In situ Self-transforming Membrane as Solid Phase Microextraction Coating Extraction of PAHs in Environmental Water Samples
-
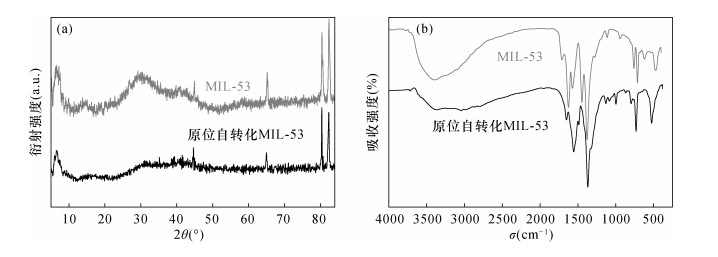
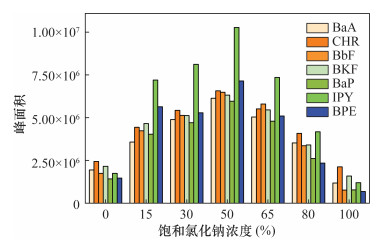
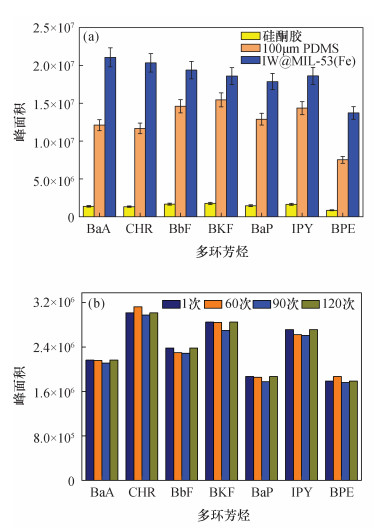
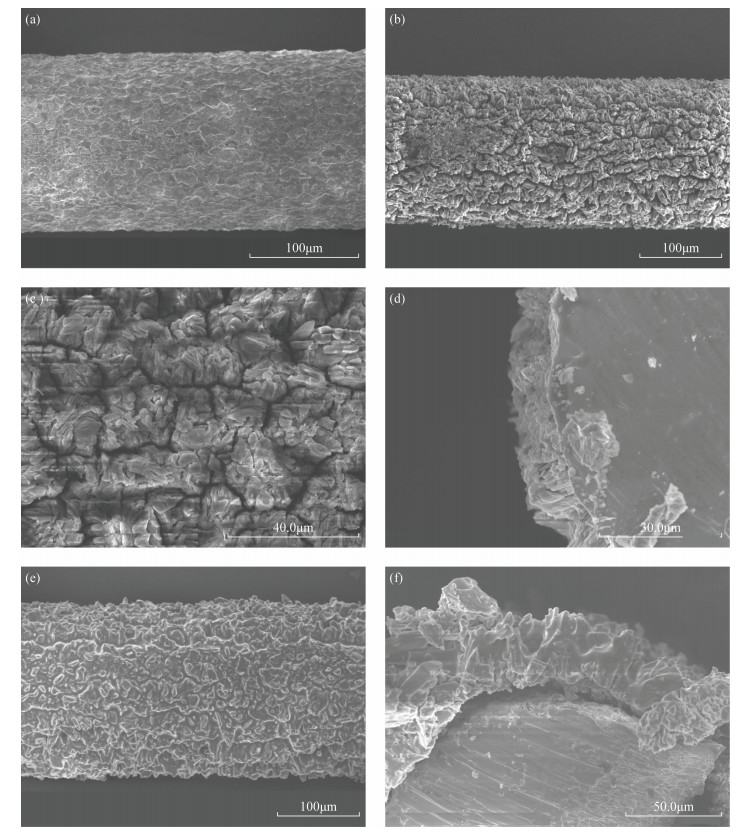
摘要: 多环芳烃(PAHs)是一类具有致癌作用且难以降解的持久性有机污染物,广泛存在于环境中。环境中痕量PAHs的直接分析往往因检测手段的检出限达不到要求而存在困难,需要结合分离富集手段。常规的样品前处理技术如索氏提取、液液萃取等存在耗时长、使用大量有机溶剂等问题。因此为了提高效率、避免对自然环境的二次污染,有必要开发一种简便、环境友好的新型样品前处理技术。固相微萃取(SPME)是一种集采样、富集、进样于一体的无溶剂前处理技术,与气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)等技术联用可实现复杂基质中痕量有机物的快速富集和检测。目前SPME技术的研究热点主要集中在改善涂层的萃取性能以及提高其机械强度方面。本文采用铁丝(IW)作为载体,同时又提供了铁离子来源,以原位自转化的方式在具有良好机械稳定性的铁丝上生长出一层多孔结构的金属有机骨架化合物多孔膜[MIL-53(Fe)];将其作为固相微萃取涂层[IW@MIL-53(Fe)],以7种难挥发的稠环PAHs作为目标分析物,以浸入式模式进行萃取,并结合GC-MS作为检测手段验证其萃取性能。结果表明:新涂层的萃取性能是商用100μm PDMS涂层的1~2倍,且涂层可稳定使用120次以上。该方法的检出限为0.03~2.25ng/L,线性范围为250~10000ng/L,相关系数为0.9903~0.9991。将建立的方法应用于自然水体中PAHs的检测,加标回收率为80.1%~108.5%。本研究不仅为高性能SPME涂层简单、快速制备提供了新思路,而且所建立的方法有望应用于水体中痕量有机污染物的准确和高灵敏检测。
-
关键词:
- 固相微萃取涂层 /
- MIL-53(Fe)膜 /
- 气相色谱-质谱法 /
- 多环芳烃 /
- 原位自转化
Abstract:BACKGROUNDPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are one of the persistent organic pollutants which are carcinogenic and difficult to degrade, and are widespread in the environment. The direct analysis of trace PAHs in the environment is often difficult because of the low sensitivity of the detection methods. It is necessary to combine separation and enrichment methods. Conventional sample pretreatment techniques, such as Soxhlet extraction and liquid-liquid extraction, are time-consuming and use a large number of organic solvents. OBJECTIVESTo develop a new, simple, and environmentally-friendly method for sample pretreatment. METHODSSolid phase microextraction (SPME) is a solvent-free pretreatment technology which integrates sampling, enrichment and injection. Combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), it can produce the rapid enrichment and detection of trace organic compounds in a complex matrix. At present, the research focus of improving SPME technology is to improve the mechanical strength and extraction performance of the coating. Using iron wire (IW) as the carrier, which also provided the iron ion source, a porous MOFs film[MIL-53(Fe)] was grown on iron wire with good mechanical stability by in-situ self-transformation. It was used as the solid phase microextraction coating[IW@MIL-53(Fe)]. Seven kinds of non-volatile condensed ring PAHs were used as the target analyte, and immersion extraction mode combined with GC-MS as detection means were used to verify its extraction performance. RESULTSResults showed that the extraction performance of the new coating was 1-2 times higher than that of the commercial 100μm PDMS coating, and the coating can be used stably for more than 120 times. The detection limits of the methods were 0.03-2.25ng/L, the linear ranges were 250-10000ng/L, and the correlation coefficients were in the range of 0.9903-0.9991. The coating was applied successfully to the detection of PAHs in natural water, where the recoveries were from 80.1% to 108.5%. CONCLUSIONSThis study not only provides an idea for the simple and rapid preparation of high-efficiency SPME coatings, but also has great potential to be applied to determinate trace volatile organic pollutants in water with high accurateness and efficiency. -

-
表 1 IW@MIL-53(Fe)涂层SPME-GC-MS分析7种PAHs的分析性能
Table 1. Analysis performance of 7 kinds of PAHs by IW@MIL-53(Fe) coating with SPME-GC-MS
分析物 线性范围(ng/L) R2 LOD (ng/L, S/N=3) LOQ (ng/L, S/N=10) RSD(%) 涂层内(n=5) 涂层间(n=3) BaA 250~10000 0.9991 0.03 0.10 3.1 6.7 CHR 250~10000 0.9922 0.13 0.43 6.2 3.0 BbF 250~10000 0.9922 0.11 0.37 8.9 5.7 BKF 250~10000 0.9903 0.26 0.87 5.2 5.5 BaP 250~10000 0.9933 0.36 1.20 7.7 6.0 IPY 250~10000 0.9962 1.50 5.00 10.4 9.5 BPE 250~10000 0.9982 2.25 7.50 10.4 2.5 表 2 实际水样中PAHs分析结果
Table 2. Analytical results of PAHs in actual water samples
分析物 东湖水样 长江水样 浓度(ng/L) 加标浓度(ng/L) RSD (%, n=3) 回收率(%) 浓度(ng/L) 加标浓度(ng/L) RSD (%, n=3) 回收率(%) BaA ND 500 11.6 89.3 ND 500 3.5 80.1 CHR ND 500 8.0 102.3 ND 500 7.0 92.5 BbF ND 500 8.8 96.5 ND 500 10.6 84.6 BKF ND 500 5.5 91.1 ND 500 6.4 89.5 BaP ND 500 11.1 90.6 ND 500 9.6 83.0 IPY ND 500 8.6 91.8 ND 500 5.1 108.5 BPE ND 500 4.9 99.7 ND 500 14.4 91.8 注:ND表示未检出。 -
[1] Li J L, Wang Y X, Zhang C X, et al.The source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the topsoil in Xiaodian sewage irrigation area, north of China[J]. Ecotoxicology, 2014, 23(10):1943-1950. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4b646c4957fc09cd12fb3d62c9bb547f
[2] Kim K H, Jahan S A, Kabir E, et al.A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects[J]. Environment International, 2013, 60(1):71-80. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ac240dcd8d5ce7db797fae5535c66d55
[3] Locatelli M, Forcucci L, Sciascia F, et al.Extraction and detection techniques for PAHs determination in Beverages:A review[J]. Current Chromatography, 2014, 1(2):122-138.
[4] Alizadeh R, Najafi N M.Quantification of PAHs and chlorinated compounds by novel solid-phase microex-traction based on the arrays of tin oxide nanorods[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(9):7353-7563.
[5] 顾涛, 帅琴, 高强, 等.新型固相微萃取装置的研制及在有机磷农药检测中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(1):71-76. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120109
Gu T, Shuai Q, Gao Q, et al.A study on solid phase micro-extraction device and application of organophosphorus pesticides determination[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(1):71-76. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120109
[6] 熊茂富, 任敏, 杜伊, 等.顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱质谱联用法同时测定湖库水中12种氯苯甲醚的条件优化[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6):724-733. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901210016
Xiong M F, Ren M, Du Y, et al.Simultaneous determination of 12 chloroanisoles in lake reservoir waters by headspace solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6):724-733. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901210016
[7] Arthur C L, Pawliszyn J.Solid-phase microextraction with thermal-desorption using fused-silica optical fibers[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1990, 62(19):2145-2148.
[8] Koziel J, Jia M Y, Khaled A, et al.Field air analysis with SPME device[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1999, 400(1):153-162.
[9] Xu Y, Zhou X, Zhang D Y, et al.Headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MS) analysis of volatile profiles during the stir-frying process of malt[J]. Analytical Methods, 2016, 8(7):1699-1704. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e043b1414bafb312acab136a9b7aaf36
[10] Li L, Huang L J, Sun S T, et al.An amino-func-tionalized ordered mesoporous polymer as a fiber coating for solid phase microextraction of phenols prior to GC-MS analysis[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2019, 186(9):6651-6658.
[11] Risticevic S, Niri V H, Vuckovic D, et al.Recent developments in solid-phase microextraction[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2009, 393(3):781-795.
[12] Spietelun A, Pilarczyk M, Kloskowski A, et al.Current trends in solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibre coatings[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(11):4524-4537. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=842fec4c66cc651db6f5cbeb6f0596c6
[13] Anbia M, Khazaei M.Ordered nanoporous carbon-based SPME and determination by GC[J]. Chromatographia, 2011, 73(3-4):379-384. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f8fd2deb2f5c6ab0663d1852ca1d2bbf
[14] Silva E A S, Risticevic S, Pawliszyn J.Recent trends in SPME concerning sorbent materials, configurations and in vivo applications[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 43(1):24-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1a24558ea7eded9e4d4d18f2cd8e3dad
[15] Zhang X Q, Liang Q L, Han Q, et al.Metal-organic frameworks@graphene hybrid aerogels for solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and selective enrichment of proteins[J]. Analyst, 2016, 141(13):4219-4226. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8ae4568964c576e6f642dd63e3a094ce
[16] Tian J, Lu C, He C T, et al.Rapid separation of non-polar and weakly polar analytes with metal-organic framework MAF-5 coated capillary column[J]. Talanta, 2016, 152(1):283-287. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fe81b6a1d34e05ac9688568fa943dabe
[17] Lirio S, Liu W L, Lin C L, et al.Aluminum based metal-organic framework-polymer monolith in solid-phase microextraction of penicillins in river water and milk samples[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1428(1):236-245. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=992fbc2e79f53abd01319b5bd18845e0
[18] van Nguyen Thi T, Luu C L, Hoang T C, et al.Synthesis of MOF-199 and application to CO2 adsorption[J]. Advances in Natural Sciences:Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2013, 4(3):1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cuihuaxb201511011
[19] Zhao Y, Song Z X, Li X, et al.Metal organic frameworks for energy storage and conversion[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 2(1):35-62. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wnkb-e202004001
[20] Zheng J, Li S Y, Wang Y, et al.In situ growth of IRMOF-3 combined with ionic liquids to prepare solid-phase microextraction fibers[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2014, 829(1):22-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5a0f2fadc4591ad080c1dddd97c8f5ab
[21] Hu Y L, Lian H X, Zhou L J, et al.In situ solvothermal growth of metal-organic framework-5 supported on porous copper foam for noninvasive sampling of plant volatile sulfides[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(1):406-412. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e0da1ff3e39ba06fc79839004399e21b
[22] Huang L J, He M, Chen B B, et al.Magnetic Zr-MOFs nanocomposites for rapid removal of heavy metal ions and dyes from water[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 199:435-444. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5cce554d0f9bbf6a739b3bdcf22ee2dc
[23] Ai L H, Li L L, Zhang C H, et al.MIL-53(Fe):A metal-organic framework with intrinsic peroxidase-like catalytic activity for colorimetric biosensing[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2013, 19(45):15105-15108. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gyscl201701007
[24] Chen X F, Zang H, Wang X, et al.Metal-organic framework MIL-53(Al) as a solid-phase microextraction adsorbent for the determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Analyst, 2012, 137(22):5411-5419. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f74d4649ae52b2cd148bc91e2165e1bc
[25] Zhang S L, Du Z, Li G K.Metal-organic framework-199/graphite oxide hybrid composites coated solid-phase microextraction fibers coupled with gas chromatography for determination of organochlorine pesticides from complicated samples[J]. Talanta, 2013, 115(1):32-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=aa946fdc3bae20d492f99165755032c8
[26] Zhang G J, Zang X H, Li Z, et al.Polydimethylsiloxane/metal-organic frameworks coated fiber for solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in river and lake water samples[J]. Talanta, 2014, 129(1):600-605. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ac90c768ad2d997c3bac8b7c15b7f5df
[27] Sun S T, Huang L J, Xiao H Y, et al.In situ self-transformation metal into metal-organic framework membrane for solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Talanta, 2019, 202(1):145-151. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8a7a5a1acbe1d524b0b25004e902fbd7
[28] Lü F, Gan N, Huang J, et al.A poly-dopamine based metal-organic framework coating of the type PDA-MIL-53(Fe) for ultrasound-assisted solid-phase microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls prior to their determination by GC-MS[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2017, 184(8):2561-2568. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d44457e5348a533ac8499dbf1dcf6a36
[29] Tian J Y, Xu J Q, Zhu F.Application of nanomaterials in sample preparation[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1300(1):2-16.
[30] 赖永忠.顶空进样-固相微萃取测定饮用水源水中吡啶[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(5):596-600. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110514
Lai Y Z.Determination of pyridine in drinking source water by head space sampling-solid phase micro-extraction[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(5):596-600. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110514
[31] Jalili V, Barkhordari A, Ghiasvand A.Solid-phase microextraction technique for sampling and preconcentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons:A review[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2020, 157:104967.
[32] Harati F, Ghiasvand A, Dalvand K, et al.Fused-silica capillary internally modified with nanostructured octadecyl silica for dynamic in-tube solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous media[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2020, 155:104672.
[33] 欧阳钢锋, Pawliszyn Janusz.固相微萃取:原理与应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2012.
Ouyang G F, Pawliszyn J.Solid phase microextraction:Principle and application[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2012.
-



 下载:
下载: