Study on Porosity Measurement Determination Methods of a Shale Reservoir in the Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin
-
摘要:
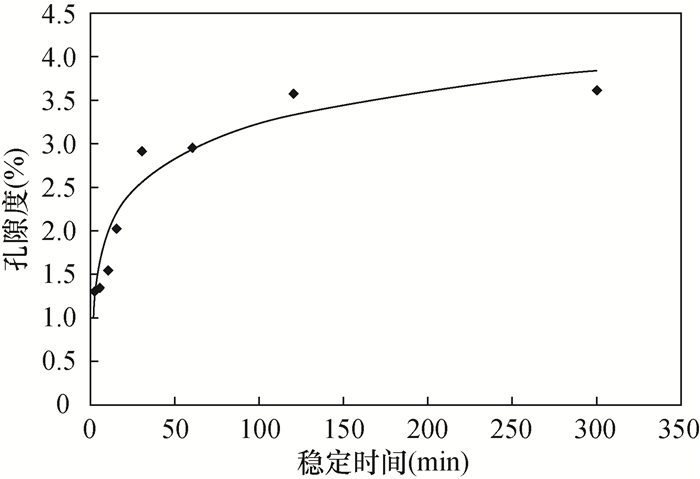
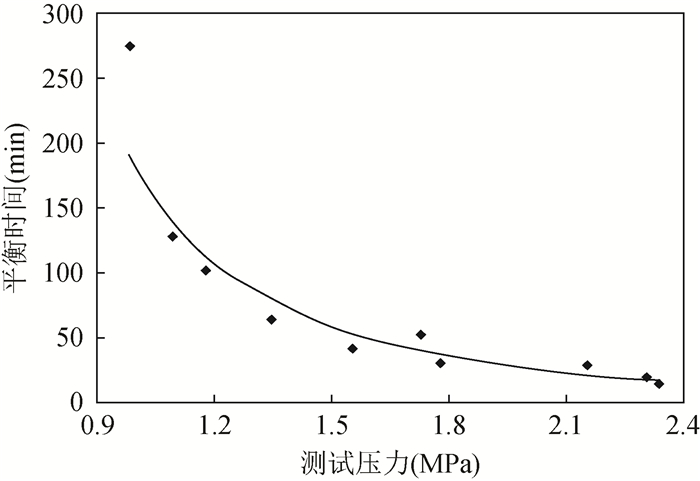
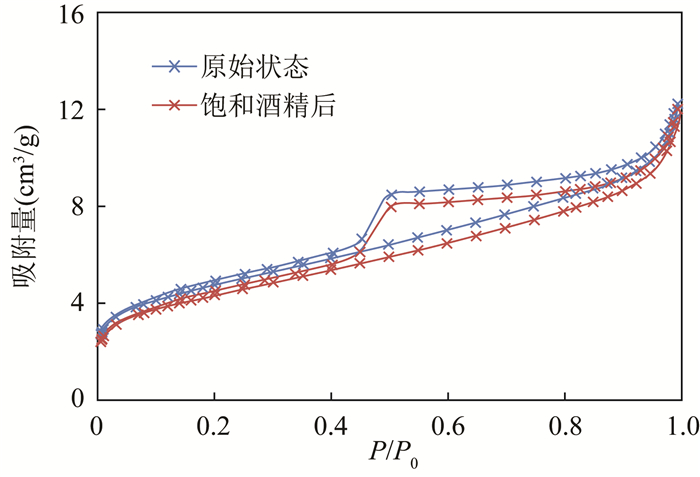
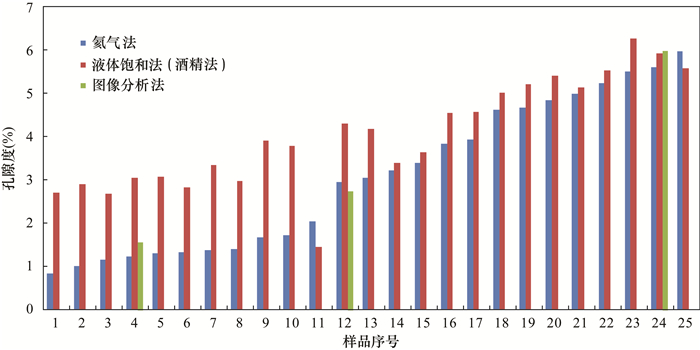
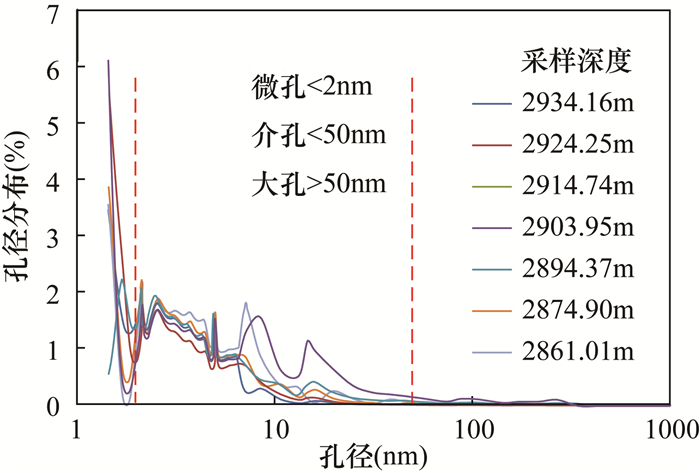
孔隙度是页岩气藏勘探、评价的关键参数,快速、准确测定页岩孔隙度对于储量计算至关重要。目前有氦气法、液体饱和法、图像分析法应用于页岩孔隙度测定,但方法间、实验室间比对效果欠佳。本文选取69件四川盆地下志留统龙马溪组页岩样品,应用X射线衍射、氩离子抛光-扫描电镜、压汞-氮气吸附等分析测试技术研究样品特征,开展方法间的孔隙度测定比对实验,分析各方法的适用性。结果表明:①龙马溪组页岩黏土含量高、有机质孔隙多、孔喉细小、渗流能力差,导致了外来液体和气体难以快速进入孔隙中,对岩心图像资料的分辨率有很高要求;②液体饱和法(酒精法)使用20MPa压力饱和样品24h,导致了岩心损伤,测得的孔隙度偏离真实值;图像分析法因忽略了矿物基质中的微孔(孔径 < 2nm)和介孔(孔径 < 50nm)等因素使孔隙度测定结果不可靠;③氦气法孔隙度测定结果与烘干温度、稳定时间密切相关,温度越高则测得的孔隙度越大,稳定时间过短会使孔隙度结果偏小。在60℃下烘干岩心24h以上至恒重状态后,通过设置合理的稳定时间,氦气法可获得准确的孔隙度结果,适当提高注入压力有助于加快实验速率。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Porosity is a key parameter for exploration and evaluation of shale gas reservoirs. Rapid and accurate determination of shale porosity is crucial for reserve calculation. At present, there are helium gas method, liquid saturation method and image analysis method applied to shale porosity determination, but the comparison between methods and laboratories is lacking.
OBJECTIVES To evaluate the applicability of different methods for determining shale porosity.
METHODS The characteristics of 69 shale samples from the Longmaxi Formation were studied by analyzing and testing techniques such as X-ray diffraction, argon ion polishing-scanning electron microscopy, and mercury injection-nitrogen adsorption method. Comparison experiments for porosity measurement were conducted among helium method, liquid saturation method and image analysis method.
RESULTS The Longmaxi Formation shale had high clay content, many organic pores, small pore throats, and poor seepage capacity, which made it difficult for foreign liquids and gases to quickly enter the pores, which required high resolution of core image data. The liquid saturation method (alcohol method) used 20MPa pressure to saturate the sample for 24 hours, resulting in core damage, and the measured porosity deviated from the true value. The image analysis method ignored the micropores (pore size < 2nm) and mesopores (pore size < 50nm) in the mineral matrix and other factors, making the porosity measurement result unreliable. The porosity measurement result of the helium method was closely related to the drying temperature and stabilization time. The higher the temperature, the larger the measured porosity, and if the stabilization time is too short, the porosity result will be smaller than the real values.
CONCLUSIONS After drying the core at 60℃ for more than 24 hours to a constant weight, by setting a reasonable stabilization time, accurate porosity results can be obtained by the helium method. Properly increasing the injection pressure helps to speed up the experimentation rate.
-
Key words:
- shale porosity /
- nitrogen adsorption /
- sample damage /
- helium method /
- drying temperature /
- settling time
-

-
[1] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等. 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6): 641-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201006003.htm
Zou C N, Dong D Z, Wang S J, et al. Geological characteristics, formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6): 641-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201006003.htm
[2] 龙胜祥, 彭勇民, 刘华, 等. 四川盆地东南部下志留统龙马溪组一段页岩微-纳米观地质特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(9): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201709006.htm
Long S X, Peng Y M, Liu H, et al. Micro- and nano-scale geological characteristics of the shale in the first member of lower Silurian Longmaxi Fm in SE Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(9): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201709006.htm
[3] 曹茜, 王兴志, 戚明辉, 等. 页岩油地质评价实验测试技术研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 337-349. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202001060005
Cao Q, Wang X Z, Qi M H, et al. Research progress on experimental technologies of shale oil geological evaluation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 337-349. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202001060005
[4] 孙建孟, 宗成林, 董旭, 等. 基于核磁共振的页岩粉碎样品孔隙度研究[J]. 测井技术, 2017, 41(5): 512-516. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS201705003.htm
Sun J M, Zong C L, Dong X, et al. Porosity measurement of crushed shales using NMR[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2017, 41(5): 512-516. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS201705003.htm
[5] 李磊, 郝景宇, 肖继林, 等. 微米级X射线断层成像技术对四川元坝地区页岩微裂缝的定量表征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 362-372. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202001150011
Li L, Hao J Y, Xiao J L, et al. Quantitative characterization of shale micro-fracture in the Yuanba area of the Sichuan Basin by micro X-ray tomography[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 362-372. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202001150011
[6] 张涛, 张希巍. 页岩孔隙定性与定量方法的对比研究[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2017, 40(4): 34-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT201704008.htm
Zhang T, Zhang X W. Comparative study on qualitative and quantitative methods for shale pore characterization[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2017, 40(4): 34-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT201704008.htm
[7] 于萍, 张瑜, 闫建萍, 等. 四川盆地龙马溪组页岩吸水特征及3种页岩孔隙度分析方法对比[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(7): 1016-1027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202007015.htm
Yu P, Zhang Y, Yan J P, et al. The characteristics of water uptake and the comparative studies on three methods of determining porosity in organic-rich shale of Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(7): 1016-1027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202007015.htm
[8] 王世谦. 页岩岩心样品分析数据对比及其影响因素分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 160-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001031.htm
Wang S Q. Correlation of shale core analysis results and its influencing factors[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 160-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001031.htm
[9] 陈思宇, 田华, 柳少波, 等. 致密储层样品体积测量对孔隙度误差的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(6): 850-856. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201606021.htm
Chen S Y, Tian H, Liu S B, et al. Influence of bulk volume measurement on porosity error in tight reservoir core plug analysis[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(6): 850-856. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201606021.htm
[10] 李新, 刘鹏, 罗燕颖, 等. 页岩气储层岩心孔隙度测量影响因素分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(5): 2181-2187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201505025.htm
Li X, Liu P, Luo Y Y, et al. Analysis of influencing factors on porosity measurement of shale gas core[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(5): 2181-2187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201505025.htm
[11] 高效曾. 核磁共振孔隙度和岩性有关[J]. 测井技术, 1998(4): 71-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS804.015.htm
Gao X Z. NMR porosity is related with lithology[J]. Well Logging Technology, 1998(4): 71-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS804.015.htm
[12] 朱晴, 乔向阳, 张磊. 高压压汞在致密气藏孔喉分布表征和早期产能评价中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 373-383. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201909230138
Zhu Q, Qiao X Y, Zhang L. Application of high-pressure mercury injection in pore-throat distribution characterization and early productive evaluation of tight gas reservoir[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 373-383. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201909230138
[13] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等. 纳米CT页岩孔隙结构表征方法研究——以JY-1井为例[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(11): 1253-1261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201811005.htm
Gou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al. Characterization method of shale pore structure based on nano-CT: A case study of Well JY-1[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(11): 1253-1261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201811005.htm
[14] 戚明辉, 李君军, 曹茜. 基于扫描电镜和JMicroVision图像分析软件的泥页岩孔隙结构表征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(3): 260-269. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901160008
Qi M H, Li J J, Cao Q. The pore structure characteri-zation of shale based on scanning electron microscopy and JMicroVision[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(3): 260-269. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901160008
[15] 白名岗, 夏响华, 张聪, 等. 场发射扫描电镜及PerGeos系统在安页1井龙马溪组页岩有机质孔隙研究中的联合应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3): 225-234. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201803260030
Bai M G, Xia X H, Zhang C, et al. Study on shale organic porosity in the Longmaxi Formation, AnYe-1 well using field emission-scanning electron microscopy and PerGeos system[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3): 225-234. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201803260030
[16] Keller L M, Schuetz P, Erni R, et al. Characterization of multi-scale microstructural features in Opalinus Clay[J]. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 170: 83-94.
[17] 贾宁洪, 吕伟峰, 常天全, 等. 高效无损岩心孔隙度精确测量新方法[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(7): 824-828, 844.
Jia N H, Lyu W F, Chang T Q, et al. A new method for precisely measuring core porosity with high efficiency and no destruction[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(7): 824-828, 844.
[18] 胡钦红, 张宇翔, 孟祥豪, 等. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近系沙河街组页岩油储集层微米-纳米级孔隙体系表征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(5): 681-690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201705004.htm
Hu Q H, Zhang Y X, Meng X H, et al. Characterization of micro-nano pore networks in shale oil reservoirs of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(5): 681-690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201705004.htm
[19] 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等. 页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 301-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201302013.htm
Yang F, Ning Z F, Hu C P, et al. Characterization of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 301-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201302013.htm
[20] Brunauer S, Deming L S, Deming W E, et al. On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1940, 62(7): 1723-1732. doi: 10.1021/ja01864a025
[21] Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark A V, et al. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report)[J]. Chemistry International Newsmagazine for IUPAC, 2016, 38(1): 25.
[22] 郭旭升, 李宇平, 刘若冰, 等. 四川盆地焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构特征及其控制因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(6): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406002.htm
Guo X S, Li Y P, Liu R B, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of micro-pore structures of Longmaxi shale play in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406002.htm
[23] 王玉满, 王宏坤, 张晨晨, 等. 四川盆地南部深层五峰组—龙马溪组裂缝孔隙评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(4): 531-539. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201704008.htm
Wang Y M, Wang H K, Zhang C C, et al. Fracture pore evaluation of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng to lower Silurian Longmaxi Formations in southern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(4): 531-539. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201704008.htm
[24] 张峰, 荣莽, 乌效鸣, 等. 陆相与海相页岩水相润湿渗吸特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(32): 126-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201932020.htm
Zhang F, Rong M, Wu X M, et al. Characteristics of wettability and imbibition between continental and marine shale[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(32): 126-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201932020.htm
[25] 薛华庆, 周尚文, 蒋雅丽, 等. 水化作用对页岩微观结构与物性的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(6): 1075-1081. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806017.htm
Xue H Q, Zhou S W, Jiang Y L, et al. Effects of hydration on the microstructure and physical properties of shale[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(6): 1075-1081. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806017.htm
[26] 蒋裕强, 付永红, 谢军, 等. 海相页岩气储层评价发展趋势与综合评价体系[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(10): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201910001.htm
Jiang Y Q, Fu Y H, Xie J, et al. Development trend of marine shale gas reservoir evaluation and a suitable comprehensive evaluation system[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(10): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201910001.htm
[27] 付永红, 司马立强, 张楷晨, 等. 页岩岩心气测孔隙度测量参数初探与对比[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(3): 144-148, 174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201803028.htm
Fu Y H, Sima L Q, Zhang K C, et al. Preliminary study and comparison of shale core gas-porosity test parameters[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(3): 144-148, 174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201803028.htm
[28] Testamanti M N, Rezaee R. Determination of NMR T2 cut-off for clay bound water in shales: A case study of Carynginia Formation, Perth Basin, western Australia[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2017, 149: 497, 503.
[29] Luffel D L, Guidry F K, Curtis J B. Evaluation of Devonian shale with new core and Log analysis methods[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1992, 44(11): 1192-1197. doi: 10.2118/21297-PA
[30] 杨海, 石孝志, 尹丛彬, 等. 不同类型液体水化作用下海相页岩巴西劈裂破坏特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(5): 72-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202005012.htm
Yang H, Shi X Z, Yin C B, et al. Brazilian tensile failure characteristics of marine shale under the hydration effect of different fluids[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(5): 72-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202005012.htm
[31] 周尚文, 董大忠, 张介辉, 等. 页岩气储层孔隙度测试方法关键参数优化[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(5): 20-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202105004.htm
Zhou S W, Dong D Z, Zhang J H, et al. Optimization of key parameters for porosity measurement of shale gas reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(5): 20-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202105004.htm
-



 下载:
下载: