The Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in River Sediments and Suspended Matter in Small Tributaries of the Abandoned Wanshan Mercury Mines, Guizhou Province
-
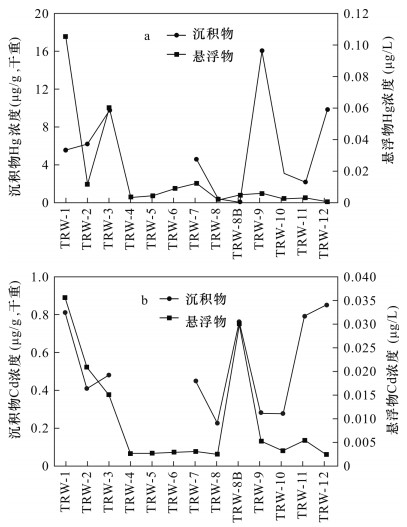
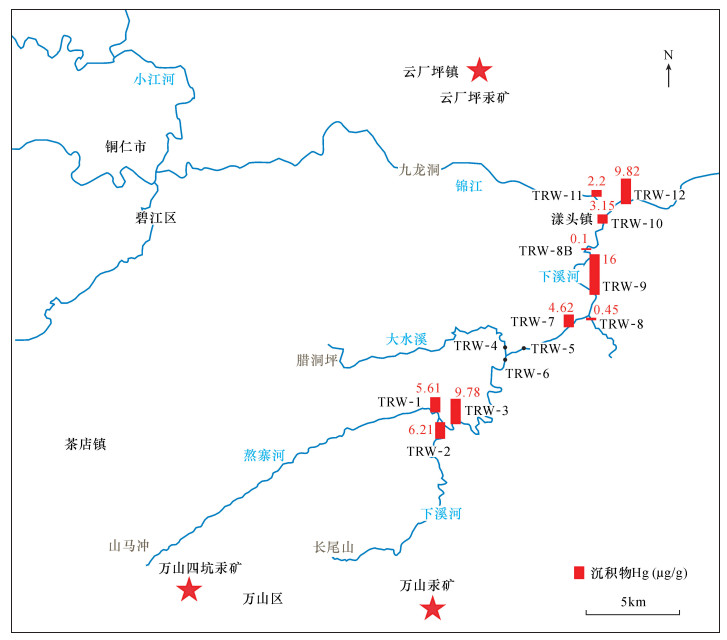
摘要: 废弃矿山虽已不再开采,但废弃矿坑、旧冶炼场地、埋填的尾矿坝受雨水淋滤仍可通过地表径流对下游地区造成污染。研究废弃矿山水系沉积物及悬浮物中重金属的沿河道分布及相互关系具有重要的现实意义。本文以贵州万山汞矿区下溪河小流域系统作为研究区域,对沉积物及悬浮物中重金属元素进行初步调查,为监测和污染耕地进行修复提供基础资料。通过湿法消解的前处理方法,利用电感耦合等离子体质谱和原子荧光光谱法测定了沉积物及悬浮物样品中Cr、Ni、Cu、Cd、Pb、As、Hg、Zn、Co含量,查明污染现状及空间分布特征,以获取矿区污染物向下游迁移、扩散的信息。结果表明:沉积物中Hg含量范围为0.10~16.0μg/g(干重),平均值为5.79μg/g,是《国家土壤环境质量标准》二级土壤Hg限值的几十倍;Cd在部分站点超标;Ni、Cu、Co含量平均值均不超标;Hg和Cd的变异系数较大,显示空间分布不均的特征。沉积物中Hg为高潜在生态风险级别。研究区沉积物及悬浮物中的Hg浓度与河段的水动力条件有关,最大值出现在河道宽阔、水流平缓的站点。由于万山汞矿早已停止开采和冶炼,本研究提出,自然条件下废弃矿区的风化淋滤引起颗粒物输送是造成河流下游Hg和Cd污染的原因。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDAlthough abandoned mines are no longer exploited, waste mines, old smelting sites and buried tailings can still pollute downstream areas through rainwater leaching and surface runoff. The study on the distribution and relationship of heavy metals in sediments and suspended particulate matter (SPM) along rivers in abandoned mines has important significance. OBJECTIVESTo preliminarily investigate heavy metals in river sediments and SPM in Wanshan Mercury Mines, and provide basic information for monitoring and remediation of contaminated cultivated land. METHODSThe contents of Cr, Ni, Cu, Cd, Pb, As, Hg, Zn and Co in sediments and SPM samples were determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) and Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) with wet digestion pretreatment. The pollution status and spatial distribution characteristics were identified in order to obtain information of pollutant migration and diffusion downstream. RESULTSThe total mercury content (Hg) in sediments ranged from 0.10 to 16.0μg/g (dry weight), averaging 5.79μg/g, which was ten times higher than the Hg limit of the Class Ⅱ soil environmental quality standard of China. The average contents of Ni, Cu and Co were not higher than the standard. The variation coefficients of Hg and Cd were large, indicating the heterogeneously spatial distribution of Hg and Cd. Mercury in sediments reached a high potential ecological risk level. CONCLUSIONSThe Hg in sediments and SPM in the study area are related to the hydrodynamic conditions, and the maximum values occurred at the sites with broad river channel and low flow rate. As the mining and smelting of Wanshan Mercury Mine has been stopped for a long time, the weathering and leaching of the abandoned mining area under natural conditions will cause Hg and Cd pollution in the lower reaches of the river. -
Key words:
- small tributary /
- sediment /
- suspended matter /
- heavy metals /
- Wanshan Mercury Mines
-

-
表 1 方法检出限、准确度和加标回收率
Table 1. Detection limits, accuracy and recoveries of the method
检测项目 样品浓度范围
(μg/g)检出限
(μg/g)室内相对偏差
(%)加标回收率
(%)Cr 0.1~200 0.02 ±25 85~110 Ni 0.05~200 0.3 ±30 80~110 Cu 0.05~1000 0.3 ±20 85~105 Cd 0.005~200 0.02 ±35 75~110 Pb 0.1~200 0.1 ±30 80~110 As 0.05~100 0.02 ±20 85~105 Hg 0.001~2 0.001 ±35 75~110 Zn 0.1~200 0.5 ±25 85~110 Co 0.05~200 0.3 ±10 85~110 表 2 研究区水系沉积物中重金属含量及标准限值
Table 2. Heavy metal concentrations in the research areas and their standard limits
沉积物样品 干重(μg/g) Cr Ni Cu Cd Pb As Hg Zn Co TRW-1-CJ 74.2 39.1 37.6 0.81 31.3 12.5 5.61 117 15.0 TRW-2-CJ 48.0 15.5 18.9 0.41 20.7 6.11 6.21 70.2 9.69 TRW-3-CJ 56.8 22.3 23.8 0.48 19.2 8.28 9.78 79.9 11.1 TRW-7-CJ 62.2 27.1 31.3 0.45 28.7 12.0 4.62 85.9 11.9 TRW-8-CJ 38.0 14.8 17.1 0.23 17.4 8.49 0.45 76.4 10.1 TRW-8B-CJ 50.1 21.4 26.7 0.76 20.7 7.19 0.10 85.4 9.08 TRW-9-CJ 49.5 19.2 22.9 0.28 19.4 9.34 16.0 71.5 10.0 TRW-10-CJ 57.1 19.3 21.8 0.28 16.0 11.2 3.15 65.7 9.17 TRW-11-CJ 85.2 37.1 33.1 0.79 26.5 17.1 2.20 104 13.6 TRW-12-CJ 89.0 37.2 32.5 0.85 37.4 12.0 9.82 113 15.3 平均值 61.0 25.3 26.6 0.53 23.7 10.4 5.79 86.9 11.5 标准偏差 16.8 9.3 6.8 0.24 6.9 3.2 4.9 18.3 2.4 变异系数 0.21 0.21 0.37 0.46 0.26 0.29 0.31 0.85 0.27 中值 57.0 21.9 25.3 0.47 20.7 10.3 5.1 82.7 10.6 最大值 89.0 39.1 37.6 0.85 37.4 17.1 16.0 117.0 15.3 最小值 38.0 14.8 17.1 0.23 16.0 6.1 0.10 65.7 9.1 地壳丰度 100 80 50 0.11 14 1.5 0.05 75 20 一级土壤* 90 90 35 0.2 35 15.0 0.15 100 - 二级土壤* 250 250 50 0.3 250 30.0 0.50 200 - 三级土壤* 400 - 400 1.0 500 60.0 1.50 500 - 注:“*”代表《国家土壤环境质量标准》限值(中性土壤)。
“-”代表没有限值。表 3 研究区河水中悬浮物中重金属含量
Table 3. Heavy metal concentrations in suspended materials from the rivers in the research areas
悬浮物样品野外编号 金属含量(μg/L) Cr Ni Cu Cd Pb As Hg Zn Co TRW-1-XF 6.04 3.05 4.60 0.036 2.31 0.491 0.105 14.76 0.982 TRW-2-XF 0.71 1.20 6.49 0.021 0.71 0.060 0.012 19.3 0.096 TRW-3-XF 2.29 1.60 3.95 0.015 0.95 0.236 0.060 7.5 0.400 TRW-4-XF 0.35 0.73 2.84 0.003 0.10 0.080 0.004 2.7 0.029 TRW-5-XF 0.36 0.29 1.04 0.003 0.35 0.042 0.005 5.2 0.035 TRW-6-XF 0.98 0.60 4.85 0.003 0.22 0.025 0.009 2.9 0.053 TRW-7-XF 0.71 0.45 2.07 0.003 0.35 0.047 0.012 2.1 0.087 TRW-8-XF 0.27 0.17 0.78 0.003 0.11 0.005 0.002 1.3 0.025 TRW-8B-XF 1.11 0.71 1.98 0.030 0.65 0.089 0.005 3.7 0.218 TRW-9-XF 0.47 0.38 2.36 0.005 0.33 0.029 0.006 2.8 0.062 TRW-10-XF 1.02 0.62 2.93 0.003 0.16 0.013 0.003 1.7 0.049 TRW-11-XF 1.69 0.45 2.51 0.005 0.27 0.051 0.003 2.7 0.095 TRW-12-XF 0.31 0.27 3.13 0.002 0.12 0.027 0.001 1.7 0.045 平均值 1.25 0.81 3.04 0.010 0.51 0.092 0.017 5.3 0.167 标准偏差 1.55 0.78 1.59 0.012 0.60 0.133 0.031 5.6 0.266 中值 0.71 0.60 2.84 0.003 0.33 0.047 0.005 2.8 0.062 最大值 6.04 3.05 6.49 0.036 2.31 0.491 0.105 19.3 0.982 最小值 0.27 0.17 0.78 0.002 0.10 0.005 0.001 1.3 0.025 表 4 研究区水系沉积物的重金属污染潜在生态危害系数分级
Table 4. Classification of potential ecological risk of heavy metal pollution in the sediments in the study area
水系沉积物样品编号 单个重金属潜在生态危害系数(Eri) RI值 潜在生态风险 Cr Ni Cu Cd Pb As Hg Zn TRW-1 0.6 0.8 3.8 81 0.6 4.2 748.0 0.6 840 高 TRW-2 0.4 0.3 1.9 41 0.4 2.0 828.0 0.4 874 高 TRW-3 0.5 0.4 2.4 48 0.4 2.8 1304.0 0.4 1359 高 TRW-7 0.5 0.5 3.1 45 0.6 4.0 616.0 0.4 670 高 TRW-8 0.3 0.3 1.7 23 0.3 2.8 60.0 0.4 89 低 TRW-8B 0.4 0.4 2.7 76 0.4 2.4 13.3 0.4 96 低 TRW-9 0.4 0.4 2.3 28 0.4 3.1 2133.3 0.4 2168 高 TRW-10 0.5 0.4 2.2 28 0.3 3.7 420.0 0.3 455 较高 TRW-11 0.7 0.7 3.3 79 0.5 5.7 293.3 0.5 384 较高 TRW-12 0.7 0.7 3.3 85 0.7 4.0 1309.3 0.6 1404 高 平均值 0.5 0.5 2.7 53.4 0.5 3.5 772.5 0.4 834 高 毒性响应系数(Tri) 2 5 5 30 5 10 40 1 - - -
[1] Dave J, Hugh P, Ceri J, et al.Abandoned Mines and the Water Environment[R].Science Project SC030136-41, UK Environment Agency, 2008.
[2] Ciszewski D, Aleksander-Kwaterczak U, Pociecha A, et al.Small effects of a large sediment contamination with heavy metals on aquatic organisms in the vicinity of an abandoned lead and zinc mine[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(12):9825-9842. doi: 10.1007/s10661-013-3295-z
[3] Lecce S A, Pavlowsky R T.Floodplain storage of sediment contaminated by mercury and copper from historic gold mining at Gold Hill, North Carolina, USA[J].Geomorphology, 2014, 206:122-132. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.10.004
[4] DeGraff J V.Addressing the Toxic Legacy of Abandoned Mines on Public Land in the Western United States[M]//Reviews in Engineering Geology (Volume XⅦ).DOI: 10.1130/2007.4017(01).
[5] Unger C, Lechner A M, Glenn V, et al.Mapping Impacts and Prioritising Rehabilitation of Abandoned Mines at a National Level in Australia[R].Brisbane: Life of Mine Conference, 2012.
[6] 贵州省铜仁市万山特区政府.贵州铜仁典型区域土壤污染综合治理项目实施方案[R].2014.
Government of Wanshan Special Zone, Tongren City, Guizhou Province.Implementation Plan of Comprehensive Soil Pollution Control Project in Typical Area of Tongren City, Guizhou Province[R].2014.
[7] 尹德良, 何天容, 安艳玲, 等.万山汞矿区居民食用大米的汞暴露风险评估[J].安全与环境学报, 2016, 16(3):330-337. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/aqyhjxb201603066
Yin D L, He T R, An Y L, et al.Mercury exposure and its health assessment for the residents in Wanshan mercury-mining areas via the rice consumption[J].Journal of Safety and Environment, 2016, 16(3):330-337. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/aqyhjxb201603066
[8] 胡国成, 张丽娟, 齐剑英, 等.贵州万山汞矿周边土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J].生态环境学报, 2015, 24(5):879-885. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201505024
Hu G C, Zhang L J, Qi J Y, et al.Contaminant characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Wanshan mercury mine area, Guizhou Province[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(5):879-885. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201505024
[9] 湛天丽, 黄阳, 滕应, 等.贵州万山汞矿区某农田土壤重金属[J].土壤通报, 2017, 48(2):474-480. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201702032
Zhan T L, Huang Y, Teng Y, et al.Pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in farmland soils in Wanshan mining areas, Guizhou Province[J].Chineae Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(2):474-480. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201702032
[10] 吴兰艳, 姚元勇, 唐帮成, 等.万山汞矿区周边土壤重金属污染调查及其风险评价[J].铜仁学院学报, 2017, 19(6):85-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9639.2017.06.021
Wu L Y, Yao Y Y, Tang B C, et al.Pollution investigation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from the sourounding areas of Wanshan mining areas[J].Journal of Tongren University, 2017, 19(6):85-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9639.2017.06.021
[11] Zhang H, Feng X, Larssen T.Fractionation, distribution and transport of mercury in rivers and tributaries around Wanshan Hg mining district, Guizhou Province, Southwestern China:Part 1-Total mercury[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2010, 25:633-641. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.01.006
[12] 赵西强, 庞绪贵, 王增辉, 等.利用原子荧光光谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法研究济南市大气干湿沉降重金属含量及年沉降通量特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(2):245-251. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.02.016
Zhao X Q, Pang X G, Wang Z H, et al.Study on the characteristics of heavy metal contents and annual fluxes of atmospheric dry and wet deposition in Jinan City using AFS and ICP-MS[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(2):245-251. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.02.016
[13] 李自强, 李小英, 钟琦, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定土壤重金属普查样品中铬铜镉铅的关键环节研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1):37-41. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.007
Li Z Q, Li X Y, Zhong Q, et al.Determination of Cr, Cu, Cd and Pb in soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry for an investigation of heavy metal pollution[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(1):37-41. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.007
[14] 田衎, 杨珺, 孙自杰, 等.矿区污染场地土壤重金属元素分析标准样品的研制[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1):82-88. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.012
Tian K, Yang J, Sun Z J, et al.Preparation of soil certified reference materials for heavy metals in contaminated sites[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1):82-88. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.012
[15] 黎彤.化学元素的地球丰度[J].地球化学, 1976(3):167-174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1976.03.004
Li T.Chemical element abundances in the Earth and its major shells[J].Geochimica, 1976(3):167-174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1976.03.004
[16] 陈若思, 刘定富, 武晓阳.红枫湖沉积物中汞污染评价[J].贵州化工, 2012, 37(4):40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9411.2012.04.020
Chen R S, Liu D F, Wu X Y.An assessment of mercury pollution in sediments of Hongfeng Lake[J].Guizhou Chemical Industry, 2012, 37(4):40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9411.2012.04.020
[17] Wu B B, Wang G Q, Wu J, et al.Sources of heavy metals in surface sediments and an ecological risk assessment from two adjacent plateau reservoirs[J].PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(7).DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0102101.
[18] Chen C X, Zheng B H, Jiang X, et al.Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of mercury in sediments of Lake Taihu, China[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 25(2):316-325. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60033-3
[19] Garcia-Ordiales E, Loredo J, Covelli S, et al.Trace metal pollution in freshwater sediments of the world's largest mercury mining district:Sources, spatial distribution and environmental implications[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2017, 17(7):1893-1904. doi: 10.1007/s11368-016-1503-5
[20] 仇广乐, 冯新斌, 王少锋.贵州省万山汞矿区地表水中不同形态汞的空间分布特点[J].地球与环境, 2004, 32(3-4):77-82. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx200403015
Qiu G L, Feng X B, Wang S F.Mercury speciations and their distribution in surface water from Wanshanmercury mining district, Guizhou Province[J].Earth and Environment, 2004, 32(3-4):77-82. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx200403015
[21] USEPA.National Recommended Water Quality Criteria-Correction[R].US Environmental Protection Agency.1999822-Z-99-001.1999.
[22] Håkanson L.An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control-Sedimentological approach[J].Water Research, 1980, 14:975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[23] 赵志鹏.重金属镉的土壤空间分布机制及迁移转化过程研究[D].贵州: 贵州大学, 2015: 1-51.
Zhao Z P.Cadmium Distribution and Transformation in Soil Profile and Effection Factor[D].Guizhou: Guizhou University, 2015: 1-51.
[24] 何天容, 冯新斌, 郭艳娜, 等.红枫湖沉积物中汞的环境地球化学循环[J].环境科学, 2008, 29(7):1768-1774. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.07.002
He T R, Feng X B, Guo Y N, et al.Geochemical cycling of mercury in the sediment of Hongfeng Reservior[J].Environmental Science, 2008, 29(7):1768-1774. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.07.002
[25] Rügner H, Schwientek M, Milačič R, et al.Particle bound pollutants in rivers:Results from suspended sediment sampling in Globaqua River Basins[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 647:645-652. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.027
[26] 王珊珊, 潘存鸿, 李宏, 等.杭州湾泥沙中重金属元素的分布及影响因[J].中国环境科学, 2017, 37(12):4701-4709. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.12.036
Wang S S, Pan C H, Li H, et al.Distribution and influence factor of Cu, Pb, Hg in surficial sediments and suspended sediments of Hangzhou Bay[J].China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(12):4701-4709. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.12.036
[27] Pont D, Day J W, Ibáñez C.The impact of two large floods (1993-1994) on sediment deposition in the Rhône delta:Implications for sustainable management[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609:251-262. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.155
[28] Rimondi V, Costagliola P, Gray J E, et al.Mass loads of dissolved and particulate mercury and other trace elements in the Mt.Amiata mining district, Southern Tuscany (Italy)[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(8):5575-5585. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2476-1
[29] Balogh S J, Meyer M L, Johnson D K.Mercury and suspended sediment loadings in the Lower Minnesota River[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31(1):198-202. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1021-es960327t/
[30] Zhang J B, Zhou F X, Chen C L, et al.Spatial distri-bution and correlation characteristics of heavy metals in the seawater, suspended particulate matter and sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, China[J].PLoS ONE, 2018, 13(8).DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0201414.
[31] Zhu W, Song Y, Adediran G A, et al.Mercury transformations in resuspended contaminated sediment controlled by redox conditions, chemical speciation and sources of organic matter[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 220:158-179. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.09.045
[32] Lučić M, Jurina I, Ščančar J, et al.Sedimentological and geochemical characterization of river suspended particulate matter (SPM) sampled by time-integrated mass flux sampler (TIMS) in the Sava River (Croatia)[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2019, 19(2):989-1004. doi: 10.1007/s11368-018-2104-2
[33] Annan S T, Sanful P O, Lartey-Young G, et al.Spatial and temporal patterns of variation in environmental quality of water and sediments of streams in mined and unmined areas with emphasis on mercury (Hg) and arsenic (As)[J].Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 2018, 6(9):125-140. doi: 10.4236/gep.2018.69010
-



 下载:
下载: