Research on the Effect of Chemical Reduction-Stabilization Combined Remediation of Cr-contaminated Soil
-
摘要: 六价铬是国际公认的47种最危险废物之一,研究铬污染土壤的修复效果对污染场地风险管控具有重要的现实意义。本文以济南市某典型铬污染场地土壤作为研究对象,提出了"化学还原+固化稳定"的修复治理思路,针对修复剂类型、投加比、反应时间、还原效率、修复成本和环境效应等因素,确定了该修复工艺的最佳条件,并对污染土壤的修复效果进行评价。结果表明土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)的最佳修复条件为:以氯化亚铁作为化学还原剂,其投加比为5倍的理论投料比,还原时间为2天;以钙镁磷肥作为稳定剂,其投加比为10%(换算成钙镁磷肥与总铬的质量比为72:1)。采用以上条件修复铬污染土壤,总铬的生物可利用系数由0.4398降低至0.0017,修复后的土壤Cr(Ⅵ)含量介于0.315~0.501mg/kg,Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率大于99.5%。该结果可为土壤修复和决策提供依据。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDCr(Ⅵ) is one of the 47 internationally recognized most dangerous wastes. Study on the remedy of Cr-contaminated soil is of great significance for risk control of contaminated soil. OBJECTIVESTo build a reliable method for Cr-contaminated soil, and to screen the optimal remediation conditions. To propose a chemical reduction-stabilization combined method for remediation of Cr(Ⅵ) contaminated soil and screen the remediation conditions including choice of reductant, soil/liquid ratio and stabilizer. METHODSSoil from a typical chromium contaminated site in Jinan is used as the research object, and the idea of 'chemical reduction + solidification stability' is suggested, which is aimed at the types of repair agent, dosage ratio, reaction time, reduction efficiency, repair cost and environmental effect. The optimal conditions for the repair process were determined and the remediation effects of contaminated soil were evaluated. RESULTSThe results demonstrated that the optimal parameter for Cr(Ⅵ) treatment was using ferrous chloride as the reductant and treating for 2 days, controlling the addition amount of the reductant at 5 times of its stoichiometric need. Calcium magnesium phosphate was used as the stabilizer and its addition amount was controlled as 10%. After remediation, the bioavailable efficients of Cr in the soil reduced from 0.4398 to 0.0017. The results showed that contents of Cr(Ⅵ) in the treated soil were 0.315-0.501mg/kg, and 99.5% of Cr(Ⅵ) was reduced. CONCLUSIONSThe remedied soil satisfies the risk screen number for residual land. This result could provide reference and theoretical basis for soil remediation and decision-making. -
Key words:
- chemical reduction /
- stabilization /
- Cr(Ⅵ) /
- soil remediation /
- combined method
-
随着工业化、城市化、农业集约化的快速发展,大量未经处理的废弃物向土壤系统转移,并在自然因素的作用下汇集、残留于土壤环境中,致使土壤遭受污染[1-3]。鉴于土壤的防治和土地的再开发利用关系到人体健康及其切身利益,没有得到修复的污染场地将会对国民经济可持续发展造成难以估量的影响[4-5]。因此,必须对土壤污染的预防和污染土壤修复予以高度重视。 众多金属污染中,铬污染尤其引人关注[6-7]。铬在自然界中主要以三价铬Cr(Ⅲ)和六价铬Cr(Ⅵ)呈现,Cr(Ⅲ)是必需的营养物,而迁移性较强的Cr(Ⅵ)对活细胞具有强烈的氧化能力,对动植物具有致畸、致癌、致突变作用[8-9]。另外,Cr(Ⅵ)通过口腔进入人体可引起一系列病变,已被列为国际公认的47种最危险废物之一[10]。针对场地土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)的修复方法主要有物理修复法、化学修复法、生物修复法三大类[11-13]。其中,物理修复法包括客土法[13]、固化/稳定化法[14-16]、电动修复法[17]等;化学修复法包括化学还原法[18-20]、化学淋洗法[21];生物修复法包括植物富集[13, 22]、微生物还原[23-24]技术。Zhang等[15]研究了碱活化炉渣黏结剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的固定化潜力,以明确固化修复机制,结果表明碱活化炉渣黏结剂对固化含Cr(Ⅵ)废弃物是有效的,只是固化效果强烈依赖于氢氧化钠用量、水渣比、初始Cr(Ⅵ)含量和固化持续时间。Wu等[17]在不同电解质条件下进行了电动力修复污染土壤中铬的实验,结果表明当电解质分别为超纯水、0.1mol/L氯化钾和0.1mol/L柠檬酸时,实际土壤中的铬浓度分别下降了138.1、45.04、494.4mg/kg,使用柠檬酸溶液提高了土壤中Cr去除率。Jiang等[19]指出,弱电子供体(如草酸、酒石酸、柠檬酸、苹果酸、2-吡啶甲酸、腈基三乙酸等)和Cr(Ⅵ)之间的氧化还原反应可以被许多环境或工业生产的聚羧酸盐(PolyCAs)显著加速,这主要取决于PolyCAs的电子转移能力以及配位铬物种的能力,这种PolyCAs和铬物种之间的相互作用对Cr(Ⅵ)还原的新效应,可以为制定Cr(Ⅵ)污染修复策略提供借鉴。Zhang等[22]通过野外调查和盆栽试验,证实了李氏禾对Cr有着很大的生物耐受性,是一种Cr超积累植物,可以在铬污染土壤及水体的植物修复中发挥作用。Bai等[23]证实了在70℃葡萄糖发酵条件下,Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus菌表现出良好的Cr(Ⅵ)还原能力和Cr(Ⅲ)固定能力,其对Cr(Ⅵ)的还原可能是利用了不同的电子传递途径。以上有关Cr(Ⅵ)修复效果及机理研究都是基于单一修复技术,并没有涉及多技术联合的修复技术。 化学还原法,是指向土壤中加入廉价易得的化学还原剂将Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ),降低铬在环境中的毒性的一种方法。稳定化法,是将铬污染土壤与稳定化剂混合,通过吸附、共沉淀、络合等作用将铬固定在化合体内,以降低其生物有效性、溶出性和迁移性。本研究以山东济南市某铬渣污染场地土壤为研究对象[25],采用“化学还原+稳定化”联合治理思路,通过开展室内化学还原-稳定化修复条件优化试验,确定了该联合修复方法的最佳运行条件,并且评价了铬污染场地土壤的修复效果,拟为化学还原-稳定化联合修复技术应用于铬污染土壤治理工程提供参考和依据。 1. 铬污染场地待修复样品性状
以济南市某典型铬污染场地土壤作为研究对象。该场地自1958年开始生产铬盐产品,主导产品是铬酸酐,2009年整体搬迁至交通便捷、承载能力强的济南化工产业园区,原厂不再生产铬盐,拟规划为住宅用地和商业用地。根据该厂的铬污染补充调查工作报告,该场地因集中存放铬渣使土壤铬含量严重超标,Cr(Ⅵ)污染深度达到地表以下埋深12m,将Cr(Ⅵ)污染的土壤分为4层:第一层0~3.0m,主要为建筑垃圾层,Cr(Ⅵ)平均含量为1641mg/kg;第二层3.0~7.6m,主要为粉土层,Cr(Ⅵ)平均含量为681.4mg/kg;第三层7.6~12.2m,主要为黏土层,Cr(Ⅵ)平均含量为280.3mg/kg;第四层12.2~16.1m,主要为粉质黏土层,Cr(Ⅵ)平均含量为0.9mg/kg。其中,第二层土壤的pH值在7.86~8.40,呈弱碱性,应是易溶性铬酸盐离子部分发生水解所致。污染场地土壤的有机质含量在7.28%~9.29%之间,显著低于山东省土壤背景值[25]。2. 研究方法
2.1 采样和样品铬含量水平
土壤样品的采样点布设、样品采集及样品测试方法详见文献[25]。将采集的100件铬污染土壤样品(主要为粉土),分别选取大约1kg进行组合,充分混匀后用玛瑙研钵研磨至0.074μm(200目),作为本次修复条件优化试验研究的样品。 经测试,本次选用的铬污染土壤修复条件优化试验样品的总铬和Cr(Ⅵ)含量分别为1389、689.1mg/kg;铬离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机结合态及残渣态的含量分别为610.9、73.52、224.9、192.7、258.6mg/kg,总铬的生物可利用系数为0.4398。《土壤环境质量建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 36600—2018)规定第一类、第二类建设用地的Cr(Ⅵ)管制值分别为30、78mg/kg,经统计,待修复土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)含量超出了第一类用地和第二类用地管制值的22.97倍、8.83倍。因此,须将污染场地土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)修复治理,方可用于建设开发。2.2 修复方案设计
依据《污染场地土壤修复技术导则》(HJ 25.4—2014)要求,基于铬污染场地环境污染现状及场地未来规划,有效地开展Cr(Ⅵ)污染场地的修复工作,将场地土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)的环境风险降低到可以接受的水平即可。鉴于此,化学还原法修复铬污染土壤的优化筛选方案设计应遵循以下原则:①确保场地土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)得到安全、有效的处理和处置,并达到国家相关标准;②在Cr(Ⅵ)污染物处理处置过程中,尽可能缩短修复时间,提高修复效率;③筛选方案兼顾修复费用方面的试剂成本;④修复方法的选择是通过最简化的途径或方法达到修复目标,而不单纯追求技术的先进性。2.2.1 土液比条件筛选方案
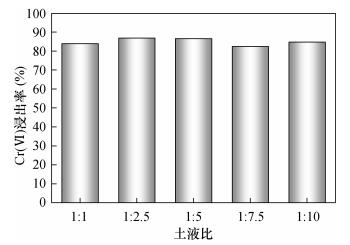
称取100g土壤样品于5只1000mL烧杯中,分别加入100、250、500、750、1000mL去离子水,使土液比分别为1:1、1:2.5、1:5、1:7.5、1:10,搅拌混匀后静置1天,通过测定上层清液中Cr(Ⅵ)浸出率来确定最佳土液比。2.2.2 化学还原条件筛选方案
称取100g土壤样品于带密封盖子的洁净塑料桶中,投加1x、5x、10x、20x、40x(x指理论投料比)的化学还原剂(氯化亚铁、硫化钠、亚硫酸钠)配制成最佳土液比体积的溶液,并将此还原剂溶液转入塑料桶中,氮气吹扫桶内空隙3min,拧紧盖子密封,并充分振荡,使土壤与还原剂溶液成分混合接触后,静置。反应至一定时间时,用移液管准确移取50mL浑浊液于离心管中,经离心机高速旋转使固、液充分分层后,上层清液用于测定总铬和Cr(Ⅵ)。2.2.3 稳定化条件筛选方案
向经过最优化还原条件处理后的土壤中加入稳定剂(氧化钙、碳酸钙、钙镁磷肥、水泥),各稳定剂添加量为土壤质量的1%、5%、10%、20%,一个月后分别测定土壤中Cr的离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机结合态及残渣态含量。3. 化学还原-稳定化法实验优化条件
3.1 土液比条件优化试验
通常土液比越小,即泥浆越浓稠,越不利于混合反应;反之,大的土液比尽管利于混合反应,但易造成大量的水体污染风险,也会增加修复工程成本。由图 1可知,在浸取1天时,不同土液比条件下Cr(Ⅵ)浸出率介于80%~90%,差异并不显著。整体而言,1:2.5和1:5的土液比条件下Cr(Ⅵ)浸出率相对高些。但是,考虑到化学还原条件优化试验中需要多次采集一定体积的上层清液进行监测,因此选择1:5的土液比作为最佳条件。3.2 化学还原条件优化试验
3.2.1 投加氯化亚铁时总铬和Cr(Ⅵ)的变化特征
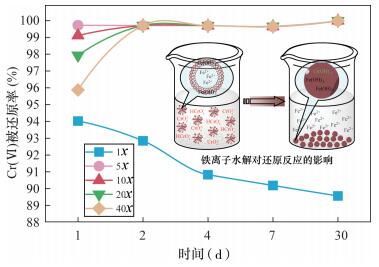
就Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率(图 2)而言,投加1x的氯化亚铁时,由于还原剂的损耗及浸出液中其他可溶性氧化物的消耗等因素,致使Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率随时间线性降低,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率介于89%~94%。而投加5x、10x、20x、40x的氯化亚铁时,仅在第1天各浸出液中Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率有所差异,表现出40x < 20x < 10x < 5x;自第2天始,投加5x、10x、20x、40x的氯化亚铁时Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率均高于99.5%,并且在第30天时,各投加比的Cr(Ⅵ)去除率更高了些,达到了99.99%。究其原因,由于Cr(Ⅵ)的还原反应发生在液-液界面,加入过量的氯化亚铁时,Fe2+、Fe3+的水解反应会生成Fe(OH)2或Fe(OH)3胶体(图 2),这些胶体在反应初期主要以团聚体的形态均匀分散在溶液中,而阻碍Fe2+与Cr(Ⅵ)的接触,并且这些团聚体的数量与亚铁盐的投加量成正比,但是随着沉淀时间的延长,团聚体会逐渐破损而沉降下来,形成较为密实的Fe(OH)2或Fe(OH)3沉淀,被释放的Fe2+才得以继续将Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ),并形成Cr(OH)3与Fe(OH)3一同沉淀下来。综合考虑后,投加氯化亚铁作还原剂的最佳运行条件确定为:氯化亚铁投加比为5x,还原时间为2天。3.2.2 投加硫化钠时总铬和Cr(Ⅵ)的变化特征
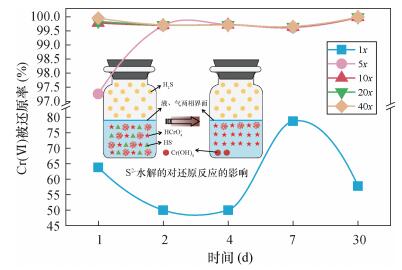
就Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率(图 3)而言,投加1x的硫化钠时,由于H2S气体的产生、还原剂的损耗及浸出液中其他可溶性氧化物的消耗等因素,致使Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率随时间变化有所波动,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率介于45%~80%,这种现象与Na2S水解生成一定量的H2S息息相关。当硫化钠投加量不足时,溶液中HS-则很快与溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)反应消耗殆尽,然后缓慢吸附水解生成的H2S气体进行还原反应,并且该反应受限于气、液两相的接触面积,以及Cr(Ⅵ)在溶液中的扩散速率(图 3),导致浸出液中Cr(Ⅵ)的浓度波动较为明显。而投加5x的硫化钠时,仅在第1天各浸出液中Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率最低,为97.27%,而自第2天始,浸出液中Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率均高于99.5%。投加10x、20x、40x的硫化钠时,各时间段的Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率均高于99.5%,并且在第30天时,各投加比的Cr(Ⅵ)去除率更高了些,达到了99.99%。 整体而言,Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率与硫化钠投加量成正比,但是当硫化钠投加量达到一定时,Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率将不再增高,而是稳定在一个较高的水平。因此,综合考虑投加硫化钠作还原剂的最佳运行条件确定为:硫化钠投加比为10x,还原时间为2天。3.2.3 投加亚硫酸钠时总铬和Cr(Ⅵ)的变化特征
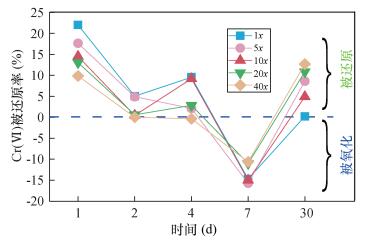
投加1x、5x、10x、20x、40x的亚硫酸钠时(图 4),Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率均呈现出“波浪状”变化特征,介于-15%~20%(还原率为负值可能是因投加亚硫酸钠时促进了总铬的浸出),其均值基本维持在0%,说明投加亚硫酸钠不能够有效地将Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ)。造成这种现象的原因,是与SO32-化学稳定性有一定关联。在水体系中S4-的SO32-并不稳定,主要以S4-的HS2O5-、S2O52-(SO32-·SO2)存在,并且S2O52-容易受pH及电位(Eh)的变化而不稳定。例如,当pH>8.5时,S2O52-可以转化为SO42-。李玲等[26]研究发现,以0.4%的50%硫酸作为酸度调节剂时,投加的亚硫酸钠可将土壤中的Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率增大到70%,但是,施加大量的硫酸会致使土壤呈酸性,影响Cr(Ⅲ)沉淀的生成。本研究认为,投加亚硫酸钠作为还原剂时,在本实验条件下(弱碱性条件)不能有效地修复土壤中的Cr(Ⅵ)。3.2.4 最佳还原剂的确定
表 1总结了氯化亚铁、硫化钠、亚硫酸钠三种还原剂的理论投料比条件(1x)、最佳投料比条件下土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率,以及三种还原剂成本、反应副产物等因素,认定以氯化亚铁作为化学还原剂时,各个因素的表现均较优异。鉴于此,修复土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)的最佳化学还原试剂及其最佳运行条件为:氯化亚铁作为化学还原剂,其投加比为5x,还原时间为2天。在此条件下Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率>99.5%。表 1. 最佳还原剂的筛选Table 1. Screen of optimal reductant还原剂 还原剂市场价格 理论还原(1x)条件下Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率 最佳投加条件下Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率 反应副产物及环境风险 氯化亚铁 400元/吨 89%~94% >99.5% Fe(OH)3沉淀,环境风险较小 硫化钠 6600元/吨 45%~80% >99.5% 单质硫及硫化氢气体,环境风险较大 亚硫酸钠 2400元/吨 -15%~20% 21% 易溶的SO42-,环境风险一般 3.3 稳定化条件优化试验
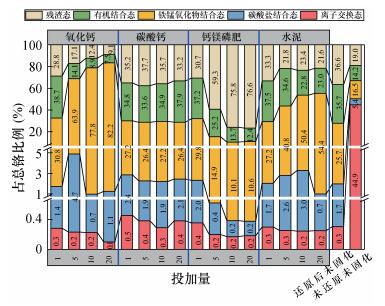
以下分析投加不同比例的稳定剂时土壤中铬形态所占总铬的比例。如图 5所示,投加1%~20%的碳酸钙作为稳定剂时,离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机结合态、残渣态铬所占总铬的比例,与氯化亚铁还原后未固化时的铬形态所占总铬的比例均基本吻合,说明了投加碳酸钙作为稳定剂没有明显的固化效果。投加1%~20%的氧化钙及水泥作为稳定剂时,离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态铬与氯化亚铁还原后未固化时,这两种形态铬所占总铬的比例均基本吻合;铁锰氧化物结合态铬所占比例随着投加比例的增加也具有增大趋势;而有机结合态、残渣态铬所占总铬的比例则呈现出逐渐降低趋势。造成这种现象的原因是,氧化钙、水泥与水反应释放出一定量的OH-,这些OH-会破坏有机态和残渣态中铬的赋存状态,使有机结合态和残渣态铬向铁锰氧化物结合态铬转化,只是水泥在转化程度上较氧化钙显得更为柔和。因此,可以认为投加氧化钙或水泥作为稳定剂没有积极的固化效果,反而破坏了还原后未固化时铬赋存体系的稳定性。 投加1%~20%的钙镁磷肥作为稳定剂时,离子交换态铬与氯化亚铁还原后未固化时的离子形态铬所占总铬的比例均基本吻合;碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机结合态铬所占总铬比例随着投加比例的增加,具有逐渐降低趋势;而残渣态铬所占总铬的比例则呈现出逐渐增高趋势,在投加10%的钙镁磷肥作为稳定剂时,残渣态铬占总铬的76%,是还原后未固化时的2.1倍,是未还原未固化时的4.0倍,固化效果非常显著。钙镁磷肥是一种含有磷酸根(PO43-)的硅铝酸盐复合体,其主要成分包括Ca3(PO4)2、CaSiO3、MgSiO3,是一种多元素肥料,水溶液呈碱性,在土壤中能够缓慢释放出PO43-,而PO43-可以与Cr3+反应生成磷酸铬(CrPO4),磷酸铬化学性质极其稳定,不溶于水、盐酸及王水,仅与近沸硫酸或强碱作用[27-29]。由于CrPO4溶解度较Cr(OH)3更低,使铬更多地赋存于残渣态之中。 综上所述,确定钙镁磷肥作为稳定剂时,残渣态铬占总铬的比例最为优越。固化土壤中铬元素的最佳稳定试剂及其最佳运行条件为:钙镁磷肥作为稳定剂,其投加比例为10%(换算成钙镁磷肥与总铬的质量比则为72:1),总铬的生物可利用系数降为0.0017。 自然土壤中的铬主要以Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)形式存在,二者在一定条件下可通过氧化还原反应、络合、溶解、沉淀、吸附和解吸等过程发生迁移转化。由于自然土壤中通常存在大量的还原性物质(亚铁氧化物、有机质),将土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)还原成Cr(Ⅲ)相比将Cr(Ⅲ)氧化成Cr(Ⅵ)更易发生,主要是因为土壤中大部分Cr(Ⅲ)都是以沉淀的形式存在,故能被直接氧化的Cr(Ⅲ)量较少,在很大程度上取决于Cr(Ⅲ)沉淀的溶解量的大小[30]。另外,修复后的土壤中通过添加适度过量的还原试剂及固化试剂,会有效阻碍Cr(Ⅲ)向Cr(Ⅵ)转化,使修复效果具有长期稳定性,但是对修复后土壤Cr(Ⅵ)仍需周期性监测。4. 污染场地土壤修复效果验证
为了考察最佳修复方法对场地污染土壤中Cr的修复效果,将采集的10件土壤样品分别采用最佳化学还原条件及固化条件进行修复养护,再次分析此时土壤中的Cr(Ⅵ),并与污染土壤修复前的状况相比较,对修复效果进行评判。 修复前土壤的Cr(Ⅵ)含量在658.5~816.3mg/kg,平均值为746.1mg/kg;修复后的Cr(Ⅵ)含量介于0.315~0.501mg/kg,平均值为0.408mg/kg。就修复前后Cr(Ⅵ)平均含量而言,Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率超过99.5%。依据GB 36600—2018对第一类用地(包括住宅用地)的风险筛选值3.0mg/kg和管制值30mg/kg,修复后的Cr(Ⅵ)均能满足风险筛选值的限值要求;依据HJ 25.3—2014相关要求,针对修复后土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)健康风险评估的暴露途径仅涉及经口摄入土壤途径、皮肤接触土壤途径和吸入土壤颗粒物途径等三种途径,选择最大值0.501mg/kg进行评估,经计算,修复后土壤中Cr(Ⅵ)的总致癌风险为6.51×10-7(小于可接受水平10-6),总危害熵为1.47×10-2(小于可接受水平1.0),说明采用本研究方法对铬污染场地修复,土壤Cr(Ⅵ)的健康风险基本可以忽略,适于作为第一类建设用地开发。5. 结论
本研究采用“化学还原+稳定化”联合治理的思路,确定了联合修复方法的最佳实验条件为:以氯化亚铁作为化学还原剂,其投加比为5倍的理论投料比,还原时间为2天;以钙镁磷肥作为稳定剂,其投加比列为10%(换算成与总铬含量的质量比例为72:1)。经本方案修复的土壤,其总铬的生物可利用系数为0.0017,Cr(Ⅵ)含量显著降低。本研究成果为其他铬污染场地的治理和预防提供了参考和决策依据。要点
- (1) 采用了“化学还原+稳定化”的联合治理思路。
- (2) 剖析了该联合修复方法的最佳运行条件,并且揭示了其影响规律。
HIGHLIGHTS
- (1) A chemical reduction-stabilization combined method for remediation of Cr(Ⅵ) contaminated soil was adopted.
- (2) The optimal operational condition and the parameters of the method were investigated.
-
表 1 最佳还原剂的筛选
Table 1. Screen of optimal reductant
还原剂 还原剂市场价格 理论还原(1x)条件下Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率 最佳投加条件下Cr(Ⅵ)被还原率 反应副产物及环境风险 氯化亚铁 400元/吨 89%~94% >99.5% Fe(OH)3沉淀,环境风险较小 硫化钠 6600元/吨 45%~80% >99.5% 单质硫及硫化氢气体,环境风险较大 亚硫酸钠 2400元/吨 -15%~20% 21% 易溶的SO42-,环境风险一般 -
[1] Tardif S, Cipullo S, SøH U, et al. Factors governing the solid phase distribution of Cr, Cu and As in contaminated soil after 40 years of ageing[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 652:744-754. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.244
[2] 田衎, 杨珺, 孙自杰, 等.矿区污染场地土壤重金属元素分析标准样品的研制[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1):82-88. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.012
Tian K, Yang J, Sun Z J, et al.Preparation of soil certified reference materials for heavy metals in contaminated sites[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1):82-88. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.012
[3] Lü J S, Wang Y M.Multi-scale analysis of heavy metals sources in soils of Jiangsu Coast, Eastern China[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 212:964-973. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.155
[4] Ma R, Zhou X N, Shi J S.Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in critical zone of Luan River catchment in the North China Plain[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2018, 18:47-57. doi: 10.1144/geochem2017-010
[5] Wang Q, Liu J F, Chen Z, et al.A causation-based method developed for an integrated risk assessment of heavy metals in soil[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642:1396-1405. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.118
[6] Diao Z H, Du J J, Jiang D, et al. Insights into the simultaneous removal of Cr6+ and Pb2+ by a novel sewage sludge-derived biochar immobilized nanoscale zero valent iron:Coexistence effect and mechanism[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642:505-515. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.093
[7] 邓日欣, 罗伟嘉, 韩奕彤, 等.膨润土负载纳米铁镍同步修复地下水中三氯乙烯和六价铬复合污染[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(5):541-548. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801280013
Deng R X, Luo W J, Han Y T, et al.Simultaneous removal of TCE and Cr(Ⅵ) in groundwater by using bentonite-supported nanoscale Fe/Ni[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(5):541-548. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801280013
[8] Economou-Eliopoulos M, Megremi I, Vasilatos C.Geochemical constraints on the sources of Cr(Ⅵ) contamination in waters of Messapia (Central Evia) Basin[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2017, 84:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.05.015
[9] Séby F, Vacchina V. Critical assessment of hexavalent chromium species from different solid environmental, industrial and food matrices[J].Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 104:54-68. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2017.11.019
[10] Clemention M, Shi X L, Zhang Z.Oxidative stress and metabolic reprogramming in Cr(Ⅵ) carcinogenesis[J].Current Opinion in Toxicology, 2018, 8:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2017.11.015
[11] Khalid S, Shahid M, Niazi N K, et al.A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 182:247-268. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.11.021
[12] 陈保冬, 张莘, 伍松林, 等.丛枝菌根影响土壤-植物系统中重金属迁移转化和累积过程的机制及其生态应用[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(1):1-25. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807110083
Chen B D, Zhang X, Wu S L, et al.The role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in heavy metal translocation, transformation and accumulation in the soil-plant continuum:Underlying mechanisms and ecological implications[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(1):1-25. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807110083
[13] Liu L W, Li W, Song W P, et al.Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils:Principles and applicability[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633:206-219. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.161
[14] Choppala G, Kunhikrishnan A, Seshadri B, et al.Compa-rative sorption of chromium species as influenced by pH, surface charge and organic matter content in contaminated soils[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 184:255-260. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.07.012
[15] Zhang M T, Yang C H, Zhao M, et al.Immobilization potential of Cr(Ⅵ) in sodium hydroxide activated slag pastes[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 321:281-289. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.019
[16] Ballesteros S, Rincón J M, Rincón-Mora B, et al.Vitrifi-cation of urban soil contamination by hexavalent chromium[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 174:132-139. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.07.011
[17] Wu J N, Zhang J, Xiao C Z.Focus on factors affecting pH, flow of Cr and transformation between Cr(Ⅵ) and Cr(Ⅲ) in the soil with different electrolytes[J].Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 211:652-662. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.06.048
[18] Dhal B, Thatoi H N, Das N N, et al.Chemical and micro-bial remediation of hexavalent chromium from contaminated soil and mining/metallurgical solid waste:A review[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 250-251:272-291. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389413000666
[19] Jiang B, He H H, Liu Y J, et al.pH-dependent roles of polycarboxylates in electron transfer between Cr(Ⅵ) and weak electron donors[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 197:367-374. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.047
[20] Li Y Y, Liang J L, Yang Z H, et al.Reduction and immobilization of hexavalent chromium in chromite ore processing residue using amorphous FeS2[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658:315-323. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.042
[21] Li D, Ji G Z, Hu J, et al.Remediation strategy and electrochemistry flushing & reduction technology for real Cr(Ⅵ)-contaminated soils[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334:1281-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.074
[22] Zhang X H, Liu J, Huang H T, et al.Chromium accu-mulation by the hyperaccumulator plant Leersia hexandra Swartz[J].Chemosphere, 2007, 67:1138-1143. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.11.014
[23] Bai Y N, Lu Y Z, Shen N, et al.Investigation of Cr(Ⅵ) reduction potential and mechanism by Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus under glucose fermentation condition[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 344:585-592. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.059
[24] Zhang Q, Amor K, Galer S J G, et al.Variations of stable isotope fractionation during bacterial chromium reduction processes and their implications[J].Chemical Geology, 2018, 481:155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.02.004
[25] 赵庆令, 安茂国, 陈洪年, 等.济南市某废弃化工厂区域土壤地球化学特征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2):201-208. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201708240135
Zhao Q L, An M G, Chen H N, et al.Research on geochemical characteristics of soil in a chemical industrial factory site in Jinan city[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2):201-208. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201708240135
[26] 李玲, 唐晓声, 李海建.六价铬污染土壤还原稳定修复[J].广东化工, 2016, 43(3):95-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2016.03.049
Li L, Tang X S, Li H J.Reduction and stabilization remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2016, 43(3):95-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2016.03.049
[27] 纪柱.含铬的磷酸盐[J].无机盐工业, 2005, 37(8):8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2005.08.003
Ji Z.Chromium:Containing phosphate[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2005, 37(8):8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2005.08.003
[28] Gomm J R, Schwenzer B, Morse D E.Textured films of chromium phosphate synthesized by low-temperature vapor diffusion catalysis[J].Solid State Sciences, 2007, 9:429-431. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2007.03.012
[29] Li Y Y, Cundy A B, Feng J X, et al.Remediation of hexa-valent chromium contamination in chromite ore processing residue by sodium dithionite and sodium phosphate addition and its mechanism[J].Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 192:100-106.
[30] Markelova E, Couture R M, Parsona C T, et al.Specia-tion dynamics of oxyanion contaminants (As, Sb, Cr) in argillaceous suspensions during oxic-anoxic cycles[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 91:75-88. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.12.012
期刊类型引用(18)
1. 宋骏杰,许奕敏,李伟平,谢荣焕,刘桂建. 还原菌Staphylococcus sp.修复六价铬污染土壤的中试研究. 安全与环境学报. 2024(04): 1581-1586 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张兆鑫,曹宁宁,李林记,刘素青,李佳昊,曹翠,李和平,张凯,石勇丽. 原位吸附技术修复六价铬污染土壤. 岩矿测试. 2024(02): 302-314 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 张伟琦,谢涛,孙稚菁,王茂林,蔡喜运. 微波消解火焰原子吸收光谱法测定土壤中六价铬. 环境科学研究. 2023(01): 44-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 黄文涛,王孙崯,邓呈逊,梁广秋,侍子刚,程功弼. 还原稳定化材料在铬污染土壤修复中的应用进展. 环境科技. 2023(02): 66-70+76 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李佩珊,冯志刚,黄冲,刘威,张兰英. Cr(Ⅵ)污染土壤的还原钝化修复研究. 南华大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 16-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 裴一青,杨一鸣,杨艺鹏,宋玲彦. 半干旱区铬污染土壤还原-稳定化修复试验研究. 西北民族大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(03): 6-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陶玲,仝云龙,余方可,杨万辉,王艺蓉,王丽,任珺. 碱改性凹凸棒石对土壤中镉化学形态及环境风险的影响. 岩矿测试. 2022(01): 109-119 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 林康,文志刚,王念,卢雨萱,夏华南,聂艳. 铬污染土壤修复技术研究进展. 绿色科技. 2022(04): 49-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张敏,马乾方,唐姗姗,杨晓强,郭园园,王岩. 钙镁磷肥和沸石粉对制革污泥免烧骨料性能的改善. 西部皮革. 2022(11): 22-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 任学昌,张曦,时秋红,张玉杰,陈仁华. FeSO_4联合固化剂修复铬污染土壤的稳定化研究. 安全与环境学报. 2022(04): 2231-2240 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 陈龙,李启婷,钱坤鹏. 重金属铬污染土壤的修复技术研究进展. 应用化工. 2022(10): 3058-3062 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 赵庆令,李清彩,谭现锋,安茂国,陈娟,毛秀丽. 微波碱性体系消解-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定固体废物中的六价铬. 岩矿测试. 2021(01): 103-110 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 宋文,成少平,迟晓杰,艾艳君,谷海红. 重金属污染土壤修复遥感监测研究进展. 矿产综合利用. 2021(04): 21-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 章长松. 河道疏浚底泥堆土镉污染修复技术分析. 煤田地质与勘探. 2021(05): 200-208 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 李瑛. 土壤环境中重金属铬污染现状及智能监测方法. 石化技术. 2021(11): 152-153 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 何雨江,陈德文,张成,袁广祥. 土壤重金属铬污染修复技术的研究进展. 安全与环境工程. 2020(03): 126-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 徐红纳,靳立国,由丽梅,程艳. 一阶导数分光光度法同时测定水样中Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ). 岩矿测试. 2020(05): 785-792 .  本站查看
本站查看
18. 傅小丽,曾德升. 我国土壤污染修复治理技术研究进展. 热带农业工程. 2020(06): 66-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(17)
-





 下载:
下载: