A Fully Automated Chemical Separation and Purification System and Its Application to Isotope Analysis
-
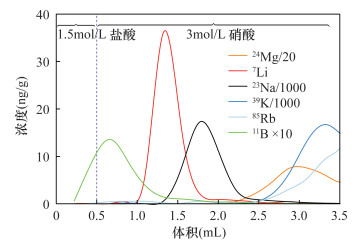
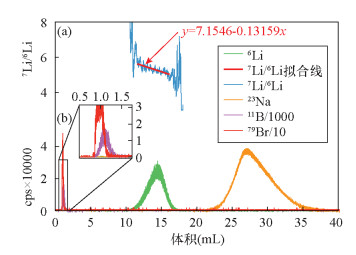
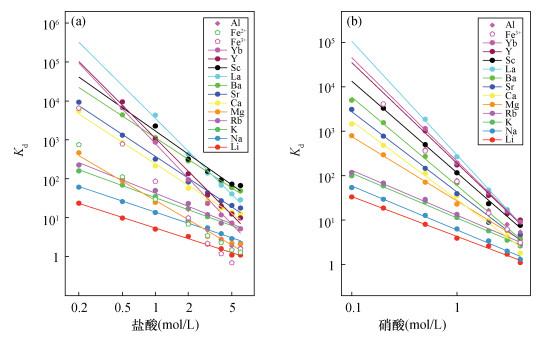
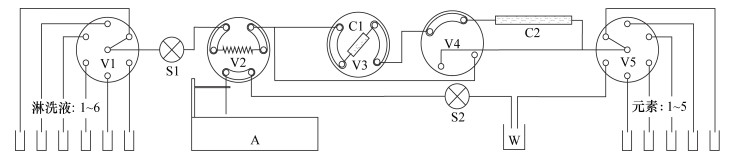
摘要: 传统自然流速层析柱法存在离子容易扩散、流速不可控等问题,而元素的自动分离提纯技术可以提高同位素分析效率,压缩在室内提纯化学元素所需的时间。为了降低这种扩散效应、缩短淋洗时间,本文研制了一种自动分离提纯系统,用于元素的自动分离、提纯。该系统由流体切换阀、柱塞泵、自动进样器等部件构成,所有部件与计算机联接,每个部件可单独控制。该系统装配了两根层析柱,通过控制切换阀,可使两者组合使用,甚至能进行逆向淋洗,这与传统自然流速法完全不同。将海水样品分别通过传统自然流速法和本系统进行淋洗提纯,使用加压自动分离提纯系统后,元素(尤其是阴离子)的扩散效应得到明显改善。上样量均为1.0mL时,采用传统自然流速法,硼元素的淋洗峰宽为2.5~3.0mL,而采用本系统淋洗峰宽仅为1.0mL。自然流速法下,不同酸度淋洗液的淋洗速度不同,而本系统的流速精确可控,可确保流速稳定。本文研制的自动分离提纯系统在分离效果和分离能力上均比传统重力法表现优异,在分离元素进行同位素分析方面具有较大的应用前景。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDCritical problems such as ion diffusion and uncontrollable flow rate exist when applying the traditional natural flow chromatography column method to isotope analysis. The proposed automated chemical purification system improves the efficiency of isotope analysis, and reduces the time required for element purification. OBJECTIVESTo develop an automated chemical separation and purification system. METHODSThe automated chemical separation and purification system was composed of multi-way valves, plunger pump, autosampler, etc. All of the components were connected using a computer and each of them can be controlled independently. By combining two chromatographic columns multiple functions can be achieved, including reversed elution, which cannot be achieved by the traditional natural flow chromatography column method. In order to investigate the performance of the automated chemical separation and purification system, fresh seawater was purified with the proposed system and the traditional method simultaneously. RESULTSThe elution peak of boron had a width of 2.5mL to 3.0mL for the traditional method, but only ca. 1.0mL for the proposed system, if the loading volume of seawater was 1.0mL. The flow rate of the elution depended on the acidity using the traditional natural flow chromatography column method. However, the flow rate could be strictly controlled with the automated chemical separation and purification system. CONCLUSIONSThe precisely controlled flow rate of the system makes an easier prediction of the elution time and elution peak. The reversed column technology of the system can be applied to the separation and purification of elements for isotope analysis. -

-
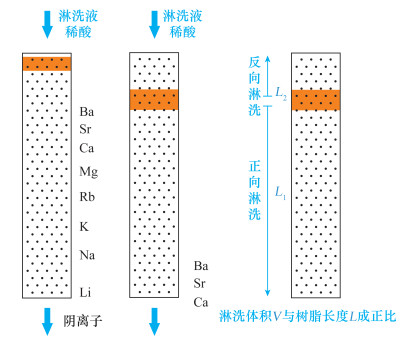
表 1 V3与V4阀的组合使用实现两根层析柱的多种用法
Table 1. Multiple functions of the two columns achieved by switching the valves V3 and V4
V3状态 V4状态 功能 1 1 C1正向与C2串联使用 1 2 C1正向单独使用 1 3 无树脂流路 1 4 C2单独使用 2 1 C1反向与C2串联使用 2 2 C1反向单独使用 2 3 无树脂流路 2 4 C2单独使用 -
[1] Ireland T J, Tissot F L H, Yokochi R, et al.Teflon-HPLC:A novel chromatographic system for application to isotope geochemistry and other industries[J].Chemical Geology, 2013, 357:203-214. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0231544326/
[2] Romaniello S J, Field M P, Smith H B, et al.Fully automated chromatographic purification of Sr and Ca for isotopic analysis[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30:1906-1912. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c099fd3cc1716bbc5990d4eb17e3f16d
[3] Retzmann A, Zimmermann T, Pröfrock D, et al.A fully automated simultaneous single-stage separation of Sr, Pb, and Nd using DGA resin for the isotopic analysis of marine sediments[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2017, 409:1-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4aa6185fb08d96d3114e957bc771d0c6
[4] Wuttig K, Townsend A T, van der Merwe P, et al.Critical evaluation of a sea FAST system for the analysis of trace metals in marine samples[J].Talanta, 2019, 197:653-668.
[5] Zhu Z Y, Yang T, Zhu X K.Achieving rapid analysis of Li isotopes in high- matrix and low-Li samples with MC-ICP-MS:New developments in sample preparation and mass bias behavior of Li in ICPMS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2019, 34:1503-1513. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/ja/c9ja00076c#!
[6] Zhu Z Y, Jiang S Y, Yang T, et al.Improvements in Cu-Zn isotope analysis with MC-ICP-MS:A revisit of chemical purification, mass spectrometry measurement and mechanism of Cu/Zn mass bias decoupling effect[J].International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2015, 393:34-40.
[7] 刘纯瑶, 苟龙飞, 邓丽, 等.离子交换过程中锂同位素分馏对锂同位素测试准确度的影响[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(1):35-44. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201806060070
Liu C Y, Gou L F, Deng L, et al.Effects of Li isotopic fractionation during ion exchange on the measurement accuracy of Li isotopes[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(1):35-44. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201806060070
[8] 濮魏, 高剑锋, 凌洪飞, 等.利用DCTA和HIBA快速有效分离Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd的方法[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 41(2):445-450. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb200504017
Pu W, Gao J F, Ling H F, et al.Separation method of Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd using DCTA and HIBA[J].Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2005, 41(2):445-450. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb200504017
[9] 尹鹏, 何倩, 何会军, 等.离子交换树脂法分离沉积物中锶和钕的影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(4):379-387. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804170046
Yin P, He Q, He H J, et al.Study on the factors influencing the separation of Sr and Nd in sediments by ion exchange resin[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(4):379-387. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804170046
[10] 唐索寒, 李津, 梁细荣, 等.钕同位素比值143Nd/144Nd标准溶液研制[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(2):163-170. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.02.010
Tang S H, Li J, Liang X R, et al.Reference material preparation of 143Nd/144Nd isotope ratio[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(2):163-170. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.02.010
[11] 张乐, 任钟元, 丁相礼, 等.微钻取样-TIMS/MC-ICPMS和LA-MC-ICPMS分析矿物岩石87Sr/86Sr比值的技术比较[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(5):615-624. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/6c79f5d0-4923-40da-8965-4e2bcd8be542
Zhang L, Ren Z Y, Ding X L, et al.A comparison of microdrilling-TIMS/MC-ICPMS and LA-MC-ICPMS for micro-sample Sr isotope measurement[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(5):615-624. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/6c79f5d0-4923-40da-8965-4e2bcd8be542
[12] Glennon K J, Osborn J M, Burns J D, et al.Measuring key Sm isotope ratios in irradiated UO2 for use in plutonium discrimination nuclear forensics[J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2019, 320(2):405-414. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=715e4b04ca9efce70b3b7d219758eaad
[13] Garcia-Valls R, Hrdlicka A, Perutka J, et al.Separation of rare earth elements by high performance liquid chromatography using a covalent modified silica gel column[J]. Analytica Chemica Acta, 2001, 439:247-253. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003267001010443
[14] 李立武, 刘艳, 王先彬, 等.高真空与脉冲放电气相色谱联用装置研发及其在岩石脱气化学分析中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):222-230. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201609080137
Li L W, Liu Y, Wang X B, et al.Development of a combined device with high vacuum and pulsed discharge gas chromatography and its application in chemical analysis of gases from rock samples[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):222-230. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201609080137
[15] Schwantes J M, Rundberg R S, Taylor W A, et al.Rapid, high-purity, lanthanide separations using HPLC[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 418(1-2):189-194. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ028502003/
[16] Datta A, Sivaraman N, Srinivasan T G, et al.Single- stage dual-column HPLC technique for separation and determination of lanthanides in uranium matrix:Application to burnup measurement on nuclear reactor fuel[J].Nuclear Technology, 2013, 182(1):84-97.
[17] Liu X M, Li W S.Optimization of lithium isotope analysis in geological materials by quadrupole ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2019, 34(8):1708-1717. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/ja/c9ja00175a
[18] Brugger J, McPhail D C, Black J, et al.Complexation of metal ions in brines:Application of electronic spectroscopy in the study of the Cu(Ⅱ)-LiCl-H2O system between 25℃ and 90℃[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(16):2691-2708.
[19] Bjerrum J, Lukes I.The iron(Ⅲ)-chloride system.A study of the stability constants and of the distribution of the tetrachloro species between organic solvents and aqueous chloride solutions[J].Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 1986, A40:31-40.
[20] Lee S G, Tanaka T.Determination of Eu isotopic ratio by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry using a Sm internal standard[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 156:42-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=113c0d2ad8155f68cfb267d5f02bed63
[21] Lee S G, Asahara Y, Tanaka T, et al.La-Ce and Sm-Nd isotopic systematics of Early Proterozoic leucogranite with tetrad REE pattern[J].Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3-4):360-373. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cbe57b7049bf919cc523112be017a1aa
[22] Panigrahi M, Grabda M, Kozak D, et al.Liquid-liquid extraction of neodymium ions from aqueous solutions of NdCl3 by phosphonium-based ionic liquids[J].Separation and Purification Technology, 2016, 171:263-269. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=33100a023b28a56254faab40f2e29e52
[23] Tanaka T, Lee S G, Kim T, et al.Precise determination of 14 REEs in GSJ/AIST geochemical reference materials JCp-1(coral) and JCt-1(giant clam) using isotope dilution ICP-quadrupole mass spectrometry[J].Geochemical Journal, 2018, 52(1):75-79. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=J-STAGE_1410877
[24] Colim A N, do Nascimento P C, Wiethan B A, et al.Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of 15 rare earth elements in surface water sample collected in a mining area from Lavras do Sul/RS, Brazil[J].Chromatographia, 2019, 82(5):843-856. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=66c76f76242bac5b88d9fa8377007e39
[25] Amr M A, Dawood N D A, Helal A I, et al.Rare earth elements and 143Nd/144Nd isotope ratio measurements using tandem ICP-CRC-MS/MS:Characterization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.)[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(8):1554-1565.
[26] Lei H L, Yang T, Jiang S Y, et al.A simple two-stage column chromatographic separation scheme for strontium, lead, neodymium and hafnium isotope analyses in geological samples by thermal ionization mass spectrometry or multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Separation Science, 2019, 42(20):3261-3275. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zpxb201603003
[27] Golloch A.Handbook of rare earth elements[M].De Gruyter Press, 2017.
[28] Small H, Stevens T S, Bauman W C.Novel ion exchange chromatographic method using conductimetric detection[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1975, 47:1801-1809. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac60361a017
[29] Horwitz E P, Bloomquist C A.Chemical separations for super-heavy element searches in irradiated uranium targets[J].Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry, 1975, 37:425-434. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022190275803502
[30] Pin C, Zalduegui J.Sequential separation of light rare-earth elements, thorium and uranium by miniaturized extraction chromatography:Application to isotopic analyses of silicate rocks[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 1997, 339:79-89. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1007-s12144-011-9125-y/
[31] Strelow F W E.Distribution coefficients and ion exchange behavior of 46 elements with a macroreticular cation exchange resin in hydrochloric acid[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1984, 56:1053-1056. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac00270a045
[32] Strelow F W E.An ion exchange selectivity scale of cations based on equilibrium distribution coefficients[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1960, 32:1185-1188.
-



 下载:
下载: