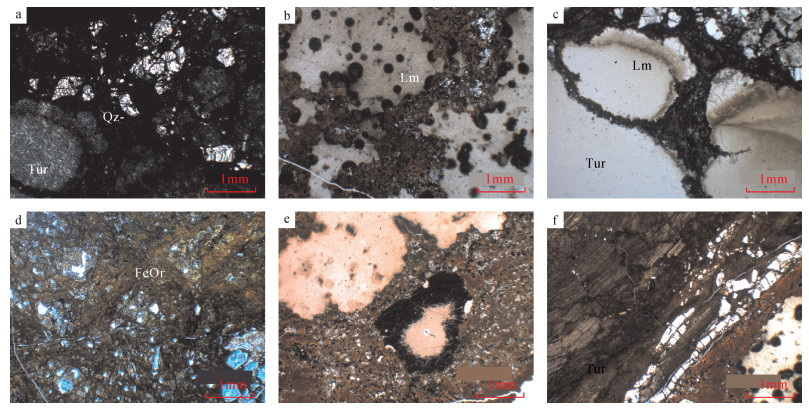
Application of EMPA-XRD-SEM to Study the Mineralogical Characteristics of Turquoise from Xichuan, Henan Province
-
摘要: 河南省淅川县位于我国重要绿松石产区——秦岭东部绿松石矿区东延部分,与淅川毗邻的许多早期考古遗址中出土了大量的绿松石制品,因此淅川绿松石的矿料流布受到许多考古学者的关注。研究淅川绿松石的矿物学特征有助于完善我国不同矿区绿松石矿物学研究,为追溯我国早期绿松石文物的矿料来源提供重要的数据支撑。本文利用偏光显微镜观察、扫描电镜、粉晶X射线衍射等技术对淅川绿松石进行结构研究,辅以电子探针、背散射电子图像观察等方法研究了淅川绿松石的矿物组合。结果表明:淅川绿松石主要由细小的鳞片状、短柱状、板片状微晶集合体组成,可见环带状、结核状、碎斑碎粒状结构;通过对比不同样品的微晶结构,可知其微晶的大小、晶型和分布状态会影响淅川绿松石集合体的致密程度和颜色;淅川绿松石集合体中常见石英、玉髓和铁氧化物,部分样品含有硫磷铝锶矿。通过对比其他矿区绿松石矿物组合,发现淅川绿松石与湖北地区的绿松石矿物组成相近,主要杂质为石英、褐铁矿,明显区别于安徽地区以高岭石为主要杂质矿物的绿松石。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDThe Xichuan turquoise mining area in Henan Province belongs to the east extension of the turquoise metallogenic belt in the junction of Hubei and Shaanxi Provinces. A lot of turquoise artifacts have been excavated in many early archaeological sites near Xichuan. Therefore, the distribution of the Xichuan turquoises has attracted wide attention of many archaeologists. OBJECTIVESTo study mineralogical characteristics of Xichuan turquoise in order to improve the mineralogical study of turquoise in different mining areas in China and provide important data support for tracing the mineral resources of early turquoise artifacts in China. METHODSTechnologies including polarizing micro-scope, scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction were applied to study the texture and structure of turquoise. Electron probe microanalysis and back scattered electron imaging were applied to study the mineral assemblage of Xichuan turquoise. RESULTSXichuan turquoise, ring-like, nodular and patchy granular was primarily composed of fine scaly, short columnar and lamellar microcrystalline aggregates. By comparing the microcrystalline structures of different samples, it was noted that the sizes, shapes and distributions could affect the densification and color of Xichuan turquoise. Quartz, chalcedony and iron oxide were common in the Xichuan turquoise aggregate. Svanbergite could also be observed in some samples. CONCLUSIONSBy comparing the mineral assemblages of turquoise in other mining areas, it was found that Xichuan turquoise was similar to the turquoise in Hubei Province with quartz and limonite as main mineral impurities, different from the turquoise in Anhui Province with kaolinite as main mineral impurities. -

-
表 1 河南淅川绿松石样品的特征
Table 1. Regular gemological characteristics of turquoise from Xichuan area of Henan Province
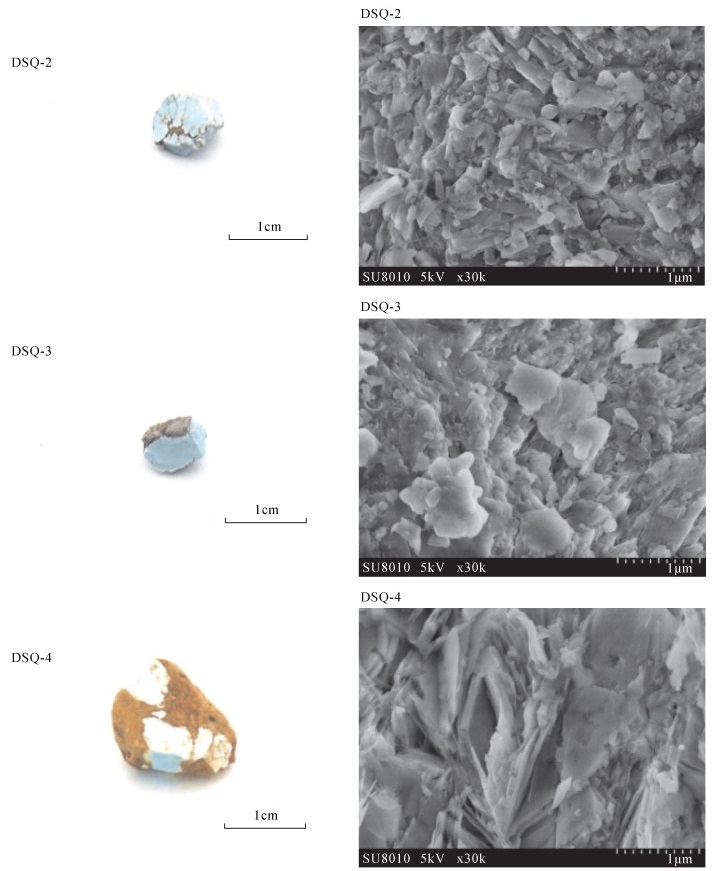
样品编号 外观特征 DSQ-1 浅蓝色、蓝色;土状光泽;绿松石为结核状;围岩为层状页岩,黄褐色,靠近松石的边缘处为深褐色 DSQ-2 蓝色;玻璃光泽;绿松石为致密块状;表面可见不规则网状分布的黑色杂质,俗称“铁线” DSQ-3 浅蓝色;玻璃光泽;边缘为浅白色风化层;绿松石为致密块状; 围岩为黑色 DSQ-4 浅蓝色、蓝白色、表面有白色风化层;土状光泽;绿松石呈镶嵌状;围岩为褐黄色 DSQ-5 深蓝色;玻璃光泽;绿松石为结核状;围岩为褐黄色,紧紧包裹着绿松石 DSQ-6 蓝色;玻璃光泽;绿松石为结核状、脉状;围岩为褐黄色 表 2 河南淅川绿松石电子探针分析结果
Table 2. EMPA analysis of turquoise from Xichuan area of Henan Province
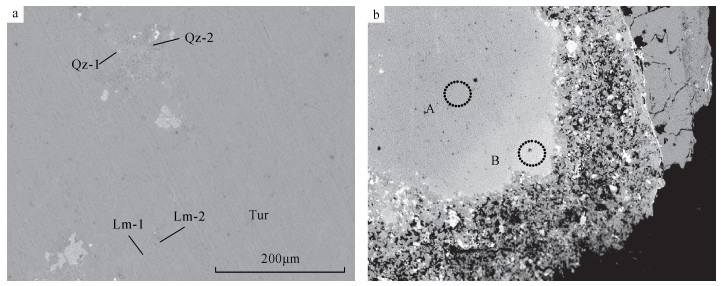
成分 绿松石 硫磷铝锶矿
(图 3b-B区)石英 褐铁矿 Tur(图 3a) Tur(图 3b-A区) Qz-1(图 3a) Qz-2(图 3a) Lm-1(图 3a) Lm-2(图 3a) SiO2 0.478 0.519 1.237 89.262 97.162 0.604 7.731 FeO 0.158 0.137 0.088 0.017 0.105 55.402 69.386 SO3 0.379 0.393 4.519 0.005 0.205 0.143 0.117 Al2O3 39.716 40.66 32.639 0.019 0.408 4.406 1.088 CuO 6.61 5.973 0.449 - 0.224 0.209 0.382 P2O5 33.86 35.124 20.185 - 0.121 1.306 0.314 SrO 0.428 0.741 7.542 - - 0.011 - V2O3 - 0.14 0.685 - 0.027 8.125 3.173 CaO 0.55 0.983 7.728 0.042 0.034 0.356 0.382 MgO 0.042 0.037 0.071 0.032 - 0.047 0.071 ZnO 1.34 1.188 - - - 2.029 - BaO 0.085 0.07 1.324 0.002 - 0.078 0.215 MnO 0.051 0.029 0.015 0.033 0.038 0.035 0.093 K2O 0.08 0.1 0.412 0.048 0.035 0.137 0.108 TiO2 0.073 - 0.064 0.025 - 0.263 0.339 PbO - - 0.032 - - - - 总量 83.85 86.094 76.99 89.485 98.359 73.151 83.399 注:①由于绿松石中含水,故测试结果总和低于100。②“-”表示低于电子探针检测限。 表 3 河南淅川绿松石样品DSQ-5B粉晶X射线衍射数据和硫磷铝锶矿标准卡片对比
Table 3. X-ray powder diffraction data of sample DSQ-5B area and the standard card of Svanbergite
PDF#39-1361 Svanbergite标准卡片 样品DSQ-5B 2θ d(nm) 2θ d(nm) 15.602 0.5675 15.7 0.56398 25.524 0.3487 25.49 0.34916 30.032 0.2973 30.049 0.29714 30.283 0.2949 30.38 0.29398 36.789 0.2441 36.87 0.24358 40.341 0.22339 40.91 0.22041 46.235 0.19619 47.979 0.18946 52.444 0.17433 52.279 0.17484 63.965 0.14543 63.021 0.14738 65.743 0.14192 65.664 0.14207 68.52 0.13683 68.543 0.13679 69.611 0.13495 69.183 0.13568 73.854 0.12821 73.618 0.12856 80.148 0.11965 80.04 0.11978 表 4 不同产地绿松石的杂质矿物组合
Table 4. Associated minerals of turquoise from different origin places
-
[1] 张蓓莉.系统宝石学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010.
Zhang B L.Systematic Gemmology[M].Beijing:The Geological Publishing House, 2010.
[2] Čejka J, Sejkora J, Macek I, et al.Raman and infrared spectroscopic study of turquoise minerals[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2015, 149:173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2015.04.029
[3] 庞小霞.中国出土新石器时代绿松石器研究[J].考古学报, 2014(2):139-168. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=49495555
Pang X X.The researches on the turquoise objects of the neolithic age unearthed in China[J].Acta Archaeologica Sinica, 2014(2):139-168. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=49495555
[4] 涂怀奎.陕鄂相邻地区绿松石矿地质特征[J].陕西地质, 1996(2):59-64. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91282B/199602/683886889199602006.html
Tu H K.Geological characteristics of turquoise ore in the areas adjacent to Shaanxi and Hubei Provinces[J]. Geology of Shaanxi, 1996(2):59-64. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91282B/199602/683886889199602006.html
[5] 付宝国, 侯青亚.绿松石的矿物学特征及成矿地质条件[J].华北国土资源, 2017(5):33-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7487.2017.05.016
Fu B G, Hou Q Y.Study on mineralogical characteristics and metallogenic geological conditions of turquoise[J].Huabei Land and Resources, 2017(5):33-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7487.2017.05.016
[6] 赵新科, 李金良, 刘亚莉, 等.安康市白河绿松石矿资源概况及成因浅析[J].陕西地质, 2017, 35(2):46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2017.02.008
Zhao X K, Li J L, Liu Y L, et al.Resources and genesis of turquoise mineral in Baihe of Ankang city[J].Geology of Shaanxi, 2017, 35(2):46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2017.02.008
[7] Nikbakht T, Kakuee O, Lamehi-Rachti M, et al.An efficient ionoluminescence analysis of turquoise gemstone as a weakly luminescent mineral[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2017, 179:171-177. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.02.038
[8] 刘喜锋, 林晨露, 李丹丹, 等.新疆哈密绿松石的矿物学和光谱学特征研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(4):1231-1239. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201804042
Liu X F, Lin C L, Li D D, et al.Study on mineralogy and spectroscopy of turquoises from Hami, Xinjing[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(4):1231-1239. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201804042
[9] 严俊, 刘晓波, 王巨安, 等.应用FTIR-XRD-XRF分析测试技术研究新型仿制绿松石的矿物学特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5):544-549. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.05.008
Yan J, Liu X B, Wang J A, et al.Determination of mineral compositions of new imitated turquoise by FTIR-XRD-XRF[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5):544-549. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.05.008
[10] 周彦, 亓利剑, 戴慧, 等.安徽殿庵山绿松石的宝石学特征研究[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2013, 15(4):37-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bshbsxzz201304005
Zhou Y, Qi L J, Dai H, et al.Study on gemological characteristics of turquoise from Dian'anshan, Anhui Province[J].Journal of Gem and Gemmology, 2013, 15(4):37-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bshbsxzz201304005
[11] Hamid S.A combinative technique to recognise and dis-criminate turquoise stone[J].Vibrational Spectroscopy, 2018, 99:93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.vibspec.2018.09.002
[12] 陈文君, 施光海, 王妍, 等.湖北与安徽产高品质绿松石的红外与拉曼光谱特征及意义[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(4):1059-1065. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201804012
Chen W J, Shi G H, Wang Y, et al.Infrared and Raman spectra of high-quality turquoise from Hubei and Anhui, China:Characteristics and significance[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(4):1059-1065. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201804012
[13] 顾星宇, 秦晓玲, 戴正之, 等.红外光谱在绿松石鉴定中的应用[J].上海计量测试, 2018, 45(2):29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2235.2018.02.012
Gu X Y, Qin X L, Dai Z Z, et al.Application of infrared spectroscopy in turquoise identification[J].Shanghai Measurement and Testing, 2018, 45(2):29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2235.2018.02.012
[14] 刘玲.中国绿松石颜色的成因、影响因素及分级研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
Liu L.Study on Origin, Factors and Grading of the Color of Turquoise from China[D].Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018.
[15] 罗泽敏, 沈锡田, 朱勤文, 等.绿松石结构的致密性对其颜色量化研究的影响[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2016, 18(2):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.02.001
Luo Z M, Shen X T, Zhu Q W, et al.How structure compactness impacts the quantitative colour research of turquoise[J].Journal of Gem and Gemmology, 2016, 18(2):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.02.001
[16] 戴正之, 吕晓瑜, 顾星宇, 等.绿松石在均匀色度坐标中的颜色分析[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2016, 18(2):9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.02.002
Dai Z Z, Lü X Y, Gu X Y, et al.Colour analysis of turquoise using uniform chromaticity coordinate[J].Journal of Gem and Gemmology, 2016, 18(2):9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.02.002
[17] 郭倩, 徐志.我国绿松石致色机理研究进展[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(增刊1):136-140. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94932X/2014S1/89837587504849528349485051.html
Guo Q, Xu Z.Progress in the study of color emerging mechanism of turquoise[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2014, 33(Supplement 1):136-140. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94932X/2014S1/89837587504849528349485051.html
[18] 李延祥, 张登毅, 何驽, 等.山西三处先秦遗址出土绿松石制品产源特征探索[J].文物, 2018(2):86-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8697.2018.02.030
Li Y X, Zhang D Y, He N, et al.The study of turquoise objects three Pre-Qin unearthed sites in Shanxi Province[J].Cultural Relics, 2018(2):86-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8697.2018.02.030
[19] 何煦, 陈林, 李青会, 等.竹山和马鞍山绿松石微量元素和稀土元素特征[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(6):709-713. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.06.011 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/434bd3e5-eb41-44a9-8cd1-ccb81f08f2bf
He X, Chen L, Li Q H, et al.Trace elements and rare earth elements characteristics of turquoise from Zhushan and Ma'anshan area[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(6):709-713. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.06.011 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/434bd3e5-eb41-44a9-8cd1-ccb81f08f2bf
[20] 先怡衡, 李延祥, 杨岐黄.便携式X荧光光谱结合主成分分析鉴别不同产地的绿松石[J].考古与文物, 2016(3):112-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7830.2016.03.015
Xian Y H, Li Y X, Yang Q H.Application of portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer with principal component analysis to distinguish the different turquoise mines[J].Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 2016(3):112-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7830.2016.03.015
[21] 先怡衡, 李延祥, 谭宇辰, 等.初步运用LA-ICP-AES区分不同产地的绿松石[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(10):3313-3319. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201610050
Xian Y H, Li Y X, Tan Y C, et al.Application of LA-ICP-AES to distinguish the different turquoise mines[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(10):3313-3319. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201610050
[22] Saul L, Alyson M, John R, et al.Revisited:New inves-tigations of a Late Prehispanic turquoise mine, Arizona, USA[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2017, 87:44-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2017.09.004
[23] Hull S, Fayek M, Mathien F J, et al.A new approach to determining the geological provenance of turquoise artifacts using hydrogen and copper stable isotopes[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2008, 35(5):1355-1369. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2007.10.001
[24] 赵虹霞, 伏修锋, 干福熹, 等.不同产地绿松石无损检测及岩相结构特征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2007, 26(2):141-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.02.015 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20070249
Zhao H X, Fu X F, Gan F X, et al.Study on mineralogical characteristics of turquoise samples from different provenances by nondistrctive analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(2):141-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.02.015 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20070249
[25] 周世全, 江富建.河南淅川的绿松石研究[J].南阳师范学院学报, 2005, 4(3):63-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6132.2005.03.019
Zhou S Q, Jiang F J.The research of the turquoise in Xichuan of Henan[J].Journal of Nanyang Teachers' College, 2005, 4(3):63-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6132.2005.03.019
[26] 河南省文物考古研究所.舞阳贾湖[M].北京:科学出版社, 1999.
Henan Provincial Cultural Relics Archaeological Research Institute.Jiahu of Wuyang[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1999.
[27] 冯敏, 毛振伟, 潘伟斌, 等.贾湖遗址绿松石产地初探[J].文物保护与考古科学, 2003(3):9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1538.2003.03.002
Feng M, Mao Z W, Pan W B, et al.Preliminary research on turquoise in Jiahu site[J].Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 2003(3):9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1538.2003.03.002
[28] 丁文, 张杰, 邓秋凤, 等.四川某地硫磷铝锶矿的矿物组成及工艺特征[J].化工矿物与加工, 2016, 45(10):29-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgkwyjg201610009
Ding W, Zhang J, Deng Q F, et al.Mineral compositions and mineralogical characteristics of svanbergite in Sichuan[J].Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2016, 45(10):29-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgkwyjg201610009
[29] 罗远飞, 余晓艳, 周越刚, 等.陕西洛南绿松石的结构构造特征研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(1):115-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.01.012
Luo Y F, Yu X Y, Zhou Y G, et al.A study of texture and structure of turquoise from Luonan, Shaanxi Province[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2017, 36(1):115-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.01.012
[30] 张智勇.河南淅川下寒武统水沟口组黑色岩系沉积环境分析[D].焦作: 河南理工大学, 2012.
Zhang Z Y.Sedimentary Environmental Analyses of the Lower Cambrian Shuigoukou Formation Black Rock Series in Xichuan, Henan[D].Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2012.
[31] 李亚光.不同产地的绿松石特征浅析[J].文物鉴定与鉴赏, 2017(6):82-83. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wwjdyjs201706023
Li Y G.The study on characteristics of turquoise from different resources[J].Identification and Appreciation to Cultural Relics, 2017(6):82-83. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wwjdyjs201706023
[32] 丁文, 张杰, 邓秋凤, 等.四川某地硫磷铝锶矿有用元素赋存状态和综合利用探讨[J].化工矿物与加工, 2017, 46(2):14-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgkwyjg201702004
Ding W, Zhang J, Deng Q F, et al.Discussion on occurrence state and comprehensive utilization of useful elements in a scanbergite in Sichuan[J].Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2017, 46(2):14-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgkwyjg201702004
-



 下载:
下载: