Research on the Relationship between Urbanization and Atmospheric Environmental Quality in the Economic Development of Major Cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region
-
摘要:
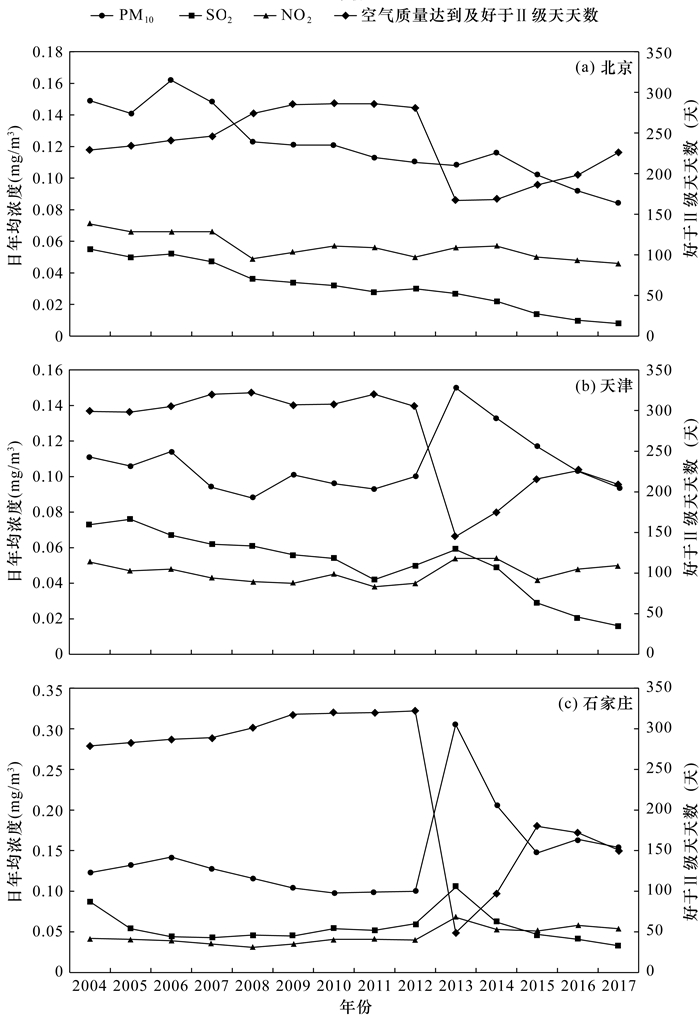
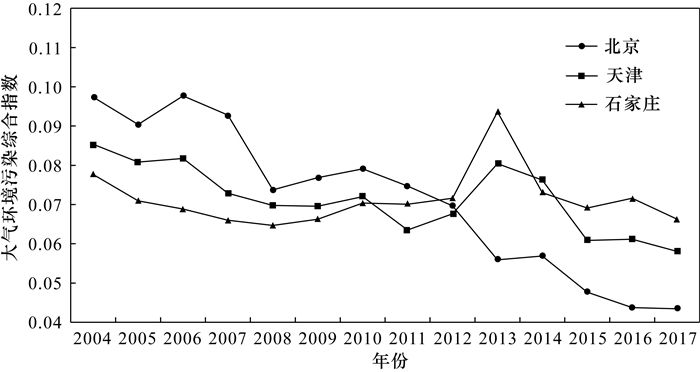
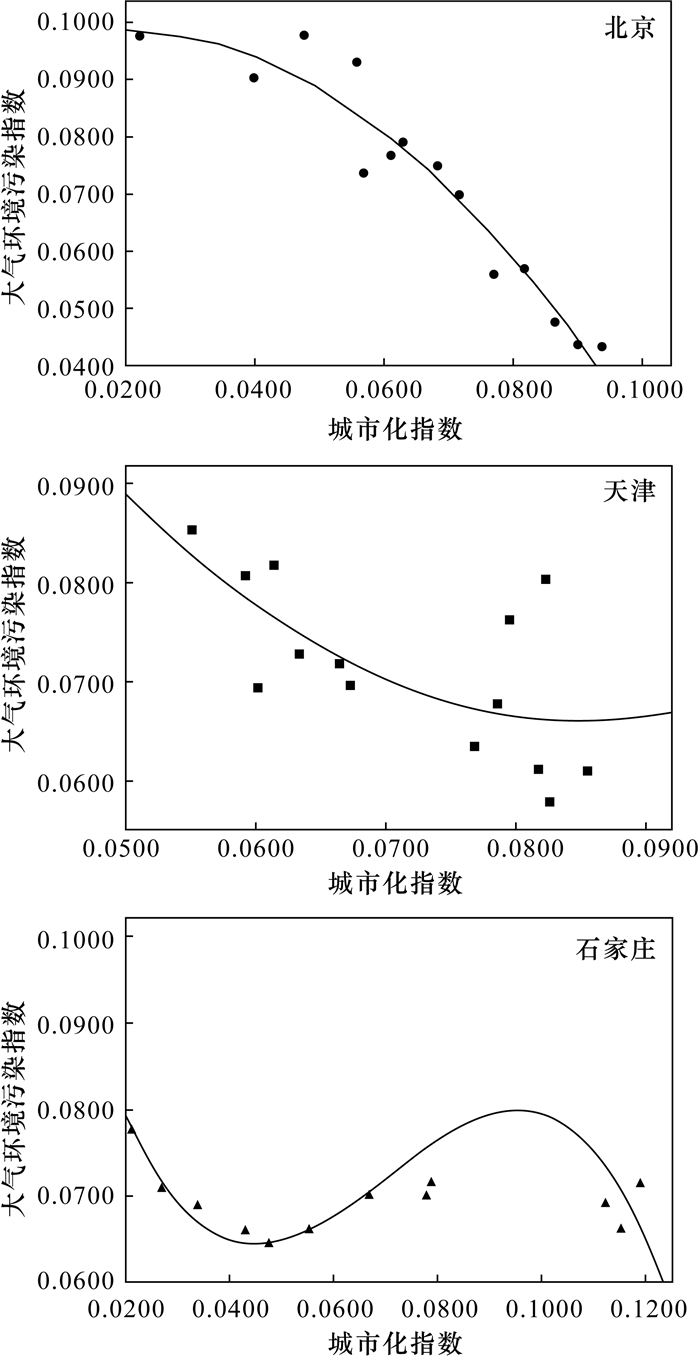
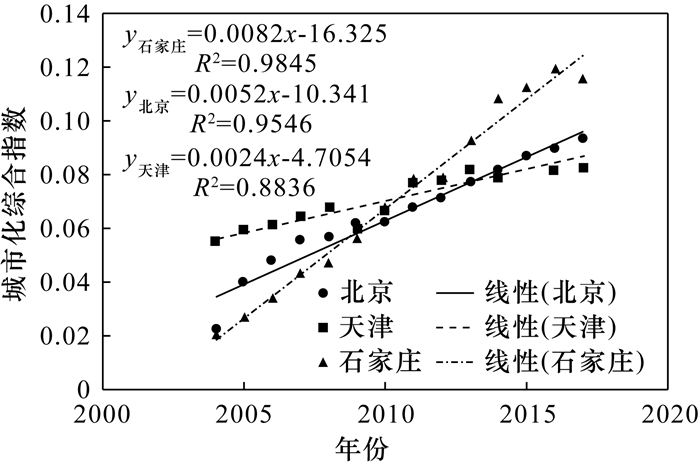
京津冀城市群在快速城市化进程中,“高耗能、高污染、高排放”的粗放型经济发展模式带来了一系列大气污染问题,亟需协调经济发展与大气环境质量之间的关系。本文基于2004-2017年北京市、天津市、石家庄市的大气环境质量与城市化各指标数据,运用熵值法多维度研究了城市化进程中大气环境质量的演化规律。选取城市空气主要污染物SO2、NO2、PM10的年均浓度、好于Ⅱ级天天数4个指标反映城市大气环境质量水平,选取地区生产总值、人均GDP、三产比重、建成区面积等10个指标反映城市化发展水平,分别进行综合指数模型构建和回归拟合。分析表明,城市化对大气环境质量的影响是各因素共同作用的结果,京津冀三市的城市化综合指数与大气环境污染综合指数分别呈“倒U型”、“正U型”和“倒N型”。将10个城市化指标分别归类为结构效应、规模效应以及活动效应,进一步分析了各类效应对大气环境污染指数的影响。对于北京市,三类效应各因变量对大气环境均产生负向影响;对于天津市,结构效应、规模效应中的建成区面积和活动效应中的人均GDP、生产总值、居民消费水平和社会消费品零售总额与大气环境质量呈现负相关关系;对于石家庄市,由于分析数据的时间序列有限,三种效应的各因变量对大气环境质量的影响不明确。本文研究结果可为京津冀地区的城市生态文明建设提供基础数据支撑。
Abstract:BACKGROUND During rapid urbanization of cities in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, the extensive economic development mode of 'high energy consumption, high pollution and high emission' has caused a series of atmospheric pollution problems. It is crucial to coordinate the relationship between economic development and atmospheric environmental quality.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the relationship between the urbanization and the atmospheric environmental quality of the three cities of Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang.
METHODS Based on the data of various indicators of atmospheric environmental quality and urbanization in Beijing, Tianjin, and Shijiazhuang from 2004 to 2017, the entropy method was used to study the evolution of atmospheric environmental quality in the process of urbanization in multiple dimensions. The annual average concentration of urban atmospheric pollutants SO2, NO2, PM10, and the number of days better than level 2 were 4 atmospheric environmental quality indicators, and 10 development indicators including regional GDP, per capita GDP, proportion of tertiary industries, and built-up area were selected to construct comprehensive index models and regression fitting.
RESULTS The impact of urbanization on atmospheric environmental quality was the result of the combined effect of various factors. The relationship between comprehensive urbanization index and comprehensive atmospheric environmental pollution index in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei was 'inverted U-shaped', 'positive U-shaped' and 'inverted N-shaped', respectively. The 10 urbanization indicators were classified into structural effects, scale effects and activity effects, and further analyze the impact of various effects on the atmospheric environmental pollution index. For Beijing, the dependent variables of the three types of effects all had negative impacts on atmospheric environmental quality. For Tianjin, the built-up area in the structure effect and scale effect, and the per capita GDP, GDP, resident consumption level and the total retail sales of consumer goods in the activity effect had negative correlations with atmospheric environmental quality. The impact of each dependent variable of the three effects on atmospheric environmental quality was unclear for Shijiazhuang.
CONCLUSIONS The EKC hypothesis can reflect the relationship between the urbanization and atmospheric environmental quality to a certain extent. For the cities like Beijing that have basically completed the transformation of economic development, the EKC hypothesis is established obviously. But for the cities like Tianjin and Shijiazhuang that have not completed the economic restructuring, the relationship between urbanization and atmospheric environmental quality is uncertainty. Further study should be necessary.
-
Key words:
- urbanization /
- atmospheric environmental quality /
- EKC curve /
- fitting relationship
-

-
表 1 城市化与大气环境质量相关性指标体系
Table 1. Index system of urbanization and atmospheric environmental quality
项目 指标 指标代号 单位 城市化 地区生产总值 X1 万元 人均GDP X2 元 三产比重 X3 % 城市化率 X4 % 固定资产投资 X5 万元 居民消费水平 X6 元 社会消费品零售总量 X7 万元 城市人均居住面积 X8 m2 建成区面积 X9 km2 城市绿化覆盖率 X10 % 大气环境质量 可吸入颗粒物浓度(年日均值) Y1 mg/m3 SO2浓度(年日均值) Y2 mg/m3 NO2浓度(年日均值) Y3 mg/m3 空气质量达到及好于Ⅱ级的天数 Y4 天 表 2 京津冀城市化与大气环境污染各指标权重值
Table 2. Weight values of urbanization index and atmospheric environmental pollution index in the three cities
城市 权重(wj) X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 北京 0.089 0.089 0.129 0.144 0.089 0.088 0.089 0.099 0.088 0.095 0.171 0.159 0.166 0.505 天津 0.097 0.100 0.074 0.096 0.123 0.097 0.097 0.100 0.091 0.123 0.145 0.158 0.149 0.548 石家庄 0.102 0.101 0.079 0.101 0.098 0.097 0.097 0.109 0.096 0.119 0.130 0.122 0.132 0.616 注:X表示城市化的各指标,Y表示大气环境污染的各指标。 表 3 京津冀城市大气环境污染综合指数与城市化综合指数的模型拟合结果
Table 3. Curve fitting between the comprehensive atmospheric environmental pollution index and the comprehensive urbanization index for the three cities
城市 模型 β0 β1 β2 β3 R2 F检验P值 北京 线性回归 0.129 -0.888 - - 0.868 0.000 二元线性回归 0.094 (0.000) 0.413 (0.032) -10.754 (0.007) - 0.935 0.000 三元线性回归 0.071 (0.030) 1.935 (0.292) -39.657 (0.248) 165.881 (0.390) 0.940 0.000 天津 线性回归 0.109 -0.533 - - 0.423 0.012 二元线性回归 0.202 -3.212 18.920 - 0.447 0.039 三元线性回归 0.202 -3.212 18.920 0.000 0.447 0.039 石家庄 线性回归 0.070 0.026 - - 0.015 >0.5 二元线性回归 0.069 0.032 -0.040 - 0.015 >0.5 三元线性回归 0.123 -3.101 50.733 -241.459 0.521 0.050 注:所有分析均在5%显著水平上进行回归分析。括号内数据为t检验P值。 表 4 大气环境污染指数与标准化后的各城市化因变量指标之间的相关关系
Table 4. Correlation between atmospheric environmental pollution index and the dependent variables of urbanization after standardization
项目 结构效应 规模效应 活动效应 三产比重 城市化率 固定资产投资 建成区面积 建成区绿化率 人均GDP 生产总值 居民消费水平 社会消费品零售总额 城市人均居住面积 北京大气环境污染指数 (0.635)* (0.730)** (0.954)** (0.843)** (0.912)** (0.964)** (0.969)** (0.968)** (0.968)** (0.916)** 天津大气环境污染指数 (0.69)** 0.53 (0.08) (0.81)** (0.05) (0.66)** (0.71)** (0.70)** (0.70)** 0.30 石家庄大气环境污染指数 (0.04) 0.19 0.12 (0.05) 0.02 0.15 0.16 0.10 0.11 0.23 注:“**”表示相关性在0.01水平上显著(双侧),“*”表示相关性在0.05水平上显著(单侧),括号内数据表示负数。 -
[1] Grossman G M, Krueger A B. Economic growth and the environment[J]. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 1995, 110(2): 353-377. doi: 10.2307/2118443
[2] 谭梦薇. 经济增长与环境污染实证研究[J]. 合作经济与科技, 2020(16): 42-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-190X.2020.16.018
Tan M W. An empirical study on economic growth and environmental pollution[J]. Co-Operative Economy & Science, 2020(16): 42-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-190X.2020.16.018
[3] Al-Mulali U, Weng-Wai C, Sheau-Ting L, et al. Investigating the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2015(48): 315-323. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1470160X14003951
[4] Richard T C, Yongil J, Donald R M. The relationship between air pollution emissions and income: US data[J]. Environment and Development Economics, 1997, 20(12): 433-450.
[5] R-Roda I, Comas J, Poch M. Automatic knowledge acquisition from complex processes for the development of knowledge-based system[J]. Industrial Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(15): 3353-3360. doi: 10.1021/ie000528c
[6] Stern D I, Dijk J V. Economic growth and global particulate pollution concentrations[J]. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 2016, 142(3-4): 1-16. http://ideas.repec.org/p/ags/ancewp/249523.html
[7] Noroglu E, Robert M. Kuznets and Environmental Kuznets Curves for developing countries[M]//Yülek M. Industrial policy and sustainable growth, sustainable development. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2017. DOI10.1007/978-981-10-3964-5_12-1.
[8] Sinha A, Bhattacharya J. Estimation of Environmental Kuznets Curve for SO2 emission: A case of India cities[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 72: 881-894. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.09.018
[9] 李雅男, 丁振民, 邓元杰, 等. 中国城市工业化发展与PM2.5的关系: 兼论EKC曲线形成的内在机制[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(4): 1987-1995. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202004058.htm
Li Y N, Ding Z M, Deng Y J, et al. Relationship between urban industrialization and PM2.5 concentration in China and the internal mechanism of EKC[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(4): 1987-1995. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202004058.htm
[10] 李茜, 宋金平, 张建辉, 等. 中国城市化对环境空气质量影响的演化规律研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 22(9): 2402-2411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201309008.htm
Li Q, Song J P, Zhang J H, et al. Dynamics in the effect of China's urbanization on air quality[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 22(9): 2402-2411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201309008.htm
[11] 周茜. 中国区域经济增长对环境质量的影响: 基于东、中、西部地区环境库兹涅茨曲线的实证研究[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2011, 26(10): 45-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2011.10.008
Zhou Q. The effect of China's regional economic growth on the environmental quality: Based on the empirical study of eastern, central and western Kuznets Curve[J]. Statistics & Information Forum, 2011, 26(10): 45-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2011.10.008
[12] 刘华军, 裴延峰. 我国雾霾污染的环境库兹涅茨曲线检验[J]. 统计研究, 2017, 34(3): 45-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYJ201703004.htm
Liu H J, Pei Y F. An empirical test of the Environmental Kuznets Curve of China's Haze pollution[J]. Statistical Analysis, 2017, 34(3): 45-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYJ201703004.htm
[13] 崔秀萍. 经济发展中城市化与大气污染曲线拟合相关性研究——以内蒙古呼和浩特市为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(11): 44-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201711008.htm
Cui X P. Curve fitting of urbanization and air pollution in economic development of Hohhot City, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(11): 44-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201711008.htm
[14] 王盈晓, 刘目兴, 张永利, 等. 武汉市城市化进程与大气污染关系探究[J]. 环境保护科学, 2016, 42(1): 77-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJBH201601017.htm
Wang Y X, Liu M X, Zhang Y L, et al. Study on the relationship between urbanization process and air pollution in Wuhan City[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2016, 42(1): 77-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJBH201601017.htm
[15] 张喆, 王金南, 杨金田, 等. 城市空气质量与经济发展的曲线估计研究[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2007(4): 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2007.04.015
Zhang Z, Wang J N, Yang J T, et al. Study on the curve estimation of urban air quality and economic development[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2007(4): 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2007.04.015
[16] 唐倩, 郑博, 薛文博, 等. 京津冀及周边地区秋冬季大气污染物排放变化因素解析[J]. 环境科学, 2020, https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202007218. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202007218
Zheng Q, Zheng B, Xue W B, et al. Contributors to air pollutant emission changes in autumn and winter in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and its surrounding areas[J]. Environmental Sciences, 2020, https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202007218. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202007218
[17] 沈楠驰, 周丙锋, 李珊珊, 等. 2015-2019年天津市大气污染物时空变化特征及成因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(9): 1862-1873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ202009019.htm
Shen N C, Zhou B F, Li S S, et al. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and origin analysis of air pollutants in Tianjin from 2015 to 2019[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(9): 1862-1873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ202009019.htm
[18] 杜颖. 河北省经济增长与大气污染关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
Du Y. Study on the relationship between economic growth and air pollution in Hebei Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (北京), 2016.
[19] 高明, 郭峰. 城市化对空气质量的影响研究——以京津冀城市群为例[J]. 环境经济研究, 2018(3): 88-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJN201803008.htm
Gao M, Guo F. The influence of urbanization on air quality: A case of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration[J]. Environmental Economic Research, 2018(3): 88-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJN201803008.htm
[20] 孙能浩. 城市化对环境污染的影响机制分析——基于268个地级市面板数据的实证研究[D]. 天津: 南开大学, 2015.
Sun N H. The analysis of influence mechanism between urbanization and environment pollution basing on empirical research of panel data of 268 cities[D]. Tianjin: Nankai University, 2015.
[21] 邵咪咪. 中国城市化和工业化阶段的环境污染因素及应对策略[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2011.
Shao M M. China's environmental pollution under urbanization and industrialization process, influence factors and abatement policies[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2011.
[22] 杨柳青青. 产业格局、人口集聚、空间溢出与中国城市生态效率[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.
Yang L Q Q. Industrial pattern, population agglomeration, spatial spillover and city ecological efficiency in China[D]. Wuhan: Huanzhong University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[23] 高明, 郭施宏, 夏玲玲. 福州市城市化进程与大气污染关系研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2015, 37(5): 44-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR201505009.htm
Gao M, Guo S H, Xia L L. Relationship between urbanization and air pollution in Fuzhou City[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 2015, 37(5): 44-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR201505009.htm
[24] 吴玥弢, 仲伟周. 城市化与大气污染——基于西安市的经验分析[J]. 当代经济科学, 2015, 37(3): 71-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DJKX201503010.htm
Wu Y T, Zhong W Z. Urbanization and atmospheric pollution-based on the empirical analysis of Xi'an City[J]. Modern Economic Science, 2015, 37(3): 71-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DJKX201503010.htm
[25] 李景刚, 张效军, 高艳梅, 等. 基于改进熵值模型的城市土地集约利用动态评价——以广州市为例[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2012, 31(4): 118-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYYY201204026.htm
Li J G, Zhang X J, Gao Y M, et al. Dynamic analysis and evaluation on the degree of urban land intensive use based on improved entropy model: A case of Guangzhou City[J]. Area Research and Development, 2012, 31(4): 118-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYYY201204026.htm
[26] 周瑾. 基于熵值法的上海市大气污染排放水平综合评价研究[J]. 上海节能, 2020(10): 1141-1144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJL202010014.htm
Zhou J. Research on comprehensive evaluation of Shanghai air pollution emission level based on entropy evaluation method[J]. Shanghai Energy Conservation, 2020(10): 1141-1144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJL202010014.htm
[27] 李小胜, 宋马林, 安庆贤. 中国经济增长对环境污染影响的异质性研究[J]. 南开经济研究, 2013(5): 96-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKJJ201305008.htm
Li X S, Song M L, An Q X. The heterogeneity research of the impact of China's economic growth on environmental pollution[J]. Nankai Economic Studies, 2013(5): 96-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKJJ201305008.htm
[28] Cole M A, Rayner A J, Bates J M. The Environmental Kuznets Curve: An empirical analysis[J]. Environment and Development, 1997, 2(4): 433-450. doi: 10.1017/S1355770X97000235
[29] 刘满芝, 杨继贤, 马丁, 等. 基于LMDI模型的中国主要大气污染物的空间差异及其影响因素分析[J]. 资源科学, 2015, 37(2): 333-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY201502014.htm
Liu M Z, Yang J X, Ma D, et al. Spatial disparity and factor analysis of major air pollutant emission in China based on LMDI methods[J]. Resource Science, 2015, 37(2): 333-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY201502014.htm
[30] Fujii H, Managi S, Kaneko S. Decomposition analysis of air pollution abatement in China: Empirical study for ten industrial sectors from 1998 to 2009[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2013, 59(15): 22-31. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652613004629
[31] Wu L, Zeng W. Research on the contribution of structure adjustment on SO2 emissions reduction——Case study Shijingshan District, Beijing[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2013, 18: 849-855. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1878029613002466
[32] 赵惠, 吴金希. 基于环境库兹涅茨曲线的京冀区际环境污染转移的测度研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(5): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ202005010.htm
Zhao H, Wu J X. Measurement of environmental pollution transfer in Beijing-Hebei Region based on the Environmental Kuznets Curve[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2020, 30(5): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ202005010.htm
[33] Pfaff A, Chaudhuri S, Nye H. Household production and Environmental Kuznets Curves-Examining the desirability and feasibility of substitution[J]. Environmental & Resource Economics, 2004, 27(2): 187-200. doi: 10.1023/B%3AEARE.0000017279.79445.72
[34] 林伯强, 蒋竺均. 中国二氧化碳的环境库兹涅茨曲线预测及影响因素分析[J]. 管理世界, 2009(4): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLSJ200904005.htm
Lin B Q, Jiang Z J. Environmental Kuznets Curve prediction and influence factor analysis of carbon dioxide in China[J]. Management World, 2009(4): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLSJ200904005.htm
[35] 高宏霞, 杨林, 付海东. 中国各省经济增长与环境污染关系的研究与预测[J]. 经济学动态, 2012(1): 52-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJXD201201011.htm
Gao H X, Yang L, Fu H D. Research and forecast on the relationship between economic growth and environmental pollution in Chinese provinces[J]. Economic Perspectives, 2012(1): 52-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJXD201201011.htm
[36] 陈佳贵, 黄群慧, 钟宏武. 中国地区工业化进程的综合评价和特征分析[J]. 经济研究, 2006(6): 4-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJYJ200606001.htm
Chen J G, Huang Q H, Zhong H W. The synthetic evaluation and analysis on regional industrialization[J]. Economic Research, 2006(6): 4-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJYJ200606001.htm
[37] Shafik N, Bandyopadhyay S. Economic growth and environment quality: Time-series and cross-country evidence[R]. World Bank, 1992.
-



 下载:
下载: