Inorganic-Organic Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Typical Underground River System in Southwest China
-
摘要:
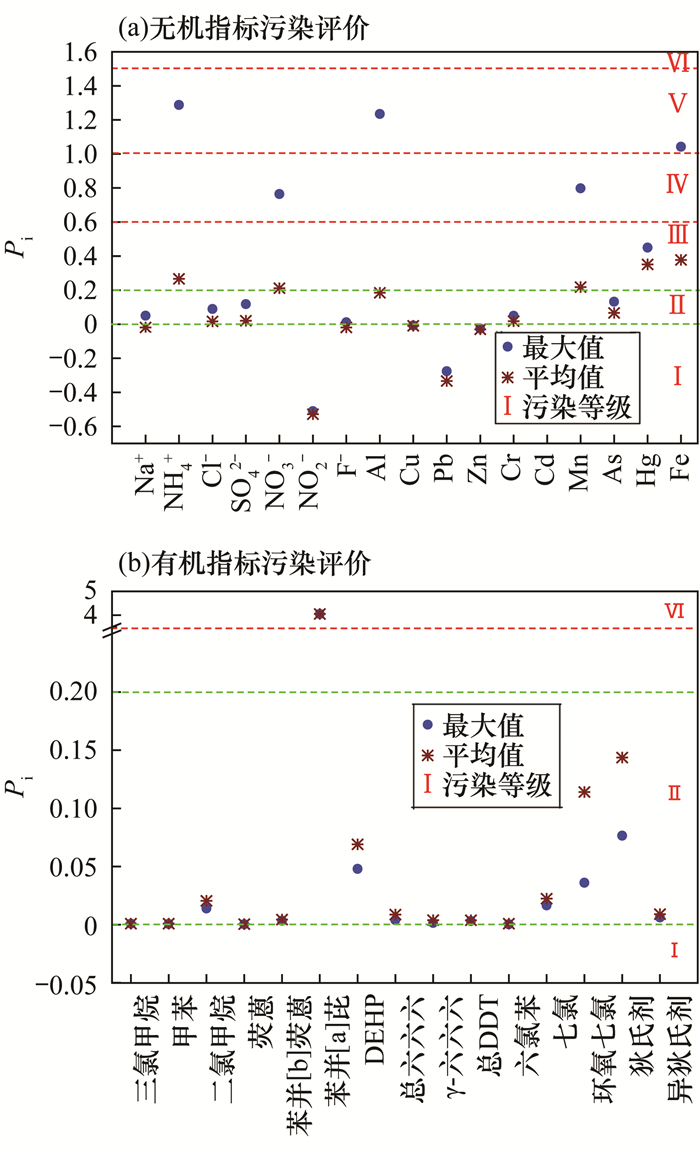
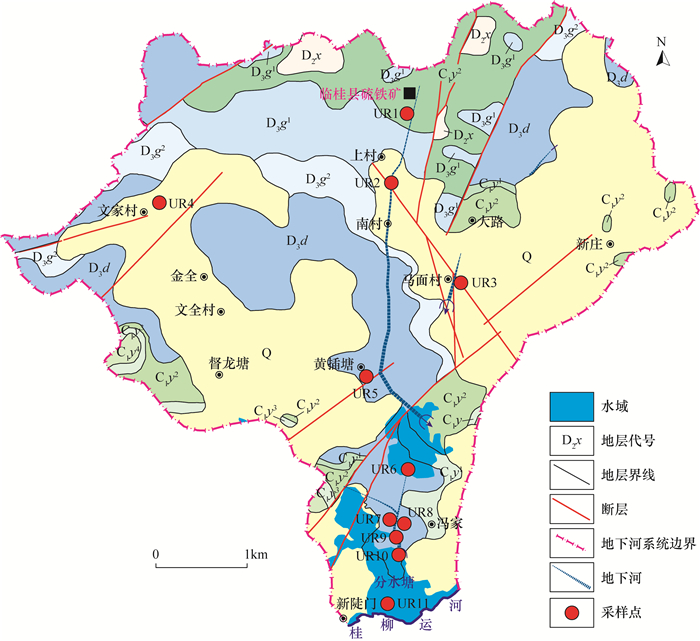
岩溶地下水为全球约25%的人口提供饮用水源,地下河作为主要岩溶地下水类型,是中国西南岩溶区重要供水水源,掌握其水质污染状况及人体健康风险,对岩溶区水资源保护与安全用水具有重要意义。本文以广西桂林会仙狮子岩地下河系统为例,采集地下河水样品22组(无机和有机样品各11组),采用电感耦合等离子体质谱、离子色谱、气相色谱-质谱等方法测定11项无机离子、10项金属元素及41项有机指标的质量浓度,运用单指标污染标准指数法、健康风险评价模型揭示了研究区无机与有机指标分布、污染及健康风险。结果表明:①狮子岩地下河水中无机超标指标有NH4+(1.33倍)、Fe(1.2倍)、Al(1.5倍)和Mn(1.01倍),超标点多位于地下河排泄区;检出18项有机物,其中挥发性有机物(VOCs)、半挥发性有机物(SVOCs)和有机氯农药(OCPs)检出率分别为18.75%、30.77%和91.67%,研究区存在普遍的农药残留(49.14~109.83ng/L)。②与地下水对照值相比,研究区受到10项无机指标的轻度~中度污染、14项有机指标的轻度污染,个别采样点受到NO3-、Fe、Al和Mn的较严重~严重污染,一处采样点遭受苯并[a]芘的极严重污染。③经饮用水和皮肤接触两种途径暴露的非致癌健康风险(成人9.98×10-3a-1,儿童1.09×10-2a-1)和致癌健康风险(成人1.33×10-7a-1,儿童2.82×10-7a-1)均在可接受范围内。本文认为研究区存在不同程度的无机和有机污染,但污染物指标对人体暂不构成非致癌和致癌健康风险。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Karst groundwater provides drinking water for about 25% of the world's population. As the main type of karst groundwater, underground rivers are an important water supply source for karst areas in Southwest China. It is of great significance to master the water quality, pollution status and human health risk for water resources protection and safety use in southern karst areas.
OBJECTIVES To reveal the chemical compositions, pollution degree and health risk of underground river water.
METHODS 22 groups of underground river water samples (half inorganic and half organic samples) from the underground river system of Shiziyan in Huixian, Guilin, Guangxi were collected. The concentrations and spatial distribution of 21 inorganic ions and 41 organic indices were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), ion chromatography (IC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS).The single index pollution standard index method was used to evaluate the pollution of 17 inorganic ions and 15 detected organic compounds. The health risk assessment model recommended by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) was used to study the human health risk of 10 major pollutants.
RESULTS The results showed that: (1) Ca2+ and HCO3- were the dominant ions in the Shiziyan underground river. The concentrations of NH4+, Fe, Al and Mn in the underground river exceeded the groundwater quality standard by 1.33, 1.2, 1.5 and 1.01 times, respectively, and the exceeding points were mostly located in the discharge area of the underground river. 18 organic compounds were detected, of which the detection rates of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), semi volatile organics (SVOCs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) were 18.75%, 30.77% and 91.67% respectively. (2) Compared with the groundwater background values, the underground river water in the study area was slightly-moderately polluted by 10 inorganic indicators and 14 organic compounds. Some sampling points were seriously polluted by NO3-, Fe, Al and Mn, and one sampling point (UR8) was extremely polluted by benzo [a] pyrene. (3) According to the results of health risk assessment, the non-carcinogenic health risks of being exposed to drinking water and for skin exposure were 9.98×10-3 per year for adults and 1.09×10-2 per year for children, and carcinogenic health risks were 1.33×10-7 per year for adults and 2.82×10-7 per year for children, which were within acceptable levels.
CONCLUSIONS There are various degrees of inorganic and organic pollution in the study area, but the pollutant indicators do not pose a non-carcinogenic or carcinogenic health risk to the population.
-

-
表 1 狮子岩地下河有机测试指标和测试方法
Table 1. Statistics of organic indices and analytical methods in the Shiziyan underground river
有机指标类型 测试指标数 测试项目 测试方法 VOCs 16项 三氯甲烷、四氯化碳、苯、甲苯、二氯甲烷、1, 2-二氯乙烷、1, 1, 1-三氯乙烷、1, 1, 2-三氯乙烷、1, 2-二氯丙烷、三溴甲烷、氯乙烯、1, 1-二氯乙烯、四氯乙烯、乙苯、二甲苯、苯乙烯 气相色谱-质谱法 SVOCs 13项 1, 2-二氯苯、1, 4-二氯苯、1, 2, 4-三氯苯、2, 4-二硝基甲苯、2, 6-二硝基甲苯、萘、蒽、荧蒽、苯并[b]荧蒽、苯并[a]芘、双(2-乙己基)邻苯二甲酸酯、2, 4, 6-三氯苯酚、五氯苯酚 气相色谱-质谱法 OCPs 12项 总六六六、α-六六六、β-六六六、γ-六六六、δ-六六六、总DDT、六氯苯、七氯、艾氏剂、环氧七氯、狄氏剂、异狄氏剂 气相色谱法 表 2 单指标污染标准指数评价分级
Table 2. Single factor standard index grade
污染指数 污染等级 污染类别 Pi≤0 Ⅰ 未污染 Pi>(0~0.2) Ⅱ 轻污染 Pi>(0.2~0.6) Ⅲ 中污染 Pi >(0.6~1.0) Ⅳ 较重污染 Pi>(1.0~1.5) Ⅴ 严重污染 Pi>1.5 Ⅵ 极重污染 表 3 健康风险评价模型相关参数取值
Table 3. Values of parameters related to health risk assessment
评价指标 参数 SF[(kg·d)/mg] RfD[mg/(kg·d)] PC
(cm/h)饮用水途径 皮肤入渗途径 饮用水途径 皮肤入渗途径 非致癌指标 NH4+ - - 0.97 0.97 0.001 NO3- - - 1.6 1.6 0.001 Al - - 0.14 0.14 0.01 Mn - - 0.046 0.0018 0.0001 Hg - - 0.0003 0.0003 0.0018 Fe - - 0.3 0.045 0.0001 异狄氏剂 - - 0.0003 0.0003 0.001 苯并[a]芘 7.3 37.47 - - 0.001 致癌指标 总六六六 1.8 1.8 - - 0.001 总DDT 0.34 0.34 - - 0.001 注:“-”表示无相应参考标准值。 表 4 狮子岩地下河无机离子及金属元素化学特征统计
Table 4. Statistics of chemical characteristics of inorganic ions and metals in Shiziyan underground river
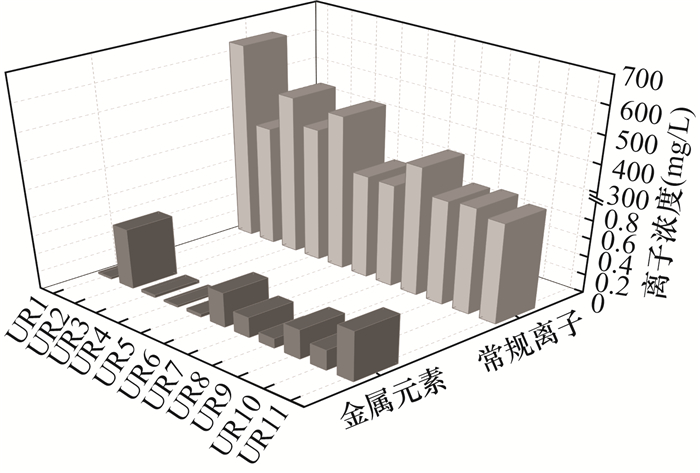
统计量 指标类型——无机离子 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ NH4+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- NO3- NO2- F- 最大值(mg/L) 47.75 18.80 119.47 16.66 0.85▲ 25.81 41.47 390.37 72.01 0.12 0.09 最小值(mg/L) 0.16 0.65 64.53 1.12 nd 2.96 7.38 203.86 nd nd nd 平均值(mg/L) 9.20 4.89 82.39 5.16 0.09 7.59 17.08 252.95 14.64 0.03 0.06 标准差(mg/L) 15.27 6.26 17.38 4.59 0.25 7.00 12.86 54.96 23.85 0.04 0.03 变异系数 1.66 1.28 0.21 0.89 2.84 0.92 0.75 0.22 1.63 1.26 0.47 超标率(%) 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 9.09 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 统计量 指标类型——金属元素 Al Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd Mn As Hg Fe 最大值(μg/L) 300▲ 2.37 0.94 8.77 4.46 nd 101▲ 1.72 0.75 360▲ 最小值(μg/L) nd nd nd nd 1.95 nd 0.98 nd nd nd 平均值(μg/L) 81.76 0.36 0.16 1.67 2.89 / 43.03 0.97 0.41 102.18 标准差(μg/L) 91.70 0.70 0.29 2.97 0.75 / 38.18 0.49 0.34 122.95 变异系数 1.12 1.95 1.73 1.78 0.26 / 0.89 0.51 0.81 1.20 超标率(%) 9.09 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 / 9.09 0.00 0.00 9.09 注:nd表示未检出;“/”表示无参考值及相应计算值;标注“▲”数值表示此浓度超标。 表 5 狮子岩地下河有机指标检出情况统计
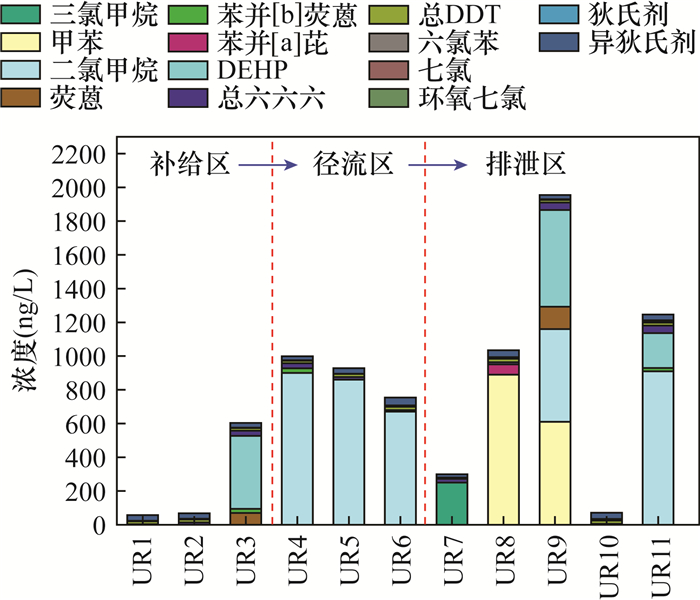
Table 5. Detection of organics in Shiziyan underground river
有机指标类型 总检出率
(%)单项检出指标统计 标准限值
(ng/L)检出项目 检出率(%) 最小值(ng/L) 最大值(ng/L) 平均值(ng/L) 三氯甲烷 9.09 250.00 250.00 250.00 60000a VOCs 18.75 甲苯 18.18 610.00 890.00 750.00 700000a 二氯甲烷 54.55 550.00 910.00 778.00 20000a SVOCs 30.77 荧蒽 18.18 69.60 133.00 101.30 240000a 苯并[b]荧蒽 27.27 19.30 27.50 23.73 4000a 苯并[a]芘 9.09 60.50▲ 60.50▲ 60.50▲ 10a DEHP 36.36 207.00 573.00 404.33 8000a 总六六六 100.00 2.85 44.30 20.89 5000a α-六六六 27.27 3.65 13.40 7.96 / β-六六六 90.91 1.81 15.80 4.87 / γ-六六六 72.73 1.42 8.87 4.07 2000a δ-六六六 90.91 2.17 31.20 11.32 / OCPs 91.67 总DDT 100.00 7.24 20.20 16.92 1000a 六氯苯 54.55 2.48 5.75 3.34 1000a 七氯 18.18 5.40 9.91 7.66 400a 环氧七氯 63.64 1.35 4.62 2.28 30b 狄氏剂 18.18 1.48 5.51 3.50 30b 异狄氏剂 100.00 19.80 46.40 32.02 2000b 注:标注“▲”数值表示此浓度超标;a表示《地下水质量标准》(GB/T 14848—2017)Ⅲ类质量标准;b表示WTO《饮用水水质准则》限值;“/”表示无参考值。 表 6 无机和有机污染物分别经饮用水途径和皮肤入渗途径产生的个人年健康风险值
Table 6. Per capita annual health risks caused by inorganic-organic pollutants though drinking and skin penetration pathway, respectively
致癌性 污染指标 个人年健康风险值(a-1) 饮用水途径 皮肤接触途径 合计 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 非致癌物 NH4+ 1.06×10-4 1.15×10-4 5.48×10-7 3.85×10-7 1.06×10-4 1.16×10-4 NO3- 7.53×10-3 8.21×10-3 3.90×10-5 2.74×10-5 7.57×10-3 8.24×10-3 Fe 2.80×10-4 3.06×10-4 9.68×10-7 6.80×10-7 2.81×10-4 3.07×10-4 Al 3.36×10-4 3.67×10-4 1.74×10-5 1.22×10-5 3.54×10-4 3.79×10-4 Mn 4.90×10-4 5.34×10-4 6.49×10-6 4.55×10-6 4.96×10-4 5.39×10-4 Hg 1.14×10-3 1.24×10-3 1.06×10-5 7.44×10-6 1.16×10-3 1.23×10-3 异狄氏剂 2.79×10-5 6.10×10-5 2.90×10-7 2.03×10-7 2.82×10-5 6.12×10-5 总健康风险 9.91×10-3 1.08×10-2 7.54×10-5 5.29×10-5 9.98×10-3 1.09×10-2 致癌物 苯并[a]芘 1.16×10-7 2.52×10-7 6.15×10-9 4.32×10-9 1.23×10-7 2.57×10-7 总六六六 9.85×10-9 2.15×10-8 1.02×10-10 7.16×10-11 9.959×10-9 2.16×10-8 总DDT 1.51×10-9 3.29×10-9 1.56×10-11 1.10×10-11 1.52×10-9 3.30×10-9 总健康风险 1.27×10-7 2.77×10-7 6.27×10-9 4.40×10-9 1.33×10-7 2.82×10-7 -
[1] Reberski J L, Terzí J, D. Maurice L, et al. Emerging organic contaminants in karst groundwater: A global level assessment[J/OL]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127242.
[2] 邹胜章, 卢海平, 周长松, 等. 岩溶区地下水环境质量调查评估技术方法与实践[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.
Zou S Z, Lu H P, Zhou C S, et al. Technical method and practice of groundwater environmental quality investigation and evaluation in karst area[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021.
[3] Zhou C S, Zou S Z, Zhu D N, et al. Pollution pattern of underground river in karst area of the southwest China[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 71-83.
[4] Li J, Yang G L, Zhu D N, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of karst groundwater for the environmental and health risk assessment: The case of the suburban area of Chongqing (southwest China)[J/OL]. Geochemistry, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2022.125866.
[5] 詹兆君, 陈峰, 杨平恒, 等. 西南典型岩溶地下河系统水文地球化学特征对比: 以重庆市青木关、老龙洞为例[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(9): 3365-3374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201609015.htm
Yan Z J, Chen F, Yang P H, et al. Comparison on the hydrogeochemical hharacteristics of hypical karst groundwater system in southwest China, a sase of Qingmuguan and Laolongdong in Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(9): 3365-3374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201609015.htm
[6] 叶凯, 孙玉川, 贾亚男, 等. 岩溶地下水水体中有机氯农药和多氯联苯的残留特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5448-5457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202012028.htm
Ye K, Sun Y C, Jia Y N, et al. Residual characteristics and health assessment analysis of OCPs and PCBs in karst groundwater[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5448-5457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202012028.htm
[7] 蓝家程, 孙玉川, 田萍, 等. 岩溶地下河流域水中多环芳烃污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(10): 3722-3730. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201410012.htm
Lan J C, Sun Y C, Tian P, et al. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and in karst underground river catchment[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(10): 3722-3730. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201410012.htm
[8] 朱琳跃, 蓝家程, 孙玉川, 等. 典型岩溶区土壤和地下水中多环芳烃的分布特征及健康风险研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(9): 3361-3374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202009030.htm
Zhu L Y, Lan J C, Sun Y C, et al. Distribution characteristics and health risks of PAHs in soils and groundwater in typical karst areas[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(9): 3361-3374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202009030.htm
[9] 盛婷, 杨平恒, 谢国文, 等. 基于δ15N和δ18O的农业区地下河硝酸盐污染来源[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 4547-4555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201810021.htm
Sheng T, Yang P H, Xie G W, et al. Nitrate-nitrogen pollution sources of an underground river in karst agricultural area using 15N and 18O isotope technique[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4547-4555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201810021.htm
[10] Xiang S Z, Wang X S, Ma W, et al. Response of microbial communities of karst river water to antibiotics and microbial source tracking for antibiotics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 706: 135730. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135730
[11] 张新钰, 辛宝东, 王晓红, 等. 我国地下水污染研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 2011, 39(3): 415-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201103022.htm
Zhang X Y, Xin B D, Wang X H, et al. Progress in research on groundwater pollution in our country[J]. Earth and Environment, 2011, 39(3): 415-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201103022.htm
[12] 张兆吉, 费宇红, 郭春艳, 等. 华北平原区域地下水污染评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(5): 1456-1461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201205019.htm
Zhang Z J, Fei Y H, Guo C Y, et al. Regional groundwater contamination assessment in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(5): 1456-1461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201205019.htm
[13] 李军, 赵一, 邹胜章, 等. 会仙岩溶湿地丰平枯时期地下水金属元素污染与健康风险[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1): 184-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202101021.htm
Li J, Zhao Y, Zou S Z, et al. Metal pollutions and human health risks on groundwater from wet, normal, and dry periods in Huixian karst wetland, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1): 184-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202101021.htm
[14] 李军, 邹胜章, 赵一, 等. 会仙岩溶湿地地下水主要离子特征及成因分析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 1750-1760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202104018.htm
Li J, Zou S Z, Zhao Y, et al. Major ionic characteristics and factors of karst groundwater at Huixian karst wetland, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4): 1750-1760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202104018.htm
[15] Huang L L, Rad S, Xu L, et al. Heavy metals distribution, sources, and ecological risk assessment in Huixian wetland, South China[J/OL]. Water, 2020, 12(2), doi: 10.3390/w12020431.
[16] Qin L T, Pang X R, Zeng H H, et al. Ecological and human health risk of sulfonamides in surface water and groundwater of Huixian karst wetland in Guilin, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134552.
[17] 朱丹尼, 邹胜章, 周长松, 等. 桂林会仙岩溶湿地水位动态特征及水文生态效应[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(4): 661-670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202104013.htm
Zhu D N, Zou S Z, Zhou C S, et al. Dynamic characteristics of water level and hydro-ecological effects in Huixian karst wetland in Guilin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 661-670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202104013.htm
[18] 吴伊琳. 河北省某市地下水有机污染特征及评价[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 2020.
Wu Y L. Characteristics and evaluation of groundwater organic pollution in a city of Hebei Province[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei GEO University, 2020.
[19] Li J, Miao X Y, Hao Y P, et al. Health risk assessment of metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, Hg, Se) in angling fish with different lengths collected from Liuzhou, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health, 2020, 17: 2192. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17072192
[20] Miao X Y, Hao Y P, Tang X, et al. Analysis and health risk assessment of toxic and essential elements of the wild fish caught by anglers in Liuzhou as a large industrial city of China[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 243: 125337. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125337
[21] 张春艳, 高柏, 郭亚丹, 等. 鄱阳湖区域地下水有机污染物特征与风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2016, 11(2): 524-530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201602063.htm
Zhang C Y, Gao B, Guo Y D, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of organic pollutants in groundwater of Poyang Lake[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2016, 11(2): 524-530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201602063.htm
[22] 张清华, 韦永著, 曹建华, 等. 柳江流域饮用水源地重金属污染与健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(4): 1598-1607. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201804019.htm
Zhang Q H, Wei Y Z, Cao J H, et al. Heavy metal pollution of the drinking water sources in the Liujiang River Basin, and related health risk assessments[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4): 1598-1607. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201804019.htm
[23] 周巾枚, 蒋忠诚, 徐光黎, 等. 铁矿周边地下水金属元素分布及健康风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(5): 1934-1944. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.017
Zhou J M, Jiang Z C, Xu G L, et al. Distribution and health risk assessment of metals in groundwater around iron mine[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(5): 1934-1944. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.017
[24] 罗庆, 孙丽娜, 张耀华. 细河流域地下水中持久性有机氯污染物的健康风险评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2011, 18(6): 119-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201106025.htm
Luo Q, Sun L N, Zhang Y H. Health risk assessment of persistent organochlorine pollutants in groundwater from Xihe River area[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 18(6): 119-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201106025.htm
[25] 赵庆令, 李清彩, 谢江坤, 等. 鲁中南地区双村岩溶水系统地下水中化学致癌物和非致癌物的健康风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1): 90-97. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.015
Zhao Q L, Li Q C, Xie J K, et al. Health risk assessment of carcinogenic and non-carcingenic substances in underground water from the Shuangcun karst system of central southern Shandong Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(1): 90-97. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.015
[26] 陈卫平, 彭程伟, 杨阳, 等. 北京市地下水有机氯和有机磷农药健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(1): 117-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201801015.htm
Chen W P, Peng C W, Yang Y, et al. Health risk evaluation of organochlorine and organophosphorous pesticides in groundwater in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(1): 117-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201801015.htm
[27] 李丽君, 王海娇, 马健生. 下辽河平原地下水中挥发性有机物的污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 930-943. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202108200105
Li L L, Wang H J, Ma J S. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in groundwater in the Lower Liaohe River Plain[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 930-943. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202108200105
[28] 段磊, 王文科, 孙亚乔, 等. 关中盆地浅层地下水氮污染的健康风险评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2011, 38(3): 92-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.03.017
Duan L, Wang W K, Sun Y Q, et al. Health risk assessment of "Three Nitrogen" in shallow groundwater in the Guanzhong Basin[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(3): 92-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.03.017
[29] 朱丹尼, 邹胜章, 周长松, 等. 不同城镇功能区岩溶地下水化学敏感因子识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4): 484-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201804002.htm
Zhu D N, Zou S Z, Zhou C S, et al. Identification of hydrochemical sensitive factors of karst groundwater in different functional urban areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4): 484-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201804002.htm
[30] Li J, Zhu D N, Zhang S, et al. Application of the hydro- chemistry, stable isotopes and MixSIAR model to identify nitrate sources and transformations in surface water and groundwater of an intensive agricultural karst wetland in Guilin, China[J/OL]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 231, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113205.
[31] 周巾枚, 蒋忠诚, 徐光黎, 等. 崇左响水地区地下水水质分析及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2675-2685. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201906022.htm
Zhou J M, Jiang Z C, Xu G L, et al. Waterquality analysis and health risk assessment for groundwater at Xiangshui, Chongzuo[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6): 2675-2685. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201906022.htm
[32] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等. 水文地质学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.
Zhang R Q, Liang X, Jin M G, et al. General hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011.
[33] 朱丹尼, 邹胜章, 李军, 等. 会仙岩溶湿地丰平枯水期地表水污染及灌溉适用性评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(5): 2240-2250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202105017.htm
Zhu D N, Zou S Z, Li J, et al. Pollution and irrigation applicability of surface water from wet, normal, and dry periods in the Huixian karst wetland, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(5): 2240-2250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202105017.htm
[34] 孔祥胜, 祁士华, Oramah I T, 等. 广西大石围天坑群地下河水中多环芳烃的污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(4): 1081-1087. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201104027.htm
Kong X S, Qi S H, Oramah I T, et al. Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water in underground river of Dashiwei Tiankeng Group in karst area, Guangxi[J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(4): 1081-1087. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201104027.htm
[35] 徐蓉桢, 刘菲, 荆继红, 等. 典型浅层孔隙水和岩溶水中多环芳烃分布特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(4): 411-418. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801120004
Xu R Z, Liu F, Jin J H, et al. Distribution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in typical shallow pore water and karst water[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(4): 411-418. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801120004
[36] 张坤锋, 昌盛, 赵少延, 等. 克鲁伦河流域地下水饮用水水源中挥发性有机物的污染特征与风险评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2021, 11(6): 1083-1091. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKWZ202106006.htm
Zhang K F, Chang S, Zhao S Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in groundwater drinking water sources in Klulun River Basin[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2021, 11(6): 1083-1091. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKWZ202106006.htm
[37] Pan H, Lei H, He X, et al. Spatial distribution of organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides in soil-groundwater systems and their associated risks in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2019, 41: 1833-1845. doi: 10.1007/s10653-017-9970-1
[38] Moreau M, Hadfield J, Hughey J, et al. A baseline assessment of emerging organic contaminants in New Zealand groundwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 686: 425-439. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.210
[39] Dong W H, Xie W, Su X S, et al. Review: Micro-organic contaminants in groundwater in China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26: 1351-1369. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1760-z
[40] 韦丽丽, 郭芳, 王健哲, 等. 柳州岩溶地下河水体有机氯农药分布特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.01.003
Wei L L, Guo F, Wang J Z, et al. Distribution characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in karst subterranean river in Liuzhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.01.003
[41] Kurwadkar S R, Kanel S, Nakarmi A. Groundwater pollution: Occurrence, detection, and remediation of organic and inorganic pollutants[J]. Water Environment Research, 2020, 92(10): 1659-1668. doi: 10.1002/wer.1415
[42] 李海明, 陈鸿汉, 郑西来, 等. 地下水中苯并[a]芘来源探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2006, 33(6): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.06.006
Li H M, Chen H H, Zheng X L, et al. A discussion of the source of B[a]P in groundwater[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2006, 33(6): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.06.006
-



 下载:
下载: