Determination of Multiple Elements in Soils Surrounding Iron Deposits from Guyang County, Baotou City, and Health Risk Assessment
-
摘要:
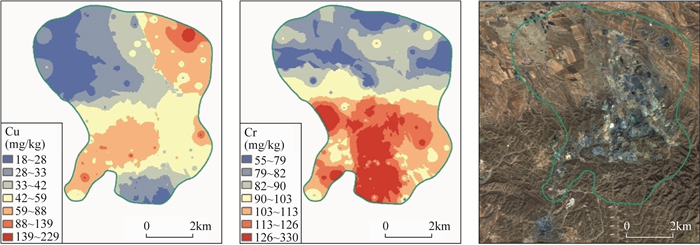
矿产的开发利用会向周边土壤释放重金属元素,当人体摄入或接触受污染的土壤则可能会产生健康危害。铁矿是中国分布最为广泛的矿种之一,但前人对铁矿区土壤重金属健康风险的研究较少,尤其是干旱区铁矿。干旱区生态脆弱,修复困难,因此需要更加科学地对土壤加强管理。本文以内蒙古包头市固阳县某铁矿区为研究对象,采集表层土壤101件,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱/发射光谱法和原子荧光光谱法测定了土壤中的重金属含量,研究元素的特征,并利用健康风险评价法评价重金属对人体的健康危害,提出土壤污染筛选值。结果显示:①研究区土壤中Cu、Cr、Ni变异系数大于0.5,平均含量明显高于河套平原背景值;②Cu的高值区主要分布于尾矿库与选矿厂周边,Cr、Ni的高值区主要分布于基岩山区;③健康风险评价结果表明各元素的危害商(HQ)均小于1,由大到小顺序为As>Cr>Ni>Cu>Cd>Zn>Hg,总危害商(HI)的平均值为0.542,有1个点HI大于1,位于矿区南部基岩区,Cr、Ni、As的贡献率分别为59%、25%、15%,总致癌风险指数(CR)均小于10-4;④基于人体健康计算提出研究区土壤Cr、Ni、As的污染筛选值为541、579、32.8mg/kg。本研究揭示了:①研究区Cr、Ni主要受到成土母质影响,Cu主要受到选矿活动影响;②土壤重金属总体上健康危害较低,受成土母质影响较大,但仍需关注尾矿库周边污染元素的累积情况,并避免经口摄入污染物;③不同地区或不同类型的铁矿中的伴生元素不同,仍需对各气候分区内不同类型的铁矿进一步开展研究。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The exploitation of minerals releases heavy metals into the surrounding soil, which can cause health hazards when biological entities are exposed to contaminated soil. Iron ore is one of the most widely distributed minerals in China, but there are few studies on the health risk of soil heavy metals in iron mines, especially in arid areas. The ecosystem of the arid area is fragile and difficult to repair once it has been polluted.
OBJECTIVES To perform environmental health risk assessment for topsoil surrounding iron deposits from Guyang County, Baotou City.
METHODS 101 topsoil samples were collected from an iron mine in Guyang County, Baotou City. Heavy metals were measured by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry/optical emission spectrometry and atomic fluorescence spectrometry, to study element characteristics. The health risk assessment method was used to evaluate and calculate the screening value.
RESULTS The results showed that the variation coefficients of copper, chromium, and nickel in the study area were higher than 0.5, and the average contents of these elements were significantly higher than that in the Hetao Plain. The high value areas of copper were mainly distributed around tailings ponds and concentrators, while the high value areas of chromium or nickel were mainly distributed in bedrock mountains. The assessment of health hazards showed that the hazard quotient of all elements was less than 1, and the order was As>Cr>Ni>Cu>Cd>Zn>Hg. The average of total hazard quotient was 0.542. There was a sample in the bedrock mountain south of the iron mine, which had a total hazard quotient exceeding 1, and the contribution rates of chromium, nickel and arsenicwere 59%, 25%, and 15%, respectively. The carcinogenic hazard index of all elements was below 10-4. Soil screening levels of chromium, nickel and arsenic in the study area were 579mg/kg, 622mg/kg and 32.8mg/kg base on human health.
CONCLUSIONS Chromium and nickel in the study soil are mainly affected by parent materials of soil formation, while copper is mainly affected by mineral processing activities. In general, the health hazard of heavy metals in soil is relatively low, and is greatly influenced by the parent materials of soil formation. However, it is still necessary to pay attention to the accumulation of polluted elements in the areas around tailings ponds, and to avoid oral intake of pollutants. And it is also necessary to further study the feature of soil heavy metals from different kinds of iron mines and different regions that have not been studied before, because the associated elements of iron ore in different regions or types are not the same.
-

-
表 1 健康风险评价模型暴露因子参数
Table 1. Exposure factor parameters of health risk assessment model
参数 具体描述 数值单位 参考值 OISERn 非致癌(致癌)效应下经口摄入土壤暴露量 - - DCSERn 非致癌(致癌)效应下皮肤接触土壤暴露量 - - PISERn 非致癌(致癌)效应下吸入土壤颗粒暴露量 - - OISR 每日摄入土壤量 mg/d 100Ⅰ ED 暴露时长 a 25Ⅰ EF 暴露频率 d/a 250Ⅰ ABS0 经口摄入吸收效率因子 无量纲 1Ⅰ BW 平均体重 kg 61.8Ⅰ ATn 非致癌(致癌)效应平均时长 d 27740Ⅰ(致癌), 9125Ⅰ(非致癌) DAIR 每日空气呼吸量 m3/d 14.5Ⅰ PM10 空气中可吸入悬浮颗粒物总量 mg/m3 0.07Ⅱ PIAF 吸入土壤颗粒物在体内滞留比例 无量纲 0.75Ⅰ fspo 室内空气中来自土壤的颗粒物所占比例 无量纲 0.8Ⅰ EFO 室内暴露频率 d/a 187.5Ⅰ fspi 室外空气中来自土壤的颗粒物所占比例 无量纲 0.5Ⅰ EFI 室外暴露频率 d/a 62.5Ⅰ SAE 皮肤暴露面积 cm2 3033Ⅲ SSAR 皮肤表面土壤黏附系数 mg/cm2 0.2Ⅰ ABSd 皮肤接触吸收效率因子 无量纲 0.001Ⅰ(镉),0.03Ⅰ(砷) E 每日皮肤接触事件频率 次/d 1Ⅰ 注:标注Ⅰ的数据直接引自HJ 25.3—2019;Ⅱ为包头市政府公布数据;Ⅲ根据HJ 25.3—2019计算得出。 表 2 土壤重金属不同暴露途径的RfD和SF值
Table 2. RfD and SF values for different exposure pathways of heavy metals in soil
重金属元素 参考剂量[mg/(kg·d)] 致癌斜率因子[kg·d/mg] RfD0 数据来源 RfDi 数据来源来源 RfDd 数据来源来源 SF0 数据来源来源 SFi 数据来源来源 SFd 数据来源来源 Cr 3.00×10-3 Ⅲ - - - - - - 5.12×10-2 Ⅳ - - Ni 2.00×10-2 Ⅰ 2.11×10-5 Ⅱ - - - - 1.11 Ⅱ - - Zn 3.00×10-1 Ⅰ - - - - - - - - - - Cu 4.00×10-2 Ⅰ - - - - - - - - - - Cd 1.00×10-3 Ⅰ 2.35×10-6 Ⅱ 2.50×10-5 Ⅱ - - 7.67 Ⅱ - - As 3.00×10-4 Ⅰ 3.52×10-6 Ⅱ 3.00×10-4 Ⅱ 1.50 Ⅰ 18.3 Ⅱ 1.50 Ⅱ Hg 3.00×10-4 Ⅰ 7.04×10-5 Ⅱ - - - - - - - - 注:标注Ⅰ的数据直接引自HJ 25.3—2019;Ⅱ根据HJ 25.3—2019中外推公式引用Ⅰ计算得出;Ⅲ直接引自OSWER 9355.4-24;Ⅳ根据HJ 25.3—2019中外推公式引用Ⅲ计算得出。 表 3 土壤重金属参数统计
Table 3. Parameter statistics of heavy metals in soil
重金属元素 最小值(mg/kg) 最大值(mg/kg) 平均值(mg/kg) 标准差(mg/kg) 变异系数 河套平原表层土壤背景值[38] (mg/kg) Cr 48 382 109 55 0.51 56 Ni 22 173 44 23 0.51 25 Zn 43.7 177.3 81.1 24.5 0.30 55.7 Cu 16.6 519.9 53.0 59.8 1.13 19.2 Cd 0.03 0.33 0.10 0.04 0.36 0.12 Pb 4.28 61.18 18.13 7.27 0.40 18.76 As 1.21 14.85 8.29 2.60 0.31 9.68 Hg 0.0032 0.0492 0.0214 0.0088 0.41 0.0249 表 4 不同暴露途径土壤重金属危害商
Table 4. Hazard quotient of heavy metals in soil under different exposure pathways
参数 危害商 最小值 最大值 平均值 HQoisCr 8.95×10-2 7.05×10-1 2.01×10-1 HQoisNi 5.97×10-3 4.78×10-2 1.23×10-2 HQpisNi 3.12×10-2 2.50×10-1 6.45×10-2 HQoisZn 8.06×10-4 3.28×10-3 1.50×10-3 HQoisCu 2.30×10-3 7.20×10-2 7.34×10-3 HQoisCd 1.39×10-4 1.83×10-3 5.82×10-4 HQdcsCd 3.36×10-5 4.45×10-4 1.41×10-4 HQpisCd 3.25×10-4 4.31×10-3 1.37×10-4 HQoisAs 2.24×10-2 2.74×10-1 1.53×10-1 HQdcsAs 4.07×10-3 4.99×10-2 2.79×10-2 HQpisAs 1.05×10-3 1.29×10-1 7.20×10-2 HQoisHg 5.94×10-5 9.10×10-4 3.95×10-4 HQpisHg 1.40×10-6 2.14×10-5 9.28×10-6 表 5 所有暴露途径土壤重金属危害商
Table 5. Hazard quotient of heavy metals in soil under all exposure pathways
参数 危害商 最小值 最大值 平均值 HQCr 8.95×10-2 7.05×10-1 2.01×10-1 HQNi 3.72×10-2 2.98×10-1 7.68×10-2 HQZn 8.06×10-4 3.28×10-3 1.50×10-3 HQCu 2.30×10-3 7.20×10-2 7.34×10-3 HQCd 4.98×10-4 6.59×10-3 2.09×10-3 HQAs 3.69×10-2 4.53×10-1 2.53×10-1 HQHg 6.08×10-5 9.31×10-4 4.04×10-4 HI 3.21×10-1 1.20 5.42×10-1 表 6 土壤重金属致癌健康风险指数
Table 6. Carcinogenic hazard index of heavy metals in soil
参数 健康风险指数 最小值 最大值 平均值 CRoisAs 6.62×10-7 8.12×10-6 4.53×10-6 CRdcsAs 1.20×10-7 1.48×10-6 8.25×10-7 CRpisAs 4.46×10-8 5.48×10-7 3.06×10-7 CRAs 8.27×10-7 1.01×10-5 5.67×10-6 CRCr 4.99×10-9 3.93×10-8 1.12×10-8 CRNi 4.81×10-8 3.85×10-7 9.94×10-8 CRCd 3.86×10-10 5.11×10-9 1.62×10-9 表 7 研究区土壤重金属筛选值
Table 7. Screening levels of heavy metals in soil from the study area
重金属元素 筛选值(mg/kg) 基于HQois 基于HQpis 基于HQdcs 基于HQ 基于CRois 基于CRpis 基于CRdcs 基于CR 建议筛选值 GB36600筛选值 Cr 5.41×102 - - 5.41×102 - 9.71×105 - 9.71×105 5.41×102 - Ni 3.61×103 6.90×102 - 5.79×102 - 4.48×104 - 4.48×104 5.79×102 9.00×102 Zn 5.41×104 - - 5.41×104 - - - - 5.41×104 - Cu 7.22×103 - - 7.22×103 - - - - 7.22×103 1.80×104 Cd 1.80×102 7.68×101 7.44×102 5.02×101 - 6.48×103 - 6.48×103 5.02×101 6.50×101 As 5.41×101 1.15×102 2.97×102 3.28×101 1.83×102 2.71×103 1.00×103 1.46×102 3.28×101 6.00×101 Hg 5.41×101 2.30×103 - 5.29×101 - - - - 5.29×101 3.80×101 注:“-”表示无相关风险,无需计算。 -
[1] 李建中, 张进德. 我国矿山地质环境调查工作探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2018, 45(4): 169-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201804025.htm
Li J Z, Zhang J D. Discussion on the work of mine geo-environmental investigation of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(4): 169-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201804025.htm
[2] 张进德, 郗富瑞. 我国废弃矿山生态修复研究[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(21): 7921-7930. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202021034.htm
Zhang J D, Xi F R. Study on ecological restoration of abandoned mines in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(21): 7921-7930. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202021034.htm
[3] 张素荣, 王昌宇, 刘继红, 等. 雄安新区西南部土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4): 238-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202104031.htm
Zhang S R, Wang C Y, Liu J H, et al. Assessments of heavy metal pollution in soils of the southwestern Xiong'an District and its ecological risk[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(4): 238-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202104031.htm
[4] 邢怡, 张素荣, 刘继红, 等. 农作物根系土对农产品安全的影响分析——以保定东部地区为例[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(3): 219-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.03.008
Xing Y, Zhang S R, Liu J H, et al. Effect of crop root soil on agricultural product safety: Take the eastern part of Baoding, Hebei Province as an example[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2019, 42(3): 219-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.03.008
[5] 孙晓艳, 罗立强. 重金属生物有效性在矿山环境评价中应用研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(1): 100-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH201901021.htm
Sun X Y, Luo L Q. Research progress on the application bioavailability of heavy metals to evaluate ecological risk in mining area[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 39(1): 100-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH201901021.htm
[6] 张进德, 田磊, 裴圣良. 矿山水土污染与防治对策研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(2): 157-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202102019.htm
Zhang J D, Tian L, Pei S L. A discussion of soil and water pollution and control countermeasures in mining area of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(2): 157-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202102019.htm
[7] 赵立群, 王春女, 张敏, 等. 中国铁矿资源勘查开发现状及供需形势分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(3): 635-643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202003016.htm
Zhao L Q, Wang C N, Zhang M, et al. Current exploration status and supply-demand situation of iron ore resources in China mainland[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(3): 635-643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202003016.htm
[8] 胡国成, 张丽娟, 齐剑英, 等. 贵州万山汞矿周边土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(5): 879-885. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201505024.htm
Hu G C, Zhang L J, Qi J Y, et al. Contaminant characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Wanshan mercury mine area, Guizhou Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(5): 879-885. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201505024.htm
[9] 李三中, 徐华勤, 陈建安, 等. 某矿区砷碱渣堆场周边土壤重金属污染评价及潜在生态风险分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(6): 1141-1148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201706016.htm
Li S Z, Xu H Q, Chen J A, et al. Pollutions and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soils around waste arsenic-containing alkaline sites[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(6): 1141-1148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201706016.htm
[10] 陶美霞, 胡虎, 胡兰文, 等. 上饶市某铜矿废弃地土壤重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(6): 1153-1159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201806021.htm
Tao M X, Hu H, Hu L W, et al. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in polluted abandon soil of Shangrao, Jiangxi[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(6): 1153-1159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201806021.htm
[11] 邬光海, 王晨昇, 陈鸿汉. 内蒙古废弃钨钼矿区周围土壤重金属污染生态环境评价及成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1838-1852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006020.htm
Wu G H, Wang C S, Chen H H. Eco-environmental assessment and genetic analysis of heavy metal pollution in the soil around the abandoned tungsten-molybdenum mine area in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1838-1852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006020.htm
[12] 于沨, 王伟, 于扬, 等. 川西九龙地区锂铍矿区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 408-424. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
Yu F, Wang W, Yu Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Jiulong Li-Be mining area, western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 408-424. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
[13] 李晶, 杨超元, 殷守强, 等. 草原型露天煤矿区土壤重金属污染评价及空间分布特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(12): 3676-3684. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201912008.htm
Li J, Yang C Y, Yin S Q, et al. Evaluation and spatial distribution characteristics of soil heavy metals pollution in grassland open-pitcoal mine area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(12): 3676-3684. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201912008.htm
[14] Niu S, Fang Q, Yu J, et al. Heavy metals present in the soils from extremely large opencast iron mine pit[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2021, 107(6): 984-989. doi: 10.1007/s00128-021-03266-9
[15] Chung S Y, Senapathi V, Park K H, et al. Source and remediation for heavy metals of soils at an iron mine of Ulsan City, Korea[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 11: 769. doi: 10.1007/s12517-018-4141-y
[16] Hosseini S M, Rezazadeh M, Salimi A, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in soils and indigenous plants near an iron ore mine in northwest Iran[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(5): 363-367. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2018.02.004
[17] 黄兴星, 朱先芳, 唐磊, 等. 密云水库上游某铁矿区土壤重金属含量及形态研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(9): 1632-1639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.09.014
Huang X X, Zhu X F, Tang L, et al. Studies on the distribution and chemical speciation of heavy metals in a iron mine soil of the upstream area of Miyun Reservoir, Beijing[J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(9): 1632-1639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.09.014
[18] 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 贾凤超, 等. 承德伊逊河钒钛磁铁矿小流域土壤重金属地球化学基线及生态风险累积效应[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(2): 588-604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202102021.htm
Sun H Y, Wei X F, Jia F C, et al. Geochemical baseline and ecological risk accumulation effect of soil heavy metals in the small-scale drainage catchment of V-Ti magnetite in the Yixun River Basin, Chengde[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(2): 588-604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202102021.htm
[19] 宋凤敏, 张兴昌, 王彦民, 等. 汉江上游铁矿尾矿库区土壤重金属污染分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(9): 1707-1714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201509015.htm
Song F M, Zhang X C, Wang Y M, et al. Heavy metal pollution in soils surrounding an iron tailings in upstream areas of Hanjiang River, Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(9): 1707-1714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201509015.htm
[20] 王蕊, 陈楠, 张二喜, 等. 龙岩市某铁锰矿区土壤重金属地球化学空间分布特征与来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1114-1122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103009.htm
Wang R, Chen N, Zhang E X, et al. Geochemical patterns and source analysis of soil heavy metals in an iron and manganese ore area of Longyan City[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1114-1122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103009.htm
[21] 杨伟光, 王美娥, 陈卫平. 新疆干旱区某矿冶场对周围土壤重金属累积的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 445-452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201901054.htm
Yang W G, Wang M E, Chen W P. Effect of a mining and smelting plant on the accumulation of heavy metals in soils in arid areas in Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(1): 445-452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201901054.htm
[22] 贺灵, 吴超, 曾道明, 等. 中国西南典型地质背景区土壤重金属分布及生态风险特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 384-396. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101260016
He L, Wu C, Zeng D M, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and ecological risk of soils in the typical geological background region of southwest China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 384-396. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101260016
[23] 白宇明, 李永利, 房利民. 包头市矿山地质环境现状和防治建议[J]. 中国矿业, 2020, 29(S1): 114-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2020S1027.htm
Bai Y M, Li Y L, Fang L M. The current situation and prevention proposals of the mine geological environment in Baotou City[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2020, 29(S1): 114-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2020S1027.htm
[24] 程莉, 宁小莉. 包头市生态城市建设中社会进步指标评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(11): 12-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201411003.htm
Cheng L, Ning X L. The assessment of social progress index in the eco-city construction for Baotou[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(11): 12-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201411003.htm
[25] 张连科, 张花娟, 黄学敏, 等. 包头市不同功能区土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2016, 23(2): 352-356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201602064.htm
Zhang L K, Zhang H J, Huang X M, et al. Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in different function areas in Baotou[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 23(2): 352-356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201602064.htm
[26] 孙鹏, 李艳伟, 张连科, 等. 包头市典型工业区表层土壤中重金属污染状况及其潜在生态风险研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(4): 433-439. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.016
Sun P, Li Y W, Zhang L K, et al. Heavy metal pollution in topsoil from the Baotou industry area and its potential ecological risk evaluation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(4): 433-439. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.016
[27] 黄哲, 曲世华, 白岚, 等. 包头城区土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(5): 149-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201705032.htm
Huang Z, Qu S H, Bai L, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metal soils in urban areas of Baotou[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(5): 149-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201705032.htm
[28] 李卫平, 王非, 杨文焕, 等. 包头市南海湿地土壤重金属污染评价及来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(11): 1977-1984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201711019.htm
Li W P, Wang F, Yang W H, et al. Pollution assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in Nanhai Wetland soil of Baotou City[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(11): 1977-1984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201711019.htm
[29] 郭伟, 赵仁鑫, 张君, 等. 内蒙古包头铁矿区土壤重金属污染特征及其评价[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(10): 3099-3105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201110052.htm
Guo W, Zhao R X, Zhang J, et al. Distribution characteristics and assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in the iron mining of Baotou in Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(10): 3099-3105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201110052.htm
[30] 刘飞, 苏尚国, 余晓艳, 等. 内蒙古文圪气镁铁-超镁铁质杂岩体中环带角闪石矿物学特征及成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(1): 206-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301020.htm
Liu F, Su S G, Yu X Y, et al. Characteristics and petrogenesis of zoned amphiboles in Wengeqi mafic-ultramafic complex, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(1): 206-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301020.htm
[31] 郝国杰, 王惠初, 牛广华, 等. 中国变质大地构造研究及科学意义[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2020, 43(2): 89-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.02.004
Hao G J, Wang H C, Niu G H, et al. Metamorphic geotectonic research and scientific significance in China[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2020, 43(2): 89-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.02.004
[32] 陈梦舫, 骆永明, 宋静, 等. 中、英、美污染场地风险评估导则异同与启示[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2011, 23(3): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2011.03.004
Chen M F, Luo Y M, Song J, et al. Comparison of USA, UK and Chinese risk assessment guidelines and the implications for China[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2011, 23(3): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2011.03.004
[33] 谷阳光, 高富代. 我国省会城市土壤重金属含量分布与健康风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(1): 62-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201701006.htm
Gu Y G, Gao F D. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in provincial capital cities, China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(1): 62-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201701006.htm
[34] 冯宇佳, 赵全利, 孙洪欣, 等. 华北地区菜田土壤-蔬菜重金属污染状况和健康风险评价[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2017, 40(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CULT201701001.htm
Feng Y J, Zhao Q L, Sun H X, et al. Assessment of soil-vegetable contamination and health risk of heavy metals in vegetables around North China[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2017, 40(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CULT201701001.htm
[35] Mehr M R, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, et al. Distribution, source identification and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in urban areas of Isfahan Province, Iran[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2017, 132: 16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.04.026
[36] Qing X, Zong Y T, Lu S G. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, northeast China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 120: 377-385. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.06.019
[37] Praveena S M, Ismail S N S, Aris A Z. Health risk assess-ment of heavy metal exposure in urban soil from Seri Kembangan (Malaysia)[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2015, 8(11): 9753-9761. doi: 10.1007/s12517-015-1895-3
[38] 王喜宽, 黄增芳, 苏美霞, 等. 河套地区土壤基准值及背景值特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2007, 26(4): 287-292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.04.008 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20070495
Wang X K, Huang Z F, Su M X, et al. Characteristics of reference and background values of soils in Hetao area[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(4): 287-292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.04.008 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20070495
[39] 赵东杰, 王学求. 滇黔桂岩溶区河漫滩土壤重金属含量、来源及潜在生态风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(4): 1609-1619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.028
Zhao D J, Wang X Q. Distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the floodplain soils of the karst area of Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(4): 1609-1619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.028
[40] 李洋, 张乃明, 魏复盛. 滇东镉高背景区菜地土壤健康风险评价与基准[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(10): 4522-4530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.039
Li Y, Zhang N M, Wei F S. A benchmark study on soil health risks of vegetable fields in a high-cadmium background area in eastern Yunnan[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(10): 4522-4530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.039
[41] 南景博, 黄华, 王长乐, 等. 内蒙古固阳绿岩带条带状铁建造地球化学特征与沉积环境讨论[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(2): 331-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201702010.htm
Nan J B, Huang H, Wang C L, et al. Geochemistry and depositional setting of banded iron formations in Guyang greenstone belt, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(2): 331-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201702010.htm
[42] Su S G, Lesher C M. Genesis of PGE mineralization in the Wengeqi mafic-ultramafic complex, Guyang County, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(1-2): 197-207. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0351-x
[43] Wu S, Peng S, Zhang X, et al. Levels and health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban soils in Dongguan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 148: 71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.08.009
[44] 李如忠, 潘成荣, 徐晶晶, 等. 典型有色金属矿业城市零星菜地蔬菜重金属污染及健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(3): 1076-1085. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201303040.htm
Li R Z, Pan C R, Xu J J, et al. Contamination and health risk for heavy metals via consumption of vegetables grown in fragmentary vegetable plots from a typical nonferrous metals mine city[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(3): 1076-1085. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201303040.htm
[45] Diami S M, Kusin F M, Madzin Z. Potential ecological and human health risks of heavy metals in surface soils associated with iron ore mining in Pahang, Malaysia[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(20): 21086-21097. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7314-9
[46] 成杭新, 李括, 李敏, 等. 中国城市土壤微量金属元素的管理目标值和整治行动值[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(5): 215-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201505021.htm
Cheng H X, Li K, Li M, et al. Management target value (MTV) and rectification action value (RAV) of trace metals in urban soil in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(5): 215-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201505021.htm
-




 下载:
下载: