Water Quality and Health Risk Assessment of an Ion-adsorption Type REE Mining Area of the Huangpi River Basin, Northern Ganzhou of China
-
摘要:
水质安全和健康是保障中国赣南老区乡村振兴发展的重要因素。赣南离子型稀土矿长期开发利用,导致浸矿剂和矿体中重金属元素等危害人体健康的物质进入水循环系统,给周边乡村饮用水卫生安全带来了潜在风险。目前,针对当地复垦后稀土矿及周边地区水质和健康风险缺乏系统调查评价,本文以《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB 5749—2006)为评价依据,选择赣南北部黄陂河流域典型离子型稀土矿及周边的水体开展调查研究,采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱/质谱等技术测定锰、镉等元素含量,采用水质指数(WQI)、危害商(HQ)、致癌风险(CR)评价了锰和铅等9种指标及其健康风险。结果表明:地表水中的异常指标有氨氮(平均值750μg/L)、锰(平均值207μg/L),地下水中的异常指标有氨氮(平均值4533μg/L)、锰(平均值4009μg/L);世界卫生组织(WHO)公布的Ⅰ类致癌物砷在地表水及地下水均未见异常。WQI显示研究区内85.7%的地表水适宜饮用。地表水及地下水中氨氮的HQ平均值< 1,对人类健康没有不良影响;地下水中锰的HQ平均值>1,可能会对人类健康产生不良影响。地表水及地下水中致癌元素砷的CR值分布区间为10-6~10-4,致癌风险在可接受范围之内。建议相关部门在稀土矿复垦评估中,关注水体氨氮及重金属元素状况,加强所在流域水体锰元素的协同监测。
-
关键词:
- 离子型稀土矿 /
- 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱/质谱法 /
- 水质指数 /
- 健康风险 /
- 赣南北部
Abstract:BACKGROUND Water quality security and human health are important to ensure rural revitalization of old liberated areas. The continuous development and utilization of ion-adsorption type REE deposits in northern Ganzhou aggravate trace elements from ores and tailings to the water cycle, thereby endangering the sanitation and safety of drinking water.
OBJECTIVES To investigate and evaluate health risk and water quality on the watershed scale of rare earth ore concentration area in the Huangpi River Basin.
METHODS The contents of manganese, cadmium and other elements were determined by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry/mass spectrometry(ICP-OES/MS). By choosing "standards for drinking water quality" (GB 5749—2006) as the evaluation basis, the water quality index (WQI), hazard quotient (HQ), and cancer risk (CR)were adopted to evaluate water quality and human health risks through analyzing 9 indices including Pb and Mn.
RESULTS NH3-N and Mn were anomaly indices whether in surface water or groundwater. The average values of NH3-N were 750μg/L and 4533μg/L in surface water and groundwater, respectively. Index values of Mn were 207μg/L and 4009μg/L in surface water and groundwater, respectively. Arsenic, class I carcinogen published by the World Health Organization, had no abnormality in surface water and groundwater. Moreover, 85.7% of surface water and groundwater was found to be suitable for drinking upon analyzing the WQI values. The HQ average value of NH3-N was less than 1 in surface water and groundwater so it had no harmful effects on human health. However, the HQ average value of Mn was more than 1, which may be harmful to human health. CR values of As varying from 10-6 to 10-4 were also calculated, and the risk of cancer was acceptable.
CONCLUSIONS It is suggested that relevant departments should pay attention to the status of NH3-N and heavy metal elements in water during the reclamation evaluation of rare earth mines. The research detailed in this paper confirms that the groundwater monitoring system of manganese should be improved.
-

-
表 1 黄陂河流域地表水、地下水化学统计参数和WQI参数
Table 1. Parameters of chemical statistics and WQI obtained from surface water and groundwater in Huangpi River Basin
指标 地表水 地下水 WQI参数 最小值
(μg/L)最大值
(μg/L)平均值
(μg/L)标准差
(μg/L)最小值
(μg/L)最大值
(μg/L)平均值
(μg/L)标准差
(μg/L)水质
标准a权重
(wi)相对权重
(Wi)pH 6.43 7.03 6.85 0.14 6.96 7.43 7.19 0.23 6.5~8.5a 4 0.095 NH3(以N计) 134 1517 750 386 727 8338 4533 3805 500a 5 0.119 SO42- 457 4222 1940 869 3257 4783 4020 762 250000b 5 0.119 NO3- 0.00 10890 2721 2401 50.00 4329 2189 2139 50000b 5 0.119 As 0.22 0.84 0.58 0.18 0.33 0.44 0.38 0.06 10a 5 0.119 Cd 0.02 0.10 0.05 0.02 0.04 0.25 0.14 0.11 5a 5 0.119 Cu 0.86 10.20 3.61 2.56 0.12 0.59 0.35 0.23 1000a 2 0.048 Mn 42.0 659 207 155 782 7236 4009 3227 100a 5 0.119 Ni 0.45 1.02 0.70 0.18 1.73 8.30 5.01 3.28 20a 1 0.024 Pb 1.06 24.12 8.13 5.50 1.77 2.50 2.14 0.36 10a 5 0.119 注:a为中国《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB 5749—2006);b为世界卫生组织(WHO)标准(2011)。 表 2 地表水监测点枯水期和丰水期WQI值比较
Table 2. Comparison of WQI values of surface water monitoring points in dry season and wet season
黄陂河流域 监测站位WQI值 GNSW-19009 GNSW-19010 GNSW-19014 GMSW-19016) 丰水期 48.46 12.12 35.80 14.14 枯水期 67.83 25.77 47.38 27.01 表 3 黄陂河流域地表水和地下水危害商和致癌风险
Table 3. HQ and CR values of surface water and groundwater in Huangpi River Basin
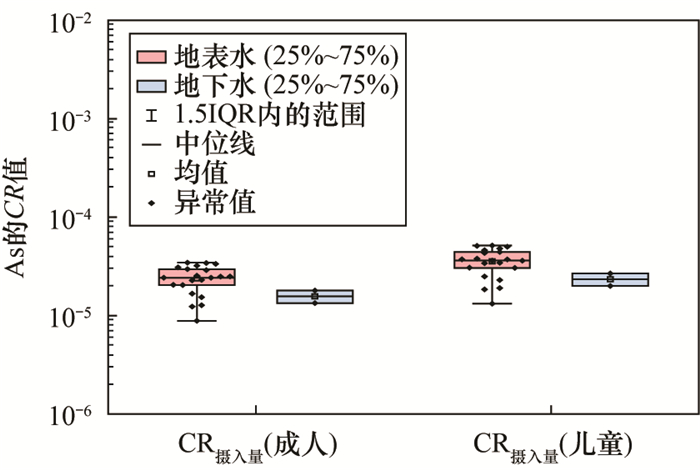
地表水中的元素 危害商(HQ) 致癌风险(CR) 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 NH3(以N计) 1.03×10-1 1.54×10-1 - - NO3- 4.66×10-2 6.96×10-2 - - As 4.66×10-2 6.96×10-2 2.39×10-5 3.56×10-5 Cd 2.85×10-3 4.26×10-3 - - Cu 3.57×10-5 5.33×10-5 - - Mn 2.37×10-1 3.54×10-1 - - Ni 9.54×10-4 1.42×10-3 - - Pb 1.59×10-1 2.38×10-1 - - 地下水中的元素 危害商(HQ) 致癌风险(CR) 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 NH3(以N计) 6.21×10-1 9.27×10-1 - - NO3- 3.75×10-2 5.60×10-2 - - As 3.49×10-2 5.21×10-2 1.57×10-5 2.34×10-5 Cd 7.84×10-3 1.17×10-2 - - Cu 2.42×10-4 3.61×10-4 - - Mn 4.58 6.84 - - Ni 6.87×10-3 1.03×10-2 - - Pb 4.18×10-2 6.25×10-2 - - 注:“-”表示无对应数值。 -
[1] Wang J, Liu G, Liu H, et al. Multivariate statistical evaluation of dissolved trace elements and a water quality assessment in the middle reaches of Huaihe River, Anhui, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 583: 421-431. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.088
[2] Wang J, Li Y, Huang J, et al. Growing water scarcity, food security and government responses in China[J]. Global Food Security, 2017, 14: 9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2017.01.003
[3] 徐敏, 张涛, 王东, 等. 中国水污染防治40年回顾与展望[J]. 中国环境管理, 2019, 11(3): 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHGL201903013.htm
Xu M, Zhang T, Wang D, et al. Review and prospect of water pollution prevention and control of China in the forty years of reform and opening-up[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 11(3): 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHGL201903013.htm
[4] 李传琼, 王鹏, 陈波, 等. 鄱阳湖流域赣江水系溶解态金属元素空间分布特征及污染来源[J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(1): 139-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201801015.htm
Li C Q, Wang P, Chen B, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution source of dissolved metals in the Ganjiang River of Lake Poyang Basin[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(1): 139-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201801015.htm
[5] Phung D, Connell D, Rutherford S, et al. Cardiovascular risk from water arsenic exposure in Vietnam: Application of systematic review and meta-regression analysis in chemical health risk assessment[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 177: 167-175. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.012
[6] 陈仁祥, 高杨, 宋勇, 等. 龙南足洞稀土矿区地下水水质特征及健康风险评价[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2021, 73(3): 111-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2021.03.017
Chen R X, Gao Y, Song Y, et al. Groundwater quality characteristics and health risk assessment in Longnan Zudong rare earth mine[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mining Section), 2021, 73(3): 111-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2021.03.017
[7] 李世龙, 熊建华, 邓超冰, 等. 西江流域柳江水体重金属污染状况及健康风险评价[J]. 广西科学, 2018, 25(4): 393-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXKK201804006.htm
Li S L, Xiong J H, Deng C B, et al. The assessment of the heavy metal pollution and health risks in the Liujiang River, Xijiang Region[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2018, 25(4): 393-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXKK201804006.htm
[8] 刘友存, 刘正芳, 刘基, 等. 赣江上游龙迳河水体氨氮与重金属污染分布特征及风险评价[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2019, 10(4): 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXYS201904014.htm
Liu Y C, Liu Z F, Liu J, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of ammonia nitrogen and heavy metal pollution in Longjing River, the upstream of Ganjiang River[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2019, 10(4): 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXYS201904014.htm
[9] 罗飞, 巴俊杰, 苏春田, 等. 武水河上游区域土壤重金属污染风险及来源分析[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(2): 195-203. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201806040069
Luo F, Ba J J, Su C T, et al. Contaminant assessment and sources analysis of heavy metals in soils from the upper reaches of the Wushui River[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(2): 195-203. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201806040069
[10] 许燕颖, 刘友存, 张军, 等. 赣江上游典型流域水体三氮及重金属空间分布特征与风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(5): 574-583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202005007.htm
Xu Y Y, Liu Y C, Zhang J, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of nitrogen and heavy metals in typical watershed of the upper reaches of Ganjiang River[J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(5): 574-583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202005007.htm
[11] Fernandes M M, Baeyens B. Cation exchange and surface complexation of lead on montmorillonite and illite including competitive adsorption effects[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2019, 100: 190-202. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.11.005
[12] Qiao J, Tang J, Xue Q. Study on Pb release by several new lixiviants in weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore leaching process: Behavior and mechanism[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 190: 110138. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110138
[13] 李凤果, 陈明, 师艳丽, 等. 赣江上游沉积物重金属空间分布及污染特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(3): 920-927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ202003024.htm
Li F G, Chen M, Shi Y L, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in sediments of the upper reaches of Ganjiang River[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(3): 920-927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ202003024.htm
[14] Gao B, Gao L, Gao J, et al. Simultaneous evaluations of occurrence and probabilistic human health risk associated with trace elements in typical drinking water sources from major river basins in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666: 139-146. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.148
[15] Song L, Dai Q, Feng Y, et al. Estimating uncertainties of source contributions to PM2.5 using moving window evolving dispersion normalized PMF[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 286: 117576. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117576
[16] Tong S, Li H, Tudi M, et al. Comparison of characteristics, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water and groundwater in China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 219: 112283. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112283
[17] Jiménez-Oyola S, Chavez E, García-Martínez M, et al. Probabilistic multi-pathway human health risk assessment due to heavy metal(loid)s in a traditional gold mining area in Ecuador[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 224: 112629. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112629
[18] Maleki A, Jari H. Evaluation of drinking water quality and non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals in rural areas of Kurdistan, Iran[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 23: 101668.
[19] 于沨, 王伟, 于扬, 等. 川西九龙地区锂铍矿区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 408-424. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
Yu F, Wang W, Yu Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Jiulong Li-Be mining area, western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 408-424. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
[20] Meng Q, Zhang J, Zhang Z, et al. Geochemistry of dis-solved trace elements and heavy metals in the Dan River Drainage (China): Distribution, sources, and water quality assessment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(8): 8091-8103. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6074-x
[21] Sener S, Sener E, Davraz A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 584-585: 131-144. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.102
[22] Xiao J, Wang L, Deng L, et al. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 2004-2012. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.322
[23] Huang S, Li Z, Yu J, et al. Vertical distribution and occurrence state of the residual leaching agent (ammonium sulfate) in the weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 299: 113642. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113642
[24] 邓振乡, 秦磊, 王观石, 等. 离子型稀土矿山氨氮污染及其治理研究进展[J]. 稀土, 2019, 40(2): 120-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201902017.htm
Deng Z X, Qin L, Wang G S, et al. Ammonia nitrogen pollution and progress in its treatment of ionic rare earth mines[J]. China Rare Earths, 2019, 40(2): 120-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201902017.htm
[25] 林圣玉, 莫明浩, 王凌云. 赣州市山水林田湖草生态保护修复问题识别和技术探析[J]. 中国水土保持, 2021(1): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2021.01.012
Lin S Y, Mo M H, Wang L Y. Identification and technical analysis of ecological protection and restoration of landscape forest, field, lake and grass in Ganzhou City[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2021(1): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2021.01.012
[26] 郑先坤, 冯秀娟, 陈哲, 等. 离子型稀土矿原地浸矿废弃地中残存的氮素垂直分布规律及意义[J]. 稀土, 2020, 41(4): 30-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ202004004.htm
Zheng X K, Feng X J, Chen Z, et al. Distribution of nitrogen residues in ion-type rare earth in-situ leached wasteland and its significance[J]. China Rare Earths, 2020, 41(4): 30-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ202004004.htm
[27] 张塞, 于扬, 王登红, 等. 赣南离子吸附型稀土矿区土壤重金属形态分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 726-738. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911050152
Zhang S, Yu Y, Wang D H, et al. Forms distribution of heavy metals and their ecological risk evaluation in soils of ion adsorption type in the rare earth mining area of southern Jiangxi, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 726-738. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911050152
[28] Zhao L, Yan Y, Yu R, et al. Source apportionment and health risks of the bioavailable and residual fractions of heavy metals in the park soils in a coastal city of China using a receptor model combined with Pb isotopes[J]. CATENA, 2020, 194: 104736. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104736
[29] 陈陵康, 陈海霞, 金雄伟, 等. 离子型稀土矿粒度、粘土矿物、盐基离子迁移及重金属释放研究及展望[J/OL]. 中国稀土学报, 2022, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2365.TG.20210928.0337.008.html.
Chen L K, Chen H X, Jin X W, et al. Research and prospect of particle size, clay minerals, base ion migration and heavy metal release of ionic rare earth ore[J/OL]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2022, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2365.TG.20210928.0337.008.html.
[30] 王学锋, 许春雪, 顾雪, 等. 典型稀土矿区周边土壤中稀土元素含量及赋存形态研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(2): 137-146. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807180085
Wang X F, Xu C X, Gu X, et al. Concentration and fractionation of rare earth elements in soils surrounding rare earth ore area[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(2): 137-146. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807180085
[31] 徐春丽, 刘斯文, 魏吉鑫, 等. 离子型稀土矿区及周边土壤中稀土、重金属元素的地球化学特征[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(4): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH202104001.htm
Xu C L, Liu S W, Wei J X, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth and heavy metal elements in ion-type rare earth mining area and surrounding soil[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(4): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH202104001.htm
[32] 陈能汪, 王德利, 鲁婷, 等. 九龙江流域地表水锰的污染来源和迁移转化机制[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(8): 2955-2964. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201808001.htm
Chen N W, Wang D L, Lu T, et al. Manganese pollution in the Jiulong River watershed: Sources and transformation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(8): 2955-2964. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201808001.htm
[33] 罗杰, 张嵚, 罗密密, 等. 某离子型稀土矿不同功能区土壤退化特征[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2022, 40(2): 229-338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB202202017.htm
[34] Jiang Y. China's water security: Current status, emerging challenges and future prospects[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2015, 54: 106-125.
[35] 卢陈彬. 赣南某离子型稀土矿区土壤中锰的赋存形态与释放特性研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2020.
Lu C B. Occurrence and release characteristics of manganese in the soil from an ion-absorbed rare earth mining area in South Jiangxi[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[36] Neslund-Dudas C M, Mcbride R B, Kandegedara A, et al. Association between cadmium and androgen receptor protein expression differs in prostate tumors of African-American and European-American men[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2018, 48: 233-238.
[37] Qing Y, Yang J, Zhu Y, et al. Cancer risk and disease burden of dietary cadmium exposure changes in Shanghai residents from 1988 to 2018[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 734: 139411.
[38] Mason L H, Harp J P, Han D Y. Pb neurotoxicity: Neuro-psychological effects of lead toxicity[J]. BioMed Research International, 2014, doi:10.1155/2014/840547.
-




 下载:
下载: