Element Fractionation and Correction Method for U-Pb Dating of Titanite by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasms-Mass Spectrometry
-
摘要: 同位素地质年代学是探索地质体时空演化及地球动力学等问题的基础学科,应用最为广泛的当属含铀副矿物的U-Pb定年技术。榍石具有相对较低的U-Pb体系封闭温度,并广泛发育于岩浆岩、各类变质岩、热液成因岩石以及少量沉积岩中,是一种理想的中高温地质事件定年矿物。利用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定榍石U-Pb年龄时,不可避免地要解决高普通铅以及元素分馏效应对测试的影响。本文对榍石LA-ICP-MS实验过程中的元素分馏行为进行研究,采用相同基体的标准样品与未知样品对比,发现了榍石不同颗粒之间元素分馏行为不一致的现象;同时采用不同的元素分馏校正方法,分别应用于锆石、独居石和榍石进行对比研究,认为分馏行为一致的副矿物定年可以采用“指数法”和“均值法”对数据进行校正,但是对于榍石这种分馏行为不一致的副矿物,定年时只有采用“截距法”对数据进行校正才可以获得正确的年龄。进而将此结论应用于秦岭造山带老牛山地区岩浆成因榍石样品,得到的结果与锆石年龄一致,表明“截距法”可以避免分馏行为不一致导致的校正不准确的问题。本研究成果为榍石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年方法的完善提供了一种思路。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDIsotope geochronology is a basic subject to explore the temporal and special evolution of geological bodies and geodynamics. The U-Pb dating technology of accessory minerals is the most widely used in isotope geochronology. Titanite has a relatively low closed temperature for U-Pb isotopic system and is common in magmatic rocks, metamorphic rocks, hydrothermal-related rocks and a few sedimentary rocks. This indicates that it is an ideal mineral for U-Pb dating to constrain the medium to high temperature geological event. OBJECTIVESTo understand the element fractionation behavior during laser ablation-inductively coupled plasms-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) U-Pb dating and propose corresponding correction methods. METHODSIn situ U-Pb dating were performed using a Geolas Pro laser-ablation system and a 7700x quadrupole ICP-MS. A stationary laser ablation spot with a beam diameter of 24μm was used for the analyses. The ablated aerosol was carried by helium and then combined with argon via a T-connector before being introduced to the ICP-MS plasma. After smoothed, the sample gas will go into quadrupole ICP-MS for U-Pb dating. Each analysis incorporated a background acquisition of approximately 10s (gas blank) followed by 40s data acquisition from the sample. After the experiments, the fractionation behavior of elements of titanite during the laser ablation were compared for using different fractionation correction methods to correct zircon, monazite and titanite separately. These correction methods were based on different mathematical model such as quadratic curve, power function and so on. The data was processed with different softwares such as GLITTER and BUSTER based on different mathematical equations, in order to look for the appropriate correction methods for different uranium-rich minerals based on different fractionation characteristics. RESULTSThe inconsistent fractionation behavior of elements between different titanite particles was revealed. After comparison, it was proposed that the 'Exponential Function Method' and the 'Average Data method' can only be used for uranium-rich minerals minerals that have consistent fractionation behavior, but it was not pragmatic for inconsistent ones. For these uranium-rich minerals minerals such as tianite, the 'Intercept Method' was an improvement on the current method, in order to ascertain the correct age. CONCLUSIONSIt is indicated that the 'Intercept Method' can avoid inaccurate correction caused by inconsistent fractionation behavior. -
Key words:
- titanite /
- LA-ICP-MS /
- U-Pb age /
- element fractionation /
- fractionation behavior /
- intercept method
-

-
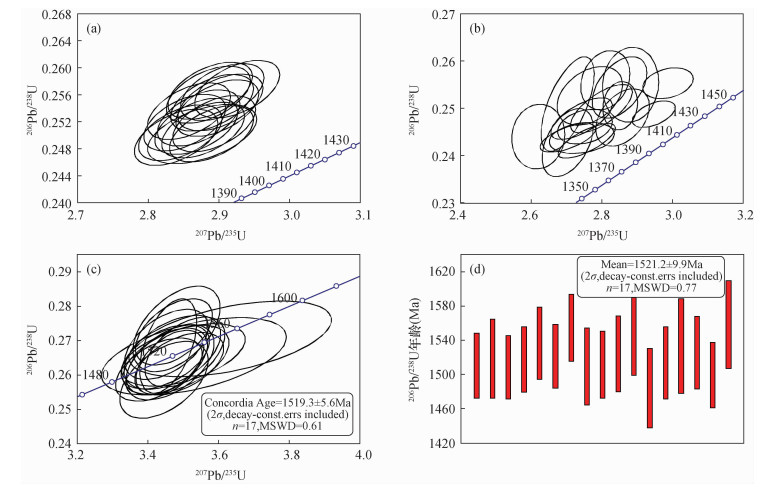
图 4 榍石标准样品MKED1年龄分析结果:(a)“均值法”校正数据谐和图;(b)“指数法”校正数据谐和图;(c)“截距法”校正数据谐和图;(d)“截距法”校正数据206Pb-238U加权平均年龄图[37]
Figure 4.
表 1 LA-ICP-MS主要工作参数
Table 1. Main working parameters of LA-ICP-MS
激光剥蚀系统分析参数 电感耦合等离子体质谱仪分析参数 能量密度(J/cm2) 6 射频发射功率(W) 1450 频率(Hz) 5 采样深度(mm) 5.5 单脉冲能量(mJ) 80 载气流量(L/min) 0.71 氦气流量(mL/min) 800 Torch-H(mm) -0.21 斑束直径(μm) 24 Torch-V(mm) -0.11 表 2 锆石、独居石和榍石样品206Pb/238U元素分馏因子
Table 2. Element fractionation factor of 206Pb/238U for zircon, monazite and titanite samples
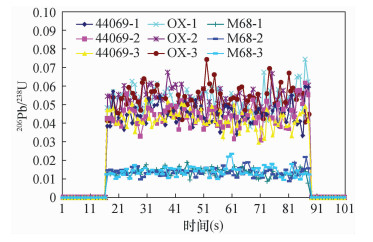
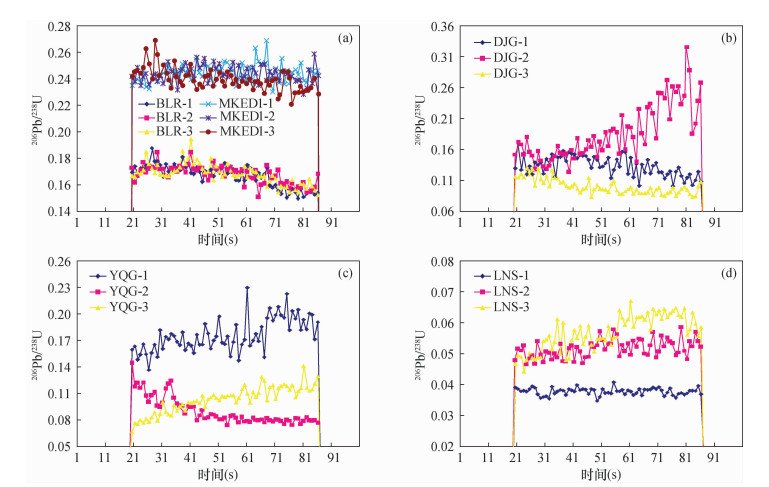
矿物种类 样品编号 分馏因子 锆石 915-1 1.12 锆石 915-2 1.13 锆石 915-3 1.14 锆石 GJ-1 1.10 锆石 GJ-2 1.10 锆石 GJ-3 1.10 锆石 H-1 1.10 锆石 H-2 1.22 锆石 H-3 1.12 独居石 44069-1 0.95 独居石 44069-2 0.96 独居石 44069-3 0.89 独居石 OX-1 0.93 独居石 OX-2 0.94 独居石 OX-3 1.06 独居石 M68-1 0.96 独居石 M68-2 0.98 独居石 M68-3 1.06 榍石 BLR-1 0.93 榍石 BLR-2 0.95 榍石 BLR-3 0.95 榍石 MKED1-1 1.01 榍石 MKED1-2 0.99 榍石 MKED1-3 0.98 榍石 YQG-1 1.12 榍石 YQG-2 0.79 榍石 YQG-3 1.24 榍石 LNS-1 1.00 榍石 LNS-2 1.05 榍石 LNS-3 1.16 榍石 DJG-1 0.87 榍石 DJG-2 1.43 榍石 DJG-3 0.88 表 3 老牛山榍石样品U-Pb定年数据
Table 3. U-Pb dating data of titanite from Laoniushan
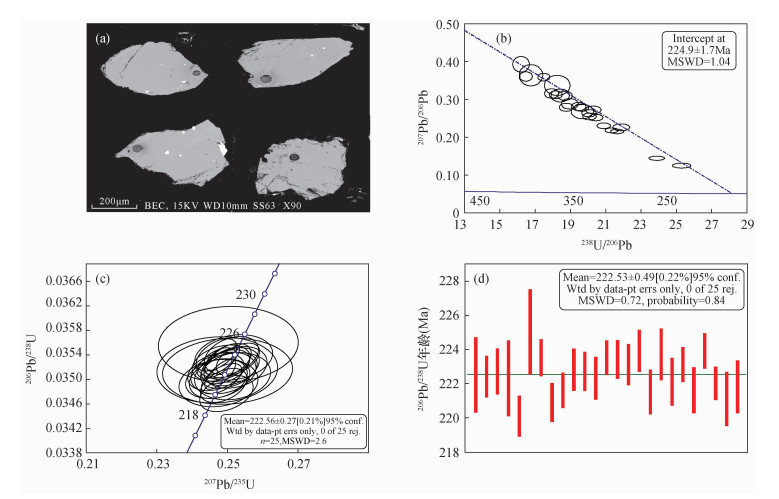
样品编号 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) Th/U 207Pb/235U ±2σ 207Pb/206Pb ±2σ 206Pb/238U ±2σ 207Pb/235U ±2σ 207Pb/206Pb ±2σ 206Pb/238U ±2σ LNS-1 2.0279 0.0717 0.2880 0.0114 0.0511 0.0011 1125 24 3407 60 321 7 4.18 LNS-2 1.5281 0.0232 0.2389 0.0038 0.0464 0.0006 942 9 3113 25 292 3 3.69 LNS-3 2.4669 0.0699 0.3274 0.0105 0.0547 0.0011 1262 20 3605 48 343 6 4.89 LNS-4 1.8544 0.0333 0.2735 0.0053 0.0492 0.0007 1065 12 3326 30 310 4 3.88 LNS-5 2.4246 0.0493 0.3266 0.0074 0.0538 0.0008 1250 15 3601 34 338 5 4.64 LNS-6 1.0037 0.0192 0.1736 0.0035 0.0419 0.0005 706 10 2593 33 265 3 1.68 LNS-7 3.4678 0.0913 0.4037 0.0126 0.0623 0.0013 1520 21 3923 46 390 8 4.13 LNS-8 1.9058 0.0342 0.2763 0.0054 0.0500 0.0007 1083 12 3342 30 315 4 4.30 LNS-9 2.1051 0.0387 0.2981 0.0060 0.0512 0.0007 1151 13 3460 31 322 4 4.25 LNS-10 1.9612 0.0374 0.2839 0.0059 0.0501 0.0007 1102 13 3385 32 315 4 3.86 LNS-11 2.9569 0.0455 0.3726 0.0063 0.0576 0.0008 1397 12 3802 25 361 5 4.52 LNS-12 1.5686 0.0231 0.2418 0.0037 0.0471 0.0006 958 9 3132 24 296 3 3.76 LNS-13 1.6780 0.0270 0.2532 0.0043 0.0481 0.0006 1000 10 3205 27 303 4 2.95 LNS-14 3.1227 0.1236 0.3767 0.0173 0.0601 0.0016 1438 30 3818 68 377 10 4.54 LNS-15 2.2435 0.0557 0.3068 0.0085 0.0530 0.0009 1195 17 3505 42 333 6 3.94 LNS-16 2.5732 0.0537 0.3322 0.0077 0.0562 0.0009 1293 15 3627 35 352 5 3.42 LNS-17 2.2066 0.0446 0.2985 0.0066 0.0536 0.0008 1183 14 3463 34 337 5 3.12 LNS-18 3.1525 0.0579 0.3738 0.0076 0.0612 0.0009 1446 14 3807 31 383 5 4.39 LNS-19 1.5754 0.0322 0.2490 0.0055 0.0459 0.0007 961 13 3178 35 289 4 2.53 LNS-20 2.5158 0.0440 0.3293 0.0063 0.0554 0.0008 1277 13 3614 29 348 5 3.87 LNS-21 0.8494 0.0201 0.1557 0.0039 0.0396 0.0006 624 11 2409 42 250 3 0.79 LNS-22 2.6741 0.1078 0.3517 0.0163 0.0552 0.0015 1321 30 3714 69 346 9 4.29 LNS-23 2.1411 0.0430 0.3006 0.0066 0.0517 0.0008 1162 14 3473 34 325 5 4.19 LNS-24 1.9925 0.0394 0.2921 0.0063 0.0495 0.0007 1113 13 3429 33 311 4 2.39 -
[1] 钟玉芳, 马昌前.含U副矿物的地质年代学研究综述[J].地球科学进展, 2006, 21(4):372-382. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.04.006
Zhong Y F, Ma C Q.A review of geochronology of U-bearing accessory minerals[J].Advance in Earth Science, 2006, 21(4):372-382. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.04.006
[2] 范晨子, 胡明月, 赵令浩, 等.锆石铀-铅定年激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱原位微区分析进展[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(1):29-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.01.004 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120105
Fan C Z, Hu M Y, Zhao L H, et al.Advances in situ microanalysis of U-Pb zircon geochronology using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(1):29-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.01.004 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120105
[3] 孙金凤, 杨进辉.含U副矿物的原位微区U-Pb定年方法[J].吉林大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(4):630-649. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb200904005
Sun J F, Yang J H.A review of in situ U-Pb dating methods for the accessory U-bearing minerals[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2009, 39(4):630-649. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb200904005
[4] 孙金凤, 杨进辉, 吴福元, 等.榍石原位微区LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄测定[J].科学通报, 2012, 57(18):1603-1615. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201218002.htm
Sun J F, Yang J H, Wu F Y, et al.In situ U-Pb dating of titanite by LA-ICPMS[J].China Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(20):2506-2516. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201218002.htm
[5] 向华, 张利, 钟增球, 等.榍石:U-Pb定年及变质P-T-t轨迹的建立[J].地球科学进展, 2007, 22(12):1258-1267. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.12.006
Xiang H, Zhang L, Zhong Z Q, et al.Titanite:U-Pb dating and applications on defining P-T-t path of meta morphic rocks[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(12):1258-1267. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.12.006
[6] 周玲棣, 王扬传.碱性岩中磷灰石、榍石和锆石的稀土元素地球化学特征[J].地球化学, 1988, 9(3):224-233. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1988.03.004
Zhou L D, Wang Y C.REE geochemical characteristics of apatite, sphene and ziron from alkaline rocks[J].Geochimica, 1988, 9(3):224-233. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1988.03.004
[7] 刘春花, 吴才来, 雷敏, 等.环带钾长石、榍石和锆石的显微结构与微区组成特征分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(8):2235-2241. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)08-2235-07
Liu C H, Wu C L, Lei M, et al.The characteristics of microstructure and chemical compositions of K-feldspar, sphene and zircon with zoing structure[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 33(8):2235-2241. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)08-2235-07
[8] 潘会彬, 康志强, 杨锋, 等.粤北大宝山次英安斑岩中副矿物榍石的初步研究[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(3):44-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201403005
Pan H B, Kang Z Q, Yang F, et al.Preliminary study on the accessory mineral of sphene in dacite porphyry from Dabaoshan, Northern Guangdong Province[J].Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(3):44-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201403005
[9] 朱乔乔, 谢桂青, 蒋宗胜, 等.湖北金山店大型矽卡岩型铁矿热液榍石特征和原位微区LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(5):1322-1338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201405010.htm
Zhu Q Q, Xie G Q, Jiang Z S, et al.Characteristics and in situ U-Pb dating of hydrothermal titanite by LA-ICPMS of the Jingshandian iron skarn deposit, Hubei Province[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(5):1322-1338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201405010.htm
[10] 赵令浩, 曾令森, 高利娥, 等.岩浆与变质榍石的微量元素特征及其对花岗质岩浆形成与演化的影响[C]//2016中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集.北京: 2089-2090.
Zhao L H, Zeng L S, Gao L E.Trace Element Characteristics of Magma and Metamorphic Spites and Their Effects on the Formation and Evolution of Granitic Magma[C]//Proceedings of 2016 Annual Meeting of Chinese Geoscience Union.Beijing: 2089-2090.
[11] 李秋立, 赵磊, 张艳斌, 等.朝鲜甑山"群"变质岩中锆石-榍石-金红石U-Pb体系:古元古代-中生代构造-热事件记录[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(10):3019-3032. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201610008.htm
Li Q L, Zhao L, Zhang Y B, et al.Zircon-titanite-rutile U-Pb system from metamorphic rocks of Jungshan "Group" in Korea:Implications of tectonotermal events from Paleoproterozoic to Mesozoic[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(10):3019-3032. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201610008.htm
[12] Simonetti A, Heaman L M, Chacko T, et al.In situ petrographic thin section U-Pb dating of zircon, monazite, and titanite using laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS[J].International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2006, 253:87-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2006.03.003
[13] Storey C D, Jeffries T E, Smith M.Common lead-corrected laser ablation ICP-MS U-Pb systematics and geochronology of titanite[J].Chemical Geology, 2006, 227:37-52. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.09.003
[14] 袁继海, 孙冬阳, 赵令浩, 等.榍石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年基体效应研究[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(增刊):351-355. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201608032
Yuan J H, Sun D Y, Zhao L H, et al.Research on matrix effect of in-situ U-Pb dating of titanite by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (LA-ICP-MS)[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(Supplement):351-355. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201608032
[15] 袁继海, 孙冬阳, 赵令浩, 等.榍石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年技术研究[J].地质学报, 2016, 90(8):2059-2069. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.08.032
Yuan J H, Sun D Y, Zhao L H, et al.In-situ U-Pb dating of titanite by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (LA-ICP-MS)[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(8):2059-2069. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.08.032
[16] Spandler C, Hammerli J, Sha P, et al.MKED1:A new titanite standard for in situ analysis of Sm-Nd isotopes and U-Pb geochronology[J].Chemical Geology, 2016, 425:110-126. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.01.002
[17] Wiedenbeck M, Alle P, Corfu F, et al.Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses[J].Geostandards Newsletter, 1995, 19(91):1-23. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229884972_Three_natural_zircon_standards_for_U-Th-Pb_Lu-Hf_trace_element_and_REE_analyses
[18] Woodhead J D, Hergt J M.A preliminary appraisal of seven natural zircon reference materials for in situ Hf isotope determination[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2005, 29(2):183-195. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2005.tb00891.x
[19] Wiedenbeck M, Hanchar J M, Peck W H, et al.Further characterisation of the 91500 zircon crystal[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(1):9-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb01041.x
[20] Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al.The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to in-situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J].Chemical Geology, 2004, 211:47-69. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.017
[21] Aleinikoff J N, Schenck W S, Plank M O, et al. Deciphering igneous and metamorphic events in high-grade rocks of the Wilmington Complex, Delaware:Morphology, cathodoluminescence and backscattered electron zoning, and SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of zircon and monazite[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006, 118(1/2):39-64. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/249527274_Deciphering_igneous_and_metamorphic_events_in_high-grade_rocks_of_the_Wilmington_Complex_Delaware_Morphology_cathodoluminescence_and_backscattered_electron_zoning_and_SHRIMP_UPb_geochronology_of_zircon_and_monazite
[22] 汪双双, 韩延兵, 李艳广, 等.利用LA-ICP-MS在16μm和10μm激光束斑条件下测定独居石U-Th-Pb年龄[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(4):349-357. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.003
Wang S S, Han Y B, Li Y G, et al.U-Th-Pb dating of monazite by LA-ICP-MS using ablation spot sizes of 16μm and 10μm[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(4):349-357. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.003
[23] Aleinikoff J N, Wintsch R P, Unruh D M, et al.Ages and origin of rocks of the Killingworth Dome, South-Central connecticut:Implications for the tectonic evolution of Southern New England[J].American Journal of Science, 2007, 307:63-118. doi: 10.2475/01.2007.04
[24] 周亮亮, 魏均启, 王芳, 等.LA-ICP-MS工作参数优化及在锆石U-Pb定年分析中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(4):350-359. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701160007
Zhou L L, Wei J J, Wang F, et al.Optimization of the working parameters of LA-ICP-MS and its application to zircon U-Pb dating[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(4):350-359. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701160007
[25] Jackson S E, Longerich H P, Dunning G R, et al.The application of laser-ablation microprobe-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LAM-ICP-MS) to in situ trace-element determinations in minerals[J].Canadian Mineralogist, 1992, 30:1049-1064.
[26] Horn I, Rudnick R L, McDonough W F.Precise elemental and isotope ratio determination by simultaneous solution nebulization and laser ablation-ICP-MS:Application to U-Pb geochronology[J].Chemical Geology, 2000, 164:281-301. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00168-0
[27] Kosler J, Sylvester P J.Present trends and the future of zircon in geochronology:Laser ablation ICPMS[J].Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1):243-275. doi: 10.2113/0530243
[28] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 257:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
[29] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z X, et al.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J].Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1-2):537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
[30] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al.Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
[31] Paton C, Woodhead J D, Hellstrom J C, et al.Improved laser ablation U-Pb zircon geochronology through robust downhole fractionation correction[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2010, 11:1-36. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035772567510_bd18.html
[32] 朱碧, 朱志勇, 吕苗, 等.Iolite软件处理LA-ICP-MS线扫描数据适用性研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1):14-21. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.003
Zhu B, Zhu Z Y, Lü M, et al.Application of iolite in data reduction of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry line-scan analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1):14-21. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.003
[33] Sylvester P J, Ghaderi M.Trace element analysis of scheelite by excimer laser-ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ELA-ICP-MS) using a synthetic silicate glass standard[J].Chemical Geology, 1997, 141:49-65. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00057-0
[34] Chang Z S, Vervoort J D, McClelland W C, et al.U-Pb dating of zircon by LA-ICP-MS[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(5):1-14. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2005GC001100/full
[35] Thomson S N, Gehrels G E, Ruiz J, et al.Routine low-damage apatite U-Pb dating using laser ablation-multicollector-ICP MS[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(1):1-23. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/264666909_Routine_low-damage_apatite_U-Pb_dating_using_laser_ablationmulticollectorICPMS
[36] 李艳广, 汪双双, 刘民武, 等.斜锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年方法及应用[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(12):2400-2418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.12.015
Li Y G, Wang S S, Liu M W, et al.U-Pb dating study of baddeleyite by LA-ICP-MS:Technique and application[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(12):2400-2418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.12.015
[37] Ludwig K R.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley Gerchronology Center Special Publication, 2003: 1-70.
[38] Tera F, Wasserburg G J.U-Th-Pb systematics in three Apollo 14 basalts and the problem of initial Pb in lunar rocks[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1972, 14:281-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(72)90128-8
[39] 齐秋菊, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等.华北地块南缘老牛山杂岩体时代、成因及地质意义——锆石年龄、Hf同位素和地球化学新证据[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(1):279-301. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201201021
Qi Q J, Wang X X, Ke C H, et al.Geochronology and origin of the Laoniushan complex in the southern margin of North China Block and their implications:New evidences from zircon dating, Hf isotopes and geochemistry[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(1):279-301. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201201021
[40] 李秋立.U-Pb定年体系特点和分析方法解析[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(3):491-500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.03.005
Li Q L.Characteristics and analytical methods of the U-Pb dating system[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(3):491-500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.03.005
[41] 陈文, 万渝生, 李华芹, 等.同位素地质年龄测定技术及应用[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(11):1917-1947. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201111009
Chen W, Wan Y S, Li H Q, et al.Isotope geochronology:Technique and application[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(11):1917-1947. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201111009
[42] 刘勇胜, 胡兆初, 李明, 等.LA-ICP-MS在地质样品元素分析中的应用[J].科学通报, 2018, 43(12):4269-4282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxjsqy-z201612100
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Li M, et al.Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the elemental analyses of geological samples[J].China Science Bulletin, 2018, 43(12):4269-4282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxjsqy-z201612100
-




 下载:
下载: