Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Nickel and Scandium in Carbonate Rock Samples and Interference Correction Methods
-
摘要:
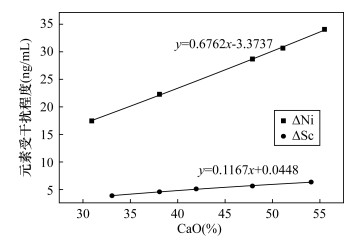
电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)已在碳酸盐岩微量元素测试中得到了广泛应用。然而,采用ICP-MS分析碳酸盐岩中含量较低的Ni(1.6~50.5μg/g)和Sc(0.3~6μg/g)时,信号值会受到高含量CaO(可高达56%)和MgO(可高达21%)的显著干扰,使测试值远高于真实值,从而无法获得准确的待测元素含量。为解决这一问题,本文通过实验探寻测试中的主要干扰因素,再据此确定相应的校正方法。首先,利用Ca和Mg的单标系列对碳酸盐岩ICP-MS测试中的高含量Ca、Mg对Ni、Sc的干扰分别进行研究,发现高含量Mg对Ni和Sc的测试存在基体效应的非质谱干扰;而高含量Ca则形成氧化物、氢氧化物及多原子离子对Ni和Sc形成质谱干扰,并且这一干扰程度与溶液中Ca含量呈良好的线性关系。然后,进一步选择碳酸盐岩国家一级标准物质作为校正载体以消除Mg的基体效应,同时根据样品溶液中CaO含量与Ni、Sc受干扰程度呈现的良好线性关系,提出了扣除拟合干扰的校正方法。相对于前人仅利用单标对实际样品进行干扰校正而言,本方法采用国家一级标准物质作为校正载体,克服了基体效应的干扰。并经GBW07108等五个碳酸盐岩国家一级标准物质验证,测定值与认定值相符,相对标准偏差(RSD,n=10)小于5.5%。将未知碳酸盐岩样品的校正结果与电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)及X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测试结果进行对比,相对偏差均小于15%。该校正方法简单易行,测定结果准确可靠。
-
关键词:
- 碳酸盐岩 /
- 镍 /
- 钪 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法 /
- 干扰校正
Abstract:BACKGROUND Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) has been widely used in the determination of trace elements in carbonate rocks. Due to the low Ni (1.6-50.5μg/g) and Sc (0.3-6μg/g) in carbonate rocks, the signal values are obviously interfered by high CaO (up to 56%) and MgO (up to 21%) during ICP-MS determination, resulting in the test value much higher than the true value.
OBJECTIVES To solve the problem of non-mass spectrum interference and mass spectrum interference of Ni and Sc during ICP-MS analysis of carbonate rocks and use appropriate correction method.
METHODS The single standard series of Ca and Mg and national first-level reference materials of carbonate rocks were used to study the interference of high content of Ca and Mg on Ni and Sc in the carbonate during ICP-MS analysis. Testing of the single standard series was aim to explore ways of interference on Ni and Sc by high content of Ca and Mg in solution. The national first-level reference material of carbonate rock was further selected as the calibration carrier to eliminate the matrix effect of Mg. At the same time, according to the good linear relationship between the content of CaO in the sample solution and the interference degree of Ni and Sc, the interference equations of CaO and △Ni and △Sc were fitted respectively, and used for interference deduction of Ni and Sc in several national first-level reference materials and unknown samples of carbonate rocks. The accurate test values of Ni and Sc in carbonate rocks by ICP-MS were obtained.
RESULTS It was found that the high content of Mg had a non-mass spectrometric interference matrix effect on the analysis of Ni and Sc. High content of Ca forms oxides, hydroxides and polyatomic ions, resulting in mass spectrometric interference on Ni and Sc. The degree of interference had a good linear relationship with the Ca content in the solution. Compared with a single standard to perform interference correction on actual samples, this method used national first-level standard materials as the calibration carrier, which overcomed the interference of matrix effects. Verified by GBW07108 and other five national primary standard materials of carbonate rocks, test values agreed with the standard values, with a relative standard deviation (RSD, n=10) of less than 5.5%. Correction results of the unknown carbonate samples were compared with the results of the inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) and the X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF), respectively, the relative deviation was less than 15%.
CONCLUSIONS The correction method proposed in this paper has solved the mass spectral interference and non-mass spectral interference in ICP-MS analysis of Ni and Sc in carbonate rocks. The method is simple and feasible, and the results are accurate and reliable.
-

-
表 1 仪器工作条件
Table 1. Working conditions of the instruments
ICP-MS ICP-OES XRF 参数 工作条件 参数 工作条件 参数 工作条件 Ni Sc 射频功率 1550W 射频功率 1150W 分析线 Kα Kα 等离子体气流速 15L/min 驱气气体流速 一般 探测器 Duplex Flow 载气流速 1.2L/min 辅助气流速 0.5L/min 检测晶体 LiF 200 LiF 200 辅助气流速 0.82L/min 雾化气压力 0.22MPa 管压 60kV 40kV 雾化气流速 1.055L/min 泵速 50r/min 管流 60mA 90mA 循环水 5L/min 积分时间 20s PHD 18~63 32~68 泵速 40r/min 检测方式 跳峰 表 2 方法准确度对比
Table 2. Comparison of accuracy of the method
校正载体 校正元素 GBW07108 GBW07128 GBW07132 GBW07133 GBW07136 认定值(μg/g) 校正值(μg/g) 相对误差(%) 允许限(%) 认定值(μg/g) 校正值(μg/g) 相对误差(%) 允许限(%) 认定值(μg/g) 校正值(μg/g) 相对误差(%) 允许限(%) 认定值(μg/g) 校正值(μg/g) 相对误差(%) 允许限(%) 认定值(μg/g) 校正值(μg/g) 相对误差(%) 允许限(%) 单标 Ni 17.8 14.3 19.8 17 4.3 2.95 31.3 21 6.6 2.04 69.1 20 4.8 1.94 59.7 21 1.6 -0.36 122 25 Sc 6 7.36 22.7 21 0.5 -0.13 127 30 1.1 0.75 31.6 27 1.9 0.72 62.1 25 0.3 -0.47 257 30 国标 Ni 17.8 16.8 5.6 17 4.3 5.16 20.0 21 6.6 5.82 11.8 20 4.8 5.13 6.9 21 1.6 1.83 14.4 25 Sc 6 7.21 20.2 21 0.5 0.56 12.0 30 1.1 1.23 11.8 27 1.9 1.82 4.2 25 0.3 0.22 26.7 30 注:相对误差=(|X校正值-X认定值|/X认定值)×100%;其中X校正值为校正值,X认定值为认定值;允许限= $ \frac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ C×(14.37X0-0.1263-7.659),其中C=1,X0为认定值。表 3 未知碳酸盐岩样品校正结果
Table 3. Calibration results of unknown carbonate samples
样品编号 CaO含量(%) MgO含量(%) Ni含量(μg/g) Sc含量(μg/g) ICP-MS校正值 ICP-OES测定值 相对偏差(%) 允许限(%) ICP-MS校正值 XRF测定值 相对偏差(%) 允许限(%) ICP-MS校正值 ICP-OES测定值 相对偏差(%) 允许限(%) S1 32.4 21.5 3.14 4.25 15.0 30 3.14 4.10 13.3 30 0.64 0.84 13.5 30 S2 31.6 21.6 4.50 4.83 3.54 30 4.50 5.00 5.26 30 0.74 0.85 6.92 30 S3 29.3 20.2 9.09 9.65 2.99 27 9.09 10.4 6.72 27 2.56 2.53 0.59 30 S4 29.3 18.3 9.92 9.47 2.32 27 9.92 12.8 12.7 26 3.69 3.10 8.69 30 S5 25.9 21.1 17.34 17.71 1.06 24 17.34 15.6 5.28 25 6.22 4.74 13.5 29 注:相对偏差=(|X校正值-x|/x)×100%;其中X校正值为校正值,x为平均值;允许限=C×(14.37x-0.1263-7.659),其中C=1,x为平均值。 表 4 方法精密度
Table 4. Precision tests of the method
元素 GBW07133分次测定结果(μg/g) 平均值(μg/g) RSD(%) Ni 5.38 5.04 4.81 5.13 4.79 4.99 4.3 4.75 5.01 5.23 4.95 4.76 Sc 1.82 1.9 1.72 1.82 1.69 1.83 5.4 1.93 1.95 1.7 1.88 1.92 -
[1] 颜佳新, 孟琦, 王夏, 等. 碳酸盐工厂与浅水碳酸盐岩台地: 研究进展与展望[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(2): 232-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201902004.htm
Yan J X, Meng Q, Wang X, et al. Carbonate factory and carbonate platform: Progress and prospects[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2019, 21(2): 232-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201902004.htm
[2] Thomas A L, Daniel P S. The role of authigenic carbonate in Neoproterozoic carbon isotope excursions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 549(116534): 1-10. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X20304787
[3] Arthur L G, Roger H M, Artur C B N, et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Morro dos Seis Lagos siderite carbonatite, Amazonas, Brazil[J]. Lithos, 2020, 360-361(105433): 1-20. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493720300700
[4] Chen W, Ying Y C, Bai T, et al. In situ major and trace element analysis of magnetite from carbonatite-related complexes: Implications for petrogenesis and ore genesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 107: 30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.01.029
[5] 李向东, 何幼斌. 宁夏香山群徐家圈组顶部石灰岩地球化学特征及其时代意义[J]. 地球化学, 2019, 48(4): 325-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201904002.htm
Li X D, He Y B. Geochemical characteristics and their epochal significance of limestones at the top of Xujiajuan Formation, Xiangshan Group in the Ningxia autonomous region, China[J]. Geochimica, 2019, 48(4): 325-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201904002.htm
[6] 陈松, 傅学海, 桂和荣, 等. 皖北新元古界望山组灰岩微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2012, 14(6): 813-820. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201206018.htm
Chen S, Fu X H, Gui H R, et al. Geochemical characteristics of trace elements in limestone of the Neoproterozoic Wangshan Formation in northern Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2012, 14(6): 813-820. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201206018.htm
[7] Ekaterina P R, Anton R C, Laura P, et al. Trace-element composition and zoning in clinopyroxene- and amphibole-group minerals: Implications for element partitioning and evolution of carbonatites[J]. Lithos, 2012, 128-131: 27-45. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.10.003
[8] 王娜, 徐铁民, 魏双, 等. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定超细粒度岩石和土壤样品中的稀土元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(1): 68-76. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201904010043
Wang N, Xu T M, Wei S, et al. Determination of rare earth elements in ultra-fine rock and soil samples by ICP-MS using microwave digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(1): 68-76. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201904010043
[9] Zhu Y B, Jhanis J G, Yang X Y, et al. Calcium fluoride as a dominating matrix for quantitative analysis by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS): A feasibility study[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2020, 1129: 24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.07.002
[10] Zhao X Y, Zhong H, Mao W, et al. Molybdenite Re-Os dating and LA-ICP-MS trace element study of sulfide minerals from the Zijinshan high-sulfidation epithermal Cu-Au deposit, Fujian Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 118(103363): 1-17. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136819310066
[11] Zhang W, Hu Z C, Liu Y S, et al. In situ calcium isotopic ratio determination in calcium carbonate materials and calcium phosphate materials using laser ablation-multiple collector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 522: 16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.04.027
[12] Robert B, Martin J W, Lorenzo M, et al. Atmospheric S and lithospheric Pb in sulphides from the 2.06Ga Phalaborwa phoscorite-carbonatite Complex, South Africa[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 530(115939): 1-14. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X19306314
[13] Corinne K, Antonio S, Wei C, et al. Boron isotopic investigation of the Bayan Obo carbonatite complex: Insights into the source of mantle carbon and hydrothermal alteration[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 557(119859): 1-18. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254120303983
[14] Daniel W, Max W S, Hannes B M. Mineral resorption triggers explosive mixed silicate-carbonatite eruptions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2019, 510: 219-230. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2019.01.003
[15] Loula M, Kaňa A, Mestek O. Non-spectral inter-ferences in single-particle ICP-MS analysis: An underestimated phenomenon[J]. Talanta, 2019, 202: 565-571. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.04.073
[16] 李冰, 杨红霞. 电感耦合等离子体质谱原理和应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005: 85-106.
Li B, Yang H X. Principle and application of inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005: 85-106.
[17] Klaus P J, Denis S, Brigitte S, et al. Accurate trace ele-ment analysis of speleothems and biogenic calcium carbonates by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 318-319: 31-44. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.05.009
[18] 门倩妮, 刘玲, 温良, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定碳酸盐岩中30种痕量元素及干扰校正研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(4): 420-423. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.04.007
Men Q N, Liu L, Wen L, et al. Determination of thirty trace elements in carbonate rocks by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and interference correction[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(4): 420-423. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.04.007
[19] 赵志飞, 李丹, 李策, 等. 高钙碳酸盐地质样品中铜镍的测定[J]. 岩矿测试, 2010, 29(2): 187-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.02.021 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100221
Zhao Z F, Li D, Li C, et al. Determination of copper and nickel in high-calcium carbonate geological samples[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2010, 29(2): 187-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.02.021 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100221
[20] 《岩石矿物分析》编委会. 岩石矿物分析(第四版第二分册)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 105-114.
The editorial committee of Rock and Mineral Analysis. Rock and mineral analysis (The fourth edition: Vol. Ⅱ)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011: 105-114.
[21] 胡圣虹, 李清澜, 林守麟, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法直接测定碳酸盐岩中超痕量稀土元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2000, 19(4): 249-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2000.04.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20000474
Hu S H, Li Q L, Lin S L, et al. Determination of ultra-trace rare earth elements in carbonate by ICP-MS[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2000, 19(4): 249-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2000.04.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20000474
[22] 田梅, 韩小元, 王江, 等. ICP-MS测量环境样品中铀的非质谱干扰内标校正研究[J]. 分析试验室, 2012, 31(8): 116-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201208033.htm
Tian M, Han X Y, Wang J, et al. Study on correction of matrix effect with different internal standards during measurement of uranium by ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2012, 31(8): 116-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201208033.htm
[23] 罗策, 雷小燕, 黄永红, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定锆及锆合金中镉含量的质谱干扰分析[J]. 分析科学学报, 2016, 32(4): 515-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKX201604015.htm
Luo C, Lei X Y, Huang Y H, et al. Mass spectrum interference analysis for inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry determination of cadmium in zirconium and zirconium alloys[J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2016, 32(4): 515-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKX201604015.htm
[24] Amy L R, Gary M H. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and electrospray mass spectrometry for speciation analysis: Applications and instrumentation[J]. Spectrochimica Acta: Part B, 2004, 59: 135-146. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2003.09.004
[25] Bussweiler Y, Giuliani A, Greig A, et al. Trace element analysis of high-Mg olivine by LA-ICP-MS-Characterization of natural olivine standards for matrix-matched calibration and application to mantle peridotites[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 524: 136-157. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.06.019
[26] Zhang W. Direct lead isotope analysis in Hg-rich sul-fides by LA-MC-ICP-MS with a gas exchange device and matrix-matched calibration[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 948: 9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.10.040
[27] Hu Y, Chen X Y, Xu Y K, et al. High-precision analysis of potassium isotopes by HR-MC-ICPMS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493: 100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.033
[28] Doucelance R, Bruand E, Matte S, et al. In-situ deter-mination of Nd isotope ratios in apatite by LA-MC-ICPMS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 550: 1-21.
[29] Qiao L, Wu Z W, Li Y, et al. A novel calibration strategy for the analysis of airborne particulate matter by direct solid sampling ETV-ICP-MS[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2020, 159: 1-17. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0026265X20322359
[30] Peter T S, Chen T Y, Laura F R, et al. Rapid uranium-series age screening of carbonates by laser ablation mass spectrometry[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2016, 31: 28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.10.004
[31] Ramon A, Francisco B, Otmar G, et al. Quantification and size characterisation of silver nanoparticles in environmental aqueous samples and consumer products by single particle-ICPMS[J]. Talanta, 2017, 175: 200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.07.048
[32] Zellmer G F, Kimura J I, Chang Q, et al. Rapid determination of initial 87Sr/86Sr and estimation of the Rb-Sr age of plutonic rocks by LA-ICPMS of variably altered feldspars: An example from the 1.14Ga Great Abitibi Dyke, Ontario, Canada[J]. Lithos, 2018, 314-315: 52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.05.024
[33] Christoper J M L, Graham P, Pedro W, et al. Element and isotopic signature of re-fertilized mantle peridotite as determined by nanopowder and olivine LA-ICPMS analyses[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 635: 1-17. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254120300036
[34] 戴洁. 高分辨电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定珊瑚中铅的同位素组成研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2010.
Dai J.Research on measurement of lead isotopes in corals with HR-ICP-MS[D].Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2010.
[35] Lebrato M, Mcclintock J B, Amsler M O, et al. From the Arctic to the Antarctic: The major, minor, and trace elemental composition of echinoderm skeletons[J]. Ecology, 2013, 94(6): 1434. doi: 10.1890/12-1950.1
-




 下载:
下载: