Thermal Infrared Spectra Characteristics of Rare Metal Minerals and Rock in the Keketuohai Deposit, Xijiang
-
摘要:
当前新型材料、新能源在各个领域应用不断深化,稀有金属矿床迎来了世界范围内的研究与勘探热潮。新疆可可托海稀有金属矿床是我国最早开发利用稀有金属矿产资源的重要基地,但对其典型矿物和围岩的热红外反射光谱的认识还很缺乏,制约了对同类型矿床开展遥感地质调查和遥感地质学研究工作的推进。本文采用便携式热红外光谱仪,对可可托海3号脉的典型矿物岩石开展热红外光谱特征研究。结果表明:热红外光谱可以有效识别锂辉石、锂云母、绿柱石、电气石等典型的稀有金属矿物。其中,与锂云母相比,含锂云母伟晶岩产生了新的特征峰;含锂辉石伟晶岩、含电气石伟晶岩相比于各自单晶矿物,其反射特征峰均明显向短波方向偏移;含绿柱石伟晶岩光谱曲线反射特征峰比绿柱石单晶反射特征峰明显向长波方向偏移。本文初步建立了可可托海典型矿物和岩石热红外光谱特征数据库,总结了以锂辉石、锂云母等稀有金属矿床矿物、含矿伟晶岩及围岩的热红外光谱特征,可为热红外光谱进行稀有金属矿物的识别及花岗伟晶岩型矿床的勘探提供必要的基础数据支撑。
Abstract:BACKGROUND At present, the application of new materials and new energy in various fields continues to deepen, and rare metal deposits have ushered in a worldwide upsurge of research and exploration. The Keketuohai rare metal deposit is the earliest developed deposit for rare metal mineral in China. However, the thermal infrared (TIR) characteristics of minerals and rocks from this deposit have not been studied, which restricts remote sensing geological survey and relevant studies.
OBJECTIVES To analyze the characteristics of thermal infrared spectra of minerals and rock assemblages from the Keketuohai deposit, and provide the basic data for rare metal exploration.
METHODS A portable thermal infrared spectrometer was used to measure the spectrum data of typical minerals and rock assemblages of Keketuohai No.3 vein. Data was analyzed using techtonics/structural geology (TSG) and related databases.
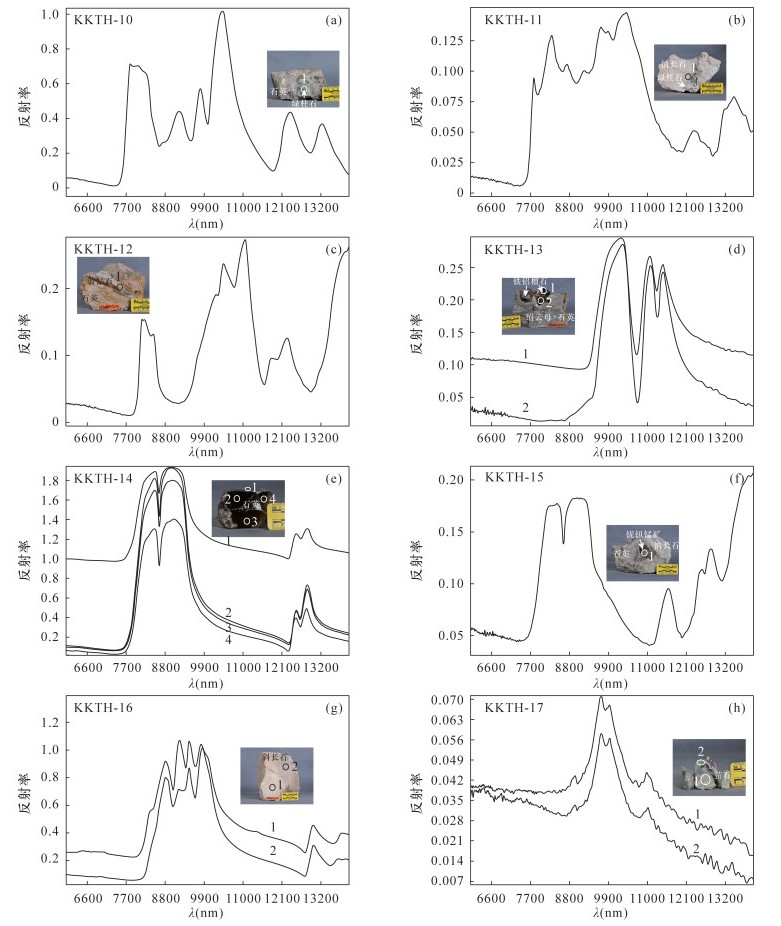
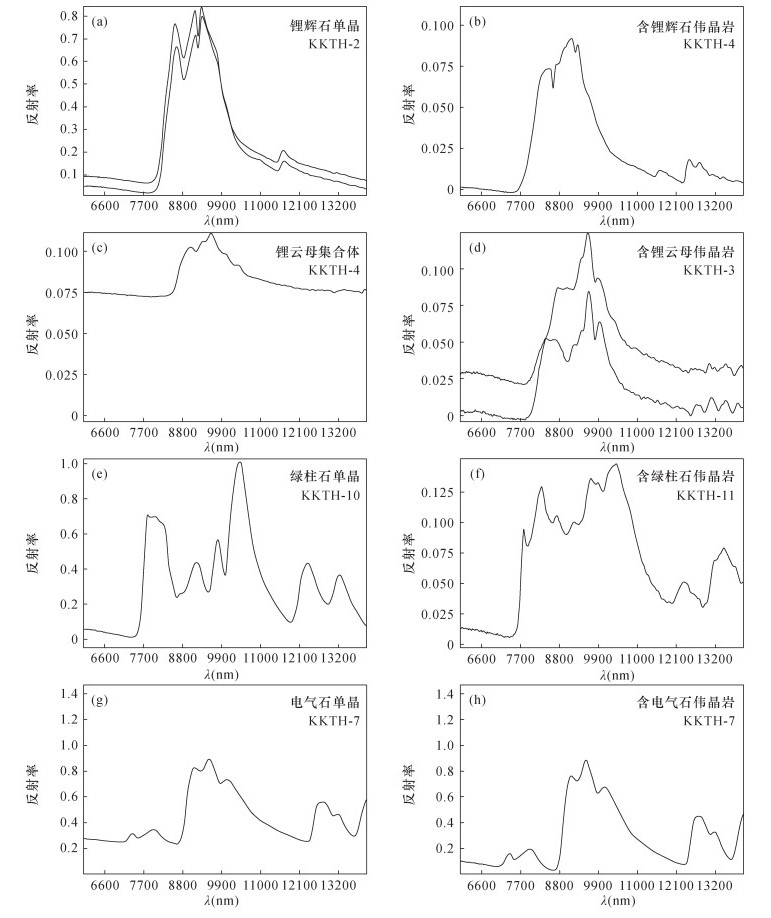
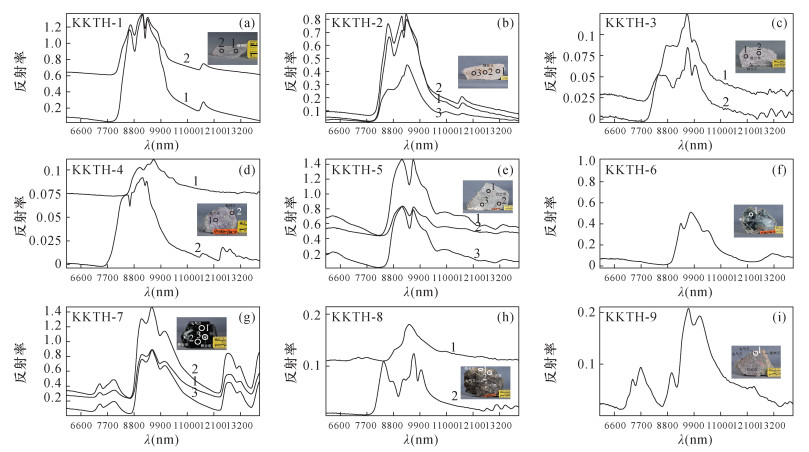
RESULTS Typical rare metal minerals like spodumene, lepidolite, beryl and tourmaline can be separated with TIR. Compared with lepidolite, there was a new diagnosed peak for the TIR spectrum of lepidolite-bearing pegmatite. The spectrum peaks of spodumene-bearing pegmatite and tourmaline-bearing pegmatite were significantly shorter than those of spodumene and tourmaline. However, the spectrum peaks of beryl-bearing pegmatite were shorter than the peaks of beryl.
CONCLUSIONS A database of thermal infrared spectroscopy characteristics of typical minerals and rocks in the Keketuohai has been established, and the thermal infrared spectroscopy characteristics of spodumene and lepidolite, ore-bearing pegmatites and surrounding rocks in rare metal deposits have been summarized in this study. Basic data support for the identification of rare metal minerals using thermal infrared spectroscopy and the exploration of granite pegmatite deposits has also been provided.
-
Key words:
- Keketuohai /
- rare metals /
- thermal infrared spectroscopy /
- spodumene /
- lepidolite
-

-
表 1 标本基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of the specimens
标本编号 标本名称 采样层位 地质特征描述 KKTH-1 锂辉石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉叶钠长石-锂辉石带(含铍铌的锂矿带)伟晶岩中 晶体属单斜晶系,柱状,无色透明,可达宝石级,其晶体内部略有瑕疵 KKTH-2 锂辉石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉叶钠长石-锂辉石带(含铍铌的锂矿带)伟晶岩中 主要矿石矿物为锂辉石,含量约占95%。脉石矿物主要为白云母、石英,含量约占5% KKTH-3 锂云母 可可托海1号坑3号脉薄片状钠长石-锂云母带(含铌钽的锂矿带)伟晶岩中 主要矿石矿物为锂云母,含量约占95%。脉石矿物为叶钠长石,含量约占5% KKTH-8 白云母 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉白云母石英带伟晶岩中 矿石完全由白云母组成,片状,淡绿色 KKTH-9 黑云母 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉文象、变文象石英斜长石带伟晶岩中 晶体为单斜晶系,集合体呈片状。由于富含高价铁,所以标本呈现黑绿色 KKTH-10 电气石单晶 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉薄片状钠长石-锂云母带(含铌钽的锂矿带)伟晶岩中 晶体为三方晶系,呈三方柱状。柱面上呈现出纵纹,横断面呈球面三角形。由于富含铁,电气石呈黑色 KKTH-11 钠长石、
电气石、
石英伟晶岩可可托海1号矿坑3号脉薄片状钠长石-锂云母带(含铌钽的锂矿带)伟晶岩中 主要矿石矿物为电气石,含量约占10%。脉石矿物主要为石英、片状钠长石,含量约占90%。电气石为三方晶系,单体呈六方柱状。柱面上呈现出纵纹,横断面呈球面三角形。由于富含锂,电气石呈粉红色 KKTH-12 电气石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉薄片状钠长石-锂云母带(含铌钽的锂矿带)伟晶岩中 主要矿石矿物为电气石,含量约占20%。脉石矿物主要为斜长石、锂云母,含量约占80%。晶体为三方晶系,单体呈六方柱状,集合体呈棒状。由于该电气石含有锂和铬,从而形成了色带现象,由中心向外形成色环,颜色由粉色向绿色过渡 KKTH-13 海蓝宝石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉糖晶状钠长石巢体带(主要含铍矿带)花岗伟晶岩中 海蓝宝石在矿物学中属于绿柱石,是一种含铍、铝的硅酸盐。晶体属六方晶系,单体呈六方柱状。由于含有Fe2+,标本呈淡蓝色。主要矿石矿物为绿柱石,含量约占10%。脉石矿物主要有长石、石英、白云母,含量约占90% KKTH-14 绿柱石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉糖晶状钠长石巢体带(主要含铍矿带)伟晶岩中 主要矿石矿物为绿柱石,含量约占5%。脉石矿物主要为叶钠长石、白云母、石英,含量约占95%。绿柱石晶体为六方晶系,单体呈六方柱状。标本呈淡绿色 KKTH-15 蓝晶石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉文象、变文象石英斜长石带伟晶岩中 晶体为三斜晶系,单体呈平行双面柱状,淡黄色 KKTH-16 铁铝榴石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉白云母石英集合体带 主要矿石矿物为铁铝榴石,含量约占5%。脉石矿物主要为绢云母、石英等,含量约占95%。铁铝榴石晶体为等轴晶系,单体为菱形十二面体和四角三八面体聚型,褐红色 KKTH-17 石英 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉块体石英带 烟灰色石英,晶体为三方晶系,单体呈六方柱状,具晶面横纹,在宝石学上称为“烟晶” KKTH-18 斜长石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉块体微斜长石带 晶体为三斜晶系,单体呈板柱状,灰白色 KKTH-19 萤石 可可托海1号矿坑3号脉石英-锂辉石带(与5带组合成含铍钽铌锂主矿带) 萤石晶体为等轴晶系,单体为六八面体。绿色或紫色,透明 -
[1] 赵元义. 中国盐湖锂资源及其开发进程[J]. 矿床地质, 2003, 22(1): 99-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200301014.htm
Zhao Y Y. Saline lake lithium resources of China and its exploitation[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2003, 22(1): 99-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200301014.htm
[2] 李建康, 刘喜方, 王登红. 中国锂矿成矿规律概要[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(12): 2269-2283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412009.htm
Li J K, Liu X F, Wang D H. The metallogenetic regularity of lithium deposit in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(12): 2269-2283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412009.htm
[3] 刘丽君, 王登红, 刘喜方, 等. 国内外锂矿主要类型、分布特点及勘查开发现状[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(2): 263-278. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201702005.htm
Liu L J, Wang D H, Liu X F, et al. The main types, distribution features and present situation of exploration and development for domestic and foreign lithium mine[J]. Geology in China, 44(2): 263-278. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201702005.htm
[4] 涂其军, 李建康, 王刚. 中国西部主要伟晶岩型锂辉石矿床成矿作用对比及找矿前景[J]. 中国地质调查, 2016, 6(6): 35-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201906005.htm
Tu Q J, Li J K, Wang G. Mineralization comparisons of the major pegmatite type spodumene deposits and their prospecting potential in West China[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2016, 6(6): 35-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201906005.htm
[5] 杨富全, 张忠利, 王蕊, 等. 新疆阿尔泰稀有金属矿地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(6): 1010-1026. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201806007.htm
Yang F Q, Zhang Z L, Wang R, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of rare metal deposits in Altay, Xinjiang[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(6): 1010-1026. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201806007.htm
[6] 王吴梦雨, 饶灿, 董传万, 等. 浙江临安石室寺NYF型伟晶岩中稀有稀土金属的矿物学行为与成矿过程[J]. 高校地质学报, 2019, 25(6): 914-931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201906011.htm
Wangwu M Y, Rao C, Dong C W, et al. Mineralogical behavior and metallogenic process of rare and rare earth metals in Shishisi NYF-type pegmatite, Lin'an, Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2019, 25(6): 914-931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201906011.htm
[7] 王汝成, 谢磊, 诸泽颖, 等. 云母: 花岗岩-伟晶岩稀有金属成矿作用的重要标志矿物[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 35(1): 69-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201901005.htm
Wang R C, Xie L, Zhu Z Y, et al. Micas: Important indicators of granite-pegmatite-related rare-metal mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 35(1): 69-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201901005.htm
[8] 王臻, 陈振宇, 李建康, 等. 云母矿物对仁里稀有金属伟晶岩矿床岩浆-热液演化过程的指示[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(5): 1039-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201905006.htm
Wang Z, Chen Z Y, Li J K, et al. Indication of mica minerals for magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of Renli rare metal pegmatite deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(5): 1039-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201905006.htm
[9] 周起凤, 秦克章, 唐冬梅, 等. 东秦岭卢氏稀有金属伟晶岩的绿柱石矿物学特征及其指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(7): 1999-2012. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201907004.htm
Zhou Q F, Qin K Z, Tang D M, et al. Mineralogical characteristics and significance of beryl from the rare-element pegmatites in the Lushi County, east Qinling, China[J]. Acta petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(7): 1999-2012. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201907004.htm
[10] 陈欢, 冯梦, 康志强, 等. 桂东北茅安塘伟晶岩中石榴子石的特征及对岩浆演化的指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(6): 2059-2076. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006020.htm
Chen H, Feng M, Kang Z Q, et al. Characteristics of garnets in pegmatites of Mao'antang, northeast Guangxi, and their implications for magmatic evolution[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(6): 2059-2076. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006020.htm
[11] 邱彩珍. 新疆阿尔泰伟晶岩锂辉石矿物学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Qiu C Z.Study on mineralogical characteristics of the spodumene in the Altay Orogen, Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geology (Beijing), 2014.
[12] 伍守荣, 赵景宇, 张新, 等. 新疆阿尔泰可可托海3号伟晶岩脉岩浆-热液过程: 来自电气石化学组成演化的证据[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(3): 299-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201503004.htm
Wu S R, Zhao J Y, Zhang X, et al. Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of the Koktokay No. 3 Pegmatite, Altay, NW China: Evidence from compositional variation of tourmaline[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(3): 299-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201503004.htm
[13] 王吴梦雨. 浙西北河桥地区花岗质岩石中稀有金属的矿物学行为和成矿过程[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019.
Wangwu M Y.Mineralogical behavior and metallogenic process of rare metals in granitic rocks of Heqiao area, northwest Zhejiang[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019.
[14] 白峰, 冯恒毅, 邹思吉力等. 河南卢氏官坡伟晶岩中锂辉石的矿物学特征研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(2): 281-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201102014.htm
Bai F, Feng H Y, Zou S J L, et al. A mineralogical study of spodumene from Guanpo pegmatites in Lushi, Henan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2011, 30(2): 281-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201102014.htm
[15] 唐宏, 张辉. 可可托海3号伟晶岩脉石英中微量元素组成特征与岩浆-热液演化[J]. 矿物学报, 2018, 38(1): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201801002.htm
Tang H, Zhang H. Characteristics of trace elements in quartz from No. 3 pegmatite, Koktokay area, Xinjiang autonomous region, China and implication for magmatic-hydrothermal evolution[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201801002.htm
[16] 代晶晶, 王登红, 代鸿章, 等. 川西甲基卡锂矿基地典型岩石及矿物反射波谱特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(5): 507-517. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701110003
Dai J J, Wang D H, Dai H Z, et al. Reflectance spectral characteristics of rocks and minerals in Jiajika lithium deposits in west Sichuan[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(5): 507-517. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701110003
[17] Vincent R K, Rowan L C, Gillespie R E, et al. Thermal-infrared spectra and chemical analyses of twenty-six igneous rock samples[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1976, 4: 199-209. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0034425775900164
[18] Cooper B L, Salisbury J W, Killen R M, et al. Midinfrared spectral features of rocks and their powders[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(E4): 1-17. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2000JE001462/full
[19] Kokaly R F, Clark R N, Swayze G A, et al.USGS spec-tral library version 7: U.S.Geological Survey Data Series[R]. 2017.
[20] 代晶晶, 赵龙贤, 姜琪, 等. 热红外高光谱遥感技术在地质找矿中的应用综述[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(8): 2520-2533.
Dai J J, Zhao L X, Jiang Q, et al. Review of thermal-infrared spectroscopy applied in geological ore exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(8): 2520-2533.
[21] 刘德长, 闫柏琨, 邱骏挺. 航空高光谱遥感固体矿产预测方法与示范应用[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(3): 349-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201603016.htm
Liu D C, Yan B K, Qiu J T. The application of airborne hyper-spectral remote sensing technology to mineral resources exploration[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(3): 349-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201603016.htm
[22] 刘德长, 邱骏挺, 田丰, 等. 区域控矿断裂带的航空高光谱遥感技术研究——以黑石山-花牛山深大断裂带为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(2): 366-375. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201502018.htm
Liu D C, Qiu J F, Tian F, et al. Application of airborne hyper-spectrum remote sensing to mapping of ore-control faults: A case study of the Heishishan-Huaniushan Fault[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2015, 51(2): 366-375. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201502018.htm
[23] 刘德长, 叶发旺, 赵英俊, 等. 航空高光谱遥感金矿床定位模型及找矿应用——以甘肃北山六院-方山口地区为例[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2015, 17(12): 1545-1553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX201512019.htm
Liu D C, Ye F W, Zhao Y J, et al. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing for gold prospecting around Liuyuan-Fangshankou area, Gansu Province, China[J]. Journal of Geo-informatics Science, 2015, 17(12): 1545-1553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX201512019.htm
[24] 黄宇飞, 李智慧, 宁慧, 等. 应用ASTER遥感图像的岩矿信息提取研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2019, 28(6): 130-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTGC201906021.htm
Huang Y F, Li Z H, Ning H, et al. Research on rock and mineral information extraction based on ASTER remote sensing image[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2019, 28(6): 130-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTGC201906021.htm
[25] 王东, 刘善军, 毛亚纯, 等. 鞍山式铁矿SiO2含量的热红外光谱分析方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(7): 2101-2106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201807025.htm
Wang D, Liu S J, Mao Y C, et al. A method based on thermal infrared spectrum for analysis of SiO2 content in Anshan-type iron[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(7): 2101-2106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201807025.htm
[26] 宋亮, 刘善军, 虞茉莉, 等. 基于可见-近红外和热红外光谱联合分析的煤和矸石分类方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(2): 416-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201702020.htm
Song L, Liu S J, Yu M L, et al. A classification method based on the combination of visible, near-infrared and thermal infrared spectrum for coal and gangue distinguishment[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(2): 416-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201702020.htm
[27] 杨国防, 赵英俊, 田新光, 等. 大柳塔矿区煤火高光谱热红外定量探测研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2016, 48(12): 103-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKSJ201612032.htm
Yang G F, Zhao Y J, Tian X G, et al. Coalfield fire quantitative detection in Daliuta mining area based on hyperspectral thermal infrared remote sensing[J]. Coal Engineering, 2016, 48(12): 103-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKSJ201612032.htm
[28] 夏军, 张飞. 热红外光谱的干旱区土壤含盐量遥感反演[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(4): 1063-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201904015.htm
Xia J, Zhang F. A study on remote sensing inversion of soil salt content in arid area based on thermal infrared spectrum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(4): 1063-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201904015.htm
[29] 买买提·沙吾提, 吐尔逊·艾山, 塔西甫拉提·特依拜, 等. 基于热红外光谱的干旱区土壤盐分监测研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(1): 181-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201701029.htm
Mamat S, Tueixun A, Tashpolat T, et al. Salt content monitoring on thermal infrared emissivity in arid area[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2017, 40(1): 181-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201701029.htm
[30] 侯艳军, 塔西甫拉提·特依拜, 张飞, 等. 荒漠土壤全磷含量热红外发射率光谱估算研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(2): 350-354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201502014.htm
Hou Y J, Tashpolat T, Zhang F, et al. Study on estimation of deserts soil total phosphorus content from thermal-infrared emissivity[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(2): 350-354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201502014.htm
[31] 郭帮杰, 张杰林, 武鼎. 热红外高光谱遥感回归分析定量反演石英含量[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(17): 125-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201817021.htm
Guo B J, Zhang J L, Wu D. Thermal hyperspectral remote rensing for the quantitative inversion of quartz content by regression analysis[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(17): 125-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201817021.htm
[32] 杜锦锦, 王俊虎, 郎朋林. 基于102F实测热红外光谱的富硅类岩石SiO2含量定量反演[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2016, 33(4): 216-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD201604006.htm
Du J J, Wang J H, Lang P L. Quantitative inversion of SiO2 contents in silicon rich rocks based on measured 102F thermal infrared spectra[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2016, 33(4): 216-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD201604006.htm
[33] 赵洁. 新疆富蕴可可托海地区稀有金属定量预测与评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2008.
Zhao J.Quantitative prediction and estimation on rare metals deposit in Koktokay, Xinjiang Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geology (Beijing), 2008.
[34] 曲梦. 新疆阿尔泰可可托海海蓝宝石的宝石矿物学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Qu M.Mineralogy and gemological study of a quamarine from Keketuohai in Aletai of Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geology (Beijing), 2014.
[35] 陈剑锋, 张辉, 张锦煦, 等. 新疆可可托海3号伟晶岩脉锆石U-Pb定年、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(9): 1832-1844. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201809015.htm
Chen J F, Zhang H, Zhang J X, et al. Geochronology and Hf isotope of zircon for Koktokay No. 3 granitic pegmatite in Xinjiang and its geological implications[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(9): 1832-1844. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201809015.htm
[36] 伍守荣, 赵景宇, 张新, 等. 新疆阿尔泰可可托海3号伟晶岩脉岩浆-热液过程: 来自电气石化学组成演化的证据[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(3): 299-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201503004.htm
Wu S R, Zhao J Y, Zhang X, et al. Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of the Koktokay No. 3 pegmatite, Altay, NW China: Evidence from compositional variation of tourmaline[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(3): 299-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201503004.htm
[37] 田野, 秦克章, 周起凤, 等. 阿尔泰可可托海伟晶岩中弧形石英白云母层的成因及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(8): 2353-2365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201508016.htm
Tian Y, Qin K Z, Zhou Q F, et al. The formation of curve shape quartz-muscovite layers in Koktokay pegmatite intrusions, Altay, and its implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(8): 2353-2365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201508016.htm
[38] 朱莹, 丁竑瑞, 李艳, 等. 不同亚类硅酸盐矿物的中红外光谱学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(2): 143-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201902005.htm
Zhu Y, Ding H R, Li Y, et al. The middle-infared spectroscopic characteristics of several common silicate minerals[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2019, 39(2): 143-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201902005.htm
[39] 郭娜, 史维鑫, 黄一入, 等. 基于短波红外技术的西藏多龙矿集区铁格隆南矿床荣那矿段及其外围蚀变填图-勘查模型构建[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(2-3): 446-457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2018Z1023.htm
Guo N, Shi W X, Huang Y R, et al. Alteration mapping and prospecting model construction in the Tiegelongnan ore deposit of the Duolong ore concentration area, northern Xizang, based on shortwave infrared technique[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(2-3): 446-457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2018Z1023.htm
-



 下载:
下载: