Electron Microprobe Analysis of Biotite with Reequilibration Texture in Altered Trachyte
-
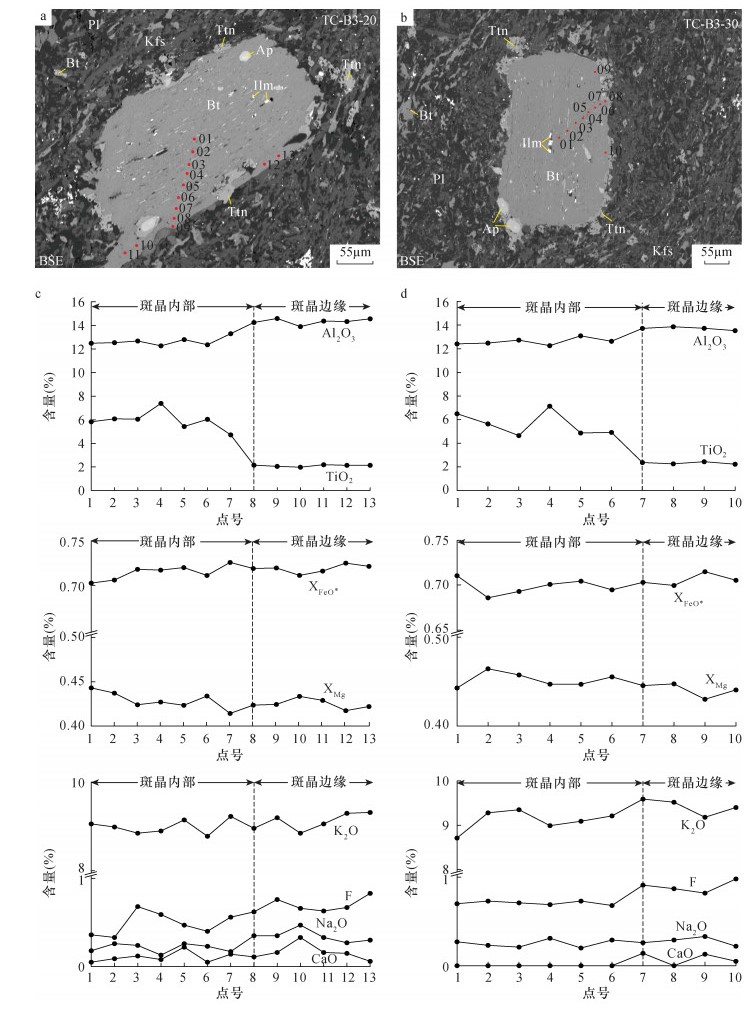
摘要: 黑云母的化学成分中蕴含着重要的成因信息,对具有交代结构的黑云母进行微区成分分析,能够精细反映交代蚀变过程中元素迁移情况,为解决矿床形成机制方面的科学问题提供矿物学证据。本文以北大巴山平利地区蚀变粗面岩中具有再平衡结构的黑云母斑晶为研究对象,进行电子探针面扫描和剖面成分分析。结果表明,斑晶内部为岩浆成因黑云母,边缘为"扩散-反应"过程所致的再平衡成因黑云母。斑晶边缘与内部相比,TiO2含量由平均5.78%降至2.22%,表明在交代蚀变过程中黑云母中Ti等高场强元素被淋滤出进入流体;而CaO含量由平均0.06%升至0.14%,F含量由平均0.60%升至0.80%,指示蚀变流体内富含Ca、F等组分。本研究揭示了粗面岩中铌矿床的形成与热液作用关系密切,成矿流体中Ca、F等组分在铌元素的迁移及富集过程中具有重要作用。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDThe chemical composition of biotite contains important genetic information. The in-situ analyses of biotite with metasomatic texture can reflect the migration of the elements during the metasomatic alteration, and provide mineralogical evidence for the ore-forming mechanism. OBJECTIVESTo investigate the migration of elements during trachyte alteration and reveal the Nb mineralization mechanism in altered trachyte. METHODSBiotite phenocryst with reequilibration texture in altered trachyte in the Pingli area of North Dabashan was studied, and the EMPA element mapping and line profile analyses were carried out. RESULTSThe results show that the phenocryst was magmatic in the core and the reequilibrated origin on the rim, caused by diffusion-reaction process. Compared with the core, the TiO2 content decreased from an average of 5.78% to 2.22% in the rim, indicating that Ti was leached out into the fluid during the exchange alteration. The CaO content increased from 0.06% to 0.14% on average, and the F content increased from 0.60% to 0.80% on average, suggesting that the alteration fluid is rich in Ca and F. CONCLUSIONSThe formation of Nb deposits in trachyte is closely related to the hydrothermal activity, and the components such as Ca and F in the ore-forming fluid play an important role in the migration and enrichment of Nb. -
Key words:
- biotite /
- electron microprobe analysis /
- reequilibration textures /
- Nb deposit /
- trachyte
-

-
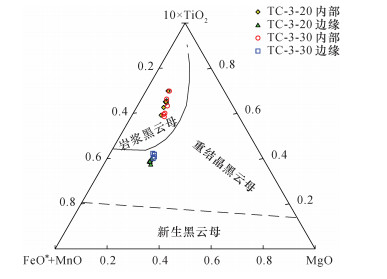
图 4 黑云母成分10×TiO2-FeO*-MgO图解(据文献[14])
Figure 4.
表 1 黑云母斑晶电子探针分析结果
Table 1. Representative electron microprobe analysis of biotite phenocrysts
成分 斑晶内部 斑晶边缘 TC-B3-20(7个分析点) TC-B3-30(6个分析点) 平均值
(%)TC-B3-20(6个分析点) TC-B3-30(4个分析点) 平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)SiO2 34.62 36.02 35.30 34.00 35.56 34.89 35.10 35.81 36.36 36.11 35.72 36.56 36.25 36.18 TiO2 4.72 7.39 5.93 4.65 7.14 5.62 5.78 1.98 2.19 2.11 2.23 2.44 2.33 2.22 Al2O3 12.27 13.30 12.63 12.26 13.09 12.60 12.62 13.90 14.59 14.33 13.53 13.86 13.71 14.02 FeOT 21.30 22.50 21.82 20.32 21.52 21.17 21.50 22.06 23.08 22.48 21.65 22.36 21.98 22.23 MnO 0.97 1.28 1.16 1.25 2.00 1.51 1.34 1.21 1.36 1.31 1.23 1.43 1.33 1.32 MgO 8.92 9.50 9.19 9.22 10.27 9.82 9.51 9.14 9.52 9.32 9.47 9.85 9.73 9.53 CaO 0.05 0.22 0.11 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 0.06 0.33 0.16 0.05 0.14 0.11 0.14 Na2O 0.13 0.26 0.21 0.20 0.31 0.25 0.23 0.27 0.47 0.35 0.22 0.33 0.28 0.32 K2O 8.78 9.23 8.99 8.71 9.35 9.11 9.05 8.85 9.32 9.12 9.18 9.59 9.42 9.27 F 0.33 0.68 0.48 0.68 0.73 0.71 0.60 0.62 0.83 0.70 0.82 0.98 0.90 0.80 总量 94.25 96.57 95.34 94.70 95.22 94.96 95.15 94.82 95.91 95.27 94.75 95.49 95.11 95.19 XFeO* 0.70 0.73 0.72 0.69 0.71 0.70 0.71 0.71 0.72 0.72 0.70 0.71 0.71 0.72 基于22个O原子计算阳离子数 成分 斑晶内部 斑晶边缘 TC-B3-20(7个分析点) TC-B3-30(6个分析点) 平均值
(%)TC-B3-20(6个分析点) TC-B3-30(4个分析点) 平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)最小值
(%)最大值
(%)平均值
(%)Si 5.45 5.56 5.51 5.37 5.54 5.48 5.50 5.58 5.69 5.64 5.63 5.70 5.67 5.66 AlⅣ 2.22 2.45 2.33 2.25 2.44 2.33 2.33 2.31 2.42 2.36 2.30 2.37 2.33 2.35 AlⅥ 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.24 0.33 0.28 0.18 0.23 0.20 0.24 Ti 0.56 0.85 0.70 0.55 0.84 0.66 0.68 0.23 0.26 0.25 0.26 0.29 0.27 0.26 Fe 2.76 2.95 2.85 2.64 2.84 2.78 2.82 2.88 3.01 2.94 2.82 2.95 2.88 2.91 Mn 0.13 0.17 0.15 0.16 0.27 0.20 0.18 0.16 0.18 0.17 0.16 0.19 0.18 0.18 Mg 2.06 2.24 2.14 2.14 2.40 2.30 2.22 2.14 2.22 2.17 2.22 2.30 2.27 2.22 Ca 0.01 0.04 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.06 0.03 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.02 Na 0.04 0.08 0.06 0.06 0.09 0.08 0.07 0.08 0.14 0.10 0.07 0.10 0.08 0.09 K 1.74 1.84 1.79 1.75 1.87 1.82 1.81 1.77 1.85 1.82 1.84 1.90 1.88 1.85 XMg 0.41 0.44 0.43 0.44 0.46 0.45 0.44 0.42 0.43 0.42 0.43 0.45 0.44 0.43 T(℃) 737 792 766 738 792 763 765 601 622 614 625 645 635 625 注:FeOT表示电子探针测试的全铁含量;XFeO*=FeO*/(FeO*+MgO);FeO*=FeOT+MnO;XMg=Mg/(Mg+Fe)。T(℃)计算据公式:T={[ln(Ti)-a-c×(XMg)3]/b}0.333[21]。 -
[1] 陈雷, 闫臻, 王宗起, 等.陕西山阳-柞水矿集区燕山期岩体矿物学特征:对岩浆性质及成矿作用的指示[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(1):109-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2014.01.026
Chen L, Yan Z, Wang Z Q, et al.Mineralogical characteristics of the Yanshanian granitic rocks in Shanyang-Zhashui ore concentration area:An indicator for the magmatic nature and metallogenesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(1):109-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2014.01.026
[2] Bao B, Webster J D, Zhang D H, et al.Compositions of biotite, amphibole, apatite and silicate melt inclusions from the Tongchang mine, Dexing porphyry deposit, SE China:Implications for the behavior of halogens in mineralized porphyry systems[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 79:443-462. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.05.024
[3] 王勇, 唐菊兴, 王立强.西藏邦铺斑岩钼(铜)矿床钾硅酸盐化热液黑云母电子探针分析及早期成矿流体特征[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(4):440-447. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.017
Wang Y, Tang J X, Wang L Q.EMPA analysis of hydrothermal biotite from the Bangpu porphyry Mo-Cu deposit of Tibet, China and the characteristics of early ore-forming fluids[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(4):440-447. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.017
[4] 杜佰松, 申俊峰, 秦玉良, 等.甘肃省沃尔给花岗岩体中黑云母的成分对其岩体碱度的响应及成岩成矿意义[J].现代地质, 2017, 31(4):672-682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.04.003
Du B S, Shen J F, Qin Y L, et al.Chemical composition of biotites responding to basicity of Woergei granite intrusion in Gansu Province and implications for petrogenesis and mineralization[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(4):672-682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.04.003
[5] Moore W J, Czamanske G K.Compositions of biotites from unaltered and altered monzonitic rocks in the Bingham Mining District, Utah[J]. Economic Geology, 1973, 68(2):269-274. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.68.2.269
[6] Jacobs D C, Parry W T.Geochemistry of biotite in the Santa Rita porphyry copper deposit, New Mexico[J]. Economic Geology, 1979, 74(4):860-887. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.74.4.860
[7] 傅金宝.斑岩铜矿中黑云母的化学组成特征[J].地质与勘探, 1981, 9(1):16-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKT198109002.htm
Fu J B.Chemical composition of biotite in porphyry copper deposits[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1981, 9(1):16-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKT198109002.htm
[8] Selby D, Nesbitt B E.Chemical composition of biotite from the Casino porphyry Cu-Au-Mo mineralization, Yukon, Canada:Evaluation of magmatic and hydrothermal fluid chemistry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 171(1-2):77-93. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00248-5
[9] 袁继海, 詹秀春, 樊兴涛, 等.硫化物矿物中痕量元素的激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱微区分析进展[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(2):122-127. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110202
Yuan J H, Zhan X C, Fan X T, et al.Development of microanalysis of trace elements in sulfide minerals by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(2):122-127. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110202
[10] Nie X, Shen J, Liu H, et al.Geochemistry of pyrite from the Gangcha gold deposit, West Qinling Orogen, China:Implications for ore genesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2017, 91(6):2164-2179. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13456
[11] 李秋立, 杨蔚, 刘宇, 等.离子探针微区分析技术及其在地球科学中的应用进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(3):310-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.03.004
Li Q L, Yang W, Liu Y, et al.Ion microprobe microanalytical techniques and their applications in earth sciences[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(3):310-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.03.004
[12] 侯江龙, 王登红, 王成辉, 等.河北曲阳县中佐伟晶岩脉中电气石的类型和成岩成矿环境研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):529-537. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201704130056
Hou J L, Wang D H, Wang C H, et al.Study on the types, and metallogenic and diagenetic environment of tourmaline from the Zhongzuo pegmatite veins in Quyang County, Hebei Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):529-537. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201704130056
[13] 代鸿章, 王登红, 刘丽君, 等.电子探针和微区X射线衍射研究陕西镇安钨-铍多金属矿床中祖母绿级绿柱石[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3):336-345. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193
Dai H Z, Wang D H, Liu L J, et al.Study on emerald-level beryl from the Zhen'an W-Be polymetallic deposit in Shaanxi Province by electron probe microanalyzer and micro X-ray diffractometer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3):336-345. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193
[14] Nachit H, Ibhi A, Abia E H, et al.Discrimination between primary magmatic biotites, reequilibrated biotites and neoformed biotites[J]. Comptes Rendus-Géoscience, 2005, 337(16):1415-1420. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2005.09.002
[15] 李洁, 钟军伟, 于洋, 等.赣南西华山花岗岩的云母成分特征及其对岩浆演化与成矿过程的指示[J].地球化学, 2013, 42(5):393-404. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201305001
Li J, Zhong J W, Yu Y, et al.Insights on magmatism and mineralization from micas in the Xihuashan granite, Jiangxi Province, South China[J]. Geochimica, 2013, 42(5):393-404. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201305001
[16] 聂潇, 尹京武, 陈浦浦, 等.河南栾川三道庄钼钨矿床石榴石的矿物学特征研究[J].电子显微学报, 2014, 33(2):108-116. doi: 10.3969/j.1000-6281.2014.02.003
Nie X, Yin J W, Chen P P, et al.Skarn mineral characteristics of Sandaozhuang Mo-W deposit and their geological significance[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2014, 33(2):108-116. doi: 10.3969/j.1000-6281.2014.02.003
[17] 徐海明, 方景玲, 樊莉, 等.陕西平利县朱家院鹰嘴岩铌矿地质特征[J].地质论评, 2016, 62(增刊1):413-414. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp2016z1201
Xu H M, Fang J L, Fan L, et al.The geology of Yingzuiyan niobium deposit at Pingli County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(Supplement 1):413-414. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp2016z1201
[18] 杨成, 刘成新, 刘万亮, 等.南秦岭竹溪县天宝乡粗面岩地球化学特征与铌成矿[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(5):605-618. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.05.002
Yang C, Liu C X, Liu W L, et al.Geochemical characteristics of trachyte and Nb mineralization process in Tianbao township, Township, Zhuxi County, Southern Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 2017, 36(5):605-618. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.05.002
[19] 朱江, 程昌红, 王连训, 等.南秦岭竹山地区早古生代碱性岩浆活动及其相关铌稀土成矿的若干认识[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(5):681-690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.05.008
Zhu J, Cheng C H, Wang L X, et al.Some new knowledge concerning Silurian alkaline magmatism and related Nb-REE mineralization in the Zhushan Region, South Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 2017, 36(5):681-690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.05.008
[20] 朱伟, 郑婧, 刘新会, 等.陕西镇坪双河口铌矿床地质地球化学特征与成因探讨[J].地质与勘探, 2018(5):929-939. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.05.005
Zhu W, Zheng Q, Liu X H, et al.Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Shuanghekou niobium deposit in South Qinling, Shaanxi[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018(5):929-939. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.05.005
[21] Henry D J, Guidotti C V, Thomson J A.The Ti-saturation surface for low-to-medium pressure metapelitic biotites:Implications for geothermometry and Ti-substitution mechanisms[J]. American Mineralogist, 2005, 90(2-3):316-328. doi: 10.2138/am.2005.1498
[22] Parsapoor A, Khalili M, Tepley F, et al.Mineral chemistry and isotopic composition of magmatic, re-equilibrated and hydrothermal biotites from Darreh-Zar porphyry copper deposit, Kerman (Southeast of Iran)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 66:200-218. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.015
[23] Chen W T, Zhou M F.Hydrothermal alteration of magmatic zircon related to NaCl-rich brines:Diffusion-reaction and dissolution-reprecipitation processes[J]. American Journal of Science, 2017, 317(2):177-215. doi: 10.2475/02.2017.02
[24] Eggleton R A, Banfield J F.The alteration of granitic biotite to chlorite[J]. American Mineralogist, 1985, 70(9-10):902-910. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_72a03e4ba33cf0c5b9944e122f069b62
[25] Corfu F, Stone D.The significance of titanite and apatite U-Pb ages:Constraints for the post-magmatic thermal-hydrothermal evolution of a batholithic complex, Berens River area, Northwestern Superior Province, Canada[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(17):2979-2995. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00225-7
[26] Broska I, Harlov D, Tropper P, et al.Formation of mag-matic titanite and titanite-ilmenite phase relations during granite alteration in the Tribec Mountains, Western Carpathians, Slovakia[J]. Lithos, 2007, 95(1):58-71. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493706002131
[27] 潘会彬, 康志强, 杨锋, 等.粤北大宝山次英安斑岩中副矿物榍石的初步研究[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(3):44-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201403005
Pan H B, Kang Z Q, Yang F, et al.Preliminary study on the accessory mineral of sphene in dacite porphyry from Dabaoshan, Northern Guangdong Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(3):44-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201403005
[28] Cuney M, Marignac C, Weisbrod A.The Beauvoir topaz-lepidolite albite granite (Massif Central, France); the disseminated magmatic Sn-Li-Ta-Nb-Be mineralization[J]. Economic Geology, 1992, 87:1766-1794. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.87.7.1766
[29] Chevychelov V Y, Zaraisky G, Borisovskii S, et al.Effect of melt composition and temperature on the partitioning of Ta, Nb, Mn, and F between granitic (alkaline) melt and fluorine-bearing aqueous fluid:Fractionation of Ta and Nb and conditions of ore formation in rare-metal granites[J]. Petrology, 2005, 13(4):305-321.
[30] Zaraisky G P, Korzhinskaya V, Kotova N.Experimental studies of Ta2O5 and columbite-tantalite solubility in fluoride solutions from 300 to 550℃ and 50 to 100MPa[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 99:287-300. doi: 10.1007/s00710-010-0112-z
[31] Timofeev A, Migdisov A A, Williams-Jones A.An experimental study of the solubility and speciation of niobium in fluoride-bearing aqueous solutions at elevated temperature[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 158:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.02.015
[32] Linnen R L.The solubility of Nb-Ta-Zr-Hf-W in granitic melts with Li and Li+F:Constraints for mineralization in rare metal granites and pegmatites[J]. Economic Geology, 1998, 93(7):1013-1025. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.93.7.1013
[33] 陈浦浦, 尹京武, 聂潇, 等.陕西省平利县朱家院碱性岩中易解石矿物学研究[J].电子显微学报, 2014, 33(1):46-54. doi: 10.3969/j.1000-6281.2014.01.008
Chen P P, Yin J W, Nie X, et al.Study on the mineralogy of aeschynite from alkaline trachyte in Zhujiayuan of Pingli County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2014, 33(1):46-54. doi: 10.3969/j.1000-6281.2014.01.008
[34] 段湘益, 王海元.陕西省安康某地区铌矿地质地球化学特征[J].矿产与地质, 2007, 21(6):657-661. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2007.06.010
Duan X Y, Wang H Y.Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Nb deposit in some area of Ankang, Shannxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2007, 21(6):657-661. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2007.06.010
[35] Linnen R L, Samson I M, Williams-Jones A E, et al.Geochemistry of the rare-earth element, Nb, Ta, Hf, and Zr deposits[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2014, 13:543-568. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201802005
[36] Salvi S, Fontan F, Monchoux P, et al.Hydrothermal mo-bilization of high field strength elements in alkaline igneous systems:Evidence from the Tamazeght Complex (Morocco)[J]. Economic Geology, 2000, 95(3):559-576.
[37] 王汝成, 谢磊, 诸泽颖, 等.云母:花岗岩——伟晶岩稀有金属成矿作用的重要标志矿物[J].岩石学报, 2019, 35(1):69-75. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8301020
Wang R C, Xie L, Zhu Z Y, et al.Mica:Important indicators of granite-pegmatite-related rare-metal mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(1):69-75. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8301020
[38] Williams-Jones A E, Samson I M, Olivo G R.The ge-nesis of hydrothermal fluorite-REE deposits in the Gallinas Mountains, New Mexico[J]. Economic Geology, 2000, 95(2):327-341. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.95.2.327
-




 下载:
下载: