Distribution Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements and Heavy Metals in a Soil-Plant System at Bayan Obo Rare Earth Mine, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
白云鄂博是世界最大的稀土矿山,研究白云鄂博矿区土壤及植物等环境介质中的稀土元素和重金属元素的分布特征,可以为调查矿区环境现状提供基础数据,同时为矿山环境修复提供参考依据。本文采集了白云鄂博稀土矿区的土壤、植物,以及背景区本巴台地区的岩石、土壤、牛粪五类样品,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定了样品中15种稀土元素(La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Sm、Eu、Gd、Tb、Dy、Ho、Er、Tm、Yb、Lu、Y)及8种重金属元素(Cr、Mn、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、As)的含量,研究这些元素地球化学行为及其在空间上的变化规律。结果表明:①矿区土壤和植物样品均显示出明显的轻稀土富集、重稀土亏损的特征。土壤和植物中含量最高的稀土元素均为Ce,分别达到49.95%及48.55%,与白云鄂博稀土矿富Ce的特征高度一致。②铁花植物的稀土元素总量在空间上呈现出主矿>东矿>东介勒格勒矿段的趋势,与三处矿体本身含矿性变化一致,说明该种植物稀土含量基本受矿体含矿性控制,对生长环境中稀土富集程度指示较准确。③矿区土壤中存在一定程度的Zn(465~778mg/kg)、Cd(1.35~2.23mg/kg)、Pb(181~431mg/kg)累积,其中部分点位Cd、Pb存在超出风险管制值的现象。综上,白云鄂博的矿石、土壤、植物样品均表现出富Ce的特征,且植物稀土含量与其所生长处的矿体含矿性强弱高度相关,三者之间稀土含量特征表现出明显继承性。此外,矿区局部点位土壤存在的Zn、Cd、Pb累积需要引起适当关注。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Rare earth resources are essential for a wide range of advanced technologies, which have received considerable attention in the world. Bayan Obo is the largest rare earth mine in the world. The study on the distribution characteristics of rare earth elements (REEs) and heavy metal elements in the environmental media such as soil and plants in the Bayan Obo mining area can provide basic data for the investigation of the environmental status of the mining area and provide reference for its environmental restoration.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the distribution characteristics of REEs and heavy metal elements in various environmental media at different areas in the Bayan Obo mine.
METHODS Nine plant samples, six soil samples, one rock sample and one cow manure sample were collected from the Bayan Obo rare earth mine and surrounding areas. The contents of 15 rare earth elements and 8 heavy metal elements of these samples were determined by ICP-MS, which were used to study the behavior of elements and the variation rules in space.
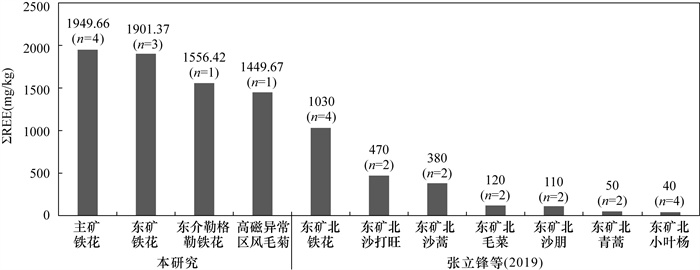
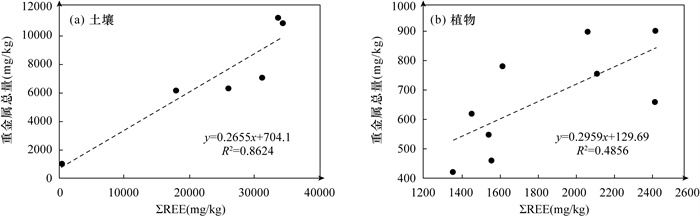
RESULTS The results showed that the distribution patterns of REEs in rocks, soil, plants, and cow manure samples were similar: obvious enrichment of light-REEs and depletion of high-REEs. The richest rare earth element in soil and plant was Ce, reaching 49.95% and 48.55%, respectively. The spatial variation law of the total content of rare earth element in Limonium bicolor (Bag.) Kuntze was consistent with the mineralization change of the three ore bodies: the main ore>the east ore>Dongjielegele ore. This indicated that the rare earth content of this plant was basically controlled by the minerality of the ore body, and it was more accurate to indicate the enrichment degree of rare earth in the growth environment. In addition, there was accumulation of Zn (465-778mg/kg), Cd (1.35-2.23mg/kg), Pb (181-431mg/kg) in the soil of the mining area. Some points of Cd and Pb were beyond the risk control value.
CONCLUSIONS The ore, soil, and plant samples in Bayan Obo all show the characteristics of Ce enrichment. Moreover, the rare earth content of plants is highly correlated with the ore body where it grows. The REE content characteristics among the three media show obvious inheritance and consistency. Special attention should be paid to the mining and agricultural activities in the main mining area in Bayan Obo because of the accumulation of Zn, Cd, and Pb in these mining areas.
-

-
图 1 白云鄂博主矿区采样点分布图(据柯昌辉等[30])
Figure 1.
表 1 白云鄂博矿区各类型样品稀土元素和重金属含量测试结果
Table 1. Contents of rare earth elements and heavy metals of samples collected from Bayan Obo mining area
样品编号 样品类型 采样位置 矿区稀土元素含量(mg/kg) La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y B8915 岩石 本巴台 7.3 8.21 1.27 4.47 0.78 0.07 0.58 0.1 0.62 0.13 0.39 0.07 0.52 0.08 3.71 B8916-1 土壤 本巴台(距白云鄂博矿区约80km) 83.4 153 17.5 63.6 9.45 1.76 6.48 1 5.84 1.13 3.31 0.47 3.26 0.49 32.7 B8916-2 牛粪 本巴台(距白云鄂博矿区约80km) 18.8 35 3.74 13.5 1.98 0.35 1.16 0.17 0.96 0.18 0.47 0.06 0.42 0.06 5.84 B8918 风毛菊 高磁异常区 387 703 70.5 238 23.2 4.55 8.52 0.77 2.73 0.36 0.58 0.05 0.31 ND 10.1 B8919 铁花 主矿南侧板岩 425 783 79.6 267 27 5.03 9.61 0.9 3.31 0.44 0.76 0.07 0.37 ND 11.7 B8920 铁花 主矿1626平台北侧 651 1163 118 397 38.8 7.31 13.7 1.25 4.43 0.6 0.96 0.08 0.50 0.05 15.4 B8921-1 铁花 主矿北侧 695 1174 112 360 34.1 6.35 12.2 1.17 4.19 0.55 0.88 0.08 0.45 ND 13.8 B8921-2 土壤 主矿北侧 9039 15368 1383 4358 402 77.2 132 14.9 53.5 6.75 11.4 0.93 5.56 0.61 141 B8922-1 铁花 主矿北侧 380 652 64.5 216 20.2 3.85 8.18 0.72 2.57 0.35 0.59 0.05 0.30 ND 8.55 B8922-2 土壤 主矿北侧 7188 12992 1198 3773 365 70.3 138 13.9 48.6 6.16 11.5 0.88 5.26 0.59 135 B8924-1 铁花 东矿西侧 553 1009 100 327 32.6 6.07 12.1 1.15 4.01 0.52 0.96 0.07 0.42 ND 12.3 B8924-2 土壤 东矿西侧 8880 16851 1608 5175 503 92.4 168 17.2 59 7.57 13.3 1.02 6.10 0.67 155 B8925-1 铁花 东矿北侧 569 1025 102 338 32.7 6.06 12.2 1.14 3.98 0.54 0.95 0.07 0.43 ND 12.7 B8925-2 土壤 东矿北侧 9044 17174 1622 5247 519 95.3 150 18.4 62.3 7.85 15.1 1.05 6.26 0.68 165 B8926-1 铁花 东矿东侧 416 746 75.5 250 23.8 4.44 9.36 0.82 2.89 0.39 0.61 0.05 0.29 ND 10 B8926-2 土壤 东矿东侧 4689 8856 870 2876 286 54.5 108 10.8 39.6 5.35 9.53 0.86 4.92 0.56 116 B8929 铁花 东介勒格勒 430 761 75 240 23.4 4.3 8.79 0.82 2.79 0.36 0.70 ND 0.30 ND 8.96 样品编号 样品类型 采样位置 矿区稀土元素总量(mg/kg) ΣLREE/ ΣHREE 矿区重金属元素含量(mg/kg) ΣREE ΣLREE ΣHREE Cr Mn Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb As 重金属总量 B8915 岩石 本巴台 28.30 22.1 6.2 3.56 170 123 65.5 12.6 6.18 0.06 55.8 0.91 481.95 B8916-1 土壤 本巴台(距白云鄂博矿区约80km) 383.39 328.71 54.68 6.01 71.3 743 35.7 29.8 87.4 0.15 21.7 12.7 1720.75 B8916-2 牛粪 本巴台(距白云鄂博矿区约80km) 82.69 73.37 9.32 7.87 15.4 277 7.09 16.9 53.8 0.26 5.38 2.97 520.80 B8918 风毛菊 高磁异常区 1449.67 1426.25 23.42 60.9 5.68 447 3.41 12.7 122 0.29 23.1 3.70 1579.88 B8919 铁花 主矿南侧板岩 1613.79 1586.63 27.16 58.42 5.34 579 5.05 12.6 146 0.49 32.4 4.75 1866.63 B8920 铁花 主矿1626平台北侧 2412.08 2375.11 36.97 64.24 7.46 705 5.08 11 137 0.43 32.2 3.57 2407.74 B8921-1 铁花 主矿北侧 2414.77 2381.45 33.32 71.47 6.44 548 3.4 8.64 70.9 0.21 19.5 2.72 2080.81 B8921-2 土壤 主矿北侧 30993.85 30627.2 366.65 83.53 54.3 6194 26 28.3 465 1.81 181 26.6 23807.01 B8922-1 铁花 主矿北侧 1357.86 1336.55 21.31 62.72 2.77 326 2.14 7.04 64.6 0.21 14.8 2.08 1388.64 B8922-2 土壤 主矿北侧 25946.19 25586.3 359.89 71.09 38.1 5297 26.6 32.6 583 1.73 202 28.9 24340.93 B8924-1 铁花 东矿西侧 2059.2 2027.67 31.53 64.31 4.3 732 3.57 8.37 102 0.29 45 2.80 2299.33 B8924-2 土壤 东矿西侧 33537.26 33109.4 427.86 77.38 40.4 9774 29.1 48.5 749 2.23 431 31.3 28893.53 B8925-1 铁花 东矿北侧 2104.77 2072.76 32.01 64.75 4.24 631 3.2 7.31 75.2 0.19 32 2.38 2282.52 B8925-2 土壤 东矿北侧 34127.94 33701.3 426.64 78.99 39.5 9454 29.2 37.7 778 2.21 420 32.1 31107.71 B8926-1 铁花 东矿东侧 1540.15 1515.74 24.41 62.1 5.05 439 3.82 7.12 71.3 0.14 23.6 1.37 1877.40 B8926-2 土壤 东矿东侧 17927.12 17631.5 295.62 59.64 58.7 5062 45.9 65 602 1.35 221 20.6 22317.55 B8929 铁花 东介勒格勒 1556.42 1533.7 22.72 67.5 2.98 380 2.34 5.22 51.2 0.09 18.9 1.58 1573.31 注:ND代表低于检出限(0.05mg/kg),未检出。 表 2 最新农用地土壤质量标准中土壤重金属筛选值及管制值与本研究土壤重金属含量对比
Table 2. Comparison of latest threshold values of heavy metals from Chinese quality standards for agricultural land and heavy metals contents in soils in this study
元素 筛选值(mg/kg) 管制值(mg/kg) 本研究土壤样品(mg/kg) Cd 0.3 1.5 1.35~2.23 Cr 150 800 38.1~58.7 Pb 70 400 181~431 Zn 200 - 465~778 Cu 50 - 28.3~65.0 As 40 200 20.6~32.1 Ni 60 - 26.0~45.9 注:“-”表示国家标准中未给出该元素限制值。 -
[1] Khan A M, Yusoff I, Bakar N, et al. Assessing anthropogenic levels, speciation, and potential mobility of rare earth elements (REEs) in ex-tin mining area[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(24): 25039-25055. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7641-x
[2] Phan Q V, Dao T T, Nguyen P, et al. An assessment of natural radioactivity in the Namxe rare earth deposit, Laichau Province, Vietnam[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(10): 602-614. doi: 10.3390/min9100602
[3] Raju K K, Raju A N. Biogeochemical investigation in south eastern Andhra Pradesh: The distribution of rare earths, thorium and uranium in plants and soils[J]. Environmental Geology, 2000, 39(10): 1102-1106. doi: 10.1007/s002540000111
[4] Pepi S, Sansone L, Chicca M, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements in soil and grape berries of Vitis vinifera cv. "Glera"[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2016, 188(8): 1-9. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039497774610_b953.html
[5] Khan A M, Yusoff I, Abubakar N K, et al. Accumulation, uptake and bioavailability of rare earth elements (REEs) in soil grown plants from ex-mining area in Perak, Malaysia[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2017, 15(3): 117-133. doi: 10.15666/aeer/1503_117133
[6] 张立锋, 刘杰民, 张翼明. 白云鄂博矿区土壤和植物中稀土元素的分布特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(5): 556-564. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201809200107
Zhang L F, Liu J M, Zhang Y M. Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements in plants and soils from the Bayan Obo mining area[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(5): 556-564. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201809200107
[7] 罗才贵, 罗仙平, 周娜娜, 等. 南方废弃稀土矿区生态失衡状况及其成因[J]. 中国矿业, 2014, 23(10): 65-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2014.10.016
Luo C G, Luo X P, Zhou N N, et al. Status and causes of ecological imbalance of abandoned rare-earth mine in South China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2014, 23(10): 65-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2014.10.016
[8] 张塞, 于扬, 王登红, 等. 赣南离子吸附型稀土矿区土壤重金属形态分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 726-738. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911050152
Zhang S, Yu Y, Wang D H, et al. Forms distribution of heavy metals and their ecological risk evaluation in soils of ion adsorption type in the rare earth mining area of southern Jiangxi, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 726-738. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911050152
[9] 陈明, 郑小俊, 陶美霞, 等. 桃江流域河流沉积物中重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(10): 2784-2791. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019072902
Chen M, Zheng X J, Tao M X, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment from Taojiang River Basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(10): 2784-2791. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019072902
[10] Pan Y, Li H. Investigating heavy metal pollution in mining brown-field and its policy implications: A case study of the Bayan Obo rare earth mine, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Environmental Management, 2016, 57(4): 879-893. doi: 10.1007/s00267-016-0658-6
[11] 王哲, 赵莹晨, 骆逸飞, 等. 内蒙古白云鄂博矿区土壤稀土元素污染特征及评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1503-1513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103054.htm
Wang Z, Zhao Y C, Luo Y F, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of soil rare earth element pollution in the Bayan Obo mining region of Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1503-1513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103054.htm
[12] 陈耕. 白云鄂博主、东矿回顾性环境影响评价[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2012.
Chen G. Retrospective environmental impact assessment of Bayan Obo main and east mine[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2012.
[13] 郭伟, 付瑞英, 赵仁鑫, 等. 内蒙古包头白云鄂博矿区及尾矿区周围土壤稀土污染现状和分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(5): 1895-1900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201305036.htm
Guo W, Fu R Y, Zhao R X, et al. Distribution characteristics and current situation of soil rare earth contamination in the Bayan Obo mining area and Baotou tailing reservoir in Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(5): 1895-1900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201305036.htm
[14] Ma Y H, Kuang L L, He X, et al. Effects of rare earth oxide nanoparticles on root elongation of plants[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(3): 273-279. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.10.050
[15] Garcia A, Espinosa R, Delgado L, et al. Acute toxicity of cerium oxide, titanium oxide and iron oxide nanoparticles using standardized tests[J]. Desalination, 2011, 269(1-3): 136-141. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.052
[16] Wang L Q, Liang T. Accumulation and fractionation of rare earth elements in atmospheric particulates around a mine tailing in Baotou, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 23(6): 747-751. http://sourcedb.igsnrr.cas.cn/yw/lw/201402/P020140218385403239278.pdf
[17] Wei B G, Li Y H, Li H R, et al. Rare earth elements in human hair from a mining area of China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 96: 118-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.05.031
[18] 梁青青, 阴海静, 郝金奇, 等. 白云鄂博矿区小学生尿中稀土元素镧铈钕水平的调查[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2014, 31(11): 1003-1004. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJYJ201411020.htm
Liang Q Q, Yin H J, Hao J Q, et al. Investigation of rare earth elements lanthanum, cerium and neodymium level in urine of pupils from Bayan Obo mining area[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2014, 31(11): 1003-1004. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJYJ201411020.htm
[19] Hao Z, Li Y, Li H, et al. Levels of rare earth elements, heavy metals and uranium in a population living in Baiyun Obo, Inner Mongolia, China: A pilot study[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 128: 161-170. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.057
[20] Gafur N A, Sakakibara M, Sano S, et al. A case study of heavy metal pollution in water of Bone River by artisanal small-scale gold mine activities in eastern part of Gorontalo, Indonesia[J]. Water, 2018, doi: 10.3390/w10111507.
[21] 王爱云, 李以科, 李瑞萍, 等. 内蒙古白云鄂博稀土资源开发利用生态环境影响成本分析[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(1): 94-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201701014.htm
Wang A Y, Li Y K, Li R P, et al. Environmental cost analysis of the development and utilization of the Bayan Obo rare earth resources, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(1): 94-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201701014.htm
[22] 高志强, 周启星. 稀土矿露天开采过程的污染及对资源和生态环境的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(12): 2915-2922. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201112039.htm
Gao Z Q, Zhou Q X. Contamination from rare earth ore strip mining and its impacts on resources and eco-environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(12): 2915-2922. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201112039.htm
[23] 王国珍. 对稀土冶炼"三废"及放射性污染治理的建议[J]. 四川稀土, 2007(3): 2-5.
Wang G Z. Suggestions on "three types of wastes" of rare earth smelting and radioactive pollution control[J]. Sichuan Rare Earth, 2007(3): 2-5.
[24] 关海波, 李金霞, 牟艳军, 等. 白云鄂博矿区外围土壤稀土元素累积空间分异[J/OL]. 稀土, 2021. https://doi.org/10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.20210041.
Guan H B, Li J X, Mu Y J, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of rare earth elements accumulation in the soil surrounding Bayan Obo mining area[J/OL]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2021. https://doi.org/10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.20210041.
[25] 王哲, 周铜, 赵莹晨, 等. 内蒙古白云鄂博矿区优势植物重金属和稀土元素富集特征[J/OL]. 中国稀土学报: 1-13[2021-07-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2365.TG.20210615.1007.002.html.
Wang Z, Zhou T, Zhao Y C, et al. Enrichment characteristics of heavy metals and rare earth elements in dominant plants in Bayan Obo mining area of Inner Mongolia[J/OL]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths: 1-13[2021-07-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2365.TG.20210615.1007.002.html.
[26] 杨占峰, 柳建勇. 白云鄂博稀土矿床探矿的必要性与可行性探讨[J]. 稀土, 2007, 28(6): 84-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2007.06.020
Yang Z F, Liu J Y. Necessity and feasibility of Baiyunebo rare earth deposit prospecting[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2007, 28(6): 84-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2007.06.020
[27] 柳建勇, 苏胜旺, 张台荣, 等. 白云鄂博矿床东矿段深部及白云向斜核部探矿的可行性探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(6): 821-825. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.06.015
Liu J Y, Su S W, Zhang T R, et al. A discussion on the practicability of prospecting in the deep part of the east mine and kernel part of the Bayan syncline, Bayan Obo ore field[J]. Geological Review, 2006, 52(6): 821-825. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.06.015
[28] 程建忠, 侯运炳, 车丽萍. 白云鄂博矿床稀土资源的合理开发及综合利用[J]. 稀土, 2007, 28(1): 70-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2007.01.019
Cheng J Z, Hou Y B, Che L P. Making rational multipurpose use of resources of REE in Baiyunebo deposit[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2007, 28(1): 70-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2007.01.019
[29] 程建忠, 车丽萍. 中国稀土资源开采现状及发展趋势[J]. 稀土, 2010, 31(2): 65-69, 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.02.015
Cheng J Z, Che L P. Current mining situation and potential development of rare earth in China[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2010, 31(2): 65-69, 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.02.015
[30] 柯昌辉, 孙盛, 赵永岗, 等. 内蒙古白云鄂博超大型REE-Nb-Fe矿床控矿构造特征及深部找矿方向[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(1): 95-109.
Ke C H, Sun S, Zhao Y G, et al. Ore-controlling structure and deep prospecting of the Bayan Obo large-sized REE-Nb-Fe ore deposit Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(1): 95-109.
[31] 李强, 杨占峰. 白云鄂博主矿各矿石类型稀土配分特征研究[J/OL]. 稀土: 1-9[2021-07-04]. https://doi.org/10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.20210042.
Li Q, Yang Z F. Study on REE distribution characteristics of different ore types in Baiyunobo main orebody[J/OL]. Chinese Rare Earths: 1-9[2021-07-04]. https://doi.org/10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.20210042.
[32] 金海龙, 候少春, 魏威, 等. 白云鄂博东矿体深部不同类型矿石的地球化学特征研究[J/OL]. 稀土: 1-9[2021-07-04]. https://doi.org/10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.20210033.
Jin H L, Hou S C, Wei W, et al. Geochemistry characteristics of various types of ores at depth of east orebody in Bayan Obo[J]. Chinese Rare Earths: 1-9[2021-07-04] https://doi.org/10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.20210033.
[33] 苗莉, 徐瑞松, 徐金鸿. 粤西地区土壤-植物系统中稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(1): 54-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.01.009
Miao L, Xu R S, Xu J H. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements (REEs) in the soil-plant system in west Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(1): 54-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.01.009
[34] 汪振立, 魏正贵, 陶冶, 等. 岩石-土壤-铁芒萁系统中稀土元素的分布、迁移和累积[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(12): 881-889. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.12.012
Wang Z L, Wei Z G, Tao Y, et al. Distribution, migration and accumulation of rare earth elements (REE) in the rock-soil-dicranopteris dichotoma (R-S-D) system[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(12): 881-889. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.12.012
[35] 张臻悦, 何正艳, 徐志高, 等. 中国稀土矿稀土配分特征[J]. 稀土, 2016, 37(1): 121-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201601022.htm
Zhang Z Y, He Z Y, Xu Z G, et al. Rare earth partitioning characteristics of China rare earth ore[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(1): 121-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201601022.htm
-




 下载:
下载: