Speciation Analysis of Inorganic Selenium in Soil by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry
-
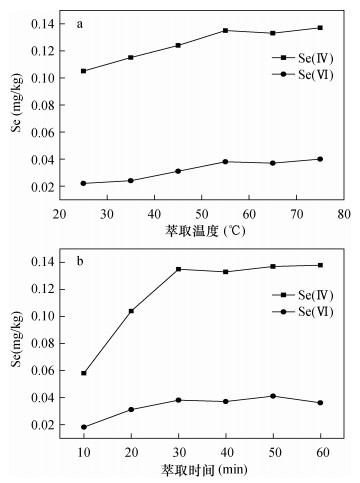
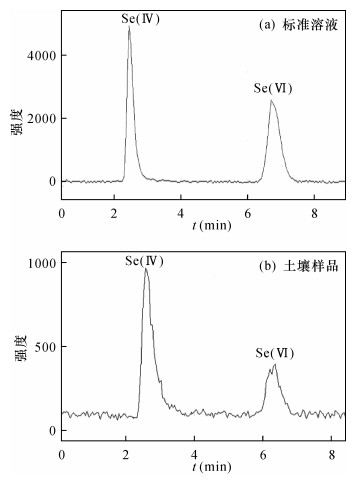
摘要: 土壤样品中亚硒酸盐Se(Ⅳ)和硒酸盐Se(Ⅵ)的形态分析中,提取剂的选择和检测方法是技术的关键。以往的提取剂容易导致硒形态发生转变或无法同时提取Se(Ⅳ)和Se(Ⅵ),常用的氢化物发生原子荧光光谱法无法直接测定Se(Ⅵ),而是通过差减法得出Se(Ⅵ)含量。本文对比了不同提取剂的提取能力,确定使用0.1 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液作为提取剂,在55℃超声萃取土壤样品30 min,提取液经高效液相色谱分离,电感耦合等离子体质谱检测,建立了土壤中Se(Ⅳ)和Se(Ⅵ)的形态分析方法。采用Hamilton PRP X-100色谱柱,以6 mmol/L柠檬酸为流动相,pH=5.5,在8 min内可完全分离Se(Ⅳ)和Se(Ⅵ),两者的检出限分别为0.15 μg/L、0.16 μg/L,线性相关系数(r2)均大于0.999。以土壤为基体进行加标回收试验,Se(Ⅳ)和Se(Ⅵ)的回收率在84.2%~95.8%之间,相对标准偏差为1.4%~5.3%(n=6)。该方法简单快速,具有良好的精密度和准确度,适用于土壤中无机硒的形态分析。
-
关键词:
- 土壤 /
- 亚硒酸盐 /
- 硒酸盐 /
- 氢氧化钠 /
- 高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUNDIn the speciation analysis of selenite Se (Ⅳ) and selenite Se (Ⅵ) in soil samples, the key problem is to select the extraction agents and detection methods. In the past, extraction agents may lead to Se species redistribution or cannot extract both Se (Ⅳ) and Se (Ⅵ). Selenium speciation has been routinely determined by Hydride Generation-Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (HG-AAS). However, Se (Ⅵ) cannot be directly measured and its concentration is calculated by the difference between analyzed total Se and Se (Ⅳ) concentrations. OBJECTIVESIn order to establish an analysis method for the determination of Se (Ⅳ) and Se (Ⅵ) in soil samples by selecting the appropriate extraction agent and determination technique. METHODSThe extraction capacity of different extraction agents was compared and 0.1 mol/L sodium hydroxide was selected for the experiment. Selenium species were quantitatively extracted in a ultrasonic field at 55℃ for 30 min. An analytical method for determination of Se (Ⅳ) and Se (Ⅵ) by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS) was established. RESULTSThe results show that Se (Ⅳ) and Se (Ⅵ) can be separated within 8 min by using a Hamilton PRP X-100 reversed-phase anion exchange column with 6 mol/L citric acid as mobile phase under pH of 5.5. The detection limits of Se (Ⅳ) and Se (Ⅵ) are 0.15 μg/L and 0.16 μg/L, respectively. Linear correlation coefficient (r2) is more than 0.999, the recoveries are 84.2%-95.8%, and the relative standard deviations are 1.4%-5.3% (n=6). CONCLUSIONSThe proposed method is simple and fast and has good accuracy and high precision, which meets the requirements for analyzing inorganic selenium in soil. -

-
表 1 使用不同提取剂提取土壤中硒形态分析结果
Table 1. Analytical results of selenium species in soil extracted with different agents
土壤样品 硒形态 提取剂 超纯水 柠檬酸 磷酸盐溶液 碳酸氢钠 氢氧化钠 土壤1 Se(Ⅳ)含量(mg/kg) ND ND 0.055 0.029 0.135 Se(Ⅵ)含量(mg/kg) ND ND ND ND 0.038 硒形态总量(mg/kg) - - 0.055 0.029 0.173 总硒(mg/kg) 0.302 0.302 0.302 0.302 0.302 硒提取率(%) - - 18.21 9.6 57.28 Se(Ⅳ)含量(mg/kg) ND ND 0.154 0.122 0.206 Se(Ⅵ)含量(mg/kg) ND ND ND ND 0.078 土壤2 硒形态总量(mg/kg) - - 0.154 0.122 0.284 总硒(mg/kg) 0.362 0.362 0.362 0.362 0.362 硒提取率(%) - - 42.54 33.70 78.49 Se(Ⅳ)含量(mg/kg) ND ND 0.063 0.035 0.118 Se(Ⅵ)含量(mg/kg) ND ND ND ND 0.022 土壤3 硒形态总量(mg/kg) - - 0.063 0.035 0.140 总硒(mg/kg) 0.218 0.218 0.218 0.218 0.218 硒提取率(%) - - 28.90 16.06 64.19 注:ND表示未检出。 表 2 Se(Ⅳ)和Se(Ⅵ)的线性范围、检出限和加标回收试验
Table 2. Linear ranges, detection limits and spiked recoveries of Se(Ⅳ) and Se(Ⅵ)
硒形态 线性范围(μg/L) 线性方程 相关系数(r2) 方法检出限(μg/L) 加标回收率试验(n=6) 标准加入量(mg/kg) 测定值(mg/kg) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 0 0.135 - - Se(Ⅳ) 0.5~500 y=667.2x+843.8 0.9996 0.15 0.100 0.223 87.7 2.5 0.200 0.322 93.4 1.4 0 0.038 - - Se(Ⅵ) 0.5~500 y=685.4x-233.0 0.9997 0.16 0.020 0.080 84.2 5.3 0.050 0.134 95.8 4.2 表 3 样品分析结果
Table 3. Analytical results of the sample
样品编号 Se(Ⅳ)含量(mg/kg) Se(Ⅵ)含量
(mg/kg)硒形态总量
(mg/kg)总硒
(mg/kg)硒提取率
(%)1 0.028 0.016 0.045 0.239 18.68 2 0.048 0.024 0.072 0.330 21.77 3 0.041 0.015 0.056 0.123 45.17 4 0.082 0.040 0.122 0.159 76.51 5 0.048 0.018 0.066 0.164 40.29 6 0.306 0.077 0.384 0.646 59.37 7 0.433 0.032 0.465 0.762 61.03 8 0.158 0.039 0.197 0.346 57.04 9 0.047 0.020 0.067 0.101 65.97 10 0.049 0.019 0.068 0.112 60.96 11 0.192 0.067 0.259 0.360 71.82 12 0.283 0.092 0.375 0.502 74.73 13 0.057 0.021 0.078 0.160 48.70 14 0.044 0.018 0.062 0.127 48.49 15 0.057 0.019 0.076 0.165 46.14 16 0.066 0.036 0.101 0.214 47.40 17 0.087 0.027 0.114 0.230 49.65 18 0.060 0.021 0.081 0.168 48.39 19 0.118 0.022 0.140 0.218 64.19 20 0.058 0.028 0.085 0.221 38.52 21 0.170 0.033 0.203 0.247 82.06 22 0.050 0.016 0.066 0.088 74.60 23 0.076 0.031 0.107 0.217 49.30 24 0.055 0.023 0.077 0.148 52.36 25 0.206 0.078 0.284 0.362 78.49 -
[1] Kápolna E, Fodor P.Speciation analysis of selenium enriched green onions (allium fistulosum) by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Microchemical Journal, 2006, 84(1):56-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a1f9c00df113dd9069484275276da325
[2] 王丙涛, 谢丽琪, 林燕奎, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用检测食品中的五种硒形态[J].色谱, 2011, 29(3):223-227. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sp201103007
Wang B T, Xie L Q, Lin Y K, et al.Determination of selenium species in food by high performance liquid chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2011, 29(3):223-227. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sp201103007
[3] Uden P C, Boakye H T, Kahakachchi C, et al.Selective detection and identification of Se containing compounds-Review and recent developments[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1050(1):85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2004.05.077
[4] 王欣, 幸苑娜, 陈泽勇, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法检测富硒食品中6种硒形态[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(11):1669-1674. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201311008
Wang X, Xing Y N, Chen Z Y, et al.Determination of 6 selenium species in selenium-enriched food by hyphenated technique of high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(11):1669-1674. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201311008
[5] Dumont E, Vanhaecke F, Cornelis R.Selenium speciation from food source to metabolites:A critical review[J].Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2006, 385(7):1304-1323. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16830114
[6] Połatajko A, Jakubowski N, Szpunar J.State of the art report of selenium speciation in biological samples[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2006, 21(7):639-654. doi: 10.1039/B605654G
[7] 邱建华, 王秋泉, 黄本立.硒形态分析研究进展[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2006, 26(9):1692-1701. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2006.09.032
Qiu J H, Wang Q Q, Huang B L.New approaches to selenium speciation[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2006, 26(9):1692-1701. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2006.09.032
[8] B'Hymer C, Caruso J A.Selenium speciation analysis using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2006, 1114(1):1. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.02.063
[9] Ogra Y, Anan Y.Selenometabolomics:Identification of selenometabolites and specification of their biological significance by complementary use of elemental and molecular mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2009, 24(11):1477-1488. doi: 10.1039/b910235c
[10] Rayman M P.Food-chain selenium and human health:Emphasis on intake[J].British Journal of Nutrition, 2008, 100(2):254-268. http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_JJ026744445
[11] Antanaitis A, Lubyte J, Antanaitis S, et al.Selenium con-centration dependence on soil properties[J].Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment, 2008, 6(1):163-167.
[12] Muchowski P.Assessing the speciation and the bioge-ochemical processes affecting the mobility of selenium from a geological repository of radioactive wastes to the biosphere[J].Analysis, 1998, 26(5):193-197.
[13] Abrams M M, Burau R G, Zasoski R J.Organic selenium distribution in selected California soils[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1990, 54(4):979-982. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1990.03615995005400040007x
[14] Zhang Y, Moore J N.Selenium fractionation and spe-ciation in a wetland system[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1996, 30(8):2613-2619.
[15] Masscheleyn P H, Delaune R D, Patrick W H J.Trans-formations of selenium as affected by sediment oxidation-reduction potential and pH[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1990, 24(1):91-96. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/19901946460.html
[16] Masscheleyn P H, Delaune R D, Patrick W H.Arsenic and selenium chemistry as affected by sediment redox potential and pH[J].Journal of Environmental Quality, 1991, 20(3):522-527. http://femsec.oxfordjournals.org/lookup/external-ref?access_num=10.1021/es00020a008&link_type=DOI
[17] 方金梅.福州市土壤硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(2):28-32. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080238
Fang J M.Selenium speciation analysis and its transformation and enrichment in soils of Fuzhou city[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(2):28-32. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080238
[18] 徐强, 迟凤琴, 匡恩俊, 等.基于通径分析的土壤性质与硒形态的关系——以黑龙江省主要类型土壤为例[J].土壤, 2016, 48(5):992-999. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201605022
Xu Q, Chi F Q, Kuang E J, et al.Relationship between soil physico-chemical properties and selenium species based on path analysis[J].Soils, 2016, 48(5):992-999. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201605022
[19] Favorito J E, Luxton T P, Eick M J, et al.Selenium speciation in phosphate mine soils and evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure using XAFS[J].Environmental Pollution, 2017, 229:911-921. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.071
[20] 耿建梅, 王文斌, 罗丹, 等.不同浸提剂对海南稻田土壤有效硒浸提效果比较[J].土壤, 2010, 42(4):624-629. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201004021
Geng J M, Wang W B, Luo D, et al.Comparative studies on effects of several extractants on available selenium of paddy soils in Hainan[J].Soils, 2010, 42(4):624-629. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201004021
[21] 温国灿, 黄艳, 郭永玲, 等.酸性土壤有效硒提取条件优化的研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(5):1996-2000. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2007.05.079
Wen G C, Huang Y, Guo Y L, et al.Optimal conditions of extraction method for available selenium in acid soils[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(5):1996-2000. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2007.05.079
[22] Wright M T, Parker D R, Amrhein C.Critical evaluation of the ability of sequential extraction procedures to quantify discrete forms of selenium in sediments and soils[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(20):4709-4716. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=09399abef22eb9cd664580b2130f7ffa
[23] Stroud J L, McGrath S P, Zhao F J.Selenium speciation in soil extracts using LC-ICP-MS[J].International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 92(2):222-236. doi: 10.1080/03067310903111661
[24] Zhang Y, Jr W T F.Determination of selenium frac-tionation and speciation in wetland sediments by parallel extraction[J].International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2003, 83(4):315-326. doi: 10.1080/0306731031000076850
[25] Bujdoš M, Kubová J, Streško V.Problems of selenium fractionation in soils rich in organic matter[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2000, 408(1):103-109. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003267099008454
[26] 薛超群, 郭敏.氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法测定土壤样品中不同价态的硒[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):980-984. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.012 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120613
Xue C Q, Guo M.Analysis of different valence states of selenium in geological samples by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):980-984. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.012 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120613
[27] 彭岚, 谈明光, 李玉兰, 等.微波辅助萃取-液质联用技术测底泥砷、硒的化学形态[J].分析试验室, 2006, 25(5):10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2006.05.003
Peng L, Tan M G, Li Y L, et al.Simultaneous speciation of arsenic and selenium by high-performance liquid chromatography on-line with inductively coupled plasma collision cell mass spectrometry in sediment samples[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Laboratory, 2006, 25(5):10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2006.05.003
[28] Hsieh Y J, Jiang S J.Determination of selenium com-pounds in food supplements using reversed-phase liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectro-metry[J].Microchemical Journal, 2013, 110(9):1-7.
[29] Zheng J, Ohata M, Furuta N, et al.Speciation of selenium compounds with ion-pair reversed-phase liquid chromatography using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry as element-specific detection[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2000, 874(1):55-64. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00077-7
-




 下载:
下载: