是有限地增加沸石比表面积,或者引入新的基团来增加对重金属离子的吸附[20-21],吸附能力有限,无法实现对重金属离子的快速“抓取”和连续吸附反应,并不能达到大批量、快速处理重金属废水的目的。因此,为了实现对溶液中重金属离子的快速“抓取”和吸附,有必要在保持天然沸石内部多孔结构的前提下,对天然沸石进行表面修饰或包覆新型结构,发展具有新型纳米介孔结构的改性沸石材料。基于此,本文采用硅酸乙酯水解生成SiO2与天然沸石复合,通过多种表征证实了该复合物兼具天然沸石和纳米SiO2孔结构的优点,可以大大提高对重金属离子的吸附能力。 1. 实验部分
1.1 实验材料和主要试剂
天然丝光沸石,购自浙江省缙云县,规格200目。主要成分SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、K2O、Na2O和CaO的含量分别为70.05%、12.02%、1.04%、1.88%、1.41%和2.69%。 正硅酸四乙酯溶液(纯度>99%,上海阿拉丁),无水乙醇溶液、氨水溶液、硝酸铅、氯化镉、氯化锌和氯化锰等试剂均为分析纯,去离子水。1.2 复合材料制备和表征
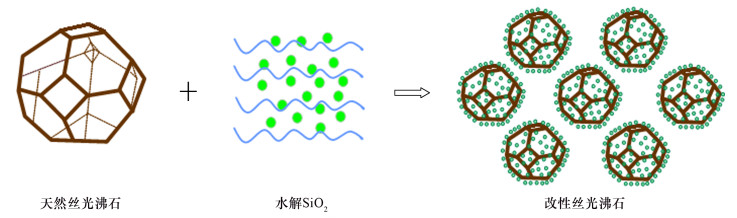
准确称取天然丝光沸石2 g用去离子水清洗干净,洗去杂质、大颗粒物等,烘干,研磨至粉末,过200目筛,备用;将清洗后的天然丝光沸石粉末与50 mL乙醇混合,超声分散30 min,然后缓慢投加正硅酸四乙酯溶液(准确称重溶液质量为1.415 g),滴加少量氨水调节pH至10左右,搅拌反应4 h。反应结束后,离心分离、烘干、研磨至粉末,得到具纳米二氧化硅孔结构的表面重构改性丝光沸石(以下简称“改性丝光沸石”)。合成过程见图 1。 分别采用美国FEI公司的Tecnai G2 F20 U-TWIN场发射透射电子显微镜、日本Rigaku公司的UltimaⅣ型X射线衍射仪(XRD,Cu靶Kα线,40 kV,20 mA)对样品的结构和形貌进行表征。用美国麦克公司的ASAP 2020(M+C)比表面积和孔隙度分析仪对样品的氮气吸附脱附情况、比表面积和孔径分布等进行BET分析,测试孔径分布使用BJH方法。1.3 吸附条件实验
1.3.1 吸附时间对铅镉锌锰吸附量的影响实验
分别配制4种500 mL重金属离子浓度为10 mg/L的Pb(NO3)2、CdCl2、ZnCl2和MnCl2溶液,各自投加0.5 g的改性丝光沸石粉末,然后在振速200 r/min、pH=7、常温的实验条件下进行磁力搅拌反应,在不同时间段(0.5 h、1 h、3 h、8 h和24 h)取混合溶液样测试其重金属离子的浓度,采用Optima 8300型电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(美国PerkinElmer公司)测定溶液中重金属浓度。相同实验条件下,相同时间段内,向相同浓度四种重金属溶液分别投加天然丝光沸石粉末和单独硅酸乙酯水解生成的SiO2粉末(以下简称“水解SiO2”)进行对照试验。控制实验条件一致:振速200 r/min,常温,pH=7。实验设计两组平行,三次重复。吸附剂对重金属离子的去除率η(%)依照公式(1)计算[22-23]:式中:C0和Ce分别为吸附前后溶液中重金属离子浓度(mg/L)。η=C0−CeC0×100% (1) 1.3.2 投加量对铅镉锌锰吸附量的影响实验
分别向Pb2+、Cd2+、Zn2+和Mn2+四种重金属浓度均为10 mg/L的溶液中投加改性丝光沸石0.01、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.5和0.8 g,常温下搅拌,测试1 h后的溶液中重金属浓度,探索改性丝光沸石不同投加量对Pb2+、Cd2+、Zn2+和Mn2+快速吸附去除的影响,在兼顾去除效果与经济成本的情况下得到最优投加量。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 改性前后天然丝光沸石的形貌
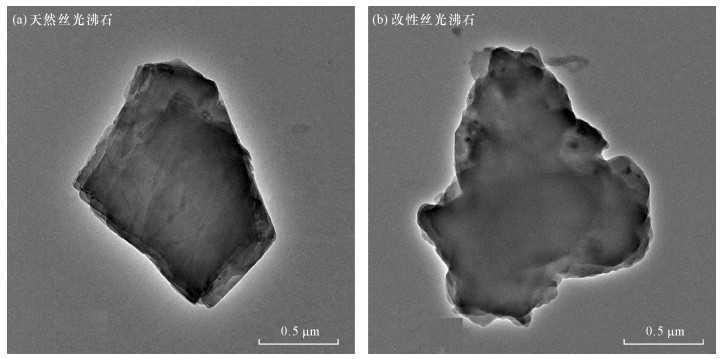
对改性前后的天然丝光沸石进行透射电镜分析,由图 2可以看出:①改性前的沸石材料晶体特征明显,表面有不规整棱角;②改性后的天然丝光沸石表面的棱角变得柔和圆润,说明在材料制备过程中天然丝光沸石表面出现重构,有特定物质包覆在原始天然丝光沸石表面。改性后的丝光沸石表面积增大,内部形貌并未有改变。2.2 改性前后天然丝光沸石的成分及结构
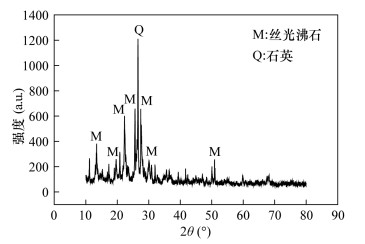
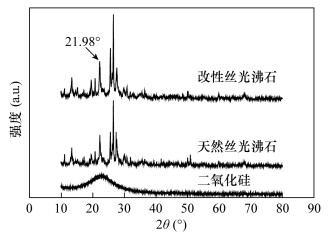
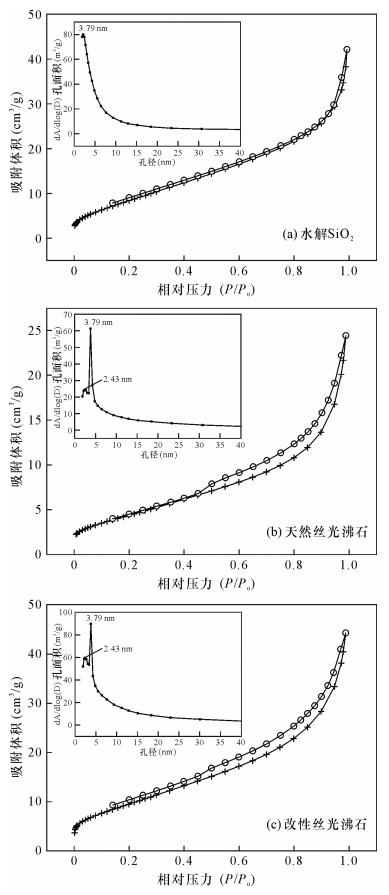
基于对改性丝光沸石形貌的认识,对天然丝光沸石和改性丝光沸石粉末进行X射线衍射表征分析来明确其成分和结构。从图 3可以看出:天然沸石在2θ=13.38°、19.58°、22.20°、25.57°、27.68°、30.85°和50.98°处分别对应丝光沸石(PDF#06-0239)的(111)、(330)、(150)、(202)、(511)和(322)晶面,在2θ=26.64°处对应石英(PDF#46-1045)的(101)晶面。明确所购天然沸石主要成分为丝光沸石,其他主要成分为石英等。 图 4为天然丝光沸石、水解硅和改性丝光沸石的X射线衍射图谱,可以看出,改性后沸石图谱由天然丝光沸石和水解SiO2的图谱叠加而成,在2θ=21.98°呈现明显叠加,表明改性丝光沸石有一定的水解SiO2包覆。改性后的沸石X射线衍射图谱除在2θ=21.98°明显叠加外,其余各个位置谱线没有发生明显变化,说明改性并未改变天然丝光沸石的原始晶体结构,仍然保留了原始天然丝光沸石的多孔结构。由图 5氮气吸附脱附结果可得水解SiO2、天然丝光沸石和改性丝光沸石的BET比表面积分别16.76、34.25和36.25 m2/g,表明天然丝光沸石经改性后的比表面积增加。改性后,吸附等温线的形状并没有发生明显变化,说明改性并未改变原始天然丝光沸石的结构,这也印证了图 4中X射线衍射分析的结论。孔径方面,水解SiO2、天然丝光沸石和改性丝光沸石的平均孔径分别为6.97、9.04和7.57 nm,改性后沸石的比表面积增加,微孔数量增加,孔径分布更均匀,孔容积更大,有利于提高吸附性能。2.3 材料模拟吸附实验
2.3.1 吸附时间对铅镉锌锰吸附量的影响
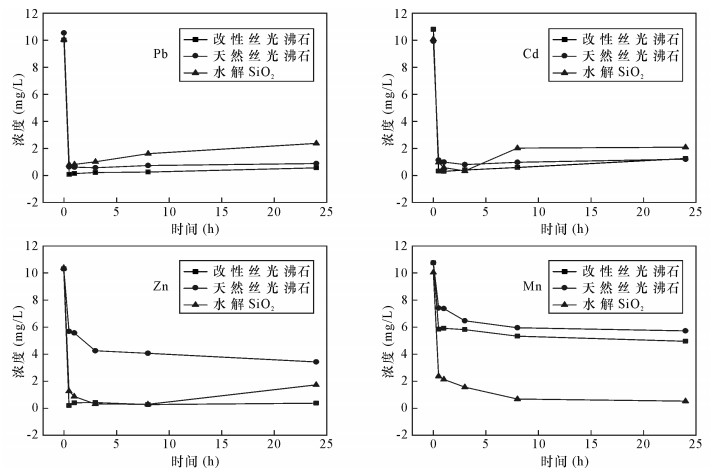
由图 6可知:①改性丝光沸石和天然丝光沸石对四种重金属离子的吸附都是在初始时(0.5~2 h)吸附较快,吸附速率大,大部分吸附过程是在开始时相当短的时间内完成的;②改性丝光沸石拥有更高的反应速率,对四种重金属在相同时间内的吸附量均大于天然丝光沸石,在反应0.5 h后改性丝光沸石对四种重金属离子的吸附率大小顺序为:Pb2+(99.3%)>Zn2+(98.3%)>Cd2+(97.1%)>Mn2+(45.7%);③改性丝光沸石对于Pb2+、Zn2+和Cd2+同时也是最高吸附率,即在0.5 h内快速达到吸附平衡。结合上述表征结果,推测是由于天然丝光沸石表面包覆的新生纳米SiO2孔结构发挥了作用,这些孔结构以外表面吸附为主,吸附速率快[24],实现了对溶液中重金属离子的快速“抓取”和吸附。同时在改性丝光沸石内部保持了天然丝光沸石的内部多孔结构,可用于储存和驻留重金属离子,增加了改性丝光沸石的吸附位点,提升了吸附容量。 水解SiO2作为对照组,对于Pb2+、Cd2+、Zn2+从3 h开始出现较多解吸,24 h时解吸附量最大,而天然丝光沸石和改性丝光沸石在0.5 h及以后时间段内均不解吸。可以看出,单独的水解SiO2对于重金属离子的吸附并不稳定,由于不具备天然丝光沸石的内部多孔结构而呈现较多解吸。2.3.2 投加量对铅镉锌锰吸附量的影响
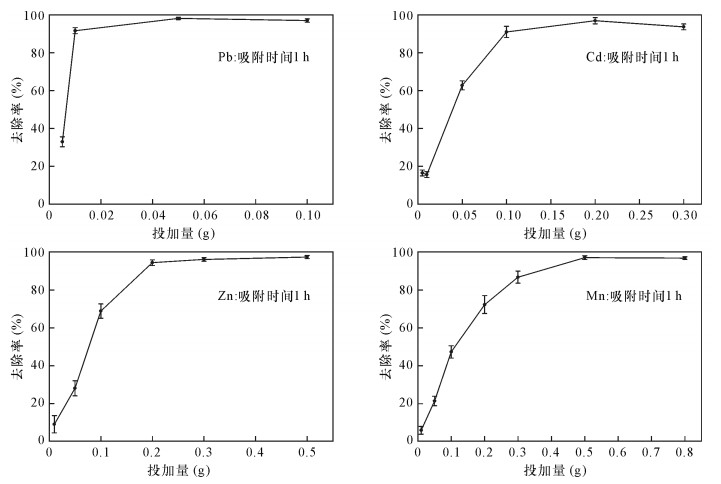
由图 7可知,改性丝光沸石对于Pb2+、Cd2+、Zn2+和Mn2+四种重金属溶液的吸附量都是随投加量的增大先增加后减小,吸附效率随投加量的增大呈增加趋势,到达一个固定值后基本保持不变或略有下降。为了既得到较好的吸附效果,又有效地利用材料,有必要确定最佳吸附投加量。分析可知,改性丝光沸石对500 mL浓度10 mg/L的Pb2+溶液在投加量为0.25 g时达到最佳吸附投加量,故0.5 g/L为改性丝光沸石吸附Pb2+的最佳投加量。当投加量达最佳后,随着投加量的增大,吸附效率出现下降。吸附材料的利用效率只有在最佳投加量时最大。投加量在0.5 g/L时,Pb2+的吸附率达98%,同理可得Cd2+、Zn2+、Mn2+的最佳吸附投加量为2 g/L、2 g/L、5 g/L,对应的吸附率:Cd2+为97%,Zn2+为94%,Mn2+为97%。由各个重金属投加量分析发现,在最佳投加量前,四种重金属的吸附量都是随投加量的增大而增大;在最佳投加量后,随投加量的增大,吸附效率降低,这是因为在达最佳投加量前,吸附剂的吸附量达饱和,吸附量受吸附剂量的制约,在最佳投加量后,吸附剂吸附容量有剩余,吸附剂质量的增加导致吸附效率的降低。故综合考虑,为了既使吸附剂容量饱和,不浪费吸附位能,尽可能减少吸附剂用量,又保证良好的吸附效果,应在中试或规模应用中使用最佳投加量[25]。2.4 改性丝光沸石与其他吸附材料综合性能比较
表 1中给出了不同天然沸石吸附材料的制备方法、吸附效果、吸附平衡时所达最大吸附量数据。比较可得,本研究所用改性方法得到的复合材料有极佳的吸附重金属效果。制备方法简便易行,不需高温热能损耗(常温反应),制备过程简单快速(一次制备),制备时间短(反应仅4 h)。所制得的改性丝光沸石对重金属离子吸附性能高,能在较短时间内(0.5 h)完成吸附,较其他材料快约0.5~1.5 h,且不易解吸,对多种重金属均有较高的吸附率,去除效果多高于文献报道值。故本研究所述改性沸石制备方法与改性沸石复合材料是一种效果好、具实用和推广价值的方法和修复材料。表 1. 不同天然沸石改性方法吸附去除水溶液中重金属效果比较Table 1. Comparison of adsorption capacity of different modified methods of zeolites for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution天然沸石改性方法 改性过程或主要步骤 改性材料投加量 吸附率 参考文献 焙烧改性 沸石300℃焙烧1.5 h 10 g/L Pb:98%
Co:40%[26] 盐酸改性 10%盐酸浸泡24 h,再去离子水冲洗,105℃烘干 100 g/L Pb:95% [27] 氢氧化钠改性 2 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液浸泡,室温振荡2.5 h,抽滤,冲洗至中性,烘干 10 g/L Cd:99% [28] 氢氧化钠改性 2 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液浸泡,室温振荡2.5 h,抽滤,冲洗至中性,烘干 5 g/L Zn:95%
Cd:97%[29] 氯化钠改性 2 mol/L氯化钠溶液浸泡24 h,烘干 1 g/L Pb:90%
Cd:90%
Ni:90%[30] 硫酸/硫酸铜复合改性 1 mol/L硫酸浸泡10 h后洗净,105℃下烘干,再1 mol/L硫酸铜溶液浸泡10 h,105℃下烘干 40 g/L Cr:94% [31] 接枝氨基 沸石先酸碱活化,后与3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷混合于甲苯中80℃搅拌24 h,洗涤,干燥 Ni:1 g/L
Cu:1 g/L
Zn:1.6 g/L
Pb:0.6 g/LNi:90%
Cu:20%
Zn:34%
Pb:90%[25] 本研究
(正硅酸乙酯表面改性)沸石粉末与硅酸-乙酯溶液在乙醇中常温搅拌5 h,洗涤,烘干 Pb:0.5 g/L
Zn、Cd:2 g/L
Mn:5 g/LPb:99.3%
Cd:97.1%
Zn:98.3%
Mn:97.0%本研究 3. 结论
通过对改性后的天然丝光沸石进行表征,包括TEM、XRD和BET分析,证实了原始天然沸石在合成过程中其表面发生重构,有特定的纳米SiO2孔结构包覆,能更好地吸附溶液中重金属离子,为天然矿物材料通过简单改性应用于水中吸附重金属提供了思路。 由吸附时间对Pb、Cd、Zn和Mn吸附量的影响可知,改性丝光沸石和天然丝光沸石对四种重金属离子的吸附都是在初始短时间内(0.5~2 h)完成的,较天然丝光沸石有更快的反应速率。实际应用中,在保证合适吸附率并考虑成本情况下应选择吸附效率最高的最佳投加量,如在本研究确定的最佳投加量条件下,改性丝光沸石对四种常见重金属的吸附率(Pb2+、Zn2+、Cd2+、Mn2+分别为98%、94%、97%、97%)明显高于原始天然丝光沸石,对多种重金属均能实现高效吸附,且多优于文献报道,操作简便,具备很好的实用价值。要点
- (1) 研究了一种新型表面改性天然丝光沸石的制备方法并对其进行表征。
- (2) 改性丝光沸石在吸附去除重金属和时间效率方面显示出较大的优势。
- (3) 研究了改性丝光沸石吸附去除水中重金属的最佳投加量。
- (4) 为天然矿物材料通过简单改性应用于水中吸附去除重金属提供了新思路。
HIGHLIGHTS
- (1) The preparation and characterization of a new type of surface modified natural mordenite were presented.
- (2) The modified mordenite showed considerable advantages in removal of heavy metals and time efficiency.
- (3) The optimum dosage of modified mordenite for removing heavy metals in water was studied.
- (4) A new idea for the removal of heavy metals in water by simple modification of natural minerals was provided.
-
表 1 不同天然沸石改性方法吸附去除水溶液中重金属效果比较
Table 1. Comparison of adsorption capacity of different modified methods of zeolites for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution
天然沸石改性方法 改性过程或主要步骤 改性材料投加量 吸附率 参考文献 焙烧改性 沸石300℃焙烧1.5 h 10 g/L Pb:98%
Co:40%[26] 盐酸改性 10%盐酸浸泡24 h,再去离子水冲洗,105℃烘干 100 g/L Pb:95% [27] 氢氧化钠改性 2 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液浸泡,室温振荡2.5 h,抽滤,冲洗至中性,烘干 10 g/L Cd:99% [28] 氢氧化钠改性 2 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液浸泡,室温振荡2.5 h,抽滤,冲洗至中性,烘干 5 g/L Zn:95%
Cd:97%[29] 氯化钠改性 2 mol/L氯化钠溶液浸泡24 h,烘干 1 g/L Pb:90%
Cd:90%
Ni:90%[30] 硫酸/硫酸铜复合改性 1 mol/L硫酸浸泡10 h后洗净,105℃下烘干,再1 mol/L硫酸铜溶液浸泡10 h,105℃下烘干 40 g/L Cr:94% [31] 接枝氨基 沸石先酸碱活化,后与3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷混合于甲苯中80℃搅拌24 h,洗涤,干燥 Ni:1 g/L
Cu:1 g/L
Zn:1.6 g/L
Pb:0.6 g/LNi:90%
Cu:20%
Zn:34%
Pb:90%[25] 本研究
(正硅酸乙酯表面改性)沸石粉末与硅酸-乙酯溶液在乙醇中常温搅拌5 h,洗涤,烘干 Pb:0.5 g/L
Zn、Cd:2 g/L
Mn:5 g/LPb:99.3%
Cd:97.1%
Zn:98.3%
Mn:97.0%本研究 -
[1] Li Z Y, Ma Z W, van Der Kuijp T J, et al.A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China:Pollution and health risk assessment[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468:843-853. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/24076505
[2] Li H X, Ji H B, Shi C J, et al.Distribution of heavy metals and metalloids in bulk and particle size fractions of soils from coal-mine brownfield and implications on human health[J].Chemosphere, 2017, 172:505-515. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.021
[3] Xu C, Zhou P J, Li H Y, et al.Contamination and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soil of Xiangxi River water-level-fluctuating zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J].Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2017, 23(4):851-863. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2017.1288562
[4] Jia Y Y, Wang L, Qu Z P, et al.Distribution, contamin-ation and accumulation of heavy metals in water, sediments, and freshwater shellfish from Liuyang River, Southern China[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(7):7012-7020. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-1068-x
[5] Momodu M A, Anyakora C A.Heavy metal contamination of ground water:The surulere case study[J].Research Journal of Environmental & Earth Sciences, 2010, 2(1):39-43. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103253931.html
[6] Ferati F, Kerolli-Mustafa M, Kraja-Ylli A.Assessment of heavy metal contamination in water and sediments of Trepca and Sitnica rivers, Kosovo, using pollution indicators and multivariate cluster analysis[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(6):DOI10.1007/s10661-015-4524-4. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=16f34c4be028c1b657a931a9e2e75ead
[7] Kastyuchik A, Karam A, Aïder M.Effectiveness of alkaline amendments in acid mine drainage remediation[J].Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2016, 6:49-59. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352186416300244
[8] Zhao Y N.Review of the natural, modified, and synthetic zeolites for zeavy metals removal from wastewater[J].Environmental Engineering Science, 2016, 33(7):443-454. doi: 10.1089/ees.2015.0166
[9] Son E B, Poo K M, Chang J S, et al.Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions using engineered magnetic biochars derived from waste marine macro-algal biomass[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 615:161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.171
[10] Rahman M M, Adil M, Yusof A M, et al.Removal of heavy metal ions with acid activated carbons derived from oil palm and coconut shells[J].Materials (Basel), 2014, 7(5):3634-3650. doi: 10.3390/ma7053634
[11] Hizal J, Tutem E, Guclu K, et al.Heavy metal removal from water by red mud and coal fly ash:An integrated adsorption-solidification/stabilization process[J].Desalination and Water Treatment, 2013, 51(37-39):7181-7193. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2013.771289
[12] Cao J S, Wang C, Fang F, et al.Removal of heavy metal Cu(Ⅱ) in simulated aquaculture wastewater by modified palygorskite[J].Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219:924-931. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.014
[13] 谭科艳, 王喆, 蔡敬怡, 等.地球化学工程技术修复江西某Pb超标耕地的应用[J].地球学报, 2017, 38(6):953-960. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201706010
Tan K Y, Wang Z, Cai J Y, et al.The application of geochemical engineering technology to the remediation of a Pb-polluted abandoned farmland in Jiangxi Province[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(6):953-960. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201706010
[14] Ciosek A L, Luk G K.Kinetic modelling of the removal of multiple heavy metallic ions from mine waste by natural zeolite sorption[J].Water, 2017, 9(7):DOI:10.3390/w9070482.
[15] Inglezakis V J, Fyrillas M M, Stylianou M A.Two-phase homogeneous diffusion model for the fixed bed sorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites[J].Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 266:164-176. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.02.045
[16] Reeve P J, Fallowfield H J.Natural and surfactant modi-fied zeolites:A review of their applications for water remediation with a focus on surfactant desorption and toxicity towards microorganisms[J].Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 205:253-261.
[17] Wen J, Yi Y J, Zeng G M.Effects of modified zeolite on the removal and stabilization of heavy metals in contaminated lake sediment using BCR sequential extraction[J].Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 178:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.04.046
[18] Mulyati S, Arahman N, Syawaliah, et al.Removal of Me-tal Iron from Groundwater Using Aceh Natural Zeolite and Membrane Filtration[C]//Proceedings of 1st Annual Applied Science and Engineering Conference (Aasec), 2017.
[19] Tran H N, Viet P V, Chao H P.Surfactant modified zeolite as amphiphilic and dual-electronic adsorbent for removal of cationic and oxyanionic metal ions and organic compounds[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 147:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.027
[20] Liu Y, Lou Z M, Sun Y, et al.Influence of complexing agent on the removal of Pb(Ⅱ) from aqueous solutions by modified mesoporous SiO2[J].Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 246:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.03.005
[21] Zendehdel M, Shoshtari-Yeganeh B, Cruciani G.Removal of heavy metals and bacteria from aqueous solution by novel hydroxyapatite/zeolite nanocomposite, preparation, and characterization[J].Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 2016, 13(10):1915-1930. doi: 10.1007/s13738-016-0908-9
[22] Kim S A, Kamala-Kannan S, Oh S G, et al.Simultaneous removal of chromium(Ⅵ) and Reactive Black 5 using zeolite supported nano-scale zero-valent iron composite[J].Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(5):447. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4855-z
[23] Lin J, Zhan Y.Adsorption of humic acid from aqueous solution onto unmodified and surfactant-modified chitosan/zeolite composites[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 200-202:202-213. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.039
[24] 吴昆明, 郭华明, 魏朝俊.改性磁铁矿对水体中砷的吸附特性研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(6):624-632. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201709110147
Wu K M, Guo H M, Wei C J.Adsorption characteristics of arsenic in water by modified magnetite[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(6):624-632. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201709110147
[25] 石太宏, 吕灿, 左莉娜.硅烷化改性沸石对重金属离子的吸附性能[J].环境工程学报, 2013, 7(3):1045-1052. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201303043
Shi T H, Lü C, Zuo L N.Adsorption of heavy metal ions by silylation modified zeolite[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(3):1045-1052. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201303043
[26] 易发成.沸石的活化处理及其对铅、钴的吸附性研究[J].矿物岩石, 2005, 25(3):118-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2005.03.026
Yi F C.The activation treatment and Pb2+, Co2+ ions adsorption capability of zeolite[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2005, 25(3):118-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2005.03.026
[27] 郝鹏飞, 梁靖, 钟颖.改性沸石对含铅废水的处理研究[J].环境科学与管理, 2009, 34(6):106-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2009.06.031
Hao P F, Liang J, Zhong Y.The research of modified zeolite to the disposal of leaded wastewater[J].Environmental Science and Management, 2009, 34(6):106-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2009.06.031
[28] 陈溪, 崔天顺, 邓晓军, 等.改性沸石对镉(Ⅱ)的交换性能研究[J].工业安全与环保, 2015, 41(4):55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2015.04.018
Chen X, Cui T S, Deng X J, et al.Research on the Cd2+ ion exchange by modified zeolite[J].Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2015, 41(4):55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2015.04.018
[29] 李蘅, 张静, 徐文炘, 等.沸石处理选矿重金属废水初步研究[J].矿产与地质, 2015, 29(5):682-687. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2015.05.025
Li H, Zhang J, Xu W X, et al.A preliminary study on treatment of heavy metal beneficiation wastewater by zeolite[J].Mineral Resources and Geology, 2015, 29(5):682-687. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2015.05.025
[30] Maretto M, Bianchi F, Vignola R, et al.Microporous and mesoporous materials for the treatment of wastewater produced by petrochemical activities[J].Journal of Cleaner Production, 2014, 77:22-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.070
[31] 文叶轩, 郝硕硕, 朱家亮, 等.天然和改性沸石对铬吸附特征研究[J].中国陶瓷, 2015, 51(7):16-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTC201507005.htm
Wen Y X, Hao S S, Zhu J L, et al.Research on adsorption characteristics of chromium on natural and modified zeolite[J].China Ceramics, 2015, 51(7):16-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTC201507005.htm
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 张玉玲,赵伟,王国建,张杰,宗晓彤,佟俊,董慧芳,裴仁彦. 丝光沸石分子筛在环境领域的研究及应用进展. 工业催化. 2024(07): 19-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林小淳,刘晓瑜,袁欣,张隆隆,刘斯文,冯亚鑫,赵晓倩,黄园英. 碱改性沸石吸附铅和氨氮性能及对稀土矿山土壤的修复作用. 岩矿测试. 2023(06): 1177-1188 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李洪涛,盛路阳,王永利,展俊岭,张钰. 金属氧化物改性丝光沸石柱状晶的制备及性能研究. 有色金属(冶炼部分). 2021(07): 62-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李超,王丽萍. 矿物材料处理废水的研究进展. 矿产保护与利用. 2020(01): 65-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邵坤,赵改红,赵朝辉. 腐植酸改性强化磁铁矿吸附水体中铅镉的实验研究. 岩矿测试. 2019(06): 715-723 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)
-





 下载:
下载: