The Occurrences of Hg and Cd in Soils around Cities and Rivers and Their Ecological Risk Assessment
-
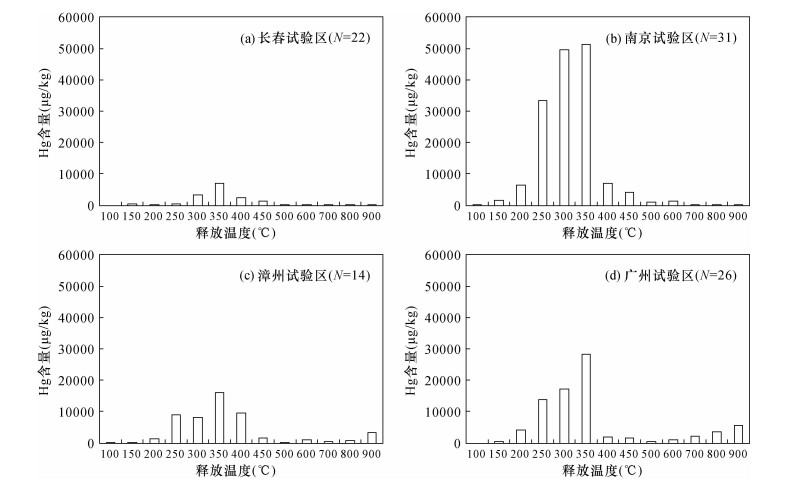
摘要: 受人类活动和自然作用双重影响,土壤中重金属元素异常普遍存在,其中尤以城镇周边的Hg异常和大江河沿岸区域Cd异常最为典型。近年来,通常采用化学分步提取的方式,探讨土壤水溶态、离子交换态、有机态、铁锰氧化物态等形态中Hg、Cd等重金属元素含量的状况,进而分析其生态效应,但对土壤中Hg、Cd等重金属元素的自然存在形式缺乏深入探讨。本文以Hg、Cd两元素为重点,选择我国代表性城市和地区,采集城镇周边Hg异常区和江河沿岸Cd异常区的土壤样品,采用王水溶样原子荧光光谱法(AFS)测定Hg含量,采用盐酸-硝酸-氢氟酸-高氯酸溶样电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定Cd含量,同时配合其他相关实验手段,对Hg、Cd的自然存在形式进行解析;并以水稻中Hg、Cd含量为依据对Hg、Cd的生态效应进行了评价。结果表明:长春、南京、漳州和广州等城镇周边土壤Hg异常区Hg主体以硫化物形式存在,而且至少有一部分是以辰砂矿物形式存在,由此决定了土壤中Hg有效态在Hg全量中所占比例较小,土壤中Hg平均含量达到500μg/kg时,水稻籽实中Hg含量超过无公害食品标准的比例为3.4%,生态效应不甚敏感;长江、珠江等江河沿岸区域Cd异常区内Cd主要呈黏土吸附形式存在,由此导致50%左右的Cd以有效态形式存在,在土壤Cd全量中所占比例较大,当土壤中Cd平均含量达到1000μg/kg时,水稻籽实中Cd含量超过无公害食品标准的比例为43%,生态效应敏感。由此揭示出土壤中Hg、Cd等重金属元素生态效应敏感程度更直接地受到自然存在形式的影响。以辰砂矿物形式存在的Hg呈现“惰性”,不容易被农作物吸收,故生态效应不敏感;以黏土矿物吸附形式存在的Cd活动性更强,容易被农作物吸收,故生态效应敏感。Hg、Cd等重金属元素被农作物乃至人体吸收后,其存在形式及其转化特性是评估该元素是否存在生态风险的关键。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDThe ecological risk of heavy metal anomaly in soil is widespread due to human activities and natural processes. Hg anomaly in urban soil and Cd anomaly along rivers are the typical cases. Recently, the chemical sequential extraction method is widely used for Hg, Cd and other heavy metals to analyze the content of water-soluble fraction, exchangeable fraction, organic bound fraction, and ferric-manganese oxidation in soil. Normally the contents of different heavy metals at the above different chemical extraction forms constitute the basis for ecological effect evaluation. However, no further discussion has been conducted on the natural occurrences of Hg and Cd in soil. OBJECTIVESTo provide basis for studies on the key factors of ecological risk assessment. METHODSThe content of Hg was determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) after dissolution by aqua regia. The content of Cd was determined by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) after digestion by hydrochloric acid-nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid-perchloric acid complexes. The existence forms of Hg were determined by chemical analysis, pyrolytic Hg method, heavy mineral identification, electronic probe and Raman spectrum. The existing forms of Cd were determined by AB-DTPA extraction, X-ray diffractometer and laser particle sizer analyzer. The ecological effects of Hg and Cd were evaluated based on the content of these elements in rice. RESULTSThe results show that sulfide was the main natural existence form of Hg in Hg anomaly soil around Changchun, Nanjing, Zhangzhou and Guangzhou. At least a part of Hg was in the form of cinnabar, which resulted in the relatively low percentage of bio-availability content to total content of Hg in soil. The proportion of rice grain with Hg content exceeding the standard of pollution-free food was only 3.4% when the average total content of Hg in soil was up to 500μg/kg. Cd in Cd anomaly area along the Yangtze River and the Pearl River presented as clay adsorption, resulting in about 50% Cd was bio-availability. The ratio of rice grain with Cd content exceeding the standard of pollution-free food was up to 43% when the average content of Cd in soil was 1000μg/kg. CONCLUSIONSThis reveals that the sensitivity of the ecological effects of heavy metal elements such as Hg and Cd in soil is more directly affected by naturally occurring forms. Hg in the form of cinnabar is 'inert' and is not easily absorbed by crops, so it is not sensitive to ecological effects. Cd in the form of clay mineral adsorption is more active and easily absorbed by crops, resulting in sensitive ecological effects. After the heavy metal elements such as Hg and Cd are absorbed by crops and even the human, their existence forms and their transformation characteristics are the keys to assess whether there is an ecological risk. -

-
表 1 土壤样品测试项目及测试方法
Table 1. Analytical items and methods of soil samples
测试项目 测试方法 测试单位 土壤中Hg、Cd含量 Hg:原子荧光光谱法
Cd:电感耦合等离子体质谱法中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所中心实验室 土壤中Hg存在形态 离子交换态、有机物结合态、硫化物态 中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所中心实验室 土壤热释谱法 中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所项目组 辰砂矿物鉴定 电子探针、拉曼光谱法 中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所 土壤中Cd、Hg有效态 AB-DTPA法 中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所中心实验室 土壤矿物组成 X射线衍射法 国家建筑材料工业地质工程勘查研究院测试中心 土壤粒级组成 激光粒度仪 石油工业油田化学剂质量监督检验中心 水稻籽实中Hg、Cd含量 Hg:原子荧光光谱法
Cd:电感耦合等离子体质谱法中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所中心实验室 表 2 水稻根系土中Hg和Cd含量统计
Table 2. Hg and Cd content in rice root soils
试验区 Hg全量(μg/kg) 有效态Hg含量(μg/kg) 有效态Hg在Hg全量中的占比(%) Cd全量(μg/kg) 有效态Cd含量(μg/kg) 有效态Cd在Cd全量中的占比(%) 黑龙江—吉林 53(N=340) 0.23 0.4 122(N=340) 82 66.8 江苏 538(N=198) 0.82 0.15 234(N=198) 105 44.7 浙江—湖南 483(N=248) 0.72 0.15 1008(N=248) 475 47.1 表 3 水稻中Hg和Cd食品卫生质量统计
Table 3. Food hygienic quality of Hg and Cd in rices
试验区 水稻中Hg含量(μg/kg) 所占比例(%) 水稻中Cd含量(mg/kg) 所占比例(%) Hg含量≤GS GS < Hg含量≤NS Hg含量>NS Cd含量≤GS GS < Cd含量≤NS Cd含量>NS 黑龙江—吉林 5.7(N=90) 92.2 6.7 1.1 0.011(N=90) 98.9 1.1 0 江苏 8.7(N=86) 71.6 25.0 3.4 0.035(N=86) 98.3 1.7 0 浙江—湖南 5.5(N=248) 94.0 6.0 0 0.47(N=248) 42.2 13.7 44.1 注:GS—绿色食品卫生标准,在此标准中,Hg限量为0.01mg/kg,Cd限量为0.1mg/kg;NS—无公害食品卫生标准,在此标准中,Hg限量为0.02mg/kg,Cd限量为0.2mg/kg。 -
[1] 黄昌勇.土壤学[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2000.
Huang C Y.Pedology[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2000.
[2] 徐友宁, 张江华, 柯海玲, 等.某金矿区农田土壤重金属污染的人体健康风险[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(8):1239-1252. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201408020
Xu Y N, Zhang J H, Ke H L, et al.Human health risk under the condition of farmland soil heavy metals pollution in a gold mining area[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(8):1239-1252. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201408020
[3] 王喆, 谭科艳, 陈燕芳, 等.南方某工业区大气总悬浮颗粒物重金属来源解析及其对土壤环境质量的影响[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1):82-89. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.014
Wang Z, Tan K Y, Chen Y F, et al.Origin of heavy metals in total suspended particle and their influence on soil environmental quality in an industrial area of South China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(1):82-89. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.014
[4] 刘硕, 吴泉源, 曹学江, 等.龙口煤矿区土壤重金属污染评价与空间分布特征[J].环境科学, 2016, 37(1):270-279. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201601035
Liu S, Wu Q Y, Cao X J, et al.Pollution assessment and spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soils of coal mining area in Longkou City[J].Environmental Science, 2016, 37(1):270-279. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201601035
[5] 孙鹏, 李艳伟, 张连科, 等.包头市典型工业区表层土壤中重金属污染状况及其潜在生态风险研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(4):433-439. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.016
Sun P, Li Y W, Zhang L K, et al.Heavy metal pollution in topsoil from the Baotou industry area and its potential ecological risk evaluation[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(4):433-439. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.016
[6] 钱贞兵, 孙立剑, 徐升, 等.淮河流域安徽段土壤重金属元素分布特征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2):193-200. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201710190168
Qian Z B, Sun L J, Xu S, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soils of the Anhui section of the Huaihe River Basin[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2):193-200. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201710190168
[7] Luo X S, Yu S, Li X D.Distribution, availability, and sources of trace metals in different particle size fractions of urban soils in Hong Kong:Implications for assessing the risk to human health[J].Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159:1317-1326.
[8] Ghrefat H A, Yusuf N, Jamarh A, et al.Fractionation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil samples collected along Zerqa River, Jordan[J].Environmental Earth Science, 2012, 66:199-208. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ec49357a7c7a6ba46f89b9d3d2e78786
[9] Xiao Q, Zong Y T, Luo S G.Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 120:377-385. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=77fa0c98c8b7d59b7d7658d00f55ebac
[10] 韩承华, 江解增.重金属污染对蔬菜生产的危害以及缓解重金属污染措施的研究进展[J].中国蔬菜, 2014(4):7-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsc201404004
Han C H, Jiang J Z.Research progress on effects of heavy metal on vegetable production and measures for releasing heavy metal stress[J].China Vegetables, 2014(4):7-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsc201404004
[11] 李一蒙, 马建华, 刘德新, 等.开封城市土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J].环境科学, 2015, 36(3):1037-1044. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201503043
Li Y M, Ma J H, Liu D X, et al.Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of urban soils in Kaifeng City, China[J].Environmental Science, 2015, 36(3):1037-1044. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201503043
[12] 王玉军, 吴同亮, 周东美, 等.农田土壤重金属污染评价研究进展[J].农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(12):2365-2378. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201712002
Wang Y J, Wu T L, Zhou D M, et al.Advances in soil heavy metal pollution evaluation based on bibliometrics analysis[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(12):2365-2378. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201712002
[13] 杨梦丽, 叶明亮, 马友华, 等.基于重金属有效态的农田土壤重金属污染评价研究[J].环境监测管理与技术, 2019, 31(1):10-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjjcglyjs201901004
Yang M L, Ye M L, Ma Y H, et al.Review on heavy metal pollution evaluation in farmland soil based on bioavailable form of heavy metal[J]. Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2019, 31(1):10-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjjcglyjs201901004
[14] Massas I, Ehaliotis C, Gerontidis S, et al.Elevated heavy metal concentrations in top soils of an Aegean island town (Greece):Total and available forms, origin and distribution[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2009, 151:105-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1007-s10661-008-0282-x/
[15] 陈卫平, 杨阳, 谢天, 等.中国农田土壤重金属污染防治挑战与对策[J].土壤学报, 2018, 55(2):261-272. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201802001
Chen W P, Yang Y, Xie T, et al.Challenges and countermeasures for heavy metal pollution control in farmlands of China[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2018, 55(2):261-272. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201802001
[16] Zhao F J, Ma Y B, Zhu Y G, et al.Soil contamination in China:Current status and mitigation strategies[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(2):750-759.
[17] Vareda J P, Valente A J M, Durães L.Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies:A review[J].Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 246:101-118.
[18] 王庆仁, 崔岩山, 董艺婷.植物修复——重金属污染土壤整治有效途径[J].生态学报, 2001, 21(2):326-331. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb200102024
Wang Q R, Cui Y S, Dong Y T.Phytoremediation an effective approach of heavy metal cleanup from contaminated soil[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(2):326-331. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb200102024
[19] 刘珺, 秦善.层状硅酸盐矿物对重金属污染的防治[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2001, 20(4):461-466. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yskwxzz200104018
Liu J, Qin S.The role of layer silicates in preventing and controlling environmental heavy metal pollution[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2001, 20(4):461-466. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yskwxzz200104018
[20] 樊霆, 叶文玲, 陈海燕, 等.农田土壤重金属污染状况及修复技术研究[J].生态环境学报, 2013, 22(10):1727-1736. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgzyzhly201904025
Fan T, Ye W L, Chen H Y, et al.Review on contamination and remediation technology of heavy metal in agricultural soil[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(10):1727-1736. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgzyzhly201904025
[21] 串丽敏, 赵同科, 郑怀国, 等.土壤重金属污染修复技术研究进展[J].环境科学与技术, 2014, 37(1):213-222. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nmghjbh201802051
Chuan L M, Zhao T K, Zheng H G, et al.Research advances in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 37(1):213-222. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nmghjbh201802051
[22] 安婧, 宫晓双, 魏树和.重金属污染土壤超积累植物修复关键技术的发展[J].生态学杂志, 2015, 34(11):3261-3270. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201511038
An J, Gong X S, Wei S H.Research progress on technologies of phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(11):3261-3270. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201511038
[23] 陶雪, 杨琥, 季荣, 等.固定剂及其在重金属污染土壤修复中的应用[J].土壤, 2016, 48(1):1-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201601001
Tao X, Yang H, Ji R, et al.Stabilizers and their applications in remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil[J].Soils, 2016, 48(1):1-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201601001
[24] 崔岩山, 王鹏飞, 琚宜文.纳米材料在土壤重金属污染修复中的应用[J].地球科学, 2018, 43(5):1737-1745. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201805032
Cui Y S, Wang P F, Ju Y W.Process of applications of nanomaterials in soil heavy metal remediation[J].Earth Science, 2018, 43(5):1737-1745. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201805032
[25] 李韵诗, 冯冲凌, 吴晓芙, 等.重金属污染土壤植物修复中的微生物功能研究进展[J].生态学报, 2015, 35(20):6881-6890. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201520034
Li Y S, Feng C L, Wu X F, et al.A review on the functions of microorganisms in the phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(20):6881-6890. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201520034
[26] 曾远, 罗立强.土壤中特异性微生物与重金属相互作用机制与应用研究进展[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):209-221. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701170009
Zeng Y, Luo L Q.Research progress on the application and interaction mechanism between specific microorganisms and heavy metals in soil[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):209-221. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701170009
[27] Zhang J R, Li H Z, Zhou Y Z, et al.Bioavailability and soil-to-crop transfer of heavy metals in farmland soils:A case study in the Pearl River Delta, South China[J].Environmental Pollution, 2018, 235:710 -719.
[28] Gasparatos D, Mavromati G, Kotsovilis P, et al. Fractionation of heavy metals and evaluation of the environmental risk for the alkaline soils of the Thriassio Plain:A residential, agricultural, and industrial area in Greece[J].Environmental Earth Science, 2015, 74:1099-1108.
[29] Yousaf B, Liu G J, Wang R W, et al.Bioavailability evaluation, uptake of heavy metals and potential health risks via dietary exposure in urban-industrial areas[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23:22443-22453. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bff4c408548239ec084835ff49d44f00
[30] Pan L B, Wang Y, Ma J.A review of heavy metal pollution levels and health risk assessment of urban soils in Chinese cities[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25:1055-1069. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bb56b7256af15f632dcaad493ed0233b
[31] 刘旭婷, 李明, 李法松, 等.四种连续提取方案在重金属污染土壤评价中的比较[J].哈尔滨师范大学自然科学学报, 2018, 34(6):84-89. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hebsfdxzrkxxb201806016
Liu X T, Li M, Li F S, et al.Comparison of four sequential extraction procedures used to evaluate trace metal distribution in a contaminated soil[J].Natural Sciences Journal of Harbin Normal University, 2018, 34(6):84-89. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hebsfdxzrkxxb201806016
[32] 余璨, 陈虎林, 李清清, 等.河流沉积物重金属形态分析方法研究[J].环境研究与监测, 2018, 31(3):1-8.
Yu C, Chen H L, Li Q Q, et al.Speciation analysis of heavy metals in river sediment[J].Environmental Study and Monitoring, 2018, 31(3):1-8.
[33] 陈岩, 季宏兵, 朱先芳, 等.北京市得田沟金矿和崎峰茶金矿周边土壤重金属形态分析和潜在风险评价[J].农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(11):2142-2151.
Chen Y, Ji H B, Zhu X F, et al.Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around the gold mine of Detiangou—Qifengcha, Beijing City, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(11):2142-2151.
[34] 叶宏萌, 李国平, 郑茂钟, 等.武夷山茶园土壤汞、镉和砷形态及茶叶有效性特征[J].热带作物学报, 2016, 37(11):2094-2099. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdzwxb201611010
Ye H M, Li G P, Zheng M Z, et al.Fraction distribution and tea bioavailability of Hg, Cd, Se in soil from Wuyishan tea garden[J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2016, 37(11):2094-2099. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdzwxb201611010
[35] 吴昆明, 魏朝俊, 刘云, 等.土壤活性组分提取剂的研制及初步试验结果[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(3):381-389. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/3342eeef-c4b4-4ea7-bd68-2036d7309272
Wu K M, Wei C J, Liu Y, et al.Research of soil activated ions extractant and preliminary test results[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(3):381-389. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/3342eeef-c4b4-4ea7-bd68-2036d7309272
[36] Zhang L Y, Guo S H, Wu B.The source, spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil from the Pearl River Delta based on the National Multi-purpose Regional Geochemical Survey[J].PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(7):1-12.
-



 下载:
下载: