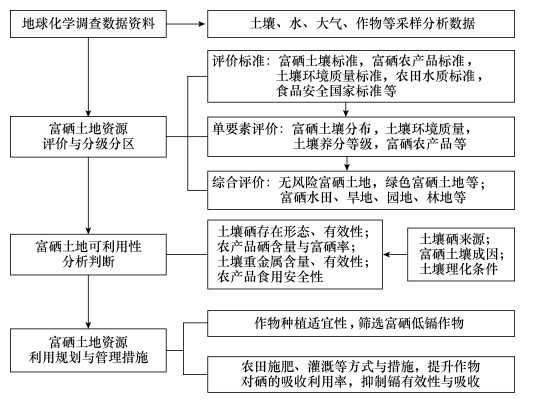
Research Progress of Selenium-enriched Land Resources and Evaluation Methods
-
摘要: 硒是重要的生命必需元素,开发富硒农产品是提升我国人体硒摄入水平的安全有效途径,富硒土地资源评价与利用规划是土地质量地球化学调查成果服务于特色农产品发展与脱贫攻坚的重要切入点。本文评述了近年来在土壤和作物硒含量、土壤硒成因来源、土壤硒赋存形态及其生物有效性影响因素、土壤-作物系统硒吸收运移、硒与重金属镉等元素之间的相互作用等调查研究成果。针对我国土壤硒背景值约0.20mg/kg,远低于世界土壤背景值0.40mg/kg,整体上处于低硒水平的实际情况,认为采用0.40mg/kg Se作为富硒土壤标准具有较强的科学依据;多数情况下土壤硒主要来源于成土地质背景,部分地区与人为活动密切有关;富硒土壤可分为地质高背景、次生富集作用、人为输入及其多种作用的叠加成因,元素地球化学性质决定了硒与镉等重金属元素共生的普遍性;土壤硒成因来源以及pH、Eh、有机质、铁铝氧化物等土壤理化条件决定了硒和重金属赋存形态与生物有效性,进而影响到富硒土地的可利用性,成为制定富硒土壤地方标准的理论基础与考虑因素;不同作物种类对硒吸收富集能力不同,筛选适应当地农田生态环境、富硒低镉的农作物具有实际意义;现有的部分富硒农产品标准未充分考虑人体补硒目的,并存在标准间协调性差等问题,急需加强富硒农产品标准的制定。本文提出,富硒土地资源评价不仅需要考虑土壤硒和重金属含量,而且需综合土壤硒成因来源及其生物有效性、土壤-作物系统硒迁移累积、硒与重金属镉等元素之间的相互作用机制,以及当地气候、土壤和景观条件下作物种植的适宜性,依据富硒土地资源可利用性进行分类分区、科学规划和合理种植管理。同时建议,为满足富硒土地资源调查评价与可利用性分析、富硒农产品健康效应研究的需要,需要加强土壤和作物硒含量及其形态的提取分离与分析测试方法技术研究与应用。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDSelenium is an important, essential element of life. The development of selenium-enriched agricultural products is a safe and effective way to increase the level of human selenium intake in China. The evaluation and utilization planning of selenium-enriched land resources are important aspects of land quality geochemical surveys, to serve the development of characteristic agricultural products and to overcome poverty. OBJECTIVESTo improve the methodology for selenium-enriched land assessment and to develop more effective and safe land-use planning methods. METHODSThe research results on selenium content in soil and crops, the origin of soil selenium, the soil selenium occurrence and its bioavailability factors, the soil-crop system selenium absorption and transport, and the interaction between selenium and heavy metal cadmium were reviewed in this article. RESULTSThe geochemical background of selenium in top soils in China was 0.2mg/kg, significantly lower than the average in world soils (0.4mg/kg). Generally, the soils had a low selenium level, and it was believed that the use of 0.40mg/kg selenium as a selenium-enriched soil standard had a strong scientific basis. Selenium in soils was mostly from a geological setting, however, in some cases anthropogenic activities may be an important source of soil selenium. The genetic mechanism of selenium-enriched soils can be categorized as high geological background, weathering accumulation and anthropogenic input as well as a multi-factor combination. The association of selenium with cadmium and other heavy metals was pervasive because of similar geochemical behavior and geological origin. The species and bio-availability of selenium in soils were mainly controlled by its source and soil physic-chemical properties such as pH, Eh, and contents of organic matter, iron oxides and aluminum oxides. In turn, these factors affect the availability of selenium-enriched land and became the theoretical basis and considerations for formulating local standards for selenium-enriched soil. The accumulation ability of selenium varied greatly between crop cultivars. Selection native crop types with higher selenium accumulation ability and low accumulation with Cd as well as other toxic metals was of practical meaning. Some existing selenium-enriched agricultural product standards did not fully consider the purpose of human selenium supplementation, and there were problems such as poor coordination between standards. It was urgent to strengthen the formulation of selenium-enriched agricultural product standards. CONCLUSIONSSelenium-enriched land suitability assessment, local selenium-enriched soil standard establishment and selenium-enriched crop plantation planning should consider the concentration of selenium and heavy metals in soils, their source and genesis, bio-availability and influencing factors, transport and accumulation in soil-crop system, the synergistic or antagonistic effects between selenium and other chemicals such as cadmium, as well as plantation suitability of crop cultivars under local climate, soil conditions and landscape. According to the availability of selenium-enriched land resources, classification, zoning, scientific planning and reasonable planting management are carried out. In order to meet the needs of investigation and evaluation of selenium-enriched land resources, availability analysis, and research on the health effects of selenium-enriched agricultural products, it is recommended to strengthen the research and application of extraction, separation, analysis, and determination methods for soil and crop selenium content and species. -

-
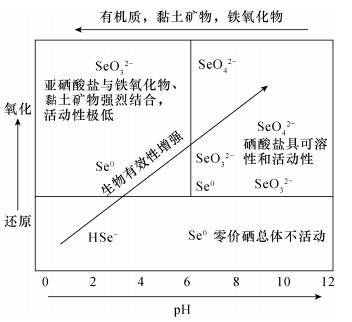
图 1 土壤硒化学形态及其生物有效性的主控因素(引自Fordyce,2013[4])
Figure 1.
-
[1] World Health Organization.Trace elements in human nutrition and health[M].Geneva:World Health Organization, 1996.
[2] Sharma V K, McDonald T J, Sohn M, et al.Assessment of toxicity of selenium and cadmium selenium quantum dots:A review[J].Chemosphere, 2017, 188:403-413. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004565351731353X
[3] Smits J E, Krohn R M, Akhtar E, et al.Food as med-icine:Selenium enriched lentils offer relief against chronic arsenic poisoning in Bangladesh[J].Environmental Research, 2019, 176:108561.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108561. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108561
[4] Fordyce F M.Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment[M]//Selinus O.Essentials of medical geology (revised edition).British Geological Survey, 2013: 373-416.
[5] 谭见安.中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M].北京:科学出版社, 1989.
Tan J A.The atlas of endemic diseases and their environments in the People's Republic of China[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1989.
[6] Dinh Q T, Cuia Z W, Huang J, et al.Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health:A review[J].Environment International, 2018, 112:294-309.
[7] Dai Z H, Imtiaz M, Rizwan M, et al.Dynamics of sele-nium uptake, speciation, and antioxidant response in rice at different panicle initiation stages[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 691:827-834.
[8] Andrade F R, da Silva G N, Guimarães K C, et al.Selenium protects rice plants from water deficit stress[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 164:562-570. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b15c712a4fa2e381ed129545e16fd6af
[9] Ulhassan Z, Ali G R, Skhawat A, et al.Dual behavior of selenium:Insights into physico-biochemical, an atomical and molecular analyses of four Brassica napus cultivars[J].Chemosphere, 2019, 225:329-341. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653519304643
[10] Kolbert Z, Molnár Á, Feigl G, et al.Plant selenium toxicity:Proteome in the crosshairs[J].Journal of Plant Physiology, 2019, 232:291-300. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0176161718306370
[11] 国土资源部中国地质调查局.中国耕地地球化学调查报告(2015年)[R].北京: 中国地质调查局, 2015.
China Geological Survey, Ministry of Land and Resources.Geochemical survey report of cultivation land in China (2015)[R].Beijing: China Geological Survey, 2015.
[12] 王云, 魏复盛.土壤环境元素化学[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1995:217-230.
Wang Y, Wei F S.Environmental element chemistry in soil[M].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press, 1995:217-230.
[13] Reimann C, Birke M, Demetriades A, et al.Chemistry of Europe's agricultural soils-Part A: Methodology and interpretation of the GEMAS data set[R].Hannover, 2014: 389-399.
[14] Swaine J D.The trace-element content of soil[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 1956, 101(12):28615-28625. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201606020
[15] 魏复盛, 吴燕玉, 郑春江, 等.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
Wei F S, Wu Y Y, Zheng C J, et al.Soil element background in China[M].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
[16] 鄢明才, 迟清华.中国东部地壳与岩石的化学组成[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997.
Yan M C, Chi Q H.Crustal and rock chemical component in East China[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1997.
[17] 王学求, 刘东盛, 韩志轩, 等.全国地球化学基准网建立与土壤地球化学基准值特征[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(5):1469-1480. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201605001
Wang X Q, Liu D S, Han Z X, et al.China soil geochemical baselines networks:Data characteristics[J].Geology in China, 2016, 43(5):1469-1480. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201605001
[18] 杨光圻, 王淑贞, 周瑞华, 等.湖北恩施地区原因不明脱发脱甲症病因的研究[J].中国医学科学院学报, 1981(增刊):1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1981-ZYKX1981S2000.htm
Yang G Q, Wang S Z, Zhou R H, et al.Study on the cause of unknown alopecia and fingernail loose in Enshi, Hubei[J].Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae, 1981(Supplement):1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1981-ZYKX1981S2000.htm
[19] 徐春燕, 丁晓英, 闫加力.湖北省富硒资源的地质特征及利用区划[J].世界地质, 2018, 37(1):340-347. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjdz201801012
Xu C Y, Ding X Y, Yan J L.Geological characteristics and usage regionalization of Se-enriched resources in Hubei[J].Global Geology, 2018, 37(1):340-347. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjdz201801012
[20] 袁知洋, 项剑桥, 吴冬妹, 等.恩施富硒土壤区主要农作物硒镉特征以及和根系土硒镉关系研究[J].资源环境与工程, 2017, 31(6):706-712. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdk201706008
Yuan Z Y, Xiang J Q, Wu D M, et al.The characteristics of selenium and cadmium in crops and its root soil in the area of Se and Cd-enriched soil in Enshi[J].Resources Environment and Engineering, 2017, 31(6):706-712. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdk201706008
[21] Fang W X, Wu P W.Elevated selenium and other min-eral element concentrations in soil and plant tissue in bone coal sites in Haoping area, Ziyang County, China[J].Plant and Soil, 2004, 261:135-146.
[22] 黄森.贵州地区富硒土壤地球化学特征及成因探讨[J].云南化工, 2018, 45(7):147-148. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ynhg201807063
Huang S.Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Se rich soil in Guizhou area[J].Yunnan Chemical Technology, 2018, 45(7):147-148. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ynhg201807063
[23] 任海利, 高军波, 龙杰, 等.贵州开阳地区富硒地层及风化土壤地球化学特征[J].地球与环境, 2012, 40(2):161-170. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx201202005
Ren H L, Gao J B, Long J, et al.Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich strata and weathered soil from Kaiyang County, Guizhou Province[J].Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(2):161-170. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx201202005
[24] 罗思亮.台山市土壤Se来源的研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(12):5333-5334. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHNY201312058.htm
Luo S L.Source analysis of selenium in soil in Taishan City[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2013, 41(12):5333-5334. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHNY201312058.htm
[25] 宋明义, 李恒溪, 魏迎春, 等.浙江省龙游志棠地区硒的地球化学研究[J].贵州地质, 2005, 22(3):176-180. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzdz200503006
Song M Y, Li H X, Wei Y C, et al.Geochemistry of the selenium, Zhitang Town, Longyou County, Zhejiang Province[J].Guizhou Geology, 2005, 22(3):176-180. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzdz200503006
[26] 吴俊.福建省寿宁县富硒土壤地球化学特征[J].物探与化探, 2018, 42(2):386-391. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201802024
Wu J.Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Shouning County of Fujian Province[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2):386-391. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201802024
[27] 杨生吉.福建周宁县表层土壤硒含量分布及影响因素[J].资源环境与工程, 2019, 33(1):42-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdk201901008
Yang S J.Distribution of soil selenium in Zhouning County of Fujian and its influencing factors[J].Resources Environment and Engineering, 2019, 33(1):42-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdk201901008
[28] 李兆谊, 罗映林, 赵喜林, 等.桂东南地区兴业县富Se土壤地球化学特征及来源浅析[J].南方农业, 2018, 12(20):189-191. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nfny201820097
Li Z Y, Luo Y L, Zhao X L, et al.Selenium-rich geochemical characteristics and source discussion in south-east Guangxi, Xingyue County[J].South China Agriculture, 2018, 12(20):189-191. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nfny201820097
[29] 黄子龙, 林清梅, 范汝海.广西全州县富硒土壤地球化学特征[J].物探与化探, 2018, 42(2):381-385. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201802023
Huang Z L, Lin Q M, Fan R H.Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Quanzhou County of Guangxi[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2):381-385. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201802023
[30] Tabelin C B, Igarashi T, Villacorte-Tabelin M, et al.Arsenic, selenium, boron, lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc in naturally contaminated rocks:A review of their sources, modes of enrichment, mechanisms of release, and mitigation strategies[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 645:1522-1553. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969718325476
[31] Xu Y F, Li Y H, Li H R, et al.Effects of topography and soil properties on soil selenium distribution and bioavailability (phosphate extraction):A case study in Yongjia County, China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633:240-248. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969718309495
[32] Mervi S, Juhani V, Stellan H, et al.Sorption and speci-ation of selenium in boreal forest soil[J].Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2016, 64:220-231. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27521902
[33] 陈秋菊, 甘义群, 张若雯.江汉平原沙洋地区表层土壤中硒的分布特征及富硒原因分析[J].安全与环境工程, 2019, 26(4):8-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzktaq201904003
Chen Q J, Gan Y Q, Zhang R W.Distribution characteristics of selenium in surface soil of Shayang area in Jianghan Plain and the cause analysis of selenium richness[J].Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2019, 26(4):8-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzktaq201904003
[34] Matos R P, Lima V M P, Windmöller C C, et al.Correlation between the natural levels of selenium and soil physicochemical characteristics from the Jequitinhonha Valley (MG), Brazil[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 172:195-202. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=21a5a4ae012b866562d2815ff15313ab
[35] 杨志强, 李杰, 郑国东, 等.广西北部湾沿海经济区富硒土壤地球化学特征[J].物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1260-1264, 1269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201406030
Yang Z Q, Li J, Zheng G D, et al.Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Beibu Gulf coastal economic zone of Guangxi[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6):1260-1264, 1269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201406030
[36] 韩笑, 周越, 吴文良, 等.富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系——以江西丰城为例[J].农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201806018
Han X, Zhou Y, Wu W L, et al.Selenium contents of farmland soils and their relationship with main soil properties in Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201806018
[37] 周国华, 孙彬彬, 方金梅.福建龙海生态地球化学研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2018:169.
Zhou G H, Sun B B, Fang J M.Eco-geochemistry research in Longhai, Fujian Province[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2018:169.
[38] 曹容浩.福建省龙海市表层土壤硒含量及影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):282-288. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201606130084
Cao R H.Study on selenium content of surface soils in Longhai, Fujian and its influencing factors[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):282-288. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201606130084
[39] 方金梅.福州市土壤硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(2):103-107. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080238
Fang J M.Selenium speciation analysis and its transformation and enrichment in soils of Fuzhou City[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(2):103-107. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080238
[40] Li Z, Liang D L, Peng Q, et al.Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability:A review[J].Geoderma, 2017, 295:69-79. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0016706116305018
[41] Cheng H X, Li M, Zhao C D, et al.Overview of trace metals in the urban soil of 31 metropolises in China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139:31-52. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7ec857151ed5b7b54c611ee72486c68a
[42] 张秀芝, 马忠社, 王荫楠, 等.河北平原土壤Se异常成因及其生态效应[J].地球与环境, 2012, 40(4):541-547. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZDQ201204013.htm
Zhang X Z, Ma Z S, Wang Y N, et al.The origin and ecological effects of selenium abnormity in soil in Hebei Plain[J].Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(4):541-547. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZDQ201204013.htm
[43] 谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等.天津市蓟州区富硒土壤成因与土壤硒来源研究[J].物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1373-1381. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201906026
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y, et al.Studies on causes and influential factors of selenium-enriched soils in Jizhou District of Tianjin[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1373-1381. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201906026
[44] Shaheen S M, Kwon E E, Biswas J K, et al.Arsenic, chromium, molybdenum, and selenium:Geochemical fractions and potential mobilization in riverine soil profiles originating from Germany and Egypt[J].Chemosphere, 2017, 180:553-563. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0045653517305908
[45] Tolu J, Tullo P D, Hécho I L, et al.A new methodology involving stable isotope tracer to compare simultaneously short- and long-term selenium mobility in soils[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2014, 406:1221-1231. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=edc68c25eb7148dee69c569aa0790c5b
[46] Di T P, Pannier F, Thiry Y, et al.Field study of time-dependent selenium partitioning in soils using isotopically enriched stable selenite tracer[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 562:280-288. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8bc23d3cb009f492bb988bf38b4523e1
[47] Li J, Peng Q, Liang D L, et al.Effects of aging on the fraction distribution and bioavailability of selenium in three different soils[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 144:2351-2359. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9367c2f16a801e8f9d250b836a3d20a0
[48] Almahayni T, Bailey E, Crout N M J, et al.Effects of incubation time and filtration method on Kd of indigenous selenium and iodine in temperate soils[J].Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2017, 177:84-90.
[49] Jia M M, Zhang Y X, Huang B, et al.Source appor-tionment of selenium and influence factors on its bioavailability in intensively managed greenhouse soil:A case study in the east bank of the Dianchi Lake, China[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 170:238-245.
[50] Statwick J, Sher A A.Selenium in soils of western Colorado[J].Journal of Arid Environments, 2017, 137:1-6. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140196316301811
[51] 郝应龙, 李崇博, 安永刚, 等.乌鲁木齐市某蔬菜基地富硒土壤地球化学特征及生物效应研究[J].新疆地质, 2019, 37(2):167-171. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjdz201902004
Hao Y L, Li C B, An Y G, et al.Study on geochemical characteristics and bio-effects of selenium-rich soil in a vegetable base in Urumqi, Xinjiang[J].Xinjiang Geology, 2019, 37(2):167-171. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjdz201902004
[52] Joy E J M, Broadley M R, Young S D, et al.Soil type influences crop mineral composition in Malawi[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 505:587-595. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bb7a1cd293c0e4300bbb6012115fd08a
[53] Silva J E C, Wadt L H O, Silva K E, et al.Natural variation of selenium in Brazil nuts and soils from the Amazon Region[J].Chemosphere, 2017, 188:650-658. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c5cd845ab18fd63c22402f3fd7979115
[54] 尹宗义, 任蕊, 晁旭, 等.三原-阎良地区富硒土壤中硒形态特征研究[J].陕西地质, 2016, 34(1):31-37. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=ZXQX201602230
Yin Z Y, Ren R, Chao X, et al.Selenium speciation in selenium-rich soil of Sanyuan-Yanliang Area[J].Geology of Shaanxi, 2016, 34(1):31-37. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=ZXQX201602230
[55] 杨奎, 李湘凌, 张敬雅, 等.安徽庐江潜在富硒土壤硒生物有效性及其影响因素[J].环境科学研究, 2018, 31(4):715-724. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxyj201804014
Yang K, Li X L, Zhang J Y, et al.Selenium bioavailability and the influential factors in potentially selenium enriched soils in Lujiang County, Anhui Province[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(4):715-724. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxyj201804014
[56] Supriatin S, Weng L P, Comans R N J.Selenium speciation and extractability in Dutch agricultural soils[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 532:368-382. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2cc428ada54a92cff6da00c8c64cd5f3
[57] Fordyce F M, Brereton N, Hughes J, et al.An initial study to assess the use of geological parent materials to predict the Se concentration in overlying soils and in five staple foodstuffs produced on them in Scotland[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(22):5295-5305. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1b4c41d3811354b30356583d4f324872
[58] Supriatin S, Weng L P, Comans R N J.Selenium-rich dissolved organic matter determines selenium uptake in wheat grown on low-selenium arable land soils[J].Plant Soil, 2016, 408:73-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ef6fb5905782569263b15a3986e70874
[59] Chistophersen O A, Lyons G, Haug A, et al.Selenium[M]//Alloway B J.Heavy metals in soils: Tarce metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability.Springer Science, 2013: 429-463.
[60] Dinh Q T, Li Z, Tran T A T, et al.Role of organic acids on the bioavailability of selenium in soil:A review[J].Chemosphere, 2017, 184:618-635. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28624740
[61] Chang C Y, Yin R S, Wang X, et al.Selenium translocation in the soil-rice system in the Enshi seleniferous area, central China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 669:83-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=790ae9d421d2cb0c71ae69033e30ac91
[62] Xiao K C, Tang J J, Chen H, et al.Impact of land use/land cover change on the topsoil selenium concentration and its potential bioavailability in a karst area of southwest China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 708:1-8. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969719351939
[63] Wang D, Dinh Q T, Thu T T A, et al.Effect of selenium-enriched organic material amendment on selenium fraction transformation and bioavailability in soil[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 199:417-426. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=61990379ebd79879307b56e3f583720f
[64] Supriatin S, Terrones C A, Bussink W, et al.Drying effects on selenium and copper in 0.01M calcium chloride soil extractions[J].Geoderma, 2015, 255-256:104-114. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fc6c5edf02608cb7ad163004b68bf11f
[65] Lessa J H L, Araujo A M, Silva G N T, et al.Adsorption-desorption reactions of selenium(Ⅵ) in tropical cultivated and uncultivated soils under Cerrado biome[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 164:271-277.
[66] 姜超强, 沈嘉, 祖朝龙.水稻对天然富硒土壤硒的吸收及转运[J].应用生态学报, 2015, 26(3):809-816. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201503022
Jiang C Q, Shen J, Zu C L.Selenium uptake and transport of rice under different Se-enriched natural soils[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(3):809-816. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201503022
[67] 李瑜.安康富硒土壤中不同农作物富硒能力比较研究[J].陕西农业科学, 2015, 61(11):13-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxnykx201511003
Li Y.Comparison on Se uptake ability of different crops in Se-rich soil at Ankong[J].Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 61(11):13-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxnykx201511003
[68] 李正文, 张艳玲, 潘根兴, 等.不同水稻品种籽粒Cd、Cu和Se的含量差异及其人类膳食摄取风险[J].环境科学, 2003, 24(3):112-115. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx200303022
Li Z W, Zhang Y L, Pan G X, et al.Grain contents of Cd, Cu and Se by 57 rice cultivars and the risk significance for human dietary uptake[J].Environmental Science, 2003, 24(3):112-115. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx200303022
[69] 王家伟, 陈雄波, 黄起东, 等.不同水稻品种对硒的吸收转化试验[J].农业工程, 2016, 6(4):82-84. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nygch201604027
Wang J W, Chen X B, Huang Q D, et al.Test on absorption and transformation of selenium in different rice varieties[J].Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 6(4):82-84. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nygch201604027
[70] Natasha, Shahid M, Niazi N K, et al.A critical review of selenium biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system with an inference to human health[J].Environmental Pollution, 2018, 234:915-934. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5debd9cfc7370ab143540aafe16e32da
[71] 姜超强, 沈嘉, 徐经年, 等.不同富硒土壤对烤烟生长及硒吸收转运的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2014, 34(11):2303-2308. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201411021
Jiang C Q, Shen J, Xu J N, et al.Effects of Se-enriched soils on the plant growth, selenium uptake and transport in flue-cured tobacco[J].Acta Botany Boreal-Occident Sinica, 2014, 34(11):2303-2308. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201411021
[72] 王雅玲, 潘根兴, 刘洪莲, 等.皖南茶区土壤硒含量及其与茶叶中硒的关系[J].农业生态环境, 2005, 21(2):54-57. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj200502012
Wang Y L, Pan G X, Liu H L, et al.Soil and tea selenium in tea gardens in south Anhui[J].Rural Eco-Environment, 2005, 21(2):54-57. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj200502012
[73] Miguel N A, Carmen C V.Selenium in food and the human body:A review[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 400:115-141. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_684a79b215da568e22abd01c52158e7b
[74] Yin H Q, Qi Z Y, Li M Q, et al.Selenium forms and methods of application differentially modulate plant growth, photosynthesis, stress tolerance, selenium content and speciation in Oryza sativa L.[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 169:911-917. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30597791
[75] Shultz C D, Bailey R T, Gates T K, et al.Simulating selenium and nitrogen fate and transport in coupled stream-aquifer systems of irrigated regions[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 560:512-529. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=021279d571e489abde1e015aeeb24aba
[76] de Feudis M, D'Amato R, Businelli D, et al.Fate of selenium in soil:A case study in a maize (Zea mays L.) field under two irrigation regimes and fertilized with sodium selenite[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 659:131-139.
[77] Hussein H A A, Darwesh O M, Mekki B B, et al.Evaluation of cytotoxicity, biochemical profile and yield components of groundnut plants treated with nano-selenium[J].Biotechnology Reports, 2019, 24.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00377. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00377
[78] Ullah H, Liu G J, Yousaf B, et al.Developmental sele-nium exposure and health risk in daily foodstuffs:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 149:291-306. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0147651317308096
[79] 郑小江, 胡蔚红, 孙必发, 等.富硒食品标准标签研究[J].中国标准化, 2003(5):19-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgbzh200305009
Zheng X J, Hu W H, Sun B F, et al.Study on the standard and label of selenium-rich food[J].Standardization in China, 2003(5):19-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgbzh200305009
[80] 辜世伟, 胡云均, 刘方菁, 等.不同加工精度对稻谷中镉含量的影响[J].中国粮油学报, 2019(8):33-39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zglyxb201908003
Gu S W, Hu Y J, Liu F J, et al.Effect of different processing precision on cadmium content in paddy rice[J].Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oil Association, 2019(8):33-39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zglyxb201908003
[81] World Health Organization.Environmental health criterion 58-Selenium[R].Geneva: World Health Organization, 1987.
[82] Liang R Y, Shuai S A, Shi Y J, et al.Comprehensive assessment of regional selenium resources in soils based on the analytic hierarchy process:Assessment system construction and case demonstration[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 605-606:618-625. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969717315693
[83] Zhou X B, Li Y Y, Lai F.Effects of different water management on absorption and accumulation of selenium in rice[J].Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2018, 25:1178-1182. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqsystbcxb201801051
[84] Wang D, Xue M Y, Wang Y K, et al.Effects of straw amendment on selenium aging in soils:Mechanism and influential factors[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 657:871-881. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969718348617
[85] 宋明义, 黄春雷, 董岩翔, 等.浙江富硒土壤成因分类及开发利用现状[J].上海地质, 2010, 31(增刊1):107-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/shdz2010z1028
Song M Y, Huang C L, Dong Y X, et al.Genetic classification and utilization situation of selenium-rich soil in Zhejiang Province[J].Shanghai Geology, 2010, 31(Supplement 1):107-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/shdz2010z1028
[86] 谢邦廷, 贺灵, 江官军, 等.中国南方典型富硒区土壤硒有效性调控实验[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
Xie B T, He L, Jiang G J, et al.Regulation and evaluation of selenium availability in Se-rich soils in southern China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
[87] Shahid M A, Balal R M, Khan N, et al.Selenium impedes cadmium and arsenic toxicity in potato by modulating carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 180:588-599. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0147651319305780
[88] Ren M M, Qin Z J, Li X, et al.Selenite antagonizes the phytotoxicity of Cd in the cattail Typha angustifolia[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109959.
[89] Dai H P, Wei S H, Skuza L D, et al.Selenium spiked in soil promoted zinc accumulation of Chinese cabbage and improved its antioxidant system and lipid peroxidation[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 180:179-184. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0147651319305469
[90] Anirban B, Saroni B, Arabinda D, et al.Spatial vari-ability and competing dynamics of arsenic, selenium, iron and bioavailable phosphate from ground water and soil to paddy plant parts[J].Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2018, 7:328-335.
[91] 王建伟, 王朝辉, 毛晖, 等.硒锌钼对黄土高原马铃薯和小白菜产量及营养元素与硒镉含量的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(11):2114-2120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NHBH201211010.htm
Wang J W, Wang Z H, Mao H, et al.Effect of Se, Zn and Mo on yield and contents of nutrient elements and selenium and cadmium of potato and cabbage on the loess plateau[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(11):2114-2120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NHBH201211010.htm
[92] 梁程, 林匡飞, 张雯, 等.不同浓度硫处理下硒镉交互胁迫对水稻幼苗的生理特性影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(5):857-866. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201205002
Liang C, Lin K F, Zhang W, et al.Effects of sulfur and selenium treatment on plant growth and some physiological characteristics of rice under cadmium stress[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(5):857-866. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201205002
[93] 铁梅, 刘阳, 李华为, 等.硒镉处理对萝卜硒镉吸收的影响及其交互作用[J].生态学杂志, 2014, 33(6):1587-1593. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201406024
Tie M, Liu Y, Li H W, et al.Uptake of Se and Cd in radish and their effects on growth[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(6):1587-1593. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201406024
[94] Zhang Z Z, Yuan L X, Qi S H, et al.The threshold effect between the soil bioavailable molar Se:Cd ratio and the accumulation of Cd in corn (Zeamays L.) from natural Se-Cd rich soils[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 688:1228-1235.
[95] Feng R W, Wei C Y, Tu S X, et al.A dual role of Se on Cd toxicity:Evidences from the uptake of Cd and some essential elements and the growth responses in paddy rice[J].Biology Trace Element Resource, 2013, 151:113-121.
[96] Li Y Y, Hu W J, Zhao J T, et al.Selenium decreases methylmercury and increases nutritional elements in rice growing in mercury-contaminated farmland[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 182:109447.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109447. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S014765131930778X
[97] Wang X N, Wang S, Pan X L, et al.Heteroaggregation of soil particulate organic matter and biogenic selenium nanoparticles for remediation of elemental mercury contamination[J].Chemosphere, 2019, 221:486-492. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=311e52f042111dc60dd157c64f0266c6
[98] Wang X N, Pan X L, Gadd G M.Soil dissolved organic matter affects mercury immobilization by biogenic selenium nanoparticles[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658:8-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0757818a40173b24f1b33eebc9b62dac
[99] Wang X N, Zhang D Y, Pan X L, et al.Aerobic and anaerobic biosynthesis of nano-selenium for remediation of mercury contaminated soil[J].Chemosphere, 2017, 170:266-273. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f87b2db845a755593dc815810444bcea
[100] Yu Y, Yuan S L, Zhuang J, et al.Effect of selenium on the uptake kinetics and accumulation of and oxidative stress induced by cadmium in Brassica Chinensis[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 162:571-580. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9ec53ed23293a8713d508350e7c26bf0
[101] 薛超群, 郭敏.氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法测定土壤样品中不同价态的硒[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):980-984. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120613
Xue C Q, Guo M.Analysis of different valence states of selenium in geological samples by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):980-984. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120613
[102] 秦冲, 施畅, 万秋月, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用检测土壤中的无机硒形态[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(6):664-670. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201803200024
Qin C, Shi C, Wan Q Y, et al.Speciation analysis of inorganic selenium in soil by high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(6):664-670. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201803200024
[103] Wang M K, Cui Z W, Xue M Y, et al.Assessing the uptake of selenium from naturally enriched soils by maize (Zeamays L.) using diffusive gradients in thin-films technique (DGT) and traditional extractions[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 689:1-9.
[104] Vinceti M, Filippini T, Malagoli C, et al.Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis incidence following exposure to inorganic selenium in drinking water:A long-term follow-up[J].Environmental Research, 2019, 179:108742. doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108742. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31629180
[105] 龚如雨, 钟松臻, 张宝军, 等.富硒非富硒大米有机硒的组成及硒的可利用度分析[J].食品研究与开发, 2017, 38(20):11-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=spyjykf201720003
Gong R Y, Zhong S Z, Zhang B J, et al.Composition of the organic selenium (Se) and the accessible Se in Se-enriched and non Se-enriched rice[J].Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(20):11-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=spyjykf201720003
[106] Lusa M, Help H, Honkanen A P, et al.The reduction of selenium(Ⅵ) by boreal Pseudomonas sp.strain T5-6-Ⅰ-Effects on selenium(Ⅳ) uptake in Brassica Oleracea[J].Environmental Research, 2019, 177:108642. doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108642.
[107] Both E B, Stonehouse G C, Lima L W, et al.Selenium tolerance, accumulation, localization and speciation in a cardamine hyperaccumulator and a non-hyperaccumulator[J].Science of the Total Environment, doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135041.
[108] Qin H B, Zhu J M, Lin Z Q, et al.Selenium speciation in seleniferous agricultural soils under different cropping systems using sequential extraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J].Environmental Pollution, 2017, 225:361-369. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7ef417f598f4f30687b6adceb6285715
[109] Alexander P, Miriam S, Susanne V A, et al.Charac-terization of selenium speciation in selenium-enriched button mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus) and selenized yeasts (dietary supplement) using X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy[J].Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2019, 51:164-168.
-



 下载:
下载: