Application of Thermal Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy in the Evaluation of Quartz Content
-
摘要:
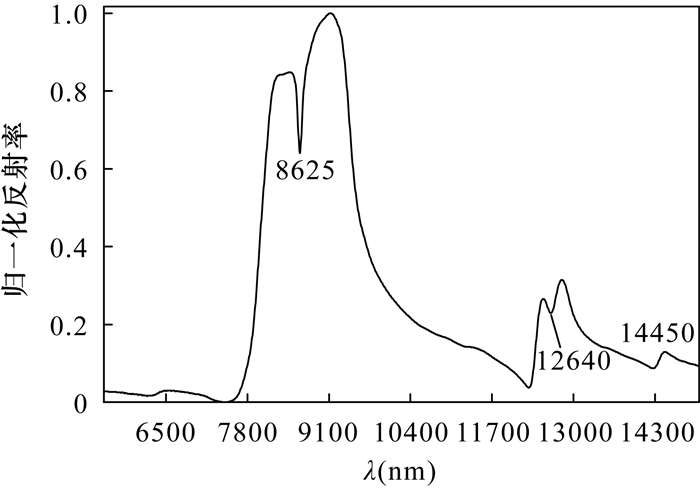
石英是热液矿床重要的找矿标志,也是影响页岩气储层可压裂性评价的关键性因素,目前主要利用X射线衍射方法和扫描电镜矿物定量分析方法进行实验室内石英定量分析。为满足野外钻井现场进行快速、大批量矿物定量分析的需求,本文以羌塘盆地泥岩、砂岩、砾岩、灰岩和白云岩等沉积岩样品为研究对象,应用热红外反射光谱技术和综合自动矿物岩石学(QEMSCAN)矿物定量分析技术,开展了石英热红外反射光谱含量评价研究。结果表明:石英在8625nm、12640nm和14450nm三个特征中心波长位置的相对深度(D8625、D12640、D14450)可以用来区分陆源碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩,当D8625>0.14或D12640>0.02或D14450>0.02时,样品岩性主要为陆源碎屑岩,否则主要为碳酸盐岩。此外,D8625、D12640、D14450三个石英光谱特征参数均与石英含量具有高度的相关性,均可以利用最小二乘法构建石英含量评价模型。以拟合优度(R2)和均方根误差(RMSE)两个指标评价三个模型的精度,其中根据D8625参数建立的石英含量估算模型的拟合优度最大(R2=0.9237),且均方根误差最小(RMSE=8.51),基于此认为D8625石英光谱参数可以作为评价石英含量的最优光谱指标。本文基于热红外反射光谱技术建立的该种野外快速估算钻井中石英含量的方法,为热液矿床找矿勘查和页岩气勘探开发提供了借鉴和参考。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Quartz is not only an important prospecting indicator of hydrothermal deposits, but also a key factor affecting the evaluation of shale gas reservoir fracturing. It is of great significance to carry out the rapid evaluation of quartz content in field drilling. However, the analysis process of conventional methods (X-ray diffraction method and scanning electron microscope) is relatively long.
OBJECTIVES To establish a rapid and large-scale quantitative evaluation model of quartz based on thermal infrared reflectance.
METHODS Handheld FTIR spectrometer and mineral quantitative analyzer were used to analysis the content and characteristic absorption peak intensity of quartz, from mudstone, sandstone, conglomerate, limestone and dolomite samples in the Qiangtang Basin.
RESULTS The relative depth (D8625, D12640, D14450) of quartz at the three characteristic center wavelength positions of 8625nm, 12640nm and 14450nm can be used to distinguish terrigenous clastic rocks from carbonate rocks. When D8625>0.14 or D12640>0.02 or D14450>0.02, the samples are mainly terrigenous clastic rocks. In addition, three quartz spectral characteristic parameters D8625, D12640, and D14450 all have a high correlation with the quartz content, and the least square method can be used to construct a quartz content evaluation model. Two indicators of goodness of fit (R2) and root mean square error (RMSE) were used to evaluate the accuracy of the three models. Among them, the quartz content estimation model based on D8625 parameters had the highest goodness of fit (R2=0.9237), with the smallest root square error (RMSE=8.51). Based on this, it is believed that the D8625 quartz spectral parameters can be used as the optimal spectral index for evaluating the quartz content.
CONCLUSIONS Based on thermal infrared reflectance spectroscopy technology, a field method for quickly estimating the content of quartz in drilling core has been established, which provides reference for prospecting and exploration of hydrothermal deposits and shale gas exploration and development.
-

-
表 1 样品中石英含量及光谱特征参数
Table 1. Quartz content and spectral characteristic parameters in samples
样品编号 岩性 石英含量(%) D8625 D12640 D14450 样品编号 岩性 石英含量(%) D8625 D12640 D14450 QZ16-7 泥岩 78.73 0.237 0.0627 0.0292 QD17-19 灰岩 9.23 0.0125 0.00738 0.00124 QZ16-17 泥岩 41.77 0.176 0.0301 0.032 QD17-36 灰岩 8.09 0.00581 0 0.00385 QZ16-5 砂岩 79.02 0.235 0.0588 0.0268 QD17-26 灰岩 7.29 0.00937 0 0.00158 QZ16-10 砂岩 75.63 0.245 0.0593 0.0307 QD17-8 灰岩 7.26 0.02 0.00571 0.00353 QZ16-9 砂岩 71.74 0.24 0.0583 0.0304 QD17-22 灰岩 6.42 0.0182 0.00748 0.0131 QD17-5 砂岩 66.82 0.209 0.0561 0.0295 QD17-15 灰岩 6.24 0.0077 0.00364 0.00462 QD17-1 砂岩 64.14 0.191 0.0609 0.0247 QD17-23 灰岩 5.97 0.0173 0.00175 0 QD17-2 砂岩 63.47 0.184 0.0605 0.0334 QZ16-20 灰岩 5.91 0.0151 0.0018 0.00199 QD17-3 砂岩 62.43 0.183 0.0524 0.0307 QD17-35 灰岩 5.69 0 0.00309 0.00768 QZ16-3 砂岩 62.30 0.227 0.061 0.0386 QD17-7 灰岩 5.67 0.00286 0.00319 0.00323 QZ16-1 砂岩 60.44 0.229 0.0534 0.0258 QD17-9 灰岩 5.28 0.0159 0.00291 0 QZ16-23 砂岩 58.86 0.226 0.0397 0.0488 QD17-16 灰岩 5.21 0 0.00336 0.00245 QD17-41 砂岩 52.97 0.187 0.0487 0.03 QD17-13 灰岩 5.19 0.00824 0.00329 0 QZ16-25 砂岩 43.44 0.155 0.035 0.0237 QD17-11 灰岩 4.72 0.00864 0.00211 0 QZ16-19 砂岩 36.94 0.161 0.0394 0.0429 QD17-10 灰岩 4.48 0.00247 0.00352 0 QZ16-8 砂岩 36.04 0.156 0.0497 0.0327 QD17-12 灰岩 4.29 0 0.00141 0 QD17-40 砂岩 35.21 0.195 0.0467 0.0317 QD17-21 灰岩 3.98 0.017 0.00258 0 QZ16-11 砂岩 34.90 0.148 0.0283 0.0251 QZ16-21 灰岩 3.79 0.00358 0.00286 0.000608 QZ16-16 砂岩 34.89 0.142 0.0352 0.0311 QD17-27 灰岩 3.79 0.00502 0.000941 0.000561 QD17-24 砂岩 34.75 0.174 0.0374 0.0194 QD17-25 灰岩 3.45 6.40E-05 0.00312 0.000744 QD17-38 砂岩 56.36 0.211 0.0527 0.0295 QD17-20 灰岩 2.46 0.00739 0.00196 0.000867 QZ16-29 砾岩 71.46 0.174 0.0413 0.0276 QD17-17 灰岩 2.05 0.0183 0.0038 0 QZ16-28 砾岩 71.24 0.214 0.0374 0.0273 QD17-29 灰岩 1.71 7.40E-05 0.000914 0.00274 QZ16-31 砾岩 62.77 0.199 0.0484 0.0107 QZ16-14 灰岩 1.59 0.00212 0.00149 0 QZ16-30 砾岩 58.09 0.218 0.0415 0.032 QD17-30 灰岩 1.03 0 0.000962 0.000291 QZ16-26 砾岩 57.63 0.196 0.0323 0.028 QD17-18 灰岩 0.93 0.00835 0.00271 0.00269 QD17-34 灰岩 26.14 0.16 0.0465 0.0355 QD17-31 灰岩 0.60 0.00821 0.0015 0 QD17-32 灰岩 14.28 0.0754 0.0133 0.00752 QZ16-27 白云岩 39.33 0.202 0.0458 0.032 QZ16-13 灰岩 12.43 0.0841 0.00925 0.00446 QZ16-22 白云岩 24.13 0.111 0.0199 0.022 QD17-14 灰岩 9.41 0.00144 0.00464 0.0027 QZ16-18 白云岩 6.29 0.00603 0.000557 0 表 2 三个模型石英含量反演结果及模型均方根误差
Table 2. Inversion results of quartz content and root mean square error of three models
样品编号 石英含量QEMSCAN分析结果(%) 三个模型预测的石英含量(%) D8625模型
(RMSE=8.51)D12640模型
(RMSE=9.28)D14450模型
(RMSE=10.38)QZ16-10 75.63 70.34 68.92 51.38 QZ16-28 71.24 61.60 44.44 46.41 QD17-2 63.47 53.14 70.26 55.33 QZ16-3 62.30 65.27 70.82 62.94 QZ16-30 58.09 62.73 49.03 53.28 QD17-41 52.97 53.99 57.07 50.36 QZ16-27 39.33 58.22 53.83 53.28 QD17-40 35.21 56.24 54.84 52.84 QD17-24 34.75 50.32 44.44 34.85 QD17-32 14.28 22.51 17.51 17.47 QD17-19 9.23 4.77 10.89 8.28 QD17-8 7.26 6.89 9.02 11.63 QD17-15 6.24 3.42 6.71 13.23 QD17-35 5.69 1.24 6.10 17.70 QD17-16 5.21 1.24 6.40 10.05 QD17-10 4.48 1.94 6.58 6.47 QZ16-21 3.79 2.25 5.84 7.36 QD17-20 2.46 3.33 4.83 7.74 QZ16-14 1.59 1.84 4.31 6.47 QD17-31 0.60 3.56 4.32 6.47 -
[1] 郭帮杰, 张杰林, 武鼎. 热红外高光谱遥感回归分析定量反演石英含量[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(17): 125-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.17.021
Guo B J, Zhang J L, Wu D. Thermal hyperspectral remote rensing for the quantitative inversion of quartz content by regression analysis[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(17): 125-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.17.021
[2] 陈静, 周涛发, 张乐骏, 等. 蚀变岩帽的特征、成因以及在华南的分布探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(11): 3380-3396. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.11.08
Chen J, Zhou T F, Zhang L J, et al. A discussion of characteristics, genesis of lithocaps and their distributions in South China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(11): 3380-3396. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.11.08
[3] 崔霄峰, 张宇, 李肖龙. 内蒙古喀喇沁旗安家营子金矿蚀变及其分布研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.001
Cui X F, Zhang Y, Li X L. Alteration and distribution of Anjiayingzi gold deposit in Harqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.001
[4] 金露英, 秦克章, 李光明, 等. 斑岩钼-热液脉状铅锌银矿成矿系统特征、控制因素及勘查指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(12): 3813-3839. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202012015.htm
Jin L Y, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Characteristics, controlling factors and exploration implications of porphyry molybdenum-hydrothermal vein-style lead-zinc-silver metallogenic systems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(11): 3813-3839. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202012015.htm
[5] 孙雨沁, 于学峰, 单伟, 等. 胶东焦家断裂带3000m深部矿化特征及金矿物赋存状态[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(6): 919-937. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202006018.htm
Sun Y Q, Yu X F, Dan W, et al. Mineralization characteristics and modes of occurrence of gold minerals at the depth of 3000 meters in Jiaojia fault zone, Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2020, 41(6): 919-937. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202006018.htm
[6] 于立栋, 张海微, 张静, 等. 东天山玉峰金矿热液蚀变作用与元素迁移规律[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5): 1597-1610. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005017.htm
Yu L D, Zhang H W, Zhang J, et al. Hydrothermal alteration and element migration in the Yufeng gold deposit, Eastern Tianshan Orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(5): 1597-1610. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005017.htm
[7] 张海坤, 胡鹏, 姜军胜, 等. 印度尼西亚苏门答腊岛马塔比(Martabe)浅成低温热液型金-银矿床的地质特征与找矿标志[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(2): 163-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202102004.htm
Zhang H K, Hu P, Jiang J S, et al. Geological features and prospecting indicators of martabe epithermal Au-Ag deposit, Sumatra, Indonesia[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(2): 163-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202102004.htm
[8] 田兴旺, 胡国艺, 苏桂萍, 等. 川南威远川南威远地区W201井古生界海相页岩矿物特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(4): 409-415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804005.htm
Tian X W, Hu G Y, Su G P, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of Paleozoic marine shales in Well W201 of Weiyuan area, Southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(4): 409-415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804005.htm
[9] 卢龙飞, 秦建中, 申宝剑, 等. 川东南涪陵地区五峰-龙马溪组硅质页岩的生物成因及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(4): 460-465. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201604007.htm
Lu L F, Qin J Z, Shen B J, et al. Biogenic origin and hydrocarbon significance of siliceous shale from the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Fuling area, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(4): 460-465. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201604007.htm
[10] 孙川翔, 聂海宽, 刘光祥, 等. 石英矿物类型及其对页岩气富集开采的控制: 以四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(11): 3692-3704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911009.htm
Sun C X, Nie H K, Liu G X, et al. Quartz type and its control on shale gas enrichment and production: A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Sichuan Basin and its surrounding areas, China[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(11): 3692-3704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911009.htm
[11] 郭雯, 董大忠, 李明, 等. 富有机质页岩中石英的成因及对储层品质的指示意义——以四川盆地东南部及周缘龙马溪组龙-1亚段为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(2): 65-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202102012.htm
Guo W, Dong D Z, Li M, et al. Quartz genesis in organic-rich shale and its indicative significance to reservoir quality: A case study on the first submember of the first member of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(2): 65-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202102012.htm
[12] 陈倩, 宋文磊, 杨金昆, 等. 矿物自动定量分析系统的基本原理及其在岩矿研究中的应用——以捷克泰思肯公司TIMA为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(2): 345-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202102010.htm
Chen Q, Song W L, Yang J K, et al. Principle of automated mineral quantitative analysis system and its applicati-ion in petrology and mineralogy: An example from TESCAN TIMA[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(2): 345-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202102010.htm
[13] 温利刚, 曾普胜, 詹秀春, 等. 矿物表征自动定量分析系统(AMICS)技术在稀土稀有矿物鉴定中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2): 121-129. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201708110129
Wen L G, Zeng P S, Zhan X C, et al. Application of the automated mineral identification and characterization system (AMICS) in the identification of rare earth and rare minerals[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2): 121-129. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201708110129
[14] 伍月, 迟广成, 刘欣. X射线粉晶衍射法在变粒岩鉴定与分类中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(4): 546-554. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201908050117
Wu Y, Chi G C, Liu X. Application of X-ray powder diffraction method in identification and classification of leptite[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(4): 546-554. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201908050117
[15] 闫柏琨, 王润生, 甘甫平, 等. 热红外遥感信息岩矿信息提取研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(10): 1116-1126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.10.011
Yan B K, Wang R S, Gan F P. Progresses in minerals information extraction using thermal remote sensing[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20(10): 1116-1126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.10.011
[16] 代晶晶, 赵龙贤, 姜琪, 等. 热红外高光谱技术在地质找矿中的应用综述[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(8): 2520-2533. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.08.026
Dai J J, Zhao L X, Jiang Q, et al. Review of thermal-infrared spectroscopy applied in geological ore exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(8): 2520-2533. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.08.026
[17] Van der Meer F D, Van der Werff H M F, Van der Ruitenbeek F J K, et al. Multi-and hyperspectral geologic remote sensing: A review[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinfor-mation, 2012, 14(1): 112-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2011.08.002
[18] Arne D, House E, Pontual S, et al. Hyperspectral interpretation of selected drill cores from orogenic gold deposits in central Victoria, Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 63(8): 1003-1025. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039630505810_873d.html
[19] Cudahy T. Mineral mapping for exploration: An Australian journey of evolving spectral sensing technologies and industry collaboration[J]. Geosciences, 2016, 6(4): 2076-3263. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040535690110_5288.html
[20] Laukamp C, Rodger A, LeGras M, et al. Mineral physicochemistry underlying feature-based extraction of mineral abundance and composition from shortwave, mid and thermal infrared reflectance spectra[J]. Minerals, 2021, 11(4): 1-37. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/350421386_Mineral_Physicochemistry_Underlying_Feature-Based_Extraction_of_Mineral_Abundance_and_Composition_from_Shortwave_Mid_and_Thermal_Infrared_Reflectance_Spectra
[21] Lampinen H M, Laukamp C, Occhipinti S A, et al. Mineral footprints of the Paleoproterozoic sediment-hosted Abra Pb-Zn-Cu-Au deposit Capricorn Orogen, western Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 104: 436-461. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.11.004
[22] Tappert M C, Rivard B, Giles D, et al. The mineral chemistry, near-infrared, and mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy of phengite from the Olympic Dam IOCG deposit, South Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 53: 26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.006
[23] 史维鑫, 易锦俊, 王浩, 等. 马坑铁矿钻孔岩心红外光谱特征及蚀变分带特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 934-943. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060004
Shi W X, Yi J J, Wang H, et al. Study on the characteristics of the infrared spectrum and the alteration zoning of drill core in the Makeng iron deposit[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 934-943. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060004
[24] Bastero C F, Lagmay A M F A. Estimating SiO2 content of lava depositsin the humid tropics using remotely sensed imagery[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2006, 151(4): 357-364. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2005.09.012
[25] Guo B J, hang J L. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing technology for polymetallic ore and uranium deposits exploration in East Junggar[J]. Acta Geolagica Sinica (Engish Edition), 2014, 88(Supplement 2): 1347-1348. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1755-6724.12381_6/pdf
[26] 杜锦锦, 王俊虎, 郎朋林. 基于102F实测热红外光谱的富硅类岩石SiO2含量定量反演[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2016, 33(4): 216-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2016.04.005
Du J J, Wang J H, Lang P L. Quantitative inversion of SiO2 contents in silicon rich rocks based on measured 102F thermal infrared spectra[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2016, 33(4): 216-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2016.04.005
[27] 郭帮杰, 张杰林, 武鼎, 等. 高光谱遥感在硅化带识别中的应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(3): 154-158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2007.04.044
Guo B J, Zhang J L, Wu D, et al. Application of hyperspectral remote sensing in silicified zone identification[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2007, 11(4): 601-608. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2007.04.044
[28] 刘道飞, 陈圣波, 陈磊, 等. 以SiO2含量为辅助因子的ASTER热红外遥感硅化信息提取[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(8): 1396-1402. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201508019.htm
Liu D F, Chen S B, Chen L, et al. Silicification information extraction based on the content of SiO2 from ASTER TIR data[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2015, 40(8): 1396-1402. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201508019.htm
[29] 王剑, 付修根, 沈利军, 等. 论羌塘盆地油气勘探前景[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(5): 1091-1113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005005.htm
Wang J, Fu X G, Shen L J, et al. Prospect of the potential of oil and gas resources in Qiangtang Basin, Xizang[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(5): 1091-1113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005005.htm
[30] 回广骥, 高卿楠, 宋利强, 等. 新疆可可托海稀有金属矿床矿物和岩石热红外光谱特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 134-144. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060001
Hui G J, Gao Q N, Song L Q, et al. Thermal infrared spectra characteristics of rare metal minerals and rock in the Keketuohai deposit, Xinjiang[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 134-144. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060001
[31] 张弘, 高卿楠, 郭东旭, 等. 花岗伟晶岩型锂矿热红外反射光谱特征及锂元素定量反演研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2021, 41(1): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS202101004.htm
Zhang H, Gao Q N, Guo D X, et al. Characteristics of thermal infrared reflectance spectra and quantitative inversion of lithium element in granite pegmatite type lithium deposit[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2011, 41(1): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS202101004.htm
[32] 李俊键, 成宝洋, 刘仁静, 等. 基于数字岩心的孔隙尺度砂砾岩水敏微观机理[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(5): 594-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201905009.htm
Li J J, Cheng B Y, Liu R J, et al. Microscopic mechanism of water sensitivity of pore-scale sandy conglomerate based on digital core[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(5): 594-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201905009.htm
[33] 吕文超, 杨志军, 周永章, 等. 钦杭结合带南段和寮铅锌多金属矿床石英的谱学特征及其指示意义[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(5): 1374-1378. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)05-1374-05
Lv W C, Yang Z J, Zhou Y Z, et al. Spectral characteristics and implications of quartz from Heliao lead-zinc polymetallic ore district in the south of Qinzhou-Hangzhou joint belt[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 33(5): 1374-1378. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)05-1374-05
[34] 尤金凤, 邢立新, 潘军, 等. 油砂光谱特性及其含油率遥感估算研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(4): 1025-1029. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)04-1025-05
You J F, Xing L X, Pan J, et al. Research on oil sands spectral characteristics and oil content by remote sensing estimation[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(4): 1025-1029. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)04-1025-05
[35] 樊瑞雪, 邢立新, 潘军, 等. 油砂的光谱特性及其遥感应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2019, 49(2): 603-610.
Fan R X, Xing L X, Pan J, et al. Oil sands spectral reflection characteristics and remote sensing application[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2019, 49(2): 603-610.
[36] 成功, 李嘉璇, 王朝鹏, 等. 离子型稀土矿含量高光谱定量反演研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(5): 1571-1578.
Cheng G, Li J X, Wang C P, et al. Study on hyperspectral quantitative inversion of ionic rare earth ore[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(5): 1571-1578.
-



 下载:
下载:

