Industrial On-line ICP-OES Analysis of Copper, Cadmium, Cobalt and Iron in Hydrometallurgical Zinc Sulfate Solution
-
摘要:
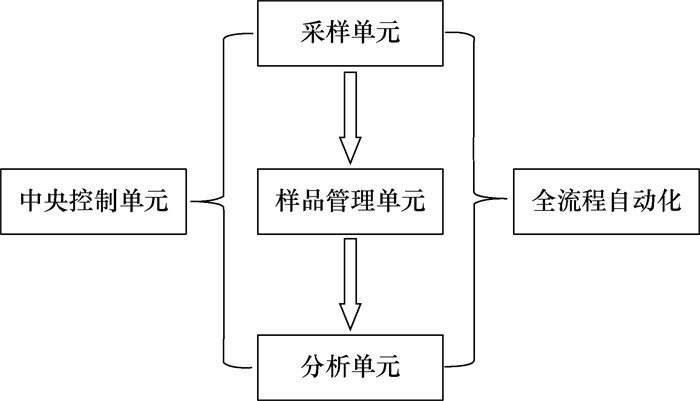
测定湿法冶炼硫酸锌溶液中的杂质元素,有助于优化电解液组成、减少能耗,精准投料,提高冶炼金属的纯度。对于杂质元素的测定,通常采用人工取样分析的方法,因杂质元素的含量较低,主元素锌和硫酸的含量较高,需要对样品进行稀释才能上机分析,难以实现自动化。为满足目前湿法冶炼的产业需求,本文建立了一种自动化工业在线过滤/稀释-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)测定锌冶炼溶液中杂质元素铜镉钴铁的分析方法。结果表明:各元素的线性关系良好,相关系数均大于0.9998,相对标准偏差为0.72%~1.39%(n=6),加标回收率为95%~110%。该工业在线自动化分析系统可以代替传统人工取样分析的过程,在线分析结果与人工取样分析结果具有良好的一致性,实现了自动化分析,操作简单,结果准确可靠。
-
关键词:
- 工业在线自动化分析系统 /
- 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 /
- 锌冶炼 /
- 远程传输
Abstract:BACKGROUND The determination of impurity elements in hydrometallurgical zinc sulfate solution is helpful to optimize the composition of electrolytes, reduce energy consumption, and accurately feed and improve the purity of smelting metal. Impurity elements in the wet zinc smelting process are usually determined by manual sampling. The sample needs to be diluted before the equipment analysis is performed due to high content of zinc and sulfuric acid, which is difficult to achieve automatic analysis.
OBJECTIVES In order to determine the online analysis of impurity elements in the solution of zinc smelting process and meet the current requirements of the hydrometallurgical industry.
METHODS An automatic industrial on-line filtration/dilution combined with inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) was used. By optimizing key parameters and selecting appropriate analysis lines, a method for the rapid determination of copper, cadmium, cobalt and iron in zinc smelting solution was developed.
RESULTS The experimental results showed that the linear relationship of each element was good, the correlation coefficient was greater than 0.9998, the relative standard deviation was 0.72%-1.39% (n=6), and the spiked recovery was 95%-110%.
CONCLUSIONS The factory on-line automatic analysis system can replace traditional manual sampling to achieve automatic analysis. The results of on-line analysis are compared with those of manual sampling in actual production, showing good consistency. This method can be used to fully achieve automatic analysis, simple operation, accurate and reliable results, and is suitable for the analysis of impurity elements in zinc smelting.
-

-
表 1 方法线性范围、相关系数与检出限
Table 1. Linear range, correlation coefficient and detection limit of the method
元素 线性范围(mg/L) 相关系数r2 检出限(mg/L) Cu 0~10 0.9999 0.0132 Cd 0~10 0.9999 0.0097 Co 0~2 0.9999 0.0056 Fe 0~2 0.9998 0.0168 表 2 样品测定对比结果
Table 2. Comparison of results of sample determination
样品编号 元素 工业在线自动化分析系统测定值(mg/L) ICP-OES人工测定值(mg/L) 稀释倍数 一段净化前液 Cu 535.1 537.8 100 Cd 629.5 625.6 100 Co 11.5 10.9 100 Fe 8.9 8.8 100 二段净化前液 Cd 59.8 60.6 100 Co 8.6 8.5 100 Fe 8.8 8.4 100 表 3 样品加标回收率
Table 3. Spiked recovery tests of the method
样品编号 元素 本底值(mg/L) 加入量(mg/L) 测定值(mg/L) 回收率(%) 一段净化前液 Cu 535.1 50 582.9 95.6 Cd 629.5 50 678.6 98.2 Co 11.5 10 22.1 106.0 Fe 8.9 10 18.8 99.0 二段净化前液 Cd 59.8 20 79.5 98.5 Co 8.6 10 18.7 101.0 Fe 8.8 10 19.7 109.0 表 4 方法精密度
Table 4. Precision tests of the method
样品编号 元素 6次测定值(mg/L) RSD (%) 一段净化前液 Cu 529.6 538.2 525.7 546.4 536.3 531.5 1.37 Cd 631.3 634.6 627.8 619.3 632.1 627.4 0.85 Co 11.7 11.6 11.7 11.6 11.5 11.3 1.30 Fe 8.9 8.8 8.7 8.8 8.7 8.6 1.20 二段净化前液 Cd 58.9 59.5 59.3 59.9 60.1 59.5 0.72 Co 8.8 8.6 8.7 8.7 8.6 8.8 1.03 Fe 8.6 8.8 8.7 8.6 8.9 8.8 1.39 -
[1] Jia L P, Huang J J, Ma Z L, et al. Research and development trends of hydrometallurgy: An overview based on hydrometallurgy literature from 1975 to 2019[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(11): 3147-3160. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65450-4
[2] Craddock P T. The origins and inspirations of zinc smelting[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(9): 2181-2191. doi: 10.1007/s10853-008-2942-1
[3] Shayesteh K, Abbasi P, Fard V V, et al. Simultaneous removal of nickel and cadmium during the cold purification of zinc sulfate solution[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2020, 45(2): 587-598. doi: 10.1007/s13369-019-04320-9
[4] 付光, 刘俊场, 曲洪涛, 等. 硫酸锌溶液净化除杂研究现状及趋势[J]. 云南冶金, 2020(2): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNYJ202002005.htm
Fu G, Liu J C, Qu H T, et al. Research status and tendency on purification and impurity removal of zinc sulfate solution[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2020(2): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNYJ202002005.htm
[5] Duan N, Jiang L H, Xu F Y, et al. A non-contact original-state online real-time monitoring method for complex liquids in industrial processes[J]. Engineering, 2018, 4(3): 392-397. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2018.05.005
[6] Song S L, Sun W, Wang L, et al. Recovery of cobalt and zinc from the leaching solution of zinc smelting slag[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(1): 102777. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.022
[7] 李坦平, 吴宜, 曾利群, 等. 电感耦合等离子体串联质谱法测定电解二氧化锰废渣浸出液中的重金属元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 682-689. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911230162
Li T P, Wu Y, Zeng L Q, et al. Determination of heavy metal elements in leaching solution of electrolytic manganese dioxide waste residue by inductively coupled plasma-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 682-689. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911230162
[8] 杨丽菊, 卢佐菊, 匡菊美. 提高硫酸锌溶液一段净化脱杂率实践[J]. 云南冶金, 2020, 49(3): 59-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNYJ202003013.htm
Yang L J, Lu Z J, Kuang J M. Practice on increasing of the purification and impurities removal rate in the first section of zinc sulfate solution[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2020, 49(3): 59-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNYJ202003013.htm
[9] Lin Y J, Wei S H, Huang C Y. Intelligent manufacturing control systems: The core of smart factory[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 39: 389-397. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.382
[10] Huang K K, Wu Y M, Long C, et al. Adaptive process monitoring via online dictionary learning and its industrial application[J]. ISA Transactions, 2021, 114: 399-412. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.12.046
[11] 黄康利, 袁齐, 林滨钰. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定硫酸锌产品中6种痕量元素[J]. 山东化工, 2018, 47(13): 73-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG201813034.htm
Huang K L, Yuan Q, Lin B Y. Determination of six trace elements in zinc sulfate products by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(13): 73-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG201813034.htm
[12] Guo Y G, Zhao H, Han Y L, et al. Simultaneous spectro-photometric determination of trace copper, nickel, and cobalt ions in water samples using solid phase extraction coupled with partial least squares approaches[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2017, 173: 532-536. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2016.10.003
[13] Butcher D J. Recent highlights in graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 2017, 52(9): 755-773. doi: 10.1080/05704928.2017.1303504
[14] Zou Z R, Deng Y J, Hu J, et al. Recent trends in atomic fluorescence spectrometry towards miniaturized instrumentation—A review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2018, 1019: 25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.01.061
[15] Zhou F B, Li C G, Yang C H, et al. A spectro-photometric method for simultaneous determination of trace ions of copper, cobalt, and nickel in the zinc sulfate solution by ultraviolet-visible spectrometry[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2019, 223: 117370. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.117370
[16] 齐妍洁, 张旭, 沈庆峰, 等. 亚硝基R盐分光光度法测定硫酸锌溶液中的钴[J]. 矿冶, 2014, 23(4): 97-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201404024.htm
Qi Y J, Zhang X, Shen Q F, et al. Determination of cobalt in zinc sulfate solution with nitroso-R-salt spectrophotometry[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2014, 23(4): 97-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201404024.htm
[17] Novaes C G, Bezerra M A, da Silva E G P, et al. A review of multivariate designs applied to the optimization of methods based on inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES)[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2016, 128: 331-346. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2016.05.015
[18] Donati G L, Amais R S, Williams C B. Recent advances in inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(7): 1283-1296. doi: 10.1039/C7JA00103G
[19] Wilschefski S C, Baxter M R. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: Introduction to analytical aspects[J]. The Clinical Biochemist Reviews, 2019, 40(3): 115. doi: 10.33176/AACB-19-00024
[20] 龚仓, 丁洋, 陆海川, 等. 五酸溶样-电感耦合等离子体质谱法同时测定地质样品中的稀土等28种金属元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 340-348. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011030136
Gong C, Ding Y, Lu H Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of 28 elements including rare earth elements by ICP-MS with five-acid dissolution[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 40(3): 340-348. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011030136
[21] Velitchkova N S, Velichkov S V, Karadjov M G, et al. Optimization of the operating conditions in inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry[J]. Bulgarian Chemical Communications, 2017, 49: 152-159.
[22] 贺攀红, 杨珍, 龚治湘. 氢化物发生-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法同时测定土壤中的痕量砷铜铅锌镍钒[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(2): 235-242. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201904160048
He P H, Yang Z, Gong Z X. Simultaneous determination of trace arsenic, copper, lead, zinc, nickel and vanadium in soils by hydride generation-inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(2): 235-242. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201904160048
[23] Trevelin A M, Marotto R E S, de Castro E V R, et al. Extraction induced by emulsion breaking for determination of Ba, Ca, Mg and Na in crude oil by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2016, 124: 338-343. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2015.09.014
[24] 严子心, 曲景奎, 余志辉, 等. 多谱线拟合-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定高纯镍中痕量钴[J]. 分析化学, 2019, 47(3): 423-428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201903014.htm
Yan Z X, Qu J K, Yu Z H, et al. Multi-spectral fitting-determination of trace cobalt in high purity nickel by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(3): 423-428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201903014.htm
[25] 胡健平, 王日中, 杜宝华, 等. 火焰原子吸收光谱法和电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定硫化矿中的银铜铅锌[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(4): 388-395. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706270110
Hu J P, Wang R Z, Du B H, et al. Determination of silver, copper, lead and zinc in sulfide ores by flame atomic absorption spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(4): 388-395. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706270110
[26] Bachari A H, Jalali F, Alahyarizadeh G. Investigation of spectral interference effects on determination of uranium concentration in phosphate ore by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy[J]. Radiochimica Acta, 2017, 105(2): 95-108. doi: 10.1515/ract-2016-2639
[27] 赵君威, 梅坛, 鄢国强, 等. 电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱分析中的光谱干扰及其校正的研究进展[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2013, 49(3): 364-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201303035.htm
Zhang J W, Mei T, Yan G Q, et al. Recent progress of researches on spectral interference and its correction in ICP-AES analysis[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2013, 49(3): 364-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201303035.htm
[28] 龚琦. 对电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法中一些问题的认识[J]. 冶金分析, 2018, 38(9): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201809005.htm
Gong Q. Understanding of some issues about inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2018, 38(9): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201809005.htm
[29] Sengupta A, Rajeswari B, Kadam R M, et al. Determination of trace elements in carbon steel by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Atomic Spectroscopy, 2011, 32(5): 200-205. doi: 10.46770/AS.2011.05.005
[30] 成勇, 刘力维, 袁金红, 等. 电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定熔盐废渣中钪和钛[J]. 冶金分析, 2021, 41(7): 75-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202107015.htm
Cheng Y, Liu L W, Yuan J H, et al. Determination of scandium and titanium in molten salt slag by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2021, 41(7): 75-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202107015.htm
-



 下载:
下载: