Mineralogical and Geochemical Characteristics of Al-rich Clays from the Longqi Hydrothermal Field, Southwest Indian Ridge
-
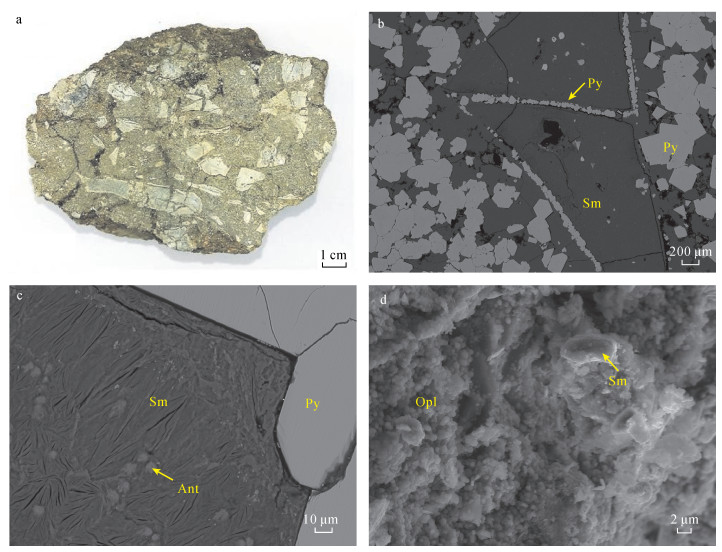
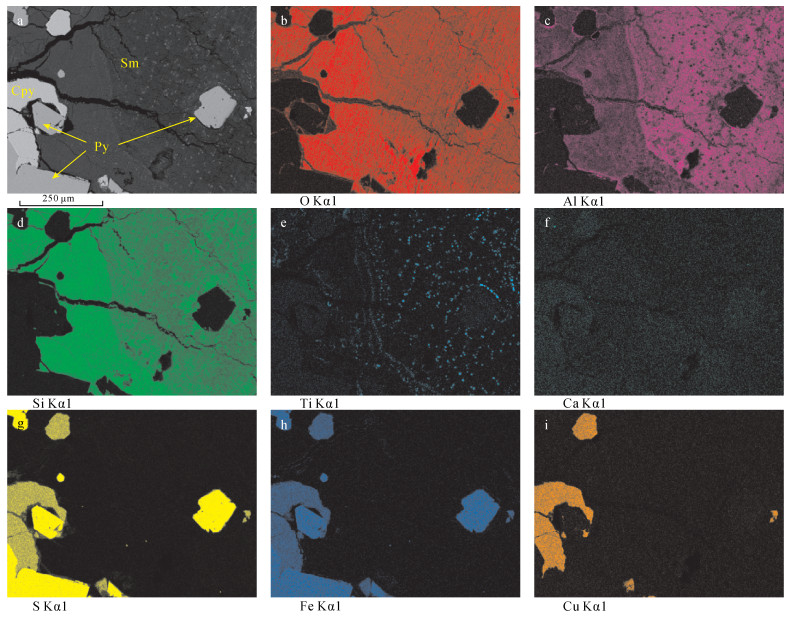
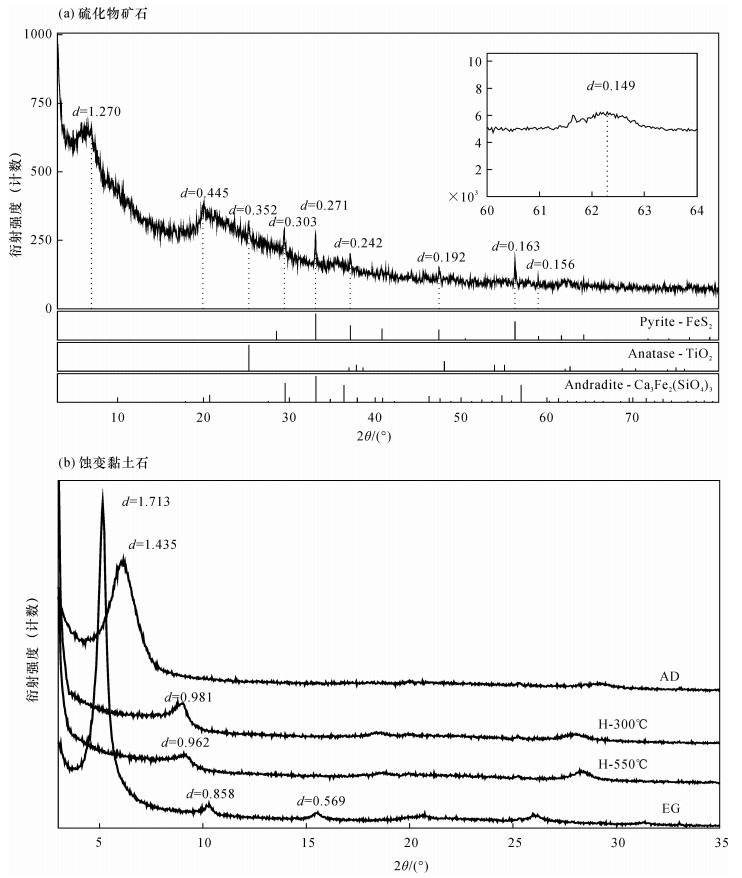
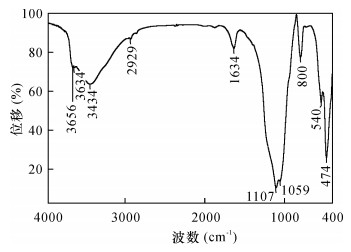
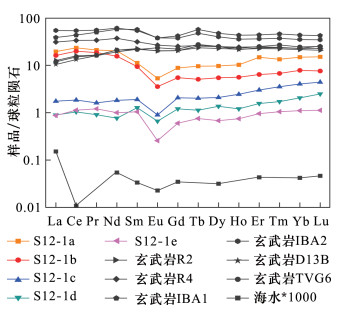
摘要: 产出于不同地质背景下的热液成因黏土矿物组成、晶体结构及化学成分等信息,可指示与海底热液作用有关的水-岩反应过程和流体的物理化学条件变化。但目前对于以西南印度洋脊为代表的超慢速扩张脊热液区的黏土矿物研究程度较低,尚未了解其经历的热液蚀变作用及形成过程。本文综合应用SEM-EDS、XRD、FT-IR、EPMA和LA-ICP-MS等多种分析测试手段对采自龙旂热液区矿化蚀变角砾的形貌结构、矿物组成及其化学成分进行系统表征。研究表明:该蚀变角砾中的共生矿物相主要由具二八面体结构、富Al端元的蒙皂石族矿物贝得石与蛋白石组成,角砾中可见呈细粒浸染状的TiO2。蚀变黏土矿物的化学成分较为单一,具有富Al、贫Mg和贫Fe的特征;其稀土元素总量普遍不高(2.43~43.45 μg/g),配分模式呈负Eu异常(0.31~0.53)而未显示Ce异常(1.09~1.16)。推断产出于硫化物堆积丘体边部的矿化角砾长期受酸性、相对还原的、低温热液流体持续叠加和淋滤改造,除Al和Ti以外大部分元素被活化迁移,形成矿物组成简单的富铝黏土矿物相。本研究查明了龙旂热液区新的蚀变黏土矿物类型及其元素地球化学特征,反映该区广泛发育低温热液蚀变作用,为进一步探讨西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊热液成矿系统的水-岩反应过程提供了一定依据。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDThe mineralogy, chemistry and crystal structure of hydrothermal clay minerals from various geologic settings have been studied to reflect the fluid-rock interaction and physico-chemical evolution of fluids in hydrothermal environments. However, clay minerals in the ultraslow-spreading Southwest Indian Ridge have received less attention. OBJECTIVESTo obtain a better understanding of the features of clay minerals and to constrain hydrothermal alteration processes in the SWIR. METHODSA fragment of massive sulfide ore with irregular-shaped breccia was collected from the Longqi hydrothermal field and studied using SEM-EDS, XRD, FT-IR, EPMA and LA-ICP-MS to determine its mineralogical and geochemical characteristics. RESULTSThe breccia sample contains disseminated micro-sized TiO2 and is mainly composed of Al-rich dioctahedral smectite (i.e., beidellite) and amorphous opal. The total content of REE (2.43 to 43.45 μg/g) in such Al-rich, Mg-poor and Fe-poor smectite is commonly low and the REE fractionation patterns exhibit no significant Ce anomaly (1.09-1.16) but yield negative δEu values (0.31-0.53). It has been suggested that continuous ore-forming fluids (typical of low-temperature, acidicity and relatively reduced solutions) might be responsible for extensive leaching and remobilization of all elements except Al and Ti, thus promoting the formation of Al-rich smectite at the periphery of the Longqi hydrothermal system. CONCLUSIONSThe altered clay mineral and its geochemical characteristics have been studied, reflecting the pervasive development of low-temperature hydrothermal alteration at the Longqi hydrothermal field. This study provides a basis for further discussion of the fluid-rock interaction in the ultraslow-spreading SWIR. -

-
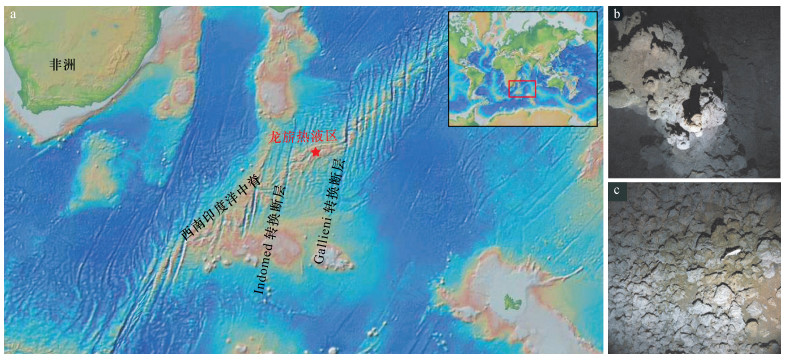
图 1 SWIR龙旂热液区地理位置图及海底照片(a底图据http://www.geomapapp.org;b、c图引自Tao等[8])
Figure 1.
表 1 蚀变角砾化学成分分析
Table 1. Chemical composition analysis of altered breccia
主量元素 含量(%) S12-1a
(n=4)S12-1b
(n=5)S12-1c
(n=4)S12-1d
(n=6)S12-1e
(n=12)SiO2 71.27 67.12 69.37 66.91 65.75 TiO2 1.68 2.33 2.15 2.81 1.34 Al2O3 13.01 13.90 13.60 13.32 15.12 FeO 0.41 0.35 0.30 0.29 0.38 MnO - 0.03 - - - MgO 0.13 0.12 0.14 0.12 0.18 CaO 0.25 0.54 0.62 0.42 0.78 Na2O 0.22 0.24 0.17 0.25 0.22 K2O 0.22 0.27 0.09 0.20 0.16 总和 87.33 85.07 86.65 84.51 84.09 微量元素 含量(μg/g) S12-1a
(n=4)S12-1b
(n=5)S12-1c
(n=4)S12-1d
(n=6)S12-1e
(n=12)La 4.64 3.84 0.41 0.21 0.21 Ce 14.40 12.20 1.14 0.64 0.69 Pr 2.01 1.77 0.15 0.09 0.11 Nd 9.46 7.30 0.85 0.36 0.47 Sm 1.72 1.44 0.29 0.20 0.16 Eu 0.31 0.21 0.05 0.04 0.01 Gd 1.82 1.13 0.42 0.25 0.12 Tb 0.36 0.19 0.08 0.04 0.03 Dy 2.46 1.39 0.53 0.35 0.17 Ho 0.58 0.32 0.14 0.07 0.04 Er 2.46 1.06 0.50 0.26 0.16 Tm 0.33 0.16 0.09 0.04 0.03 Yb 2.53 1.34 0.69 0.35 0.19 Lu 0.38 0.19 0.11 0.06 0.03 ∑REE 43.45 32.55 5.46 2.95 2.43 LREE/HREE 2.98 4.63 1.13 1.07 2.16 δEu 0.53 0.48 0.45 0.53 0.31 δCe 1.16 1.15 1.10 1.15 1.09 (La/Yb)N 1.31 2.06 0.43 0.44 0.79 (La/Sm)N 1.74 1.72 0.92 0.70 0.83 (Gd/Yb)N 0.59 0.70 0.51 0.59 0.54 注:表中n为分析点个数,数据取n个点的平均值;“-”表示低于分析检测限。 -
[1] Hazen R M, Sverjensky D A, Azzolini D, et al.Clay mineral evolution[J]. American Mineralogist, 2013, 98(11-12):2007-2029. doi: 10.2138/am.2013.4425
[2] Cuadros J, Dekov V M, Arroyo X, et al.Smectite Formation in Submarine Hydrothermal Sediments:Samples from the HMS Challenger Expedition (1872-1876)[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2011, 59(2):147-164. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590204
[3] Severmann S, Mills R A, Palmer M R, et al.The origin of clay minerals in active and relict hydrothermal deposits[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(1):73-88. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00235-7
[4] Lackschewitz K S, Botz R, Garbe-Schönberg D, et al.Mineralogy and geochemistry of clay samples from active hydrothermal vents off the north coast of Iceland[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 225(1):177-190. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3374a0f480e2c3174363b963ee157c1e
[5] Zierenberg R A, Schiffman P, Jonasson I R, et al.Altera-tion of basalt hyaloclastite at the off-axis Sea Cliff hydrothermal field, Gorda Ridge[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 126(2):77-99. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(95)00111-2
[6] Haymon R M, Kastner M.The formation of high temperature clay minerals from basalt alteration during hydrothermal discharge on the East Pacific Rise axis at 21°N[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1986, 50(9):1933-1939. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90249-8
[7] German C R, Baker E T, Mevel C, et al.Hydrothermal activity along the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Nature, 1998, 395:490-493. doi: 10.1038/26730
[8] Tao C H, Lin J, Guo S Q, et al.First active hydrothermal vents on an ultraslow-spreading center:Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geology, 2012, 40(1):47-50. doi: 10.1130/G32389.1
[9] Nakamura K, Kato Y, Tamaki K, et al.Geochemistry of hydrothermally altered basaltic rocks from the Southwest Indian Ridge near the Rodriguez Triple Junction[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 239(3):125-141. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=15a426c2e276ef895df4f0380ba7844e
[10] 王琰, 孙晓明, 徐莉, 等.西南印度洋中脊热液区海底玄武岩元素地球化学原位分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(3):796-802. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)03-0796-07
Wang Y, Sun X M, Xu L, et al.In situ analysis of element geochemistry in submarine basalt in hydrothermal areas from ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(3):796-802. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)03-0796-07
[11] 叶俊, 石学法, 杨耀民, 等.西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊49.6°E热液区硫化物矿物学特征及其意义[J].矿物学报, 2011, 31(1):17-29. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwxb201101003
Ye J, Shi X F, Yang Y M, et al.Mineralogy of sulfides from ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge 49.6°E hydrothermal field and its metallogenic significance[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011, 31(1):17-29. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwxb201101003
[12] Tao C H, Li H M, Huang W, et al.Mineralogical and geochemical features of sulfide chimneys from the 49°39'E hydrothermal field on the Southwest Indian Ridge and their geological inferences[J]. Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(26):2828-2838. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4619-4
[13] 于淼, 苏新, 陶春辉, 等.西南印度洋中脊49.6°E和50.5°E区玄武岩岩石学及元素地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2013, 27(3):497-508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.03.001
Yu M, Su X, Tao C H, et al.Petrological and geochemical features of basalts at 49.6°E and 50.5°E hydrothermal fields along the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(3):497-508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.03.001
[14] 王振波, 武光海, 韩沉花.西南印度洋脊49.6°E热液区热液产物和玄武岩地球化学特征[J].海洋学研究, 2014, 32(1):64-73. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dhhy201401008
Wang Z B, Wu G H, Han C H.Geochemical characteristics of hydrothermal deposits and basalts at 49.6°E on the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2014, 32(1):64-73. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dhhy201401008
[15] Howard K J, Fisk M R.Hydrothermal alumina-rich clays and boehmite on the Gorda Ridge[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(9):2269-2279. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90129-9
[16] Papoulis D, Tsoliskatagas P, Kalampounias A G, et al.Progressive formation of halloysite from the hydrothermal alteration of biotite and the formation mechanisms of anatase in altered volcanic rocks from Limnos Island, Northeast Aegean Sea, Greece[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2009, 57(5):566-577. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2009.0570505
[17] Monecke T, Giorgetti G, Scholtysek O, et al.Textural and mineralogical changes associated with the incipient hydrothermal alteration of glassy dacite at the submarine PACMANUS hydrothermal system, Eastern Manus Basin[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2007, 160(1):23-41. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=45d94c5189f19067c11c12326fc2f865
[18] Zhou H Y, Luo A, Yang Q H.A hydrothermal Complex Chimney Found in Dragon Flag Field, Southwest Indian Ridge[M]. Goldschmidt Abstract, 2017.
[19] Zviagina B B, McCarty D K, Środonón J, et al.Inter-pretation of infrared spectra of dioctahedral smectites in the region of OH-stretching vibrations[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2004, 52(4):399-410. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2004.0520401
[20] Cao Z M, Cao H, Tao C H, et al.Rare earth element geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 31(2):62-69. doi: 10.1007/s13131-012-0192-1
[21] Douville E, Bienvenu P, Charlou J L, et al.Yttrium and rare earth elements in fluids from various deep-sea hydrothermal systems[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(5):627-643. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00024-1
[22] Karakaya M Ç, Karakaya N, Küpeli Ş, et al.Mine-ralogy and geochemical behavior of trace elements of hydrothermal alteration types in the volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits, NE Turkey[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 48:197-224. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.03.007
[23] Sverjensky D A.Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 67(1):70-78. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90039-6
[24] Wood S A.The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium:2.Theoretical predictions of speciation in hydrothermal solutions to 350℃ at saturation water vapor pressure[J]. Chemical Geology, 1990, 88(1):99-125. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000925419090080Q
[25] Lewis A J, Palmer M R, Sturchio N C, et al.The rare earth element geochemistry of acid-sulphate and acid-sulphate-chloride geothermal systems from Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, USA[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(4):695-706. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00384-5
[26] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic sys-tematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[27] Mitra A, Elderfield H, Greaves M J.Rare earth elements in submarine hydrothermal fluids and plumes from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1994, 46(3):217-235. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(94)90079-5
[28] Honnorez J.Hydrothermal alteration vs.ocean-floor me-tamorphism.A comparison between two case histories:The TAG hydrothermal mound (Mid-Atlantic Ridge) vs.DSDP/ODP Hole 504B (Equatorial East Pacific)[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2003, 335(10-11):781-824. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2003.08.009
[29] Środoń J.Nature of mixed-layer clays and mechanisms of their formation and alteration[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1999, 27:19-53. http://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.earth.27.1.19
[30] Simmons S F.Hydrothermal minerals and precious me-tals in the Broadlands-Ohaaki geothermal system:Implications for understanding low-sulfidation epithermal environments[J]. Economic Geology, 2000, 95(5):971-999. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.95.5.971
[31] Giorgetti G, Monecke T, Kleeberg R, et al.Low-temper-ature hydrothermal alteration of trachybasalt at Conical Seamount, Papua New Guinea:Formation of smectite and metastable precursor phases[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2009, 57(6):725-741. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2009.0570606
[32] Tivey M K, Stakes D S, Cook T L, et al.A model for growth of steep-sided vent structures on the Endeavour Segment of the Juan de Fuca Ridge:Results of a petrologic and geochemical study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 1999, 104(B10):22859-22883. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900107
-



 下载:
下载: