Analysis of Mineralogical Characteristics of Leucosphenite from the Fengcheng Formation in the Junggar Basin by Electron Probe Microanalyzer and X-ray Diffractometer
-
摘要:
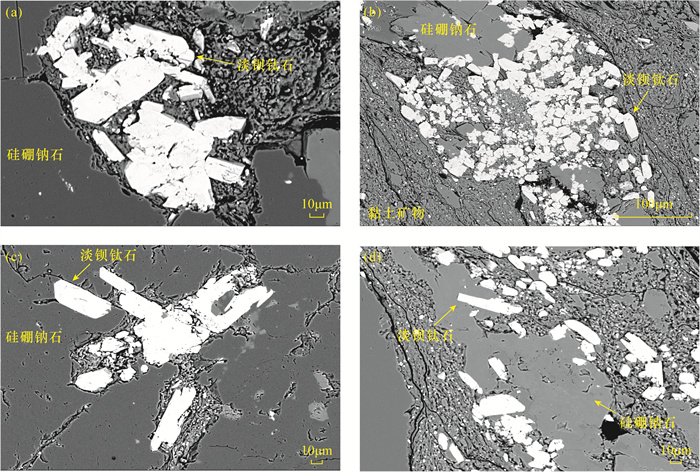
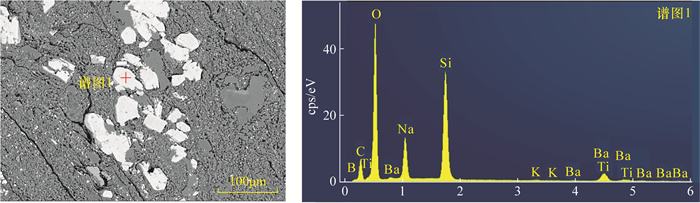
淡钡钛石为含硼硅酸盐矿物,晶体结构属二轴晶单斜晶系,是典型的热液成因矿物。产于中国准噶尔盆地风城组页岩中的淡钡钛石尚未开展矿物学研究,其成因尚不明确。本文选取了该地玛页1钻井岩心中的淡钡钛石,采用电子探针(EPMA)、X射线能谱(EDS)和X射线衍射(XRD)分析其矿物成分和晶体结构特征。结果表明:风城组淡钡钛石晶体大小为微米级,形态呈板状或短柱状,与硅硼钠石共生。矿物主要元素组成为:BaO 12.64%,TiO2 13.47%,Na2O 10.69%,SiO2 53.46%,B2O3 10.11%;d=4.22(-220)、d=8.45(-110)、d=3.37(-112)对应的三个晶面最发育。风城组淡钡钛石元素组成及晶体衍射特征与国外发现的淡钡钛石相吻合,但更富硼元素。由于热液流体中硼含量与盐度呈明显正相关,因此风城组淡钡钛石形成于更高盐度热液流体中,深部热液流体侵入到风城组页岩中依次形成硅硼钠石、淡钡钛石。该研究结果为准噶尔盆地风城组淡钡钛石矿物学的进一步研究提供了基础资料。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Leucosphenite, a borosilicate mineral with a biaxial monoclines crystal structure, is a typical hydrothermal mineral. The mineralogy of leucosphenite in the shale of the Fengcheng Formation in the Junggar Basin in China has not been studied, and its genesis is not clear.
OBJECTIVES To understand the mineralogical characteristics of leucosphenite in the Fengcheng Formation and its genesis.
METHODS Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to analyze the mineral composition and crystal structure.
RESULTS The crystal size of the leucosphenite in the Fengcheng Formation is at micron scale, and the morphology is plate-like or short columnar. Leucosphenite is associated with reedmergnerite. Leucosphenite is composed of 12.64% BaO, 13.47%TiO2, 10.69% Na2O, 53.46% SiO2, and 10.11% B2O3. Crystal planes corresponding to d=4.22(-220), d=8.45(-110), d=3.37(-112) are the three most developed planes.
CONCLUSIONS The element composition and crystal diffraction characteristics of leucosphenite in the Fengcheng Formation are consistent with that found abroad, but the former is richer in B. Due to the obvious positive correlation between B content and salinity in the hydrothermal fluid, the leucosphenite of the Fengcheng Formation was formed in the hydrothermal fluid with higher salinity. Deep hydrothermal fluids intruded into the shale of the Fengcheng Formation, forming reedmergnerite and leucosphenite in turn.
-

-
表 1 准噶尔盆地风城组淡钡钛石EPMA定量分析结果
Table 1. EPMA quantitative analysis results of leucosphenite in the Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin
淡钡钛石产地 点位 氧化物含量(%) BaO TiO2 Na2O SiO2 K2O FeO Fe2O3 Al2O3 Nb2O5 MnO MgO CaO SrO B2O3 总计 中国准噶尔盆地(中国石油新疆油田分公司实验检测研究院分析结果) 1 13.21 13.46 10.80 53.31 0.11 0.12 / / / / / / / 10.11 101.12 2 12.80 13.91 10.95 53.75 0.19 0.12 / / / / / / / 10.02 101.74 3 11.99 13.11 10.96 53.70 0.23 0.44 / / / / / / / 10.51 100.94 4 12.97 13.58 10.40 52.87 0.10 0.19 / / / / / / / 9.83 99.94 5 12.55 13.28 10.54 53.54 0.27 0.09 / / / / / / / 9.82 100.09 6 12.29 13.50 10.50 53.61 0.23 0.11 / / / / / / / 10.34 101.58 平均值 12.64 13.47 10.69 53.46 0.19 0.18 / / / / / / / 10.11 100.74 中国准噶尔盆地(新疆维吾尔自治区矿产实验研究所分析结果) 1 10.38 14.24 10.07 52.94 - - / / / / / / / 11.66 99.29 2 10.81 14.04 10.83 53.71 - - / / / / / / / 11.98 101.37 3 10.17 14.41 10.69 54.18 - - / / / / / / / 9.15 98.60 4 11.16 14.30 10.90 53.17 - - / / / / / / / 8.59 98.12 5 10.22 14.35 10.77 53.16 - - / / / / / / / 11.35 99.85 6 10.96 14.08 11.20 53.57 - - / / / / / / / 11.66 101.47 平均值 10.62 14.24 10.74 53.46 - - / / / / / / / 10.73 99.78 俄罗斯Inagli地块 平均值 13.00 13.92 10.70 54.30 0.79 / 0.28 / 0.10 trace 0.15 / 0.03 6.36 99.63 加拿大魁北克省圣希莱尔山 平均值 11.98 14.52 11.61 53.66 0.51 0.04 / 0.11 0.77 / / 0.06 / 6.60 99.86 注:“-”表示未进行测试,“/”表示低于检测限或不含该元素。 -
[1] 张龙, 陈振宇, 汪方跃, 等. 电子探针技术研究粤北龙华山岩体中独居石蚀变晕圈的结构与成分特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(2): 174-184. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202109070118
Zhang L, Chen Z Y, Wang F Y, et al. Application of electron probe microanalyzer to study the textures and compositions of alteration coronas of monazite from the Longhuashan granite, northern Guangdong Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(2): 174-184. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202109070118
[2] 闵红, 刘倩, 张金阳, 等. X射线荧光光谱-X射线粉晶衍射-偏光显微镜分析12种产地铜精矿矿物学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 74-84. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202004020038
Min H, Liu Q, Zhang J Y, et al. Study on the mineralogical characteristics of 12 copper concentrates by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, X-ray powder diffraction and polarization microscope[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 74-84. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202004020038
[3] 张元元, 李威, 唐文斌. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖烃源岩发育的构造背景和形成环境[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(1): 48-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201801012.htm
Zhang Y Y, Li W, Tang W B. Tectonic setting and environment of alkaline lacustrine source rocks in the lower Permian Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 48-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201801012.htm
[4] 李威, 张元元, 倪敏婕, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下二叠统古老碱湖成因探究: 来自全球碱湖沉积的启示[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(6): 1839-1852. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.06.013
Li W, Zhang Y Y, Ni M J, et al. Genesis of alkaline lacustrine deposits in the lower Permian Fengcheng Formation of the Mahu Sag, northwestern Junggar Basin: Insights from a comparison with the worldwide alkaline lacustrine deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(6): 1839-1852. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.06.013
[5] 秦玉娟, 余朝丰, 徐洋, 等. 应用电子探针原位微区分析技术测试硅硼钠石矿物[J]. 电子显微学报, 2016, 35(3): 217-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2016.03.006
Qin Y J, Yu C F, Xu Y, et al. A microarea analysis technique of EPMA to probe reedmergnerite[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2016, 35(3): 217-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2016.03.006
[6] 代鸿章, 王登红, 刘丽君, 等. 电子探针和微区X射线衍射研究陕西镇安钨-铍多金属矿床中祖母绿级绿柱石[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3): 336-345. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193
Dai H Z, Wang D H, Liu L J, et al. Study on emerald-level beryl from the Zhen'an W-Be polymetallic deposit in Shaanxi Province by electron probe microanalyzer and micro X-ray diffractometer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3): 336-345. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193
[7] 李萧, 劳海港, 胡秋媛, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘乌夏断裂带构造特征及物理模拟实验[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(4): 567-572.
Li X, Lao H G, Hu Q Y, et al. Tectonic evolution and its physical simulation of Wuxia Fault Belt in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(4): 567-572.
[8] 蒋宜勤, 文华国, 祁利祺, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌尔禾地区二叠系风城组盐类矿物和成因分析[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(2): 105-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201202015.htm
Jiang Y Q, Wen H G, Qi L Q, et al. Salt minerals and their genesis of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Urho area, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2012, 32(2): 105-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201202015.htm
[9] 汪梦诗, 张志杰, 周川闽, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下二叠统风城组碱湖岩石特征与成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(1): 147-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201801012.htm
Wang M S, Zhang Z J, Zhou C M, et al. Lithological characteristics and origin of alkaline lacustrine of the lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2018, 20(1): 147-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201801012.htm
[10] 孙玉善. 中国西部地区首次发现硅硼钠石[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1994, 15(3): 264-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT403.010.htm
Sun Y S. Reedmergneite was first discovered in western China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1994, 15(3): 264-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT403.010.htm
[11] 赵研, 郭佩, 鲁子野, 等. 准噶尔盆地下二叠统风城组硅硼钠石发育特征及其富集成因探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(5): 966-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202005007.htm
Zhao Y, Guo P, Lu Z Y, et al. Genesis of reedmergnerite in the lower Permian Fengcheng Formation of the Junggar Basin, NE China[J]. Acta Sedimentologic Sinica, 2020, 38(5): 966-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202005007.htm
[12] 张志杰, 袁选俊, 汪梦诗, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖沉积特征与古环境演化[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(6): 972-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806006.htm
Zhang Z J, Yuan X J, Wang M S, et al. Alkaline-lacustrine deposition and paleoenvironmental evolution in Permian Fengcheng Formation at the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(6): 972-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806006.htm
[13] 郑庆华, 刘行军, 刘乔, 等. 利用偏光显微镜反射光系统观察黑色生油岩电子探针薄片中的生烃母质特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 442-450. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911180160
Zheng Q H, Liu X J, Liu Q, et al. A method for observation of characteristics of hydrocarbon generation materials in electron probe thin sections of black source rock by the reflected-light viewing system of a polarized optical microscope[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 442-450. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911180160
[14] 杨波, 杨莉, 孟文祥, 等. 利用探针片进行X射线粉晶衍射分析在白云鄂博矿床中的应用[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2021(6): 34-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXK202106005.htm
Yang B, Yang L, Meng W X, et al. Application of X-ray powder diffraction analysis in Bayan Obo Deposit with microprobe slice[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2021(6): 34-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXK202106005.htm
[15] 张文兰, 胡欢, 谢磊, 等. Na元素的EPMA定量分析: 矿物晶体结构对Na行为的制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(3): 327-339. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103009.htm
Zhang W L, Hu H, Xie L, et al. Quantitative analysis of Na by EPMA: Constraints for the Be avior of Na by the crystal structure[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(3): 327-339. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103009.htm
[16] Brumsack H J, Zuleger E. Boron and boron isotopes in pore waters from ODP Leg 127, Sea of Japan[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1992, 113(3): 427-433.
[17] Spivack A J, Edmond J M. Boron isotope exchange between seawater and the oceanic crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(5): 1033-1043.
[18] 李方林. 两类不同矿床中Ba的地球化学特征及指示意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 1993, 12(3): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ199303012.htm
Li F L. Geochemical characteristics and indicatives significances of barium in two types of deposits[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1993, 12(3): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ199303012.htm
[19] 沈敢富, 李国武, 王凯怡, 等. 白云鄂博原型钡铁钛石晶体化学研究的新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(5): 829-836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201205017.htm
Shen G F, Li G W, Wang K Y, et al. Advances in crystal-chemistry study of type bafertisite from Bayan Obo, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(5): 829-836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201205017.htm
[20] 孙赛军, 廖仁强, 丛亚楠, 等. 钛的地球化学性质与成矿[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1): 68-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001008.htm
Sun S J, Liao R Q, Cong Y N, et al. Geochemistry and mineralization of titanium[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(1): 68-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001008.htm
[21] Manning C E. The chemistry of subduction-zone fluids[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 223(1-2): 1-16.
[22] 常海亮, 郑荣才, 郭春利, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘风城组喷流岩稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(3): 550-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201603003.htm
Chang H L, Zheng R C, Guo C L, et al. Characteristics of rare earth elements of exhalative rock in Fengcheng Formation, northwestern margin of Jungger Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(3): 550-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201603003.htm
[23] 贾斌, 文华国, 李颖博, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌尔禾地区二叠系风城组盐类矿物流体包裹体特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2015, 35(1): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201501005.htm
Jia B, Wen H G, Li Y B, et al. Fluid inclusions in the salt minerals from the Permian Fengcheng Formation in the Urho region, Junggar Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2015, 35(1): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201501005.htm
[24] 傅饶, 郑荣才, 常海亮, 等. 湖相"白烟型"喷流岩-新型的致密油储层类型——以准噶尔盆地西缘乌尔禾地区风城组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(3): 32-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201503006.htm
Fu R, Zheng R C, Chang H L, et al. Lacustrine "white smoke type" exhalative rock—A new type of tight oil reservoir: A case study from lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in Urho area, western margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(3): 32-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201503006.htm
[25] 郭顺. 俯冲-碰撞带硼循环[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(5): 1049-1060, 997. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202105007.htm
Guo S. Boron cycling in subduction-collision zones[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(5): 1049-1060, 997. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202105007.htm
[26] 林秋婷, 陈晨, 刘海洋. 硼的地球化学性质及其在俯冲带的循环与成矿初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1): 5-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001002.htm
Lin C T, Chen C, Liu H Y. Boron prospecting based on boron cycling in subduction zone[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(1): 5-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001002.htm
[27] 张生, 陈根文, Seward T M, 等. 硼在共存水蒸气-富硼熔体之间分配的实验研究及其地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 2014, 43(6): 583-591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201406003.htm
Zhang S, Chen G W, Seward T M, et al. Experimental study on boron distribution between coexisting water vapor and boron-rich melt and its geological implications[J]. Geochimica, 2014, 43(6): 583-591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201406003.htm
[28] 高媛, 王国芝, 李娜. 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系风城组硅质岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(4): 647-660. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201904011.htm
Gao Y, Wang G Z, Li N. Geochemical features and origin of siliceous rocks of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2019, 21(4): 647-660. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201904011.htm
-



 下载:
下载: