Practicality of Hand-held XRF Analyzer in Rapid Exploration of Porphyry Copper Deposit
-
摘要:
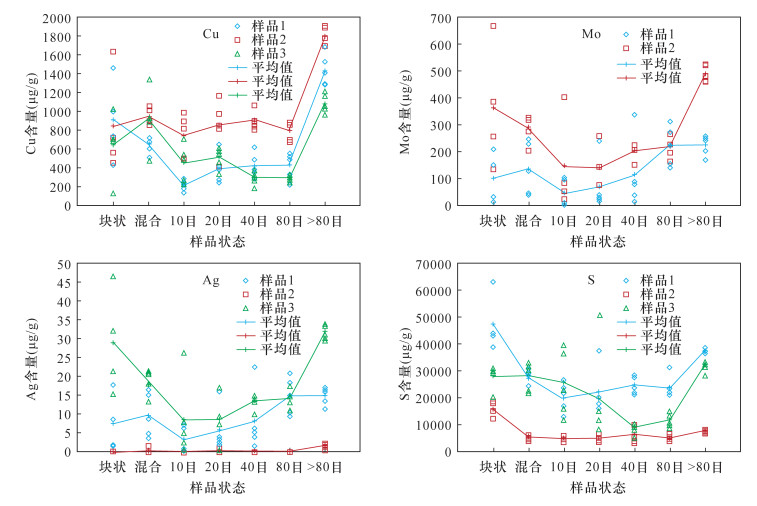
现场X射线荧光光谱(XRF)测量因样品的不平度效应、不均匀效应和湿度效应等面临的技术难题,使得手持式XRF现场原位分析结果与实验室分析结果存在一定偏差。本文现场手持式X射线荧光光谱分析仪的测试时间、样品含量、测试距离、样品干湿度和样品粒度等测试条件对测试结果的影响进行了定量研究。结果表明:在最佳测试时间90s条件下,得到Cu、Mo、Pb、Zn元素测定限分别为57μg/g、14μg/g、24μg/g、38μg/g并给出测定限计算公式;现场分析测试距离应小于5mm并保持样品表面干燥,块状样品测试方法最简单但测试结果变化最大,样品粉碎至粒径80目以上测试结果精准度最好,但制样过程较复杂,样品粉碎后的混合状态是现场测试的最佳策略。对西藏驱龙斑岩铜矿岩心扫描的实际应用表明,手持式XRF分析仪适合于现场原位分析,可满足野外斑岩铜矿圈定矿体等快速勘查评价要求,提高了工作效率并降低勘查成本。
Abstract:BACKGROUND There is a certain deviation between the on-site analysis results of hand-held XRF and the laboratory analysis results due to the unique technical difficulties in field X-ray fluorescence measurement such as roughness effect, uneven effect and humidity effect of samples.
OBJECTIVES To seek economic, rapid and practical test conditions of hand-held XRF for rapid exploration of porphyry copper ore in practical work.
METHODS Influence of test conditions, such as analytical time, sample content, test distance, sample dry humidity and sample particle size on the analytical results of Niton XL3t GOLDD+ hand-held XRF was quantitatively studied.
RESULTS The results showed that, under the best test time of 90s, the determination limits of Cu, Mo, Pb, and Zn were 57μg/g, 14μg/g, 24μg/g, and 38μg/g, respectively, and the calculation formula for the determination limit was given. The field analysis test distance should be less than 5mm and the sample surface should be kept dry. The test method for bulk sample was the simplest but the test results varied the most. When sample was crushed to a particle size of 80 mesh or above, the stability and accuracy of the results were best. Considering that it took a long time to crush sample into 80 mesh, the mixed state of the sample after crushing was better strategy for field testing.
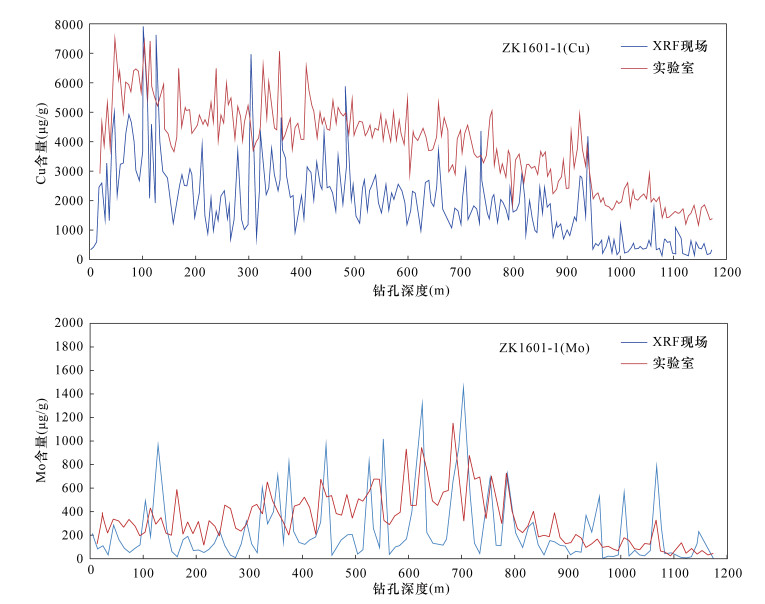
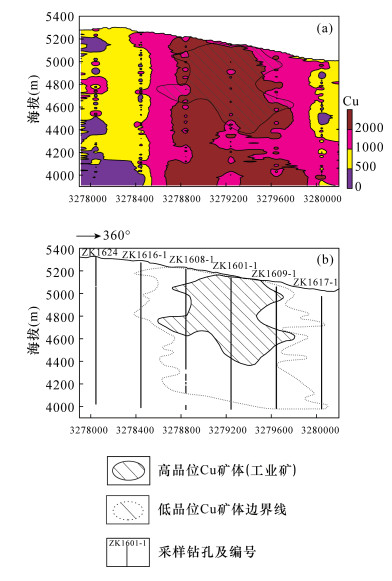
CONCLUSIONS The practical application of core scanning in Qulong porphyry copper deposit in Xizang shows that the handheld XRF analyzer is suitable for in-situ analysis and can meet the requirements of rapid exploration and evaluation such as delineation of copper ore bodies in field, which can greatly improve work efficiency and reduce exploration cost.
-

-
表 1 手持式XRF分析仪检出限(LOD)及测定限参考值
Table 1. Detection limits (LOD) and determination limit reference values of hand-held XRF analyzer
待测元素 检出限(μg/g) 测定限(μg/g) 待测元素 检出限(μg/g) 测定限(μg/g) Ba 61 202 Zn 11 38 Sb 21 69 Cu 17 57 Cd 26 87 Ni 35 118 Pd 14 46 Co 28 94 Sb 9 29 Fe 49 165 Ag A/S A/S Mn 85 283 Mo 4 14 Cr 35 115 Nb 4 14 V 17 58 Zr 4 14 Ti 17 58 Sr 4 14 Ca 87 289 Rb 4 14 K 69 231 Bi 4 14 Cl 104 346 As 4 14 S 121 404 Se 4 14 P 433 1443 Au 23 75 Si N/A N/A Pb 7 24 Al 866 2887 W 57 189 Mg 6062 20207 表 2 完全润湿与干燥状态下样品测试值比值
Table 2. Comparison of sample test values under complete wetting and drying conditions
样品编号 元素湿干比值 Cu Mo Pb Zn Rb Sr Zr Th Ba Hg Nb Co Ti Cd Sc Mn Cr ZK1608-40.2 0.76 0.82 0.94 1.04 0.91 1.01 0.83 0.87 1.00 0.90 0.78 0.95 0.71 1.02 1.02 0.86 0.95 ZK1501-170 0.93 0.94 0.07 0.86 1.09 0.96 0.99 1.06 1.04 1.07 0.94 1.10 0.82 1.05 1.05 - - 样品编号 元素湿干比值 Au As Ag Pd V Bi Fe Ca K S Al P Si Cl Mg Bal ZK1608-40.2 0.31 - - - 0.81 0.88 0.77 0.74 0.65 0.39 0.21 0.18 0.36 0.48 - 1.61 ZK1501-170 - - - - 0.75 - 0.97 0.45 0.96 0.24 0.27 - 0.53 0.56 - 1.66 注:“-”表示该元素在润湿状态下没有被检测出,即低于仪器此时的检出限。 -
[1] 王毅民, 王晓红, 高玉淑. 地球科学中的现代分析技术[J]. 地球科学进展, 2003, 18(3): 476-482. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.03.023
Wang Y M, Wang X H, Gao Y S. Modern analytical technologies in Earth sciences[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 2003, 18(3): 476-482. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.03.023
[2] Bosco G L. Development and application of portable, hand-held X-ray fluorescence spectrometers[J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 45: 121-134. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2013.01.006
[3] 詹勇, 马林霄, 曾瑞垠. 便携式X射线荧光仪在刚果(金)Kapolowe铜钴矿勘查中的应用[J]. 矿物学报, 2015(A1): 1118-1119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2015S1808.htm
Zhan Y, Ma L X, Zeng R Y. Application of portable X-ray fluorescence instrument in exploration of Kapolowe copper-cobalt deposit in Congo(King)[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015(A1): 1118-1119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2015S1808.htm
[4] 杨帆, 郝志红, 刘华忠, 等. 便携式能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪在新疆东天山浅钻化探异常查证中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(6): 665-671. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.06.010
Yang F, Hao Z H, Liu H Z, et al. Application of Minipal 4 portable energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer in the verification of geochemical anomaly delineated by shallow hole drill core in eastern Tianshan[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(6): 665-671. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.06.010
[5] 时培哲, 刘高杰, 张文, 等. 手持式XRF快速分析仪在海外地质勘查中的应用[J]. 黄金, 2018, 39(11): 79-83. doi: 10.11792/hj20181119
Shi P Z, Liu G J, Zhang W, et al. Application of handheld XRF rapid analyzer in overseas geological exploration[J]. Gold, 2018, 39(11): 79-83. doi: 10.11792/hj20181119
[6] 李孜腾, 肖福权. 便携式XRF在有色金属矿山地质勘查中的应用范围与方法——以沙溪斑岩型铜矿为例[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019(13): 120-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.13.068
Li Z T, Xiao F Q. Application range and method of portable XRF in geological exploration of non-ferrous metal deposits-To Shaxi porphyry copper deposit as an example[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019(13): 120-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.13.068
[7] Zhang W, Lentz D R, Charnley B E. Petrogeochemical assessment of rock units and identification of alteration/mineralization indicators using portable X-ray fluorescence measurements: Applications to the Fire Tower Zone(W-Mo-Bi) and the North Zone (Sn-Zn-In), Mount Pleasant deposit, New Brunswick, Canada[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 177: 61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.02.005
[8] Liao S L, Tao C H, Li H M, et al. Use of portable X-ray fluorescence in the analysis of surficial sediments in the exploration of hydrothermal vents on the southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(7): 66-76. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1085-0
[9] Ribeiro B T, Silva S H G, Silva E A, et al. Portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF) applications in tropical soil science[J]. Ciencia E Agrotecnologia, 2017, 41(3): 245-254. doi: 10.1590/1413-70542017413000117
[10] 王豹, 余建新, 黄标, 等. 便携式X射线荧光光谱仪快速监测重金属土壤环境质量[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(6): 1735-1740. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)06-1735-06
Wang B, Yu J X, Huang B, et al. Fast monitoring soil environmental qualities of heavy metal by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(6): 1735-1740. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)06-1735-06
[11] 杨桂兰, 商照聪, 李良君, 等. 便携式X射线荧光光谱法在土壤重金属快速检测中的应用[J]. 应用化工, 2016, 45(8): 1586-1591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHG201608049.htm
Yang G L, Shang Z C, Li L J, et al. Application of portable-XRF spectrometrt for rapid determination of common heavy metals in soil[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(8): 1586-1591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHG201608049.htm
[12] 邝荣禧, 胡文友, 何跃, 等. 便携式X射线荧光光谱法(PXRF)在矿区农田土壤重金属快速检测中的应用研究[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(3): 589-595. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201503025.htm
Kuang R X, Hu W Y, He Y, et al. Application of portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF) for rapid analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soils around mining area[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(3): 589-595. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201503025.htm
[13] 周树斌. 便携式X荧光仪在重金属水污染检测中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
Zhou S B.Application of portable X-fluorescemeter in heavy metal water pollution detection[D].Beijing: China University of Geolsciences (Beijing), 2017.
[14] 罗斌, 葛良全, 王卓, 等. 手持式X荧光分析仪在空气颗粒物分析中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2013, 13(6): 112-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201306026.htm
Luo B, Ge L Q, Wang Z, et al. Application of handheld X-ray fluorescence analyzer in the analysis of air particulate matter[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2013, 13(6): 112-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201306026.htm
[15] 李秋实, 葛良全, 王卓, 等. 手持式XRF分析仪快速检测大气颗粒物中Cu、Zn、Pb含量[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2014, 34(5): 667-670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2014.05.028
Li Q S, Ge L Q, Wang Z, et al. Determination of Cu, Zn, Pb in atmospheric particulate matter by the handheld X-ray fluorescence analyzer[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2014, 34(5): 667-670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2014.05.028
[16] Maria L, Matz N, Britta E. Metal contamination at recreational boatyards linked to the use of antifouling paints-Investigation of soil and sediment with a field portable XRF[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23: 10146-10157. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6241-0
[17] 聂黎行, 张烨, 朱俐, 等. 便携式X射线荧光光谱快速无损分析牛黄清心丸(局方)中汞、砷含量及均匀度[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(10): 3225-3228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201710052.htm
Nie L X, Zhang Y, Zhu L, et al. Fast and nondestructive analysis of content of mercury and arsenic and homogeneity of Niuhuang Qingxin pills by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(10): 3225-3228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201710052.htm
[18] Karydasa A G, Kotzamani D, Bernard R. A compositional study of a museum jewellery collection (7th-1st BC) by means of a portable XRF spectrometer[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, 2004, 226: 15-28. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2004.02.034
[19] 先怡衡, 李延祥, 杨岐黄. 便携式X荧光光谱结合主成分分析鉴别不同产地的绿松石[J]. 考古与文物, 2016(3): 112-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KGYW201603015.htm
Xian Y H, Li Y X, Yang Q H. Portable X-ray fluorescence spectra combined with master component analysis to identify turquoises from different origins[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 2016(3): 112-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KGYW201603015.htm
[20] Adlington L W, Freestone I C. Using handheld pXRF to study medieval stained glass: A methodology using trace elements[J]. MRS Advances, 2017, 2: 1785-1800. doi: 10.1557/adv.2017.233
[21] 吴遵红, 张立红, 吕程, 等. 便携式X射线衍射分析仪在压力管道腐蚀检测中的应用[J]. 特种设备安全技术, 2017(3): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZSB201703027.htm
Wu Z H, Zhang L H, Lv C, et al. Application of X-ray diffraction analyzer in pressure pipe corrosion detection[J]. Safety Technology of Special Equipment, 2017(3): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZSB201703027.htm
[22] 庄岩, 王晓琳, 郭威, 等. 便携式X射线荧光光谱分析仪快速检测弹着痕迹[J]. 刑事技术, 2019, 44(3): 246-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XSJS201903013.htm
Zhuang Y, Wang X L, Guo W, et al. Using portable X-ray fluorescent spectrometry to rapidly test the impact marks at gunshot spot[J]. Forensic Science and Technology, 2019, 44(3): 246-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XSJS201903013.htm
[23] Bull A, Brown M T, Turner A. Novel use of field-portable-XRF for the direct analysis of trace elements in marine macroalgae[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 220: 228-233. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.049
[24] 杜兴胜, 熊超, 窦小平, 等. 现场X射线荧光光谱分析在钻孔岩芯测量中的应用[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2014, 34(6): 775-779. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2014.06.024
Du X S, Xiong C, Dou X P, et al. Application of on-site X-ray fluorescence spectral analysis in drilling core measurement[J]. Nuclear Electronics and Detection Technology, 2014, 34(6): 775-779. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2014.06.024
[25] Bruno L. A review of pXRF(field portable X-ray fluorescence) applications for applied geochemistry[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 188: 350-363. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.02.006
[26] 唐晓勇, 倪晓芳, 商照聪. 土壤中铁元素对铬元素p-XRF测定准确度的影响与校正[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 158-165. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911200161
Tang X Y, Ni X F, Shang Z C. Effect and correction of iron in soil on accuracy of chromium determination by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 158-165. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911200161
[27] 张学华, 李强, 黄雪华, 等. 手持式X射线荧光光谱仪在富钴结壳资源勘查中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(4): 512-516. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/85c3a34d-4961-4abe-8799-360918009510
Zhang X H, Li Q, Huang X H, et al. Application of handheld X-ray fluorescence spectrometer in the exploration of cobalt-rich crust resources[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(4): 512-516. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/85c3a34d-4961-4abe-8799-360918009510
[28] McComb J Q, Rogers C, Han F X, et al. Rapid screening of heavy metals and trace elements in environmental samples using portable X-ray fluorescence spectro-meter: A comparative study[J]. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 2014, 225(12): 1-10. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4386753/
[29] 周四春, 赵友清, 张玉环. 克服矿化不均匀效应的X荧光取样最佳测网[J]. 核技术, 2000, 23(9): 632-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU200009007.htm
Zhou S C, Zhao Y Q, Zhang Y H. Best mesh for X-ray fluorescence sampling to overcome mineralization uneven effect[J]. Nuclear Technology, 2000, 23(9): 632-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU200009007.htm
[30] 张广玉, 赵世煌, 邓晃, 等. 手持式X射线荧光光谱多点测试技术在地质岩心和岩石标本预研究中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5): 501-509. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610120156
Zhang G Y, Zhao S H, Deng H, et al. Application of p-XRF multi-point analysis technique in pre-research of geological core and rock specimens[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5): 501-509. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610120156
[31] Ge L Q, Lai W C, Lin Y C. Influence of and correction for moisture in rocks, soils and sediments on in situ XRF analysis[J]. X-ray Spectrometry, 2005, 34(1): 28-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/xrs.782
[32] 张志鹏, 孙东, 曹楠, 等. 便携式XRF在快速评价矿区土壤修复效果中的应用探索[J]. 四川环境, 2019, 38(4): 156-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ201904024.htm
Zhang Z P, Sun D, Cao N, et al. Application of portable XRF in rapid evaluation the effect of soil rehabilitation in mining areas[J]. Sichuan Environment, 2019, 38(4): 156-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ201904024.htm
[33] 赵霞, 郑景明, 司莉青, 等. 水分对于便携式X射线荧光光谱仪测定土壤中元素含量的影响[J]. 冶金分析, 2018, 38(7): 24-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201807003.htm
Zhao X, Zheng J M, Si L Q, et al. Influence of water content on the determination of elements in soil by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2018, 38(7): 24-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201807003.htm
[34] 周曙光, 廖世斌, 周可法, 等. 便携式X射线荧光光谱仪在岩石样品分析中的应用研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(1): 56-63. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201704110051
Zhou S G, Liao S B, Zhou K F, et al. Application of portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer in the analysis of rock samples[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(1): 56-63. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201704110051
[35] 夏传波, 姜云, 郑建业, 等. X射线荧光光谱法测定地质样品中氯的含量[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2017, 53(7): 775-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201707006.htm
Xia C B, Jiang Y, Zheng J Y, et al. XRFS determination of chlorine in geological samples[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis(Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2017, 53(7): 775-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201707006.htm
[36] 杜海燕, 赖万昌, 石希瑜, 等. 便携式X荧光仪检出限影响因素的研究[J]. 核技术, 2018, 41(1): 17-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU201801003.htm
Du H Y, Lai W C, Shi X Y, et al. Influence factor of the detection limit of portable X-ray fluorescence instrument[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2018, 41(1): 17-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU201801003.htm
[37] 陈宇亮, 郑洪波. XRF岩心扫描在第四纪沉积物研究中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(4): 51-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201404009.htm
Chen Y L, Zheng H B. The application of XRF core scanning to quatermaty sediments[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2014, 30(4): 51-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201404009.htm
-




 下载:
下载: