Geochemical Characteristics of Soil Selenium and Influencing Factors of Selenium Bioavailability in Rice Root Soils in Qingxi Area, Ganxian County, Jiangxi Province
-
摘要:
江西赣南地区是典型的硒缺乏地理分布区,但近年来研究成果表明该地区稻谷富硒率高,土壤与稻谷富硒存在不一致的原因尚不明确,探讨土壤和稻谷硒含量特征和土壤硒的生物有效性,对赣南地区富硒土地资源利用和富硒农产品开发具有重要意义。本文以赣县清溪地区为研究对象,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱/发射光谱(ICP-MS/OES)等方法测定了研究区1734件表层土壤、57组稻谷及配套根系土硒等元素含量及硒形态地球化学指标;系统分析了区内土壤硒含量和分布特征、稻谷硒含量特征,探讨了根系土硒生物有效性的影响因素。结果表明:研究区表层土壤以足硒、富硒区为主,土壤硒含量与成土母岩关系密切,不同成土母岩区土壤硒含量规律为:古生代变质岩>中生代花岗岩>新元古代变质岩>中生代陆源碎屑岩>新生代第四系。根系土硒含量均未达到富硒土壤标准,稻谷富硒率为64.91%,稻谷对土壤硒的富集能力强(富集系数20.05%),当根系土硒含量≥0.25mg/kg时,水稻富硒率高达70.83%,能够稳定产出优质富硒水稻。硒的赋存形态是影响土壤硒生物有效性的主要因素,土壤总硒含量较低时,水溶态、离子可交换态、碳酸盐结合态硒的占比高,从而提升了硒的生物有效性;有机质含量低,对硒吸附能力弱,也是硒生物有效性高的重要原因。本研究认为,赣县清溪地区富硒、足硒土壤开发利用时,综合考虑土壤硒含量、土壤理化指标、硒形态对土壤硒生物有效性的影响,有利于科学指导天然富硒土地划定和富硒水稻产业开发。
-
关键词:
- 土壤 /
- 硒 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法 /
- 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 /
- 地球化学特征 /
- 生物有效性 /
- 影响因素
Abstract:BACKGROUND The south of Jiangxi Province is a typical geographical distribution area of selenium deficiency. However, some research results in recent years indicate that the rice has high selenium content. The reasons for inconsistency about selenium enrichment between soil and rice is still not clear. It is important to discuss the characteristics of selenium content in soil and crops for the utilization of selenium-enriched land resources and the development of selenium-enriched agricultural products.
OBJECTIVES To understand the reasons of inconsistency about selenium content between soil and crops in Qingxi area, Ganxian County.
METHODS Samples of 1734 topsoil, 57 sets of rice and corresponding root soil were collected from Qingxi area. The content of selenium and its speciation geochemistry in these samples were determined by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. The selenium content and distribution characteristics in soil and rice were systematically analyzed, and the influencing factors of selenium bioavailability in root soil were discussed.
RESULTS The topsoil in the area was dominated by selenium-enriched soil and selenium-sufficient soil. The selenium content in soil were closely related to soil parent rocks. The rules of soil selenium content in different parent-rock areas were as follows: Paleozoic metamorphic rocks>Mesozoic granite>Neoproterozoic metamorphic rocks>Mesozoic terrigenous clastic rocks>Cenozoic quaternary. The selenium content in root soil were lower than 0.4mg/kg, and selenium-enrichment rate of rice was 64.91%, indicating that it had a high capacity to enrich selenium in the soil (enrichment coefficient was 20.05%). When the selenium content in root soil was more than 0.25mg/kg, the rate of selenium-enrichment reached up to 70.83%, and would produce high-quality selenium-enriched rice stably. The form of selenium was the main factor to influence selenium bioavailability in soil. When the content of total selenium in soil was low, water-soluble, ion-exchangeable and carbonate-bound selenium accounted for a high proportion, which enhanced the bioavailability of selenium. The weak ability of selenium adsorption by low content organic matter was also an important factor for the high bioavailability of selenium.
CONCLUSIONS Selenium content in soil, soil physical and chemical index and the influence of selenium form on bioavailability of selenium in soil should be comprehensively considered when exploiting selenium-enriched soil and selenium-sufficient soil in Qingxi area, Ganxian County. It is beneficial to scientifically guide the delimitation of natural selenium-enriched land and develop selenium-enriched rice.
-

-
表 1 研究区不同成土母质区土壤硒含量对比
Table 1. Comparison of Se contents in soils derived from different parent rocks in the study area
成土母质 土壤硒含量范围
(mg/kg)硒平均值
(mg/kg)样品数
(件)新生代第四系 0.07~0.90 0.26 346 中生代陆源碎屑岩 0.08~0.84 0.28 262 中生代花岗岩 0.09~1.58 0.35 930 古生代变质岩 0.13~1.17 0.37 164 新元古代变质岩 0.14~0.71 0.32 26 表 2 研究区稻谷与根系土硒含量特征及稻谷富集系数
Table 2. Characteristics of Se contents in rice and root soil and enrichment coefficient of rice in the study area
表 3 研究区根系土硒含量分级及其对应稻谷的富硒率与重金属超标率
Table 3. Classification of Se contents in root soil, corresponding Se-enrichment rate and heavy metal excess rate of rice in the study area
根系土硒含量水平
(mg/kg)富硒水稻样本
(件)超标水稻样本
(件)水稻样本
(件)富硒率
(%)超标率
(%)Se含量≥0.15 36 4 55 65.45 7.27 Se含量≥0.20 30 3 45 66.67 6.66 Se含量≥0.25 17 0 24 70.83 0 表 4 研究区根系土总硒与各形态硒含量、形态比例的相关系数(n=14)
Table 4. Correlation coefficients of total Se in root soil vs. its species content and proportion in the study area
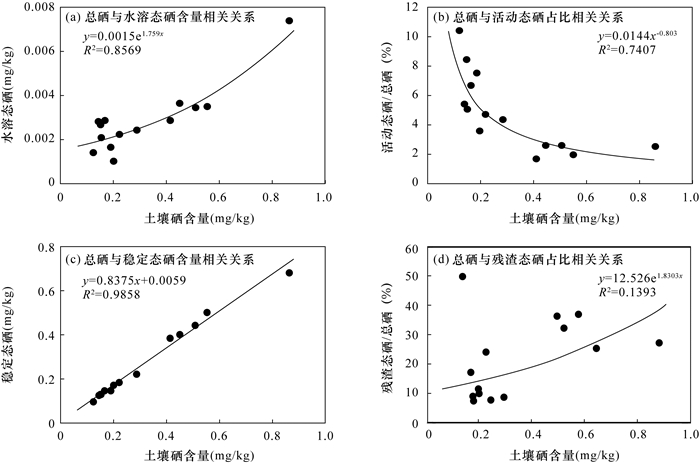
硒形态 各形态硒含量与土壤总硒的相关系数 硒形态 各形态硒比例与土壤总硒的相关系数 水溶态 0.85** 水溶态 -0.54* 离子可交换态 0.13 离子可交换态 -0.66** 碳酸盐结合态 0.06 碳酸盐结合态 -0.74** 腐植酸结合态 0.74** 腐植酸结合态 -0.09 铁锰氧化态 0.70** 铁锰氧化态 -0.64** 强有机结合态 0.84** 强有机结合态 -0.20 残渣态 0.93** 残渣态 0.40 活动态 0.52* 活动态 -0.75** 稳定态 0.99** 稳定态 0.75** 注:“**”代表在0.01水平下显著相关;“*”代表在0.05水平下显著相关。 -
[1] 周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
[2] 熊咏民, 杨晓莉, 张丹丹, 等. 硒的生物学效应与环境相关性疾病的研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1105-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806008.htm
Xiong Y M, Yang X L, Zhang D D, et al. Research progress in biological function of selenium and environmentally associated diseases[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1105-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806008.htm
[3] Smits J E, Krohn R M, Akhtar E, et al. Food as medi-cine: Selenium enriched lentils offer relief against chronic arsenic poisoning in Bangladesh[J]. Environmental Research, 2019, 176: 108561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108561. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108561
[4] 彭晓敏, 高愈希. 自然界中的硒及其生物学效应[J]. 化学教育, 2019, 40(17): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXJJ201917001.htm
Peng X M, Gao Y X. Selenium in nature and its biological effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Education, 2019, 40(17): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXJJ201917001.htm
[5] Fordyce F M. Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment[M]//Selinus O. Essentials of medical geology (revised edition). British Geological Survey, 2013: 373-416.
[6] Winkel L H E, Johnson C A, Lenz M, et al. Environmental selenium research: From microscopic processes to global understanding[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46: 571-579. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035851000110_e692.html
[7] 中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.
Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese dietary reference intakes[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013.
[8] Fordyce F. Selenium geochemistry and health[J]. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 2007, 36(1): 94-97. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[94:SGAH]2.0.CO;2
[9] Dinh Q T, Cuia Z W, Huang J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review[J]. Environment International, 2018, 112: 294-309. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035
[10] 成晓梦, 马荣荣, 彭敏, 等. 中国大宗农作物及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤标准建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6): 1367-1372. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906026.htm
Cheng X M, Ma R R, Peng M, et al. Characteristics of selenium in crops and roots in China and recommen-dations for selenium-enriched soil standards[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1367-1372. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906026.htm
[11] 周墨, 唐志敏, 张明, 等. 赣州市水稻及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤界限值[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(4): 604-609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202104017.htm
Zhou M, Tang Z M, Zhang M, et al. Selenium contents of rice and rhizosphere soil and threshold value of selenium-rich soil in Ganzhou of Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(4): 604-609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202104017.htm
[12] Favorito J E, Eick M J, Grossl P R, et al. Selenium geo-chemistry in reclaimed phosphate mine soils and its relationship with plant bioavailability[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 418(1): 541-555. doi: 10.1007/s11104-017-3299-5
[13] 刘秀金, 杨柯, 成杭新, 等. 四川省泸州市页岩和碳酸盐岩区水稻根系土Se含量和生物有效性的控制因素[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1919-1931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012007.htm
Liu X J, Yang K, Cheng H X, et al. Control factors of selenium content and bioavailability of rice root soil in shale and carbonate rock areas, Luzhou City, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(12): 1919-1931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012007.htm
[14] Supriatin S, Weng L P, Comans R N J. Selenium-rich dissolved organic matter determines selenium uptake in wheat grown on low-selenium arable land soils[J]. Plant Soil, 2016, 408: 73-94. doi: 10.1007/s11104-016-2900-7
[15] Li Z, Liang D, Peng Q, et al. Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability: A review[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 295(3): 69-79. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039830883110_59e8.html
[16] 王锐, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 等. 富硒土壤硒生物有效性及影响因素研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(7): 1647-1654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201807024.htm
Wang R, Yu T, Yang Z F, et al. Bioavailability of soil selenium and its influencing factors in selenium-enriched soil[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(7): 1647-1654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201807024.htm
[17] 钱薇, 唐昊冶, 王如海, 等. 一次消解土壤样品测定汞、砷和硒[J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(8): 1215-1221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201708024.htm
Qian W, Tang H Y, Wang R H, et al. Determination of mercury, arsenic and selenium in soils by one-time digestion[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(8): 1215-1221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201708024.htm
[18] 李蕾, 苏园, 陈楚国, 等. 微敞开体系快速石墨消解-原子荧光法测定食品及土壤中的硒[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1098-1104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202004026.htm
Li L, Su Y, Chen C G, et al. Fast determination of selenium in food and soils by micro-open graphite digestion-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1098-1104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202004026.htm
[19] 欧朝接, 吴琼婧, 韦东, 等. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定稻谷中铬、镍、铜、砷、镉、铅的含量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2019, 9(2): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2019.02.002
Ou C J, Wu Q J, Wei D, et al. Determination of chromium, nickel, copper, arsenic cadmium and lead in rice by ICP-MS with microwave digestion[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 9(2): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2019.02.002
[20] 魏复盛. 中国土壤元素平均值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
Wei F S. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
[21] 魏振山, 涂其军, 唐蜀虹, 等. 天山北坡乌鲁木齐至沙湾地区富硒土壤地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(5): 893-898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201605008.htm
Wei Z S, Tu Q J, Tang S H, et al. A discussion on the geochemical features and origin of selenium -rich soil on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains from Urumqi to Shawan County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(5): 893-898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201605008.htm
[22] 余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1119-1125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806010.htm
Yu T, Yang Z F, Wang R, et al. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1119-1125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806010.htm
[23] Long J, Luo K. Trace element distribution and enrichment patterns of Ediacaran-Early Cambrian, Ziyang selenosis area, central China: Constraints for the origin of selenium[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 172: 211-230. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.11.010
[24] 李娟, 龙健, 汪境仁. 贵州开阳地区土壤中硒的地球化学特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2004, 35(5): 579-582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2004.05.013
Li J, Long J, Wang J R. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in soils of Kaiyang region, Guizhou Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004, 35(5): 579-582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2004.05.013
[25] 周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究: 以青塘-梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806017.htm
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of south Jiangxi Province: A typical area of Qingtang-Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806017.htm
[26] 曹容浩. 福建省龙海市表层土壤硒含量及影响因素研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3): 282-288. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201606130084
Cao R H. Study on selenium content of surface soils in Longhai, Fujian and its influencing factors[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3): 282-288. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201606130084
[27] 熊平生. 江西赣县花岗岩型红土剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(3): 553-558. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201503018.htm
Xiong P S. Major elements geochemical characteristics of the granite-type laterite profile in Gan Xian, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2015, 21(3): 553-558. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201503018.htm
[28] 杨妍萍, 刘晓端, 刘久臣, 等. 川西高原地区岩石中硒的地球化学特征和影响因素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(1): 115-126. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201808290098
Yang Y P, Liu X D, Liu J C, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in rocks from the western Sichuan Plateau[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(1): 115-126. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201808290098
[29] 王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 等. 硒在土壤-农作物系统中的分布特征及富硒土壤阈值[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5571-5578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202012043.htm
Wang R, Deng H, Jia Z M, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium in a soil-crop system and the threshold of selenium-rich soils[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5571-5578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202012043.htm
[30] 陈锦平, 刘永贤, 潘丽萍, 等. 浔郁平原不同作物的硒富集特征及其影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1155-1159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806016.htm
Chen J P, Liu Y X, Pan L P, et al. Selenium accumulation characteristics and influential factors of different crops in Xunyu Plain[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1155-1159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806016.htm
[31] 管文文, 戴其根, 张洪程, 等. 硒肥对水稻生长及其重金属累积的影响[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1165-1169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806018.htm
Guan W W, Dai Q G, Zhang H C, et al. Effect of selenium fertilization on rice growth and accumulation of heavy metals in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1165-1169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806018.htm
[32] 洪涛, 孔祥胜, 岳祥飞. 贵州丹寨县土壤-水稻中硒和重金属的积累及迁移特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/52.1139.p.20210630.1108.001.html.
Hong T, Kong X S, Yue X F. Translocation and accumulation of selenium and heavy metals in paddy soil-rice plant system in Danzhai County, Guizhou Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/52.1139.p.20210630.1108.001.html.
[33] Wan Y N, Yu Y, Wang Q, et al. Cadmium uptake dynamics and translocation in rice seedling: Influence of different forms of selenium[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 133: 127-134. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.07.001
[34] 王锐, 侯宛苓, 李雨潼, 等. 高硒高镉区土地安全区划方法[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(12): 5524-5530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201912037.htm
Wang R, Hou W L, Li Y T, et al. Land safety zoning method in high-selenium and high-cadmium areas[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(12): 5524-5530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201912037.htm
[35] 梁东丽, 彭琴, 崔泽玮, 等. 土壤中硒的形态转化及其对有效性的影响研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5): 374-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJZ201705010.htm
Liang D L, Peng Q, Cui Z W, et al. Progress on selenium bioavailability and influential factors in soil[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5): 374-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJZ201705010.htm
[36] 赵禹, 白金, 刘拓. 南疆焉耆盆地土壤-小麦系统硒耦合关系及生物有效性[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1960-1970. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012012.htm
Zhao Y, Bai J, Liu T, et al. Se coupling relation and biological effectiveness study of the soil-wheat system in Yanqi Basin, southern Xinjiang[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(12): 1960-1970. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012012.htm
[37] Qin H B, Zhu J M, Lin Z Q, et al. Selenium speciation in seleniferous agricultural soils under different cropping systems using sequential extraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 225: 361-369. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.02.062
[38] 谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等. 天津市蓟州区土壤硒的有效性及影响因素[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(10): 2306-2316. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019042802
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y, et al. Bioavailability of selenium and its influencing factors in soil of Jizhou District, Tianjin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(10): 2306-2316. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019042802
[39] 马迅, 宗良纲, 诸旭东, 等. 江西丰城生态硒谷土壤硒有效性及其影响因素[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(4): 1588-1593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201704073.htm
Ma X, Zong L G, Zhu X D, et al. Effectiveness and influential factors of soil selenium in selenium valley, Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(4): 1588-1593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201704073.htm
[40] 王仁琪, 张志敏, 晁旭, 等. 陕西省安康市西部稻田土壤硒形态特征与水稻富硒状况研究[J]. 中国地质, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20201019.1838.020.html.
Wang R Q, Zhang Z M, Chao X, et al. A study of the selenium speciation in paddy soil and status of selenium-enriched rice in western part of Ankang, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20201019.1838.020.html.
[41] Wang D, Liang D L, Zhou F, et al. Selenate redistribution during aging in different Chinese soils and the dominant influential factors[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 182: 284-292. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.014
[42] 周小娟, 张嫣, 祝莉玲, 等. 武汉市侏儒-消泗地区农田系统中硒的分布特征及有效性研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4): 158-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201604025.htm
Zhou X J, Zhang Y, Zhu L L, et al. Research on selenium distribution and effectiveness in the farm system in Zhuru and Xiaosi areas, Wuhan City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(4): 158-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201604025.htm
[43] 谢邦廷, 贺灵, 江官军, 等. 中国南方典型富硒区土壤硒有效性调控与评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3): 273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
Xie B T, He L, Jiang G J, et al. Regulation and evaluation of selenium availability in Se-rich soils in southern China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3): 273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
[44] Dinh Q T, Li Z, Tran T A T, et al. Role of organic acids on the bioavailability of selenium in soil: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 184: 618-635. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039924900210_575e.html
-



 下载:
下载: