Distribution Characteristics and Sources Identification of Selenium-rich Soils in the Ecological Conservation Area of the Daqinghe River Watershed, Beijing
-
摘要: 北京是典型的硒缺乏地理分布区,但近些年研究成果表明局部地区土壤达到富硒水平,掌握该区富硒分布特征对于开展北京地区的富硒环境研究和开发利用富硒土地资源具有重要意义。本文以北京大清河流域生态涵养区1615km2地球化学调查数据为基础,采用原子荧光光谱(AFS)等方法测定了研究区1297件表层土壤、25组玉米及对应根系土壤和15件岩石中Se等地球化学指标;利用相关分析、多元统计分析方法,结合GIS技术,研究土壤和农作物中硒含量特征、富硒成因来源以及土壤硒与碳铁磷等其他元素的关系,评价富硒土地的安全性。结果表明:研究区土壤硒含量区间为0.055~0.465mg/kg,背景值为0.257mg/kg,呈现富硒特征,厘定出360.4km2富硒土地资源。当地种植的玉米硒含量变化范围为0.028~0.70mg/kg,几何均值为0.20mg/kg,80%的玉米样本为富硒农产品,且土壤富硒与作物富硒空间分布一致,指示土壤硒是作物体内硒的重要供给来源。研究认为,地质背景和成土母质是研究区富硒土地资源分布的主控因素,河流相沉积的暗色岩系是重要的土壤硒来源。富硒土地整体环境质量清洁安全,仅3.23km2(面积占比0.2%)土壤重金属(镉汞铅)含量超风险管控值,在土地开发过程中需重点关注。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDBeijing is a typical geographical distribution area of selenium deficiency. However, some research results in recent years indicate that the soils in some areas reaches the level of selenium enrichment. It is important to study the characteristics of selenium distribution in these areas for the research of a selenium-rich environment in Beijing and the development of selenium-rich land resources. OBJECTIVESTo discuss the characteristics of selenium content in soil and crops, the source of selenium and the relationship between selenium in soil and other elements such as carbon, iron and phosphorus, and to evaluate the safety of selenium-rich land. METHODSSamples of 1297 topsoil, 25 sets of corn and corresponding root soil and 15 rock samples were collected from an eco-conserving division of the Daqinghe River watershed. The content of selenium in these samples was determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Methods of correlation analysis and multivariate statistical analysis and GIS technology were used to study the characteristics of selenium content in soil and crops, the source of selenium enrichment, and the relationship between soil selenium and other elements such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur, and the safety of selenium-rich land was evaluated. RESULTSThe results showed that the soil selenium content ranged from 0.055 to 0.465mg/kg and that the background value was 0.257mg/kg, which show selenium-rich characteristics. 360.4km2 selenium-rich land resources was identified. The selenium content of corn ranged from 0.028 to 0.70mg/kg, and the geometric mean was 0.20mg/kg. 80% of the corn samples were selenium-rich products. The selenium-rich soil and the selenium-rich crops had the same spatial distribution, which indicated that the soil was an important source of selenium in crops. CONCLUSIONSGeological background and soil parent material are the key control factors affecting the distribution of selenium-rich land resources. Dark rock series of fluvial deposition are a crucial source of selenium in soil. The overall environmental quality of selenium-rich land is clean and safe, and only 0.2% of the area (3.23km2) contains soil heavy metal (Cd, Hg, Pb) content, which exceeds the level of risk management control. Due to these findings, attention needs to be paid during selenium-rich land development. -
硒是生命必需元素,在植物、动物和人类的生长发育、能量代谢、抗逆能力等方面发挥了重要的生物化学作用[1]。然而,世界土壤硒分布极不均匀,其含量范围在0.01~2.0mg/kg之间,平均含量为0.4mg/kg[2],全球硒缺乏地理分布比硒富足更为广泛,我国72%的市县属于低硒或缺硒区,存在着一条从东北地区的暗棕壤、黑土向西南方向经过黄土高原的褐土、黑垆土到川滇地区的棕壤性紫色土、红褐壤,再向西南延伸到西藏高原东部和南部的亚高山草甸土和黑毡土的低硒带[3]。低硒环境极易对人体造成不良影响,危害生命健康。为此,围绕富硒资源的开发利用等研究工作一直是关注的焦点。 前人在富硒土壤分布特征、生物有效性和溯源研究等方面取得了一定的研究进展。研究表明世界多个国家存在富硒土壤[4],包括美国、爱尔兰、英格兰等地,土壤硒的平均含量在3mg/kg以上。日本的耕作土壤中硒含量平均值为0.51mg/kg[5],也达到富硒水平。中国的富硒土壤呈现明显的地带性,形成了东南湿润和西北干旱的富硒环境[6],江西、山东、福建、广东、广西、海口等均有富硒、足硒土壤。硒的分布明显受到多种因素的控制,土壤有机质、阳离子交换量、全磷、黏粒等土壤理化性质对硒的有效性存在显著影响[7],土壤总硒与有机碳、总氮[8]、铁锰氧化物呈显著的正相关关系,与pH呈显著负相关关系[9]。但土壤硒主要来源于成土母质,如山东淄博土壤硒含量与该地区丰富的煤炭资源密切相关[8];广东普宁以侏罗系页岩母质发育的土壤全硒含量最高[10]。这些结果表明,岩石的类型和成土母质在很大程度上决定了土壤硒的含量水平。土壤硒被植物吸收利用程度是生物体补硒的主要来源,也是硒资源转化的意义所在。不同农作物硒含量差异大,海口市富硒农田中花生、芝麻作物属于高硒作物,稻谷含硒量较高[11];广西浔郁以种子为食用部分的作物其天然富硒率最高,其中玉米富硒率为100%[12]。以上地区富硒土壤的调查研究为富硒土地资源开发利用提供了基础依据。 根据硒的化学地理特征,我国分布的东北—西南走向,在纬度上跨度较大的自然环境低硒带,土壤、粮食和人体毛发硒含量偏低,其分布与克山病和大骨节病分布相吻合,北京是大骨节地方性疾病的发病区之一,也属于自然环境低硒地区[13]。近些年,围绕富硒资源分布特征,在北京也开展了少量研究工作。郭莉等[14]发现北京平原区分布有高硒土壤,沿平原区西部山前断续出现,市区内零星分布,表层土壤硒含量平均值为0.20mg/kg;黄淇等[15]指出北京房山平原区存在富硒土壤,硒含量在0.3~0.6mg/kg范围的面积达到39.11km2。本文选取北京大清河流域生态涵养区作为研究对象,分别采集表层土壤、玉米、岩石样本,对其中的硒含量进行分析,研究土壤和农作物富硒的分布特征、硒与碳氮磷硫等其他元素的关系、土壤硒来源分析以及富硒土壤的安全性,以期为北京地区的富硒环境研究工作提供基础数据,为发展富硒绿色产业提供参考。 1. 研究区地质概况
大清河流域生态涵养区位于北京西南部,涵盖房山区整个山区,并连接了门头沟区和丰台区的部分山区范围,面积为1615km2,是首都重要的生态屏障,该区自然资源丰富,历史上曾大力发展煤炭和石材等资源型产业,但矿山开发活动带来的地质环境问题不容忽视,生态环境更加脆弱敏感。为了确保“生态为基”,大清河流域生态涵养区进行了转型发展的“蜕变”,关停“黑灰”矿产,大力发展生态绿色产业。 研究区属太行山脉,温带大陆性季风气候,冬季寒冷干燥,夏季炎热多雨,年平均气温10.8℃,多年平均降雨量为644.1mm。地貌类型以中低山为主,由西北向东南海拔逐渐趋于平缓,分布有中山、低山、丘陵、岗台地。区内主要河流有拒马河、大石河、永定河和小清河。土壤类型由北至南分布有山地草甸土、棕壤、褐土等类型,土壤pH以中性-偏碱性为主。 研究区内地层出露较全,地层由老到新依次为:太古界、长城系、蓟县系、青白口系、奥陶系、寒武系、石炭—二叠系、三叠系、侏罗系、白垩系、第三系、第四系,尤以中元古界最为发育。岩浆岩以侵入岩分布范围较广泛,大多数为中、酸性岩石,火山岩分布较少。其中房山岩体最为典型且出露面积最大,另外还有“灯泡岩体”、“龙眼花岗岩”等小型侵入体。2. 实验部分
2.1 样品采集
土壤采样点位按照网格化方式布设,点位密度为1点/km2,样点尽量代表 1km2范围内主要成土母质和土壤类型。采样层位0~20cm,每件样品由周边50m范围内3~5个同一取样深度的子样等量混合均匀而成。共采集土壤样品1297件。采集的样品经过自然风干、过筛、拌匀、称重、装袋后送分析,样品加工和运输过程严禁污染。 在农业种植区采集玉米的可食用部分,取多点等量混匀组成样品,同时配套采集作物根系土,采集层位0~20cm。样品采集后当天送往实验室进行处理。共采集25组玉米及对应根系土壤样品。 针对研究区内不同地层具代表性的岩石类型,用地质锤采集未风化、未蚀变的新鲜断面岩石样品。每件样品在采样点周围10~20m范围内,采集3处以上同一岩性的新鲜岩石碎块(直径应小于30mm)组合成一件样品,详细描述各采样点岩石剖面性状与环境特征。2.2 实验方法
样品的分析测试工作由北京一零一生态地质检测有限公司完成,采用原子荧光光谱法测定Se含量[16]。土壤样品还采用X射线荧光光谱、发射光谱、氢化物发生原子荧光光谱、催化光度法、泡沫塑料吸附-石墨炉原子吸收光谱、酸度计、电感耦合等离子体质谱、离子选择电极、管式炉燃烧红外吸收法、氧化燃烧-气相色谱、电感耦合等离子体发射光谱、微波消解等方法分析了有机碳(Corg)、C、N、S、pH、重金属等53项指标(其中有机质=有机碳×1.724)。数据处理分析采用Excel2010和GeoIPAS V3.2软件,图件采用MapGIS67、CoreDraw X3和Excel2010软件绘制。2.3 质量控制
样品采集和分析测试严格执行《多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1 : 250000)》(DD2005-01)和《生态地球化学评价样品分析技术》(DD2005-03)要求。野外样点采集准确率100%。测试工作用选定分析方法对多个国家一级标准物质进行12次分析检验,分别计算各被测项目每个样品平均值与认定值之间的对数差(ΔlgC)和相对标准偏差(RSD),方法的准确度和精密度均符合《规范》的要求。测试的准确度控制是在每500件样品中插入12个国家一级标准物质(GBW系列)作为密码样,共对22件一级标准物质进行分析,标准物质合格率和各元素合格率均为100%。精密度控制共插入76件监控样品,所有元素的对数偏差(ΔlgC)和对数标准偏差(λ)均在允许限内,54项元素指标的合格率为100%,报出率在99.95%以上。3. 结果与讨论
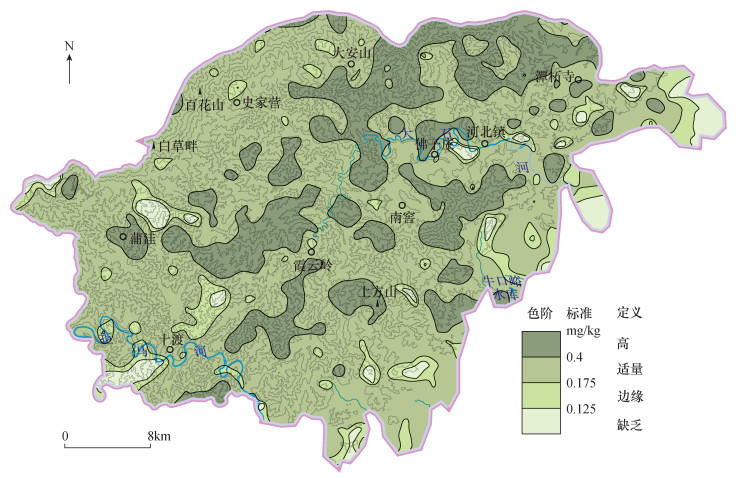
3.1 土壤硒的含量和分布特征
研究区1297个表层土壤数据,经逐步剔除平均值加减两倍标准离差的样点数据后,土壤Se含量符合对数正态分布,含量区间为0.055~0.465mg/kg,背景值为0.257mg/kg,明显高于房山平原区背景值0.1903mg/kg[15]和北京市平原区平均值0.20mg/kg[14],低于全国土壤背景值0.29mg/kg[17],表明研究区土壤在北京地区呈现相对的富硒特征。而且硒元素的变异系数为40%,元素含量变化中等起伏,属弱变异性,说明研究区土壤中硒元素的分布较为均匀,人为活动干扰程度影响较小。 依据谭见安[18]和《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295—2016)中土壤Se等级划分标准(表 1,图 1),研究区硒缺乏土壤(<0.125mg/kg)比例为3.27%,边缘硒土壤(0.125~0.175mg/kg)比例为7.31%,适量硒土壤(0.175~0.40mg/kg)比例为65.48%,高硒土壤(0.40~3.0mg/kg)比例为23.93%,无硒过剩区。整体上以适量-高硒土壤为主,其中高硒土壤分布面积为360.4km2,在研究区的东北—中部地区,呈东北—西南方向展布,空间分布上与青白口系、石炭—二叠系、侏罗—白垩系的黑色岩系地层有较好的空间耦合关系,反映了土壤硒的成土母质来源。表 1. 研究区表层土壤硒丰缺水平分布面积统计Table 1. Distribution area of selenium level in topsoils of the study area测试项目 硒缺乏土壤 边缘硒土壤 适量硒土壤 高硒土壤 硒过剩区 硒含量
(mg/kg)≤0.125 0.125~0.175 0.175~0.40 0.40~3.0 >3.0 面积(km2) 49.2 110.1 986.1 360.4 0 面积占比
(%)3.27 7.31 65.48 23.93 0 3.2 土壤硒与碳氮铁磷等元素的关系
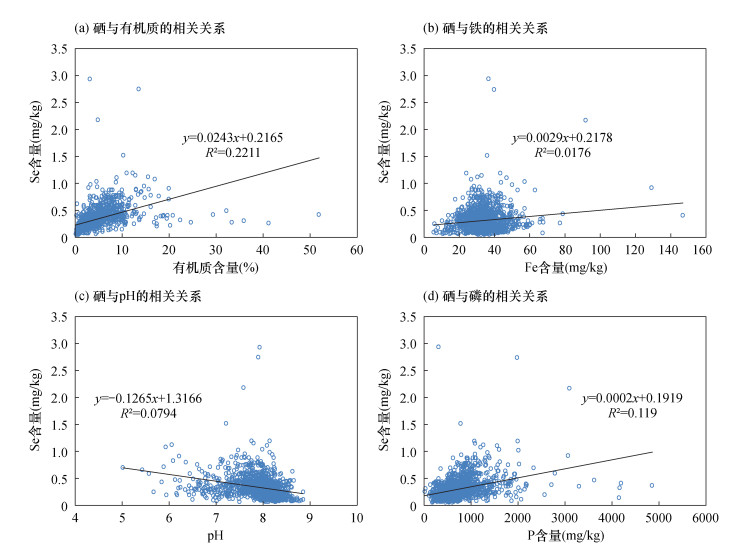
土壤元素与指标的含量和组合特征在一定程度上反映出元素之间的相互作用关系及其相似的地球化学性质。土壤Se与其他53项元素指标的聚类分析结果显示,在类间距离为0.6处,Se与C、Corg、N、S等元素归为一组,说明这些元素有着较强的共伴生关系,在富含C、Corg、N、Fe等元素的深色岩石及成土母质中明显浓集Se元素;在类间距离为0.28处,P与Se存在一定聚类关系,表明两者在化学行为上具有相似性。 前人研究揭示了土壤Se分布与土壤母质母岩、成土过程、土壤质地、土壤有机质、pH和Eh、黏土矿物以及土壤中其他元素等存在密切关系[19-22]。本次研究结果表明Se与有机质、C、N、P、TFe、pH等元素指标呈显著相关关系(n=1297,P < 0.001),相关系数(R)分别为0.4702、0.3743、0.6350、0.3450、0.1327、-0.2818(图 3)。土壤Se与有机质两者呈线性正相关(图 2a),R=0.4702(n=1297,P<0.001),表明土壤有机质越高,硒含量越丰富,推断与有机质对硒的吸附和固定作用有关[23]。有研究[24]表明,高硒区表层土壤提取液中的硒,98%以上为有机态(+6价),反映出硒多以有机结合态的方式存在,进一步说明有机质含量是影响土壤硒含量的主要因素。土壤硒的富集或贫化还与土壤中的氧化铁有关(图 2b),两者相关系数R=0.1327(n=1297,P<0.001)。这可能与土壤中氧化铁较强的吸附能力有关,致使土壤中硒与氧化铁结合或固定下来,不易溶解迁移而淋溶流失[25]。 研究区土壤pH值变化于5.01~8.83,平均值7.90,以中性-偏碱性土为主。相关性分析结果(图 2c)表明,土壤pH与硒呈负相关,R=-0.2818(n=1297,P<0.001),表明土壤pH越低,硒含量越高,反之,pH越高,土壤中硒含量越低。可见,土壤酸碱度也是影响土壤硒含量的重要因素[26]。有研究表明,土壤pH可以影响土壤硒存在形态以及相互之间的转化,中性和酸性土壤中的硒主要以四价态的SeO32-存在,而碱性条件下土壤硒则以迁移性高的六价态为主;四价态硒更易被土壤有机质和黏土矿物吸附而固定,而土壤对亚硒酸盐的吸附能力会随着pH值的升高而降低,所以酸性土壤保硒能力往往比碱性土壤强[27]。 硒和磷在土壤中的化学行为具有相似性,图 2d中两者相关系数R=0.345(n=1297,P<0.001)。磷和硒在土壤中均以含氧阴离子的形式存在,两者之间的作用主要表现在土壤表面吸附及植物吸收利用方面[28],硒和磷在土壤胶体表面通过竞争吸附行为存在[29],同时作物对磷酸盐和亚硒酸盐的吸收可能共同用一个转运通道,两者在作物吸收过程中也存在竞争吸收作用[30],进一步证明了两者在相互作用中的紧密关系。3.3 农作物富硒特征
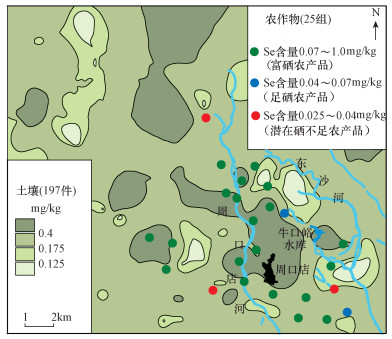
在富硒土地资源调查的基础上,开展农作物富硒特征研究,对于开发利用富硒土地资源具有指导意义。本次研究选取研究区东南部周口店镇周边农业种植区采集分析了25组玉米和根系土样品,根系土硒含量变化范围为0.060~0.820mg/kg,平均含量0.357mg/kg;玉米硒含量变化范围为0.028~0.70mg/kg,平均含量0.20mg/kg;玉米对土壤硒的平均吸收系数达56%,表明玉米富硒能力强,有利于产出富硒玉米,从而提高种植玉米的经济效益。土壤与玉米硒的相关分析显示,两者之间呈显著线性相关,R=0.703(n=22,P<0.01),表明土壤硒是作物体内硒的重要供给来源。 按照谭见安[31]提出的土壤硒分级标准,对周口店地区25组玉米根系土样品Se数据进行划分,并分别统计各土壤硒分组的玉米硒含量水平。表 2中的数据表明,随着土壤硒含量的增高,玉米硒也基本呈现同步增长的趋势。按照谭见安[31]提出的作物硒含量分级及效应标准界定,土壤硒的中等和高区种植的玉米均达富硒玉米水平,其中20件玉米样品Se含量处于0.07~1.0mg/kg,为富硒农产品;2件玉米样品Se含量处于0.04~0.07mg/kg,为足硒农产品;3件玉米样品Se含量处于0.025~0.04mg/kg,为潜在硒不足农产品。与土壤硒元素分布(图 3)对比,富硒玉米主要分布于周口店河上游的河流两侧,与富硒土壤区空间分布一致。上述结果表明,天然富硒土壤区生长的玉米硒含量明显高于非富硒区,且有部分样本达到天然富硒农产品标准,说明富硒土壤对作物硒富集起到促进作用[32-33],大清河流域生态涵养区富硒土壤具备开发富硒农产品的前景。表 2. 土壤与玉米硒含量分级统计Table 2. Selenium content grading statistics in soils and crops土壤硒含量
分级标准[31]样本量
(件)研究区内周口店农业种植区 根系土硒含量范围
(mg/kg)根系土硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)玉米硒含量范围
(mg/kg)玉米硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)缺乏
(≤0.125mg/kg)2 0.060~0.075 0.068 0.028~0.30 0.16 边缘
(0.125~0.175mg/kg)2 0.151~0.152 0.152 0.031~0.075 0.053 中等
(0.175~0.400mg/kg)12 0.186~0.382 0.268 0.12~0.50 0.18 高
(0.400~3.00mg/kg)9 0.401~0.820 0.586 0.11~0.70 0.26 过剩
(≥3.0mg/kg)0 - - - - 3.4 土壤硒来源分析
3.4.1 不同岩石类型硒的分布
研究区地貌以中低山为主,不同地层岩性的取样分析结果见表 3。可见,不同地层岩性中Se含量存在明显差别,寒武—奥陶系碳酸盐岩、房山花岗岩体中Se平均值为0.016mg/kg和0.022mg/kg,明显偏低;区内石炭—二叠系主要为一套深灰色与灰黑色碎屑岩,下部杨家屯组发育有煤系地层,岩石Se含量明显较高,为0.07mg/kg;侏罗系窑坡组与龙门组由暗色河流相泥砂岩组成,含煤层,硒含量为0.057mg/kg;与煤层共生的煤矸石中硒含量极丰富,平均值达0.11mg/kg。虽未对青白口系地层岩石进行采样分析,但按成土母质分区统计表明,青白口系地层区土壤Se呈明显富集特征,推断是由于该套地层为深色含铁粉砂质黏土岩、页片岩,对硒等元素具有明显的吸附固定作用所致。硒在岩石中的分异是不均匀的,与岩性和组成有关,一般含炭质高的细粒岩石或沉积物含硒高[34],如中生代黑色页岩和煤等富硒的沉积岩层是硒的物质来源之一[35-36];郭莉等[14]对房山部分岩石硒含量进行分析,认为煤层和炭质页岩等岩石的风化是土壤硒的主要来源,这与本次研究结果是相似的。黄淇等[15]在房山平原的富硒土壤主要分布在石楼—窦店—琉璃河一带,土壤Se含量≥0.3mg/kg的面积为28km2,该区地处大石河、周口店河、东沙河和马跑刨泉河多条水系汇聚处,地势较低,山区富硒成土母质及土壤随河流水系向下游平原迁移,在此处沉淀形成富硒土壤。可见,房山平原的富硒土壤与本研究的富硒土壤具有同源性,均来自于山区的富含有机养分的暗色岩系的成土母岩。表 3. 研究区不同时代地层岩石中Se含量分布特征Table 3. Characteristics of Se content in strata of different ages地层时代 岩石类型 样本量
(件)硒含量范围
(mg/kg)硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)寒武—奥陶系 白云岩 4 0.007~0.034 0.016 灰岩 灰岩 灰岩 石炭—二叠系 千枚岩 4 0.016~0.16 0.07 千枚岩 页岩 砂岩 侏罗系
(窑坡组—龙门组)砂岩 3 0.023~0.093 0.057 泥页岩 页岩 花岗岩 1 0.022 0.022 煤矸石 3 0.166~0.16 0.11 3.4.2 不同成土母质硒的分布
成土母质是地表岩石经风化作用使岩石破碎形成的松散碎屑风化物,是形成土壤的基本原始物质基础。以不同地层岩性划分成土母质区,研究区分为蓟县钙质岩、青白口页片岩、寒武—奥陶钙质岩、石炭—二叠硅质岩、侏罗—白垩硅质岩、岩浆岩和第四系7个成土母质区,统计不同分区表层土壤Se元素的平均含量见表 4。结果显示,青白口系页片岩成土母质区土壤明显富含Se元素,平均值为0.444mg/kg;侏罗—白垩系硅质岩成土母质区次之,平均值为0.352mg/kg;寒武—奥陶系钙质岩、石炭—二叠系硅质岩成土母质土壤Se元素含量相差不大,平均值分别为0.313mg/kg和0.311mg/kg;明显偏低的是第四系土壤和岩浆岩成土母质区,平均值分别为0.261mg/kg和0.202mg/kg。土壤成土母质在一定程度上继承了母岩的特性[37],不同成土母质土壤含硒量差异明显[38],总体反映出研究区青白口系页片岩、石炭—二叠硅质岩(含煤系)和侏罗—白垩硅质岩类成土母质区域的上覆土壤中硒元素一般呈现较明显的富集特征。综上可知,地质背景和成土母质是影响土壤硒空间分布的决定性因素,河流相沉积的暗色岩系是土壤硒的重要来源,也是控制土壤Se分布的主要因素。然而,上述硒富集的岩性地层中也往往富含重金属元素,因此,在开发富硒土地资源的同时,一定要对土壤环境质量进行科学评价。表 4. 研究区不同成土母质土壤Se元素平均值Table 4. Average values of Se in different soil parent materials of the study area成土母质区 参与统计的
样本量(件)硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)蓟县系钙质岩 377 0.302 青白口系页片岩 180 0.444 寒武—奥陶系钙质岩 248 0.313 石炭—二叠系硅质岩(含煤系地层) 164 0.311 侏罗—白垩系硅质岩(含煤系地层) 39 0.352 岩浆岩 30 0.202 第四系 165 0.261 3.5 富硒土地的安全性评价
前人研究表明,硒与重金属元素存在一定的伴生关系[39-41]。为了合理利用清洁安全的富硒土地资源,对研究区土壤进行了环境质量安全性评价。区内土地利用以耕地、林地、园地、草地为主,建设用地面积占比极小,为此,环境质量安全性评价采用《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB15618—2018)进行,评价指标包括Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn八个重金属。 土壤重金属元素含量对照标准中的筛选值和管控值,将土壤环境质量分为三区,统计各元素不同环境质量分区样点数及占比见表 5。研究区土壤中Cd含量处于标准风险筛选值和风险管制值之间的样本数为73个,占比5.63%,处于风险管制值以上的样点数为5个,占比0.39%;汞处于标准风险筛选值和风险管制值之间的样本数为3个,占比0.23%,处于风险管制值以上的样点数为1个,占比0.08%;Pb处于标准风险筛选值和风险管制值之间的样本数为4个,占比0.31%,处于风险管制值以上的样点数为1个,占比0.08%;As处于标准风险筛选值和风险管制值之间的样本数为11个,占比0.85%,处于风险管制值以上的样点数为0个;Cu、Ni和Zn处于标准风险筛选值以上的样本数分别为10、4和9个,占比分别为0.77%、0.31%和0.69%;Cr无超过风险筛选值和风险管制值的样本。由统计结果可知,研究区表层土壤重金属含量低于标准风险筛选值的样本占比在93%以上,表明整体环境质量清洁安全,对土壤环境影响相对较大的元素是Cd。绘制土壤重金属环境质量分区图,图 4显示了研究区土壤环境质量整体清洁安全,适合开发富硒土地资源。仅在蒲洼东南、史家营西、上方山、南窖西北局部地区存在1.35km2土壤镉、0.46km2土壤汞和1.42km2土壤铅元素的风险管控区(含量值大于土壤风险管控值),具有一定的环境污染风险,重金属风险管控区与富硒土壤在空间分布上局部重叠,在土地开发利用过程中,需引起适当关注。表 5. 研究区表层土壤重金属环境质量分区样点数及占比Table 5. Statistics on number of samples and proportion of topsoil in heavy metal environmental quality area重金属元素 环境质量分区 质量安全区 风险筛选区 风险管控区 ≤风险筛选值样点数(个) 占比(%) 风险筛选值~风险管制值样点数(个) 占比(%) >风险管制值样点数(个) 占比(%) Cd 1219 93.99 73 5.63 5 0.39 Hg 1293 99.69 3 0.23 1 0.08 As 1286 99.15 11 0.85 0 0.00 Pb 1292 99.61 4 0.31 1 0.08 Cr 1297 100.00 0 0.00 0 0.00 Cu 1287 99.23 10 0.77 - - Ni 1293 99.69 4 0.31 - - Zn 1288 99.31 9 0.69 - - 注:“-”表示《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018)标准中无对应的评价风险管制值标准。 4. 结论
北京大清河流域生态涵养区表层土壤硒全量变幅为0.055~0.465mg/kg,背景值为0.257mg/kg,其中360.4km2达到富硒土壤标准(0.4mg/kg < Se≤3.0mg/kg),其上种植的玉米硒含量变化范围为0.028~0.70mg/kg,平均含量0.20mg/kg,吸收率为56%,25件玉米样品有20件达到天然富硒标准,富硒率达80%。作物与土壤富硒空间分布相吻合,玉米Se与根系土Se呈显著正相关,反映出土壤硒是作物硒的重要供给来源,植物利用有效性高。 研究区富硒岩石类型包括石炭、二叠、侏罗系的页岩、泥岩、千枚岩、砂岩,不同成土母质以青白口系页片岩母质发育土壤硒含量最高(0.444mg/kg),岩浆岩母质发育土壤的硒含量则最低(0.202mg/kg),富硒土壤集中分布在青白口系、石炭—二叠系、侏罗—白垩系等河流相沉积的含碳、泥质等暗色岩系地区。影响大清河流域生态涵养区土壤硒含量的决定性因素是地质背景和成土母质,土壤有机质、TFe、pH和P对土壤硒的分布也有一定影响。 大清河流域生态涵养区土壤重金属低于标准风险筛选值的质量区面积为1612km2,占研究区总面积的99.8%,环境质量整体上是清洁安全的,但仍存在3.23km2(面积占比0.2%)土壤重金属超风险管控值,重点关注Cd、Hg和Pb元素。 综合研究区土壤硒分布及来源、作物有效性与富硒土地资源的安全性,认为本次发现的大面积的富硒土地具有较好的开发利用前景,应加强对富硒土地的有效保护和科学开发,发掘富硒土地的潜在价值。要点
- (1) 在北京大清河流域生态涵养区(1615km2)厘定出360.4km2的富硒土地资源。
- (2) 地质背景和成土母质是土壤富硒的主控因素。
- (3) 对富硒土地资源环境安全质量进行了评价。
HIGHLIGHTS
- (1) A selenium-rich land resource of 360.4km2 was identified in the eco-conserving division of the Daqinghe River watershed (1615km2) in Beijing.
- (2) Geological background and soil parent material were the key control factors affecting the distribution of selenium-rich land resources.
- (3) The environmental safety quality of selenium-rich soil resources was assessed.
-
表 1 研究区表层土壤硒丰缺水平分布面积统计
Table 1. Distribution area of selenium level in topsoils of the study area
测试项目 硒缺乏土壤 边缘硒土壤 适量硒土壤 高硒土壤 硒过剩区 硒含量
(mg/kg)≤0.125 0.125~0.175 0.175~0.40 0.40~3.0 >3.0 面积(km2) 49.2 110.1 986.1 360.4 0 面积占比
(%)3.27 7.31 65.48 23.93 0 表 2 土壤与玉米硒含量分级统计
Table 2. Selenium content grading statistics in soils and crops
土壤硒含量
分级标准[31]样本量
(件)研究区内周口店农业种植区 根系土硒含量范围
(mg/kg)根系土硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)玉米硒含量范围
(mg/kg)玉米硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)缺乏
(≤0.125mg/kg)2 0.060~0.075 0.068 0.028~0.30 0.16 边缘
(0.125~0.175mg/kg)2 0.151~0.152 0.152 0.031~0.075 0.053 中等
(0.175~0.400mg/kg)12 0.186~0.382 0.268 0.12~0.50 0.18 高
(0.400~3.00mg/kg)9 0.401~0.820 0.586 0.11~0.70 0.26 过剩
(≥3.0mg/kg)0 - - - - 表 3 研究区不同时代地层岩石中Se含量分布特征
Table 3. Characteristics of Se content in strata of different ages
地层时代 岩石类型 样本量
(件)硒含量范围
(mg/kg)硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)寒武—奥陶系 白云岩 4 0.007~0.034 0.016 灰岩 灰岩 灰岩 石炭—二叠系 千枚岩 4 0.016~0.16 0.07 千枚岩 页岩 砂岩 侏罗系
(窑坡组—龙门组)砂岩 3 0.023~0.093 0.057 泥页岩 页岩 花岗岩 1 0.022 0.022 煤矸石 3 0.166~0.16 0.11 表 4 研究区不同成土母质土壤Se元素平均值
Table 4. Average values of Se in different soil parent materials of the study area
成土母质区 参与统计的
样本量(件)硒含量平均值
(mg/kg)蓟县系钙质岩 377 0.302 青白口系页片岩 180 0.444 寒武—奥陶系钙质岩 248 0.313 石炭—二叠系硅质岩(含煤系地层) 164 0.311 侏罗—白垩系硅质岩(含煤系地层) 39 0.352 岩浆岩 30 0.202 第四系 165 0.261 表 5 研究区表层土壤重金属环境质量分区样点数及占比
Table 5. Statistics on number of samples and proportion of topsoil in heavy metal environmental quality area
重金属元素 环境质量分区 质量安全区 风险筛选区 风险管控区 ≤风险筛选值样点数(个) 占比(%) 风险筛选值~风险管制值样点数(个) 占比(%) >风险管制值样点数(个) 占比(%) Cd 1219 93.99 73 5.63 5 0.39 Hg 1293 99.69 3 0.23 1 0.08 As 1286 99.15 11 0.85 0 0.00 Pb 1292 99.61 4 0.31 1 0.08 Cr 1297 100.00 0 0.00 0 0.00 Cu 1287 99.23 10 0.77 - - Ni 1293 99.69 4 0.31 - - Zn 1288 99.31 9 0.69 - - 注:“-”表示《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018)标准中无对应的评价风险管制值标准。 -
[1] 韩晓霞, 魏洪义.硒的营养生物学研究进展[J].南方农业学报, 2015, 46(10):1798-1804. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2015.10.1798
Han X X, Wei H Y.Research progress in nutritional biology of selenium[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015, 46(10):1798-1804. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2015.10.1798
[2] Fordyce F.Selenium geochemistry and health[J].AMBIO:A Journal of the Human Environment, 2007, 36(1):94-97. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[94:SGAH]2.0.CO;2
[3] 朱晓华, 刘晓端, 刘久臣, 等.川西高原天然剖面土壤硒的含量及分布特征[J].生态环境学报, 2015, 24(4):673-682. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201504019
Zhu X H, Liu X D, Liu J C, et al.Contents and distributions characteristics of selenium in natural soil profile samples from the Western Sichuan plateau area[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(4):673-682. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201504019
[4] Fordyce F M.Selenium Deficiency and Toxicity in the Environment[M]//Selinus O.Essentials of Medical Geology.2013: 375-416.
[5] Yanai J, Mizuhara S, Yamada H.Soluble selenium content of agricultural soils in Japan and its determining factors with reference to soil type, land use and region[J].Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2015, 61(2):312-318. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2014.997147
[6] 李春生.开阳县硒资源农业开发利用研究[D].贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2000: 1-2.
Li C S.Research on Development and Utilization of Selenium Resources in Agriculture of Kaiyang County[D].Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2000: 1-2.
[7] 马迅, 宗良纲, 诸旭东, 等.江西丰城生态硒谷土壤硒有效性及其影响因素[J].安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(4):1588-1593. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/aqyhjxb201704071
Ma X, Zong L G, Zhu X D, et al.Effectiveness and influential factors of soil selenium in selenium valley, Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J].Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(4):1588-1593. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/aqyhjxb201704071
[8] 陈娟, 宋帅, 史雅娟, 等.富硒农业生产基地土壤硒资源空间分布特征及评价[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(12):2185-2190. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015040302
Chen J, Song S, Shi Y J, et al.Spatial distribution and assessment of selenium in soils of a Se-enrich agricultural production base[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(12):2185-2190. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015040302
[9] 吴俊.福建省寿宁县土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J].中国地质, 2018, 45(6):1167-1176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201806008
Wu J.The distribution of soil selenium in Shouning County of Fujian Province and its influencing factors[J].Chinese Geology, 2018, 45(6):1167-1176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201806008
[10] 蒋慧豪, 罗杰, 蔡立梅, 等.广东省普宁市土壤硒的分布特征及影响因素研究[J].现代地质, 2019, 33(1):161-168. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201901015
Jiang H H, Luo J, Cai L M, et al.Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Puning City, Guangdong Province[J].Geoscience, 2019, 33(1):161-168. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201901015
[11] 李福燕, 漆智平, 李许明.海口市农田土壤硒含量特征与农作物硒特征[J].土壤通报, 2016, 47(3):630-635. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201603019
Li F Y, Qi Z P, Li X M.Survey and research of selenium contents in farmland soil and crops of Haikou[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(3):630-635. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201603019
[12] 陈锦平, 刘永贤, 潘丽萍, 等.浔郁平原不同作物的硒富集特征及其影响因素[J].土壤, 2018, 50(6):1155-1159. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201806015
Chen J P, Liu Y X, Pan L P, et al.Selenium accumulation characteristics and influential factors of different crops in Xunyu Plain[J].Soils, 2018, 50(6):1155-1159. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201806015
[13] 李海蓉, 杨林生, 谭见安, 等.我国地理环境硒缺乏与健康研究进展[J].生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5):381-386. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjsjz201705006
Li H R, Yang L S, Tan J A, et al.Progress on selenium deficiency in geographical environment and its health impacts in China[J].Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5):381-386. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjsjz201705006
[14] 郭莉, 杨忠芳, 阮起和, 等.北京市平原区土壤中硒的含量和分布[J].现代地质, 2012, 26(5):859-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.003
Guo L, Yang Z F, Ruan Q H, et al.Content and distribution of selenium in soil of Beijing Plain[J].Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):859-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.003
[15] 黄淇, 成杭新, 陈出新, 等.北京市房山区富硒土壤调查与评价[J].物探与化探, 2013, 37(5):889-894. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201305025
Huang Q, Cheng H X, Chen C X, et al.The investigation and evaluation of selenium-rich soil in Fangshan District of Beijing City[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(5):889-894. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201305025
[16] Greco A D S, Sanjinez Argandona E J, Corazza M Z, et al.Use of chemometric tools for HG-AAS instrumental optimization in the determination of Se in nuts grown in Brazil[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(6):251-257.
[17] 中国环境监测总站.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre.Background Values of Soil Elements in China[M].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
[18] 谭见安.环境生命元素与克山病:生态化学地理研究[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社, 1996.
Tan J A.Environmental Life Elements and Keshan Disease:Eco-chemical Geography[M].Beijing:China Medical Science Press, 1996.
[19] 邹辉, 王卉, 段碧辉, 等.恩施州宣恩地区富硒土壤硒含量特征及影响因素研究[J].资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4):546-550. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9506019
Zou H, Wang H, Duan B H, et al.Study on selenium contents characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Xuanen Area of Enshi and its influencing factors[J].Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(4):546-550. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9506019
[20] 曹容浩.福建省龙海市表层土壤硒含量及影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):282-288. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201606130084
Cao R H.Study on selenium content of surface soils in Longhai, Fujian and its influencing factors[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):282-288. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201606130084
[21] 王秋爽, 罗杰, 蔡立梅, 等.广东省揭西县土壤硒的分布特征及影响因素研究[J].土壤, 2018, 50(6):1126-1133. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201806010
Wang Q S, Luo J, Cai L M, et al.Distribution of soil selenium and its influential factors in Jiexi County, Guangdong Province[J].Soils, 2018, 50(6):1126-1133. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201806010
[22] 迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等.黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J].土壤学报, 2016, 53(5):1262-1274. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201605017
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al.Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province, China[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5):1262-1274. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201605017
[23] 方金梅.福州市土壤硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(2):103-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.02.006 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080238
Fang J M.Selenium speciation analysis and its transformation and enrichment in soils of Fuzhou City[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(2):103-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.02.006 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080238
[24] 周越, 吴文良, 孟凡乔, 等.土壤中硒含量、形态及有效性分析[J].农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(6):527-532. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjyfz201406007
Zhou Y, Wu W L, Meng F Q, et al.Review on the content, specification of selenium and its availability in soils[J].Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6):527-532. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjyfz201406007
[25] 韩笑, 周越, 吴文良, 等.富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系——以江西丰城为例[J].农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201806018
Han X, Zhou Y, Wu W L, et al.Selenium contents of farmland soils and their relationship with main soil properties in Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201806018
[26] 谢邦廷, 贺灵, 江官军, 等.中国南方典型富硒区土壤硒有效性调控与评价[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
Xie B T, He L, Jiang G J, et al.Regulation and evaluation of selenium availability in Se-rich soils in Southern China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
[27] 严佳, 宗良纲, 杨旎, 等.不同pH条件和P-Se交互作用对茶园土壤Se(Ⅳ)吸附行为的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(5):935-942. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201405017
Yan J, Zong L G, Yang N, et al.Effects of pH and phosphate on Se(Ⅳ) adsorption by tea garden soil[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(5):935-942. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201405017
[28] 沈方科.土壤理化性质及磷硫水平对水稻吸收累积硒的影响[D].南宁: 广西大学, 2017.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10593-1018029104.htm Shen F K.Soil Factors, Sulfur and Phosphorus Fertilizations Affecting Selenium Accumulation in Paddy Rice[D].Nanning: Guangxi University, 2017.
[29] 严佳.磷-硒交互作用对茶园土壤硒吸附行为及有效性的影响[D].南京: 南京农业大学, 2014: 10-11.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10307-1016041793.htm Yan J.Effects of Interaction of Phosphorus-Selenium on the Adsorption Behavior and Availability of Selenium on Tea Garden Soil[D].Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014: 10-11.
[30] 王鹏, 侯振安, 冶军, 等.磷和不同价态硒对小麦硒吸收转运的影响[J].新疆农业学报, 2018, 55(1):33-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjnykx201801006
Wang P, Hou Z A, Ye J, et al.Effects of phosphorus and different valence selenium on the absorption and transport of selenium in wheat[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(1):33-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjnykx201801006
[31] 谭见安.中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M].北京:科学出版社, 1989.
Tan J A.Atlas of Endemic Diseases and Environment of the People's Republic of China[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1989.
[32] 李金峰, 聂兆君, 赵鹏, 等.土壤-植物系统中硒营养的研究进展[J].南方农业学报, 2016, 47(5):649-656. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2016.05.649
Li J F, Nie Z J, Zhao P, et al.Research progress on selenium nutrition in the soil-plant system[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2016, 47(5):649-656. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2016.05.649
[33] 朱薇, 杨守祥, 刘庆.影响植物富硒因素的研究进展[J].山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(4):636-640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2016.04.030
Zhu W, Yang S X, Liu Q.Advances of factors influencing selenium enrichment in plants[J].Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 47(4):636-640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2016.04.030
[34] 谭见安.地球环境与健康[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2004.
Tan J A.Earth Environment and Health[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2004.
[35] 夏卫平, 谭见安.中国一些岩类中硒的比较研究[J].环境科学学报, 1990, 10(2):125-131. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91840X/199002/288472.html
Xia W P, Tan J A.A comparative study of selenium content in Chinese rocks[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1990, 10(2):125-131. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91840X/199002/288472.html
[36] 廖启林, 任静华, 许伟伟, 等.江苏宜溧富硒稻米产区地质地球化学背景[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(5):1791-1802. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201605027
Liao Q L, Ren J H, Xu W W, et al.Geological and geochemical background of Se-rich rice production in Yili area, Jiangsu Province[J].Geology in China, 2016, 43(5):1791-1802. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201605027
[37] 刘晓波, 张华, 金立新, 等.四川省屏山县土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J].环境化学, 2017, 36(10):2246-2252. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017022101
Liu X B, Zhang H, Jin L X, et al.Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in Pingshan of Sichuan Province[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(10):2246-2252. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017022101
[38] 田欢.典型富硒区岩石-土壤-植物中硒的赋存状态及环境行为研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学, 2017: 30-31.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1017740241.htm Tian H.The Occurrence State and Speciation of Selenium and Its Environmental Behaviors in Rock-Soil-Plant from Typical High-Se Areas[D].Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2017: 30-31.
[39] 余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等.恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J].土壤, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201806009
Yu T, Yang Z F, Wang R, et al.Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J].Soils, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201806009
[40] 郭跃品, 傅杨荣, 何玉生, 等.琼北火山岩区农田土壤重金属和硒含量评价及来源研究[J].安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(1):330-334. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/aqyhjxb201501070
Guo Y P, Fu Y R, He Y S, et al.Evaluation and source analysis of the heavy metals and selenium in the farmland soils of volcanic area, north of Hainan Island[J].Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(1):330-334. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/aqyhjxb201501070
[41] 耿建梅, 王文斌, 温翠萍, 等.海南稻田土壤硒与重金属的含量、分布及其安全性[J].生态学报, 2012, 32(11):3477-3486. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201211020
Geng J M, Wang W B, Wen C P, et al.Concentrations and distributions of selenium and heavy metals in Hainan paddy soil and assessment of ecological security[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(11):3477-3486. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201211020
-





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: