Non-destructive and Fast Analysis of Content and Size Distribution of Vesicles in Volcanic Rock by X-ray Computed Tomography
-
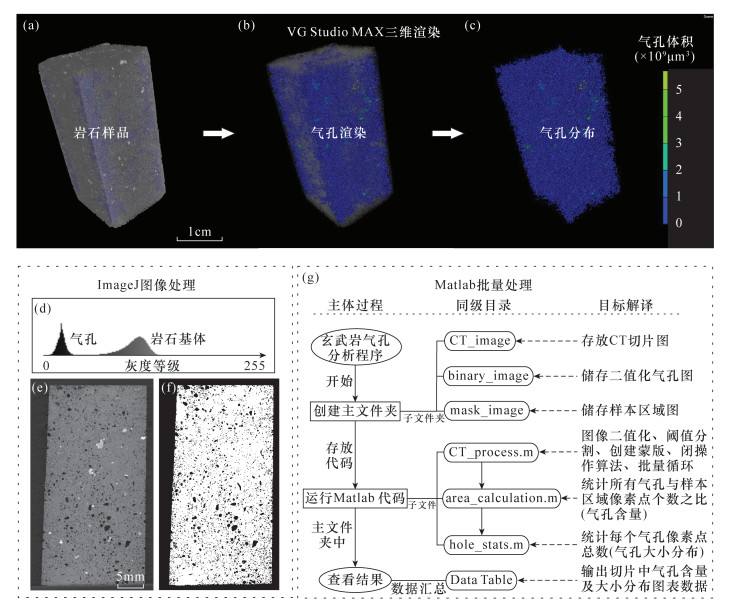
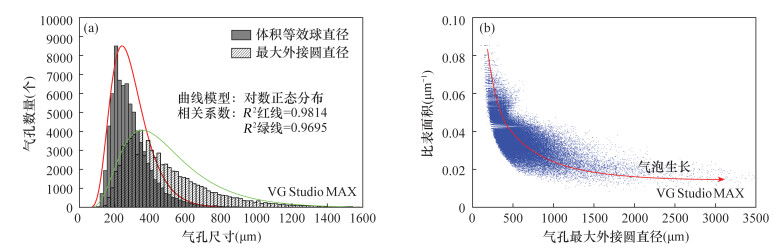
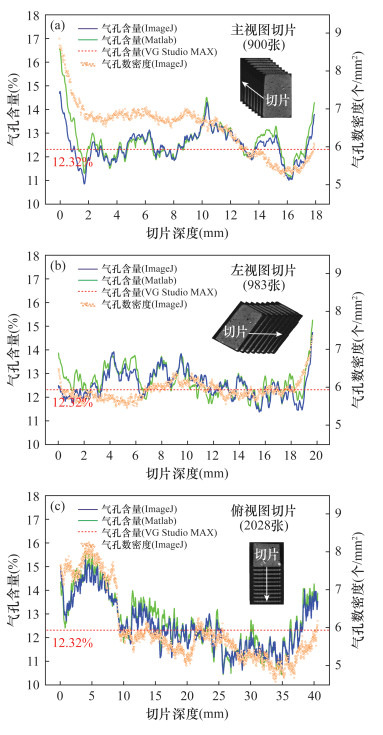
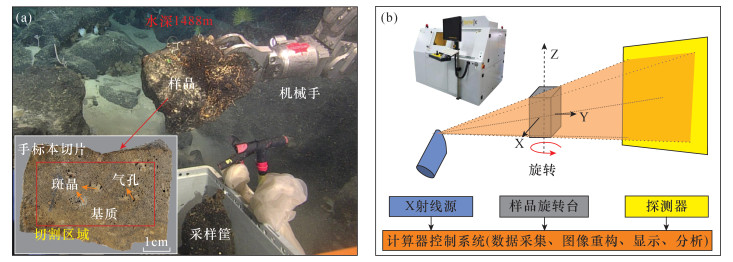
摘要: 火山岩的气孔构造记录了岩浆中挥发性气体出溶、膨胀和逃逸的过程。通过对火山岩气孔特征的详细研究,有助于了解岩浆源区的挥发份含量和岩浆的上升喷发过程。目前用来研究火山岩中气孔的方法普遍存在耗时费力、采集气孔数据较少、易破坏样品等问题。本文在通过计算机断层扫描(工业CT)技术获取玄武岩投影数据的基础上,使用商用软件VG Studio MAX对样品进行三维重构和气孔体积测量,再由开源软件ImageJ对CT切片作图像处理和二维形态学运算,同时开发程序代码批量处理CT切片,快速获取气孔的含量及大小分布情况。结果表明:南海玄武岩样品在三维空间中的气孔体积分数为12.32%,大小分布呈现出对数正态分布的特点,等效球直径和最大外接圆直径分别集中分布在180~200μm、340~360μm的区间内。剖面上二维切片中的气孔含量有较大变化,但各个数值围绕体积分数波动的幅度不大,并且与气孔数密度呈显著的正相关关系。同时,通过改进海底环境下火山岩中挥发份质量分数的计算方法,得到该样品气孔体积全部转换为CO2或H2O的质量分数分别为0.233%、0.099%。研究认为,工业CT扫描结合图像处理软件可以实现火山岩气孔的无损快速统计和分析,该方法有望提高火山岩中气孔数量、体积以及挥发份含量的计算精度,为研究火山岩成因及其岩浆过程提供帮助。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDVesicular structure of volcanic rocks records the processes of the dissolution, expansion and escape of volatile gases in the ascending magma. The detailed study of characteristics of vesicles in volcanic rocks will be helpful to understand volatile content of magma and the ascent and erupting process of magma. Although a number of methods have been developed in the last decades to study the vesicle characteristics of volcanic rocks, they generally have the problems of low efficiency, less data collection, and sample destruction. OBJECTIVESTo quantitatively characterize the content and size distribution of vesicles in volcanic rocks. METHODSOn the basis of three-dimensional reconstruction of vesicular basalt by X-ray computed tomography, the content and size distribution of vesicles were calculated with three software programs (VG Studio MAX, ImageJ, Matlab), and an improved method for conversion of vesicle volume to volatile mass fraction in volcanic rock was also proposed. RESULTSThe vesicle content in three-dimensional space for a basalt sample from the South China Sea in water depth of 1488 meter was 12.32%, and the vesicle size showed a lognormal distribution. The majority of vesicles were 180-200μm in equivalent sphere diameter and 340-360μm in maximum diameter. The content of vesicles in the two-dimensional slices on the profile varied greatly, but the amplitude of each value around the volume fraction fluctuated little, and there was a significant positive correlation with the number density of vesicles. Based on the known vesicle content, the calculated mass fractions of CO2 and H2O in the sample were 0.233% and 0.099%, respectively. CONCLUSIONSThe study demonstrates that industrial CT scanning combined with image processing software can produce non-destructive rapid statistics and analysis of volcanic vesicles. The proposed method will be an efficient tool to study the genesis of volcanic rocks and their magmatic processes. -

-
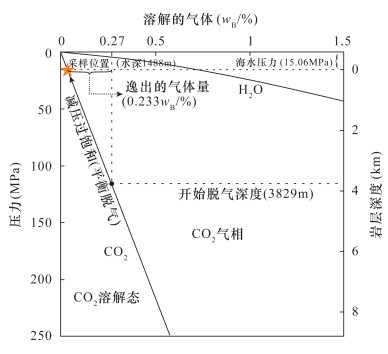
图 5 气体在玄武质岩浆中的溶解度与压力的关系(据Parfitt等[47]修改)
Figure 5.
表 1 本文与其他学者获得的气孔体积-质量分数转换结果对照
Table 1. Comparison of conversion results of vesicle volume to mass fraction between this paper and another scholar
水深(m) 气体全部为CO2(%) 气体全部为H2O(%) 本文 Head等(2003)[37] RSD(%) 本文 Head等(2003)[37] RSD(%) 500 1.913 1.935 0.57 0.801 0.802 0.06 1000 3.678 3.761 1.12 1.575 1.575 0 1500 5.343 5.520 1.63 2.335 2.337 0.04 2000 6.914 7.216 2.14 3.084 3.087 0.05 2500 8.401 8.852 2.61 3.821 3.825 0.05 3000 9.809 10.432 3.08 4.545 4.553 0.09 3500 11.145 12.147 4.30 5.258 5.359 0.95 注:气体体积分数ηCO2/H2O(vol/%)= ηvesicle(vol/%)=75%,深水压强P(MPa)=1026(kg/m3)×9.8(m/s2)×Depth(采样水深, m)/106+0.101325(MPa, 标准大气压),岩浆温度T=1255℃,熔体密度ρlava=2700(kg/m3);气体密度ρCO2/H2O(kg/m3)采用的数值不同,Head等[37]由理想气体状态方程计算得到,本文是先在系统中安装好Nist Refprop9.1,并将其加载到Excel宏中,然后在单元格中输入气体的密度函数[38]调用NIST数据库特定温压下的气体密度得到;岩石密度ρrock(kg/m3)= ρlava(kg/m3)×[1- ηCO2/H2O(vol/%)]+ ρCO2/H2O(kg/m3)× ηCO2/H2O(vol/%),气体质量分数ηCO2/H2O(wB/%)= ρCO2/H2O(kg/m3)× ηCO2/H2O(vol/%)/ ρrock(kg/m3)×100%。RSD为两种方法CO2质量分数计算值的相对标准偏差。 -
[1] Fiege A, Cicuy S B.Experimental constraints on bubble formation and growth during magma ascent:A review[J].American Mineralogist, 2015, 100(11-12):2426-2442. doi: 10.2138/am-2015-5296
[2] Le GallN, Pichavant M.Homogeneous bubble nucleation in H2O- and H2O-CO2-bearing basaltic melts:Results of high temperature decompression experiments[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2016, 327:604-621. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.10.004
[3] Mancini S, Forestier-Coste L, Burgisser A, et al.An expansion-coalescence model to track gas bubble populations in magmas[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2016, 313:44-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.01.016
[4] Sahagian D, Proussevitch A, Ancuta L D, et al.Uplift of central Mongolia recorded in vesicular basalts[J].Journal of Geology, 2016, 124(4):435-445. doi: 10.1086/686272
[5] 冯伟, 杨淑芬, 黄若寒, 等.青藏高原古高程重建研究现状[J].世界地质, 2019, 38(3):829-842, 866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2019.03.025
Feng W, Yang S F, Huang R H, et al.Present situation on paleoelevation reconstruction of Tibetan Plateau[J].Global Geology, 2019, 38(3):829-842, 866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2019.03.025
[6] Goosmann E A, Buick R, Catling D C, et al.Vesicle paleobarometry in the Pongola Supergroup:A cautionary note and guidelines for future studies[J].South African Journal of Geology, 2020, 123(1):95-104.
[7] Gardner J E, Jackson B A, Gonnermann H, et al.Rapid ascent and emplacement of basaltic lava during the 2005-2006 eruption of the East Pacific Rise at ca.9 degrees 51'N as inferred from CO2 contents[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 453:152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.08.007
[8] Liedl A, Buono G, Lanzafame G, et al.A 3D imaging textural characterization of pyroclastic products from the 1538AD Monte Nuovo eruption (Campi Flegrei, Italy)[J].Lithos, 2019, 340:316-331. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3bd4c2853a7eabe4cdd0da8eca98185e
[9] Holt S J, Carey R J, Houghton B F, et al.Eruption and fountaining dynamics of selected 1985-1986 high fountaining episodes at Kilauea volcano, Hawaii, from quantitative vesicle microtexture analysis[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2019, 369:21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2018.11.011
[10] Moore L R, Gazel E, Tuohy R, et al.Bubbles matter:An assessment of the contribution of vapor bubbles to melt inclusion volatile budgets[J].American Mineralogist, 2015, 100(4):806-823. doi: 10.2138/am-2015-5036
[11] Martel C, Iacono-Marziano G.Timescales of bubble coalescence, outgassing, and foam collapse in decompressed rhyolitic melts[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 412:173-185. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.12.010
[12] Hajimirza S, Gonnermann H M, Gardner J E, et al.Predicting homogeneous bubble nucleation in rhyolite[J].Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 2019, 124(3):2395-2416. doi: 10.1029/2018JB015891
[13] Houghton B F, Wilson C J N.A vesicularity index for pyroclastic deposits[J].Bulletin of Volcanology, 1989, 51(6):451-462. doi: 10.1007/BF01078811
[14] Sahagian D L, Anderson A T, Ward B.Bubble coalescence in basalt flows:Comparison of a numerical model with natural examples[J].Bulletin of Volcanology, 1989, 52(1):49-56. doi: 10.1007/BF00641386
[15] Whitham A G, Sparks R S J.Pumice[J].Bulletin of Volcanology, 1986, 48(4):209-223. doi: 10.1007/BF01087675
[16] Shea T, Houghton B F, Gurioli L, et al.Textural studies of vesicles in volcanic rocks:An integrated methodology[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2010, 190(3-4):271-289. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2009.12.003
[17] Mangan M T, Cashman K V, Newman S.Vesiculation of basaltic magma during eruption[J].Geology, 1993, 21(2):157-160. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0157:VOBMDE>2.3.CO;2
[18] Toramaru A.Measurement of bubble size distributions in vesiculated rocks with implications for quantitative estimation of eruption processes[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1990, 43(1-4):71-90. doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(90)90045-H
[19] Proussevitch A A, Mulukutla G K, Sahagian D L.A new 3D method of measuring bubble size distributions from vesicle fragments preserved on surfaces of volcanic ash particles[J].Geosphere, 2011, 7(1):62-69. doi: 10.1130/GES00559.1
[20] Cnudde V, Boone M N.High-resolution X-ray computed tomography in geosciences:A review of the current technology and applications[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 123:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.04.003
[21] Marone F, Schlepütz C M, Marti S, et al.Time resolved in situ X-ray tomographic microscopy unraveling dynamic processes in geologic systems[J].Frontiers in Earth Science, 2020, 7:346. doi: 10.3389/feart.2019.00346
[22] Song S R, Jones K W, Lindquist W B, et al.Synchrotron X-ray computed microtomography:Studies on vesiculated basaltic rocks[J].Bulletin of Volcanology, 2001, 63(4):252-263. doi: 10.1007/s004450100141
[23] Pistone M, Cordonnier B, Caricchi L, et al.The viscous to brittle transition in crystal- and bubble-bearing magmas[J].Frontiers in Earth Science, 2015, 3:71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000004608846
[24] Burgisser A, Chevalier L, Gardner J E, et al.The perco-lation threshold and permeability evolution of ascending magmas[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 470:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.04.023
[25] Plese P, Higgins M D, Mancini L, et al.Dynamic obser-vations of vesiculation reveal the role of silicate crystals in bubble nucleation and growth in andesitic magmas[J].Lithos, 2018, 296:532-546. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0024493717304097
[26] Baker D R, Brun F, Mancini L, et al.The importance of pore throats in controlling the permeability of magmatic foams[J].Bulletin of Volcanology, 2019, 81(9):54. doi: 10.1007/s00445-019-1311-z
[27] 卢树参, 许红, 陈勇, 等.微焦X射线扫描成像技术在岩石物性特征研究的现状[J].海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(3):64-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201603009
Lu S S, Xu H, Chen Y, et al.Current status of application of micro-focus X-ray scan imaging technology to reservoir properties description[J].Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(3):64-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201603009
[28] 王羽, 汪丽华, 王建强, 等.利用纳米透射X射线显微成像技术研究页岩有机孔三维结构特征[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(6):563-573. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703240038
Wang Y, Wang L H, Wang J Q, et al.Investigation of organic matter pore structures of shale in three dimensions of shale using nano-X-ray microscopy[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(6):563-573. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703240038
[29] 贾宁洪, 吕伟峰, 常天全, 等.高效无损岩心孔隙度精确测量新方法[J].石油学报, 2018, 39(7):824-828, 844. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201807009
Jia N H, Lü W F, Chang T Q, et al.A new method for precisely measuring core porosity with high efficiency and no destruction[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(7):824-828, 844. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201807009
[30] 王海涛, 杨叶, 张晋言, 等.地质多孔介质成像技术现状与进展[J].地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(1):191-199. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz201901026
Wang H T, Yang Y, Zhang J Y, et al.Current state and progress in imaging the microstructure of geological porous media[J].Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(1):191-199. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz201901026
[31] 王羽, 金婵, 汪丽华, 等.基于SEM图像灰度水平的页岩孔隙分割方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(6):595-602. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.06.005
Wang Yu, Jin C, Wang L H, et al.Pore segmentation methods based on gray scale of scanning electron microscopy images[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(6):595-602. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.06.005
[32] 戚明辉, 李君军, 曹茜.基于扫描电镜和JMicroVision图像分析软件的泥页岩孔隙结构表征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(3):260-269. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901160008
Qi M H, Li J J, Cao Q.The pore structure characterization of shale based on scanning electron microscopy and JMicroVision[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(3):260-269. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901160008
[33] 彭瑞东, 杨彦从, 鞠杨, 等.基于灰度CT图像的岩石孔隙分形维数计算[J].科学通报, 2011, 56(26):2256-2266. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201126016
Peng R D, Yang Y C, Ju Y, et al.The calculation of the fractal dimension of the pore in the rock based on gray CT image[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(26):2256-2266. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201126016
[34] Edmonds M, Wallace P J.Volatiles and exsolved vapor in volcanic systems[J].Elements, 2017, 13(1):29-34. doi: 10.2113/gselements.13.1.29
[35] Petrelli M, El Omari K, Spina L, et al.Timescales of water accumulation in magmas and implications for short warning times of explosive eruptions[J].Nature Communications, 2018, 9:770. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02987-6
[36] Moretti R, Arienzo I, Di Renzo V, et al.Volatile segregation and generation of highly vesiculated explosive magmas by volatile-melt fining processes:The case of the Campanian Ignimbrite eruption[J].Chemical Geology, 2019, 503:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.10.001
[37] Head J W, Wilson L.Deep submarine pyroclastic eruptions:Theory and predicted landforms and deposits[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2003, 121(3-4):155-193. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00425-0
[38] Lemmon E W, Huber M L, Mclinden M O.NIST standard reference database 23:NIST reference fluid thermodynamic and transport properties-REFPROP[M].USA:National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2013:51-54.
[39] Proussevitch A A, Sahagian D L, Carlson W D.Statistical analysis of bubble and crystal size distributions:Application to Colorado Plateau basalts[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2007, 164(3):112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2007.04.006
[40] Ohashi M, Ichihara M, Toramaru A.Bubble deformation in magma under transient flow conditions[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2018, 364:59-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2018.09.005
[41] Rust A C, Manga M, Cashman K V.Determining flow type, shear rate and shear stress in magmas from bubble shapes and orientations[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2003, 122(1-2):111-132. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00487-0
[42] 彭年, 朱晓艳, 刘永顺, 等.天池火山三期浮岩气孔形态的复杂性及其动力学成因[J].地学前缘, 2019, 26(6):271-280. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201906028
Peng N, Zhu X Y, Liu Y S, et al.Complexity and dynamics of vesicle shapes of pumices formed in the three Tianchi volcano eruptions[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6):271-280. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201906028
[43] Bottinga Y, Javoy M.Mid-ocean ridge basalt degassing:Bubble nucleation[J].Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth and Planets, 1990, 95(B4):5125-5131. doi: 10.1029/JB095iB04p05125
[44] Bottinga Y, Javoy M.MORB degassing:Bubble growth and ascent[J].Chemical Geology, 1990, 81(4):255-270. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(90)90050-H
[45] Capriolo M, Marzoli A, Aradi L E, et al.Deep CO2 in the End-Triassic Central Atlantic Magmatic Province[J].Nature Communications, 2020, 11:1670. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15325-6
[46] Yoshimura S.Diffusive fractionation of H2O and CO2 during magma degassing[J].Chemical Geology, 2015, 411:172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.07.003
[47] Parfitt E A, Wilson L.Fundamentals of physical volcanology[M].USA:Blackwell Publishing, 2008:64-76.
[48] 张茂亮, 刘真, 陈德峰, 等.利用三维CT扫描技术定量计算熔岩流气泡体积的研究与实现[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(12):3709-3716. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201412020
Zhang M L, Liu Z, Chen D F, et al.Research and implementation on vesicle volume calculation of lava flows using three-dimensional computerized tomography (CT) scanning technology[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(12):3709-3716. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201412020
-



 下载:
下载: