The Formation Mechanism and Geological Significance of Graptolite from the Longmaxi Formation: Constraints from in situ Multi-element Imaging Analysis
-
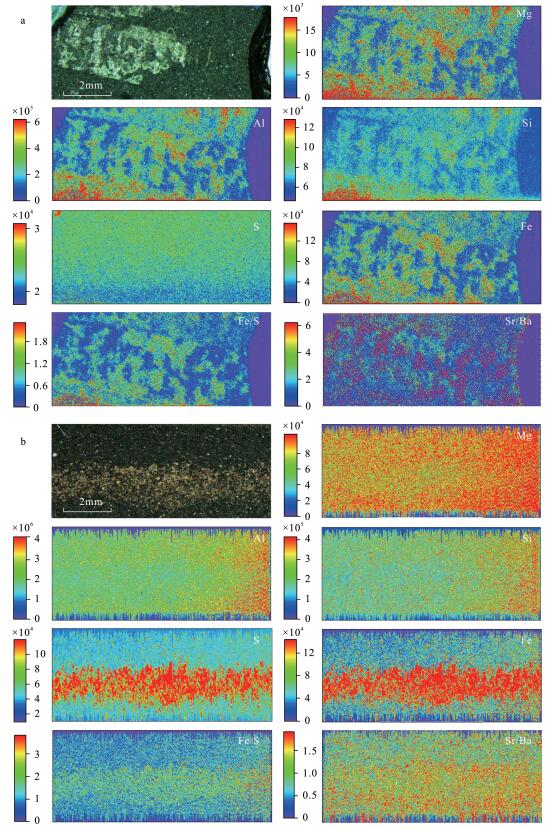
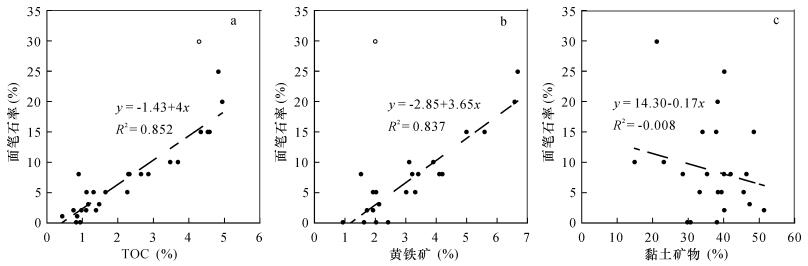
摘要: 上扬子地区龙马溪组黑色页岩富含笔石,多以碳质薄膜形式富集于富有机质层段。前期研究多关注笔石形态和成岩后的演化过程,对笔石埋藏和早成岩阶段所经历地球化学作用的研究较少,笔石成因仍缺乏直接证据。本文利用激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)技术对宁203井龙马溪组笔石进行原位微区多元素扫描成像,对主量成矿元素分布与富集程度进行解析,发现了碳质薄膜笔石体表面富集Mg、Al、Si、Fe元素,富集倍数在1.5~10倍以上,Sr/Ba值(1.4~2.3)则明显低于围岩(>5.0),指示黏土矿物包埋是笔石碳化的主要途径,包埋形成的硫化微环境导致部分笔石发生黄铁矿化。结合面笔石率、有机质、黄铁矿、黏土矿物含量和δ13Corg值的剖面垂向变化及相关性分析,提出早期微生物席繁盛和后期硫酸盐还原菌繁盛导致水岩界面孔隙水普遍缺氧,是笔石和有机质大量埋存的主要原因。本研究结果不仅揭示了龙马溪组笔石的埋藏矿化机制,也为有机质富集和黑色页岩形成的控制因素研究提供了新思路。
-
关键词:
- 龙马溪组 /
- 笔石 /
- 多元素成像 /
- 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUNDThe black shale of the Longmaxi Formation in the Upper Yangtze region is rich in graptolites. Most of them were preserved as a carbonaceous film, and enriched in organic-rich layers. Previous research focuses mainly on the graptolite morphology and evolution process after diagenesis, but the direct evidence for the fossil formation is still lacking. OBJECTIVESTo explore the formation mechanism of graptolite in the Longmaxi Formation and its geological significance on organic matter enrichment. METHODSLaser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) was used for the in situ multi-element imaging of graptolites and surrounding rocks from the Longmaxi Formation of the N203 well. RESULTSAnalysis of the distribution and enrichment degree of major ore-forming elements indicates that Mg, Al, Si, Fe were rich in the carbonaceous film surface of graptolite, with a enrichment degree ranging from 1.5 to 10. However, Sr/Ba values (1.4-2.3) of the carbonaceous film type graptolite were lower than that of the surrounding rocks (>5.0). This indicated that embedding by clay minerals was the main process of graptolite preservation. The sulfidic micro-environment caused by embedding of clay minerals benefited the pyritization of the graptolite organism. Combing with the vertical variation and correlation analysis of the cross-section graptolite ratio, organic matter, pyrite, clay mineral content and δ13Corg value, it can be concluded that the flourishing of the microbial mat in early stage and sulfate-reducing bacteria in later stage consumed oxygen in the pore water and caused anoxic bottom water, and should be the main reason of massive burial of graptolite and organic matter. CONCLUSIONSThe result revealed the burial and mineralization mechanism of graptolite in the Longmaxi Formation, and also provided a new method for studying the controlling factors of organic matter enrichment and black shale formation. -

-
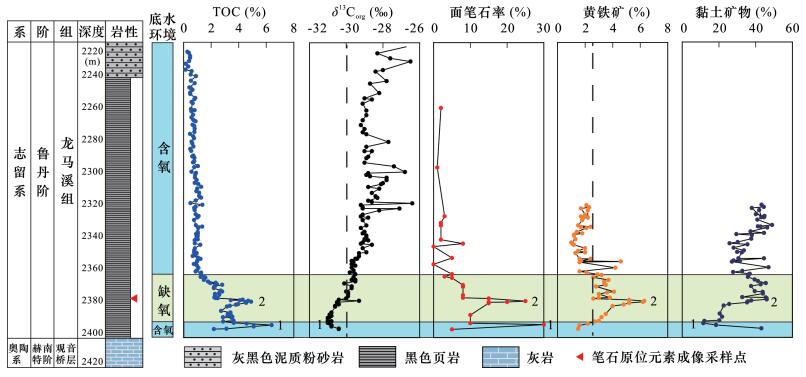
图 4 宁203井龙马溪组沉积物地球化学参数(δ13Corg和部分TOC数据引自文献[45])
Figure 4.
表 1 LA-ICP-MS工作参数
Table 1. Measurement parameters of LA-ICP-MS instrument
激光剥蚀系统
(LA)电感耦合等离子体质谱系统
(ICP-MS)脉冲频率 6Hz 射频功率 1375W 输出能量 50% 载气(He)流量 1.1L/min 脉冲能量 5mJ 辅助气(Ar)流量 0.8L/min 能量密度 7J/cm2 雾化气(Ar)流量 0.9L/min 激光波长 193nm 冷却气(Ar)流量 14.0L/min 光斑直径 20μm 停留时间 0.01s 扫描方式 线扫描 数据采集模式 时间分辨(TRM) 扫描速度 120μm/s 碰撞池模式 标准模式(STD) 扫描行距 20μm 测定元素 26Mg、27Al、29Si、34S、57Fe、88Sr、137Ba -
[1] Loydell D K.Graptolite biozone correlation charts[J].Geological Magazine, 2012, 149(1):124-132. doi: 10.1017/S0016756811000513
[2] Underwood C J.Graptolite preservation and deformation[J].Palaios, 1992:178-186. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9ff8793db10b01ba9f7745e8b3322ba5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] Chen X, Rong J Y, Mitchell C E, et al.Late Ordovician to earliest Silurian graptolite and brachiopod biozonation from the Yangtze region, South China, with a global correlation[J].Geological Magazine, 2000, 137(6):623-650. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800004702
[4] 樊隽轩, Melchin M J, 陈旭, 等.华南奥陶-志留系龙马溪组黑色笔石页岩的生物地层学[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2012, 42(1):130-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201201014
Fan J X, Melchin M J, Chen X, et al.Biostratigraphy and geography of the Ordovician-Silurian Lungmachi black shales in South China[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2011, 54(12):1854-1863. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201201014
[5] 陈清, 樊隽轩, 张琳娜, 等.下扬子区奥陶纪晚期古地理演变及华南"台-坡-盆"格局的打破[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2018, 48(6):767-777. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201806008
Chen Q, Fan J X, Zhang L N, et al.Paleogeographic evolution of the Lower Yangtze region and the break of the "platform-slope-basin" pattern during the Late Ordovician[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2018, 61(5):625-636. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201806008
[6] 陈旭, 樊隽轩, 王文卉, 等.黔渝地区志留系龙马溪组黑色笔石页岩的阶段性渐进展布模式[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 47(6):720-732. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201706005
Chen X, Fan J X, Wang W H, et al.Stage-progressive distribution pattern of the Lungmachi black graptolitic shales from Guizhou to Chongqing, Central China[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2017, 60(6):1133-1146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201706005
[7] 陈旭, 陈清, 甄勇毅, 等.志留纪初宜昌上升及其周缘龙马溪组黑色笔石页岩的圈层展布模式[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2018, 48(9):1198-1206. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201809006.htm
Chen X, Chen Q, Zhen Y Y, et al.Circumjacent distribution pattern of the Lungmachian graptolitic black shale (Early Silurian) on the Yichang Uplift and its peripheral region[J].Science China(Earth Sciences), 2018, 61(9):1195-1203. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201809006.htm
[8] 腾格尔, 申宝剑, 俞凌杰, 等.四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气形成与聚集机理[J].石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1):69-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201701008
Borjigin T, Shen B J, Yu L J, et al.Mechanisms of shale gas generation and accumulation in the Ordovician Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1):69-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201701008
[9] Luo Q Y, Hao J Y, Skovsted C B, et al.The organic petrology of graptolites and maturity assessment of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations from Chongqing, China:Insights from reflectance cross-plot analysis[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2017, 183:161-173. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2017.09.006
[10] Luo Q Y, Hao J Y, Skovsted C B, et al.Optical characteristics of graptolite-bearing sediments and its implication for thermal maturity assessment[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 195:386-401. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.06.019
[11] Luo Q Y, Zhong N N, Dai N, et al.Graptolite-derived organic matter in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations (Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian) of Southeastern Chongqing, China:Implications for gas shale evaluation[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 153:87-98. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2015.11.014
[12] 王勤, 钱门辉, 蒋启贵, 等.中国南方海相烃源岩中笔石生烃能力研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):258-264. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201611170173
Wang Q, Qian M H, Jiang Q G, et al.A study on hydrocarbon generation capacity of graptoliye in marine hydrocarbon source rocks in Southern China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):258-264. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201611170173
[13] 邱振, 邹才能, 李熙喆, 等.论笔石对页岩气源储的贡献——以华南地区五峰组-龙马溪组笔石页岩为例[J].天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(5):606-615. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TDKX201805002.htm
Qiu Z, Zou C N, Li X Z, et al.Discussion on the contribution of graptolite to organic enrichment and reservoir of gas shale:A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in South China[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(5):606-615. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TDKX201805002.htm
[14] 邹才能, 龚剑明, 王红岩, 等.笔石生物演化与地层年代标定在页岩气勘探开发中的重大意义[J].中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(1):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.001
Zou C N, Gong J M, Wang H Y, et al.Importance of graptolite evolution and biostratigraphic calibration on shale gas exploration[J].China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(1):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.001
[15] 张元动, 骆天天, 茅永强.利用背散射电子(BSE)研究奥陶纪部分笔石的始端发育和分枝方式[J].古生物学报, 2005, 44(1):125-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-6616.2005.01.014
Zhang Y D, Luo T T, Mao Y Q, et al.Interpretation of the proximal development and branching divisions of some early and middle Ordovician graptolites based on BSE images[J].Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2005, 44(1):125-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-6616.2005.01.014
[16] 陈旭, 肖承协, 陈洪冶.华南五峰期笔石动物群的分异及缺氧环境[J].古生物学报, 1987, 26(3):326-338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSWX198703013.htm
Chen X, Xiao C X, Chen H Y.Wufengian (Ashgillian) graptolite faunal differentiation and anoxic environment in South China[J].Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 1987, 26(3):326-338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSWX198703013.htm
[17] Topper T P, Strotz L C, Holmer L E, et al.Survival on a soft seafloor:Life strategies of brachiopods from the Cambrian Burgess Shale[J].Earth Science Reviews, 2015, 151:266-287. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.10.015
[18] Van R P, Briggs D E G, Gaines R R.The Fezouata fossils of Morocco:An extraordinary record of marine life in the Early Ordovician[J].Journal of the Geological Society, 2015, 172(5):541-549. doi: 10.1144/jgs2015-017
[19] Gabbott S E, Browning C, Theron J N, et al.The Late Ordovician Soom Shale Lagerstätte:An extraordinary post-glacial fossil and sedimentary record[J].Journal of the Geological Society, 2017, 174(1):1-9. doi: 10.1144/jgs2016-076
[20] Allison P A, Briggs D E G.Exceptional fossil record:Distribution of soft-tissue preservation through the Phanerozoic[J].Geology, 1993, 21(6):527-530. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0527:EFRDOS>2.3.CO;2
[21] Briggs D E G.The role of decay and mineralization in the preservation of soft-bodied fossils[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2003, 31(1):275-301. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.31.100901.144746
[22] Gaubes R R.Burgess Shale-type preservation and its distribution in space and time[J].The Paleontological Society Papers, 2014, 20:123-146. doi: 10.1017/S1089332600002837
[23] Anderson R P, Tosca N J, Gaines R R, et al.A mineralogical signature for Burgess Shale-type fossilization[J].Geology, 2018, 46(4):347-350. doi: 10.1130/G39941.1
[24] Kaczmarek Ł, Kozłowska A, Maksimczuk M, et al.The use of X-ray computed microtomography for graptolite detection in rock based on core internal structure visualization[J].Acta Geophysica Polonica, 2017, 67(2):299-306. doi: 10.1515/agp-2017-0010
[25] Morga R, Pawlyta M.Microstructure of graptolite periderm in Silurian gas shales of Northern Poland[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 189:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.02.012
[26] Mumm A S, Inan S.Microscale organic maturity deter-mination of graptolites using Raman spectroscopy[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 162:96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.05.002
[27] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al.Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies:An update[J].Chemical Geology, 2006, 232:12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
[28] Sweetapple M T, Tassios S.Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) as a tool for in situ mapping and textural interpretation of lithium in pegmatite minerals[J].American Mineralogist, 2015, 100(10):2141-2151. doi: 10.2138/am-2015-5165
[29] Ito M, Messenger S.Rare earth element measurements and mapping of minerals in the Allende CAI, 7R19-1, by nano SIMS ion microprobe[J].Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 2016, 51(4):818-832. https://www.mysciencework.com/publication/show/rare-earth-element-measurements-mapping-minerals-allende-cai-7r191-nanosims-ion-microprobe-9cacbff3
[30] Kogiso T, Suzuki K, Suzuki T, et al.Detecting micrometer -scale platinum-group minerals in mantle peridotite with micro beam synchrotron radiation X-ray fluorescence analysis[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008, 9(3):1-9.
[31] 王华建, 张水昌, 叶云涛, 等.激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱实现黄铁矿中多元素原位成像[J].分析化学, 2016, 44(11):1665-1670. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201611007
Wang H J, Zhang S C, Ye Y T, et al.In situ imaging of multi-elements on pyrite using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 44(11):1665-1670. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201611007
[32] 周文喜, 王华建, 付勇, 等.基于LA-ICP-MS多元素成像技术的早寒武世磷结核成因研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(2):97-106. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.02.002
Zhou W X, Wang H J, Fu Y, et al.Study on the formation mechanism of phosphate nodules in the Early Cambrian period using LA-ICP-MS multi-element imaging technology[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(2):97-106. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.02.002
[33] 戎嘉余, 魏鑫, 詹仁斌, 等.奥陶纪末期深水介壳动物群在湘西北的发现及其古生态意义[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2018, 48(6):753-766. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201806007
Rong J Y, Wei X, Zhan R B, et al.A deep water shelly fauna from the Uppermost Ordovician in Northwestern Hunan, South China and its paleoecological implications[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2018, 61(6):730-744. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201806007
[34] Zou C N, Qiu Z, Poulton S W, et al.Ocean euxinia and climate change 'double whammy' drove the Late Ordovician mass extinction[J].Geology, 2018, 46(6):535-538. doi: 10.1130/G40121.1
[35] Feng Z Q, Dong D Z, Tian J Q, et al.Geochemical characteristics of Longmaxi Formation shale gas in the Weiyuan area, Sichuan Basin, China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 167:538-548. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.04.030
[36] Zou C N, Yang Z, Dai J X, et al.The characteristics and significance of conventional and unconventional Sinian-Silurian gas systems in the Sichuan Basin, Central China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 64:386-402. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.03.005
[37] 陈旭.论笔石的深度分带[J].古生物学报, 1990, 29(5):507-526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX199005000.htm
Chen X.Graptolite depth zonation[J].Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 1990, 29(5):507-526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX199005000.htm
[38] May T W, Wiedmeyer R H.A table of polyatomic interferences in ICP-MS[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 1998, 19(5):150-155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cb0dcb1cf43bc194ef58e8ea42d584fb
[39] Alves L C, Wiederin D R, Houk R S.Reduction of polyatomic ion interferences in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry by cryogenic desolvation[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1992, 64(10):1164-1169. doi: 10.1021/ac00034a016
[40] Pick D, Leiterer M, Einax J W.Reduction of polyatomic interferences in biological material using dynamic reaction cell ICP-MS[J].Microchemical Journal, 2010, 95(2):315-319. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2010.01.008
[41] Novotnik B, Zuliani T, Martinčič A, et al.Effective reduction of polyatomic interferences produced by high chloride and carbon concentrations in determination of Cr(Ⅵ) by FPLC-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2012, 27(3):488-495. doi: 10.1039/C2JA10270F
[42] Van Beek P, Reyss J L, Bonte P, et al.Sr/Ba in barite:A proxy of barite preservation in marine sediments[J].Marine Geology, 2003, 199(3-4):205-220. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00220-2
[43] 吴石头, 许春雪, Klaus S, 等.193nm ArF准分子激光系统对LA-ICP-MS分析中不同基体的剥蚀行为和剥蚀速率探究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):451-459. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703290044
Wu S T, Xu C X, Klaus S, et al.Study on ablation behaviors and ablation rates of a 193nm ArF Excimer laser system for selected substrates in LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):451-459. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703290044
[44] Poulton S W, Canfield D E.Development of a sequential extraction procedure for iron:Implications for iron partitioning in continentally derived particulates[J].Chemical Geology, 2005, 214(3-4):209-221. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.09.003
[45] Wang S F, Zhao W Z, Zou C N, et al.Organic carbon and stable C-O isotopic study of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation black shales in Sichuan Basin, SW China:Paleoenvironmental and shale gas implications[J].Energy Exploration and Exploitation, 2015, 33:439-458. doi: 10.1260/0144-5987.33.3.439
[46] Batista A H, Melo V F, Gilkes R.Scanning and transmission analytical electron microscopy (STEM-EDX) identifies minor minerals and the location of minor elements in the clay fraction of soils[J].Applied Clay Science, 2017, 135:447-456. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.10.032
[47] Chen L, Lu Y C, Jiang S, et al.Heterogeneity of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in the Southeast Sichuan Basin of China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 65:232-246. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.04.003
[48] 王爱华.不同形态锶钡比的沉积环境判别效果比较[J].沉积学报, 1996, 14(4):168-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600006127
Wang A H.Discriminant effect of sedimentary environment by the Sr/Ba ratio of different existing forms[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(4):168-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600006127
[49] Liang C, Jiang Z X, Cao Y C, et al.Deep-water depositional mechanisms and significance for unconventional hydrocarbon exploration:A case study from the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Shale in the Southeastern Sichuan Basin[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(5):773-794. doi: 10.1306/02031615002
[50] Liang C, Jiang Z X, Cao Y C, et al.Sedimentary characteristics and paleoenvironment of shale in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, North Guizhou Province, and its shale gas potential[J].Journal of Earth Science, 2017, 28(6):1020-1031. doi: 10.1007/s12583-016-0932-x
[51] Zou C N, Qiu Z, Wei H Y, et al.Euxinia caused the Late Ordovician extinction:Evidence from pyrite morphology and pyritic sulfur isotopic composition in the Yangtze area, South China[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 76:159-175. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=21f4a0389492d137f2fa5648ce2cde0c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[52] Johnson C M, Beard B L, Roden E E.The iron isotope fingerprints of redox and biogeochemical cycling in modern and ancient Earth[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2008, 36:457-493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.36.031207.124139
[53] Ye Y T, Wang H J, Zhai L N, et al.Contrasting Mo-U enrichments of the basal Datangpo Formation in South China:Implications for the Cryogenian interglacial ocean redox[J].Precambrian Research, 2018, 315:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.07.013
[54] Chen C, Mu C L, Zhou K K, et al.The geochemical characteristics and factors controlling the organic matter accumulation of the Late Ordovician-Early Silurian black shale in the Upper Yangtze Basin, South China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 76:159-175. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.04.022
[55] Ma Y Q, Fan M J, Lu Y C, et al.Geochemistry and sedimentology of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi mudstone in Southwestern China:Implications for depositional controls on organic matter accumulation[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 75:291-309. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.04.024
[56] Zhao J H, Jin Z J, Jin Z K, et al.Applying sedimentary geochemical proxies for paleoenvironment interpretation of organic-rich shale deposition in the Sichuan Basin, China[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 163:52-71. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.06.015
[57] 张茜, 余谦, 王剑, 等.应用ICP-MS研究川西南龙马溪组泥页岩稀土元素特征及沉积环境[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2):217-224. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201705090078
Zhang Q, Yu Q, Wang J, et al.Application of ICP-MS to study the rare earth element characteristics and sedimentary environment of black shale in the Longmaxi Formation in the Southwestern Sichuan Basin[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2):217-224. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201705090078
[58] Zhao J H, Jin Z K, Jin Z J, et al.Origin of authigenic quartz in organic-rich shales of the Wufeng and Longmaxi Formations in the Sichuan Basin, South China:Implications for pore evolution[J].Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2017, 38:21-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.11.037
[59] Zhang S C, Wang X M, Wang H J, et al.Sufficient oxygen for animal respiration 1, 400 million years ago[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(7):1731-1736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1523449113
[60] Wang X M, Zhang S C, Wang H J, et al.Oxygen, climate and the chemical evolution of a 1400 million year old tropical marine setting[J].American Journal of Science, 2017, 317(8):861-900. doi: 10.2475/08.2017.01
[61] France R L.Carbon-13 enrichment in benthic compared to planktonic algae:Foodweb implications[J].Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1995, 124:307-312. doi: 10.3354/meps124307
[62] Xiao S H, Bykova N, Kovalick A, et al.Stable carbon isotopes of sedimentary kerogens and carbonaceous macrofossils from the Ediacaran Miaohe Member in South China:Implications for stratigraphic correlation and sources of sedimentary organic carbon[J].Precambrian Research, 2017, 302:171-179. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.10.006
[63] Gehling J G.Microbial mats in terminal Proterozoic siliciclastics; Ediacaran death masks[J].Palaios, 1999, 14(1):40-57. doi: 10.2307/3515360
[64] Butterfield N J.Exceptional fossil preservation and the Cambrian explosion[J].Integrative and Comparative Biology, 2003, 43(1):166-177. doi: 10.1093/icb/43.1.166
[65] Canfield D E.Sulfate reduction and oxic respiration in marine sediments:Implications for organic carbon preservation in euxinic environments[J].Deep Sea Research Part A:Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(1):121-138. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90022-8
-



 下载:
下载: