Effects of Phosphate on the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions onto TiO2 Nanoparticles in Water and Mechanism Analysis
-
摘要:
纳米二氧化钛(nTiO2)被广泛应用于去除水体中的重金属。磷酸盐作为水体中普遍存在的无机阴离子,能够对重金属离子在nTiO2上的吸附特征产生影响。本文聚焦磷酸盐存在条件下nTiO2胶体颗粒对典型重金属离子(Zn2+和Cd2+)的吸附行为,以电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)测定吸附平衡后水相中重金属离子的浓度。通过批量吸附实验考察不同水化学条件下(离子强度和共存阴离子),磷酸盐对nTiO2胶体颗粒吸附水体中Zn2+和Cd2+特征的影响规律。采用经典吸附等温线模型对实验数据进行拟合,并结合纳米颗粒的Zeta电位和粒径变化等表征手段揭示了相关吸附机制。研究发现:①磷酸盐的存在能有效地增强重金属在nTiO2上的吸附,Zn2+和Cd2+的最大吸附量分别由121.1mg/g和84.7mg/g增加至588.3mg/g和434.8mg/g,增加了3.8~4.1倍。这主要由于磷酸盐能够通过桥连作用形成金属-磷酸盐-nTiO2三元络合物以及增加重金属离子和胶体颗粒之间的静电引力,从而增强nTiO2对重金属离子的吸附。②背景溶液中离子强度的增加会降低nTiO2对重金属离子的吸附效果。当背景溶液中离子强度(NaCl浓度)从0增加至10mmol/L时,nTiO2与金属离子之间的静电吸引会减弱,同时Na+与重金属离子竞争nTiO2表面吸附位点亦降低了nTiO2对重金属离子的吸附。③共存竞争性阴离子(如Cl-、NO3-和SO42-)会削弱磷酸盐对nTiO2吸附金属离子的增强作用,抑制顺序为:SO42->NO3->Cl-,即与其离子半径的数量级成反比。这是由于共存阴离子与磷酸盐竞争nTiO2表面的吸附位点所致。研究结果表明,磷酸盐可以显著地增强nTiO2对重金属离子的去除效能,但是去除效能的大小会受到背景溶液中水化学条件的影响。
-
关键词:
- 纳米二氧化钛(nTiO2) /
- 重金属离子 /
- 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 /
- 磷酸盐 /
- 阴离子 /
- 吸附
Abstract:BACKGROUND Nano-titanium dioxide (nTiO2) is widely used to remove heavy metals from water. Phosphate, a common inorganic anion in the aquatic environment, can affect the adsorption characteristics of heavy metal ions on nTiO2. However, the current state of knowledge on the influences of phosphate on the adsorption behaviors of heavy metal ions onto TiO2 nanoparticles (nTiO2) is inadequate. Herein, batch adsorption experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of phosphate on the adsorption of heavy metal ions (i.e., Zn2+ and Cd2+) onto suspended nTiO2.
OBJECTIVES To elucidate the primary mechanisms controlling the adsorption behaviors of Zn2+ and Cd2+ on suspended nTiO2 in the presence of phosphate under different solution chemistry conditions.
METHODS In order to determine the effects of phosphate on the adsorption of heavy metal ions onto nTiO2, batch experiments were conducted by mixing background electrolyte ions, nTiO2, and phosphate, which contained various concentrations of Zn2+ or Cd2+ in 20mL-amber glass vials at room temperature. The pH of solution was adjusted to target 7.0 using 0.1mol/L HCl or 0.1mol/L NaOH accordingly. Then, the mixtures were rotated end-over-end for 24h. After equilibration, the liquid and solid phases were separated by centrifugation at 15000r/min for 20min, and then the supernatants were filtered through 0.22μm pore-size cellulose ester membrane filter (the loss of metal ions can be neglected). The concentrations of Zn2+ or Cd2+ in the filtrate were measured by an inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). The adsorbed metal ions were then determined by the difference between the initial and final concentrations of metal ions in the aqueous phase. Furthermore, the classic Langmuir and Freundlich sorption models were used to correlate the adsorption isotherms.
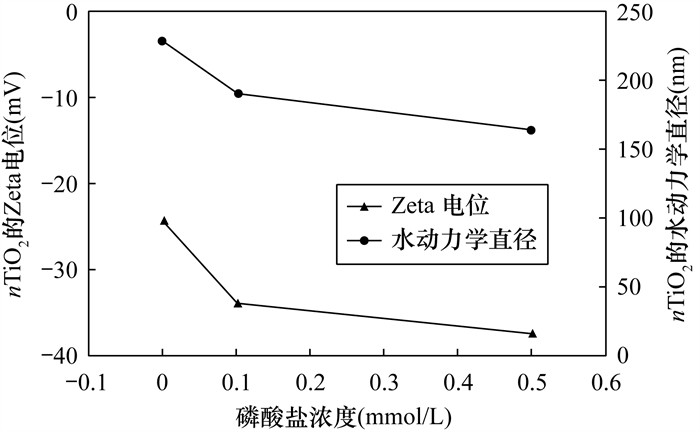
RESULTS (1) Adsorption isotherms showed that the presence of phosphate could enhance the adsorption of metal ions onto nTiO2, the maximum adsorption capacity of Zn2+ and Cd2+ increased from 121.1mg/g and 84.7mg/g to 588.3mg/g and 434.8mg/g, respectively. We propose that phosphate probably enhance the adsorption of Zn2+ and Cd2+ onto nTiO2 by the following mechanisms. Firstly, the ζ-potential of nTiO2 surface becomes more negative with the increase of phosphate concentration in aqueous phase. Consequently, the electrostatic attraction between negatively charged nanoparticles and positively charged metal ions generally increases with increasing phosphate content. Secondly, the phosphate added into nTiO2 suspension inhibits the aggregation of nanoparticles. In this case, more nTiO2 could sufficiently contact metal ions, thus increasing the adsorption sites. Thirdly, phosphate could form an inner-sphere surface complex on the nTiO2 surface, which can greatly influence the surface chemistry of nTiO2[55-57]. These products could strongly immobilize heavy metal ions[40-41]. These results might account for enhanced Zn2+ and Cd2+ adsorption on nTiO2 by forming metal-phosphate-surface ternary complexes in the presence of phosphate.
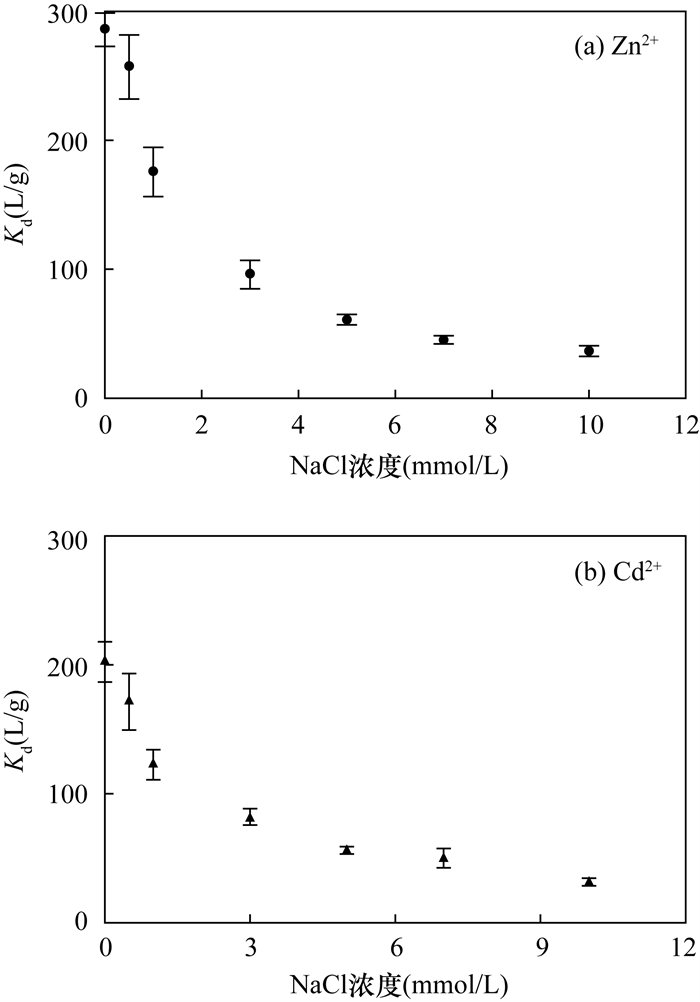
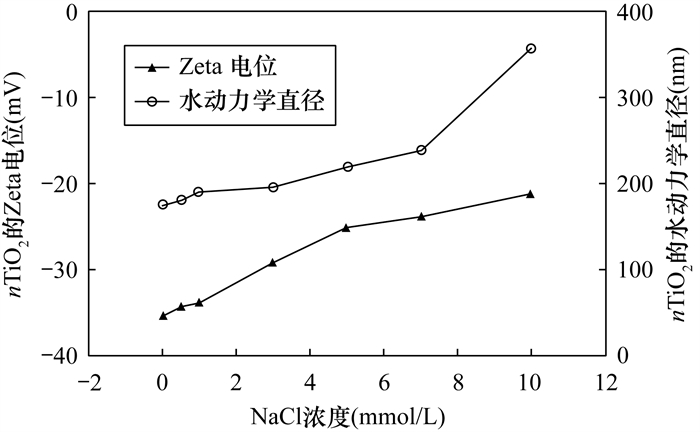
(2) The adsorption of heavy metals onto nTiO2 decreased when concentration of NaCl increased from 0 to 10 mmol/L. It is likely that ionic strength can affect the attachment of nanoparticles via three major mechanisms. Firstly, the presence of competing cations (Na+) of salt reduces the adsorption of metal ions (i.e., Zn2+ and Cd2+) and this effect may have more significant roles with increasing Na+ concentration. Secondly, this could be related to the fact that an increase in ionic strength interferes with the electrostatic attraction between nTiO2 and metal ions. Thus, adsorption of metal ions is suppressed. Thirdly, increasing ionic strength significantly enhances aggregation of nTiO2, and consequently decreases the active surface sites of nTiO2.
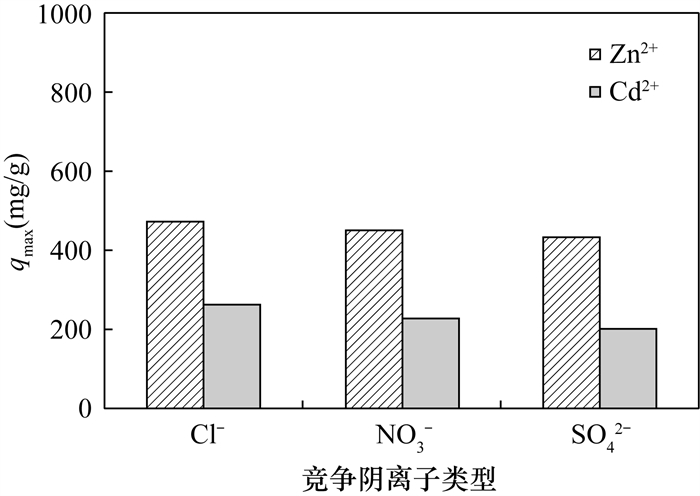
(3) The coexistence of competing anions (such as Cl-, NO3- and SO42-) weaken the enhancement effect of phosphate on the adsorption of metal ions onto nTiO2, and the order of inhibition is: SO42- >NO3->Cl-. This may be because anions with higher ionic radii (i.e., SO42-) may occupy more surface reactive sites. On the other hand, the competitive adsorption is related to the valence. It is well known that Cl- and NO3- are more likely to form "outer sphere" complexes with binding surfaces. Meanwhile, the electrostatic adsorption and the ion energy of monovalent anions (e.g., Cl- and NO3-) are weaker than those of divalent anions (e.g., SO42-). For this reason, the competitive influence of Cl- and NO3- during the adsorption of metal ions is negligible. In comparison, the divalent anion has a relatively stronger competitiveness on the adsorption of metal ions.
CONCLUSIONS The research results show that phosphate can significantly enhance the removal efficiency of nTiO2 to heavy metal ions, but the removal efficiency will be affected by the water chemical conditions in the background solution. Previous studies show that nTiO2 is promising as an adsorbent for the removal of metal ions from aqueous solution. The present study demonstrates that phosphate plays an important role in adsorption of metal ions (e.g., Zn2+ and Cd2+) onto nTiO2. Phosphate significantly enhances adsorption of Zn2+ and Cd2+ onto nTiO2 by forming metal-phosphate-surface ternary complexes and increasing electrostatic attraction. The increase of ionic strength results in the low adsorption of metal ions in the presence of phosphate, resulting from electronic shielding of the negatively charged sites on the nTiO2 surface and competition between Na+ and heavy metal ions for active surface sites. Moreover, the addition of competitive anions inhibits the adsorption of metal ions in the presence of phosphate following the order of SO42->NO3->Cl-. This phenomenon is mainly ascribed to the decrease of phosphate adsorption because of competition between anions and phosphate for adsorption sites on nTiO2 surface, resulting in decreasing the amount of metal-phosphate-surface ternary complexes. Overall, the results obtained from this study indicate that the adsorption of metal ions onto nTiO2 varies greatly with factors such as phosphate, ionic strength, and competitive anions. Therefore, these factors should be well considered to better understand the fate and toxicity of metal ions in the adsorption process for the treatment of wastewater.
-

-
表 1 nTiO2吸附Zn2+和Cd2+的Langmuir和Freundlich模型动力学参数
Table 1. Kinetic parameters for the Langmuir and Freundlich models of Zn2+ and Cd2+ adsorption onto nTiO2
实验序号 金属离子 背景电解质 磷酸盐浓度(mmol/L) Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 KL(L/mg) qmax(mg/g) R2 KF(mg1-nLn/g) n R2 1 Zn2+ 1mmol/L NaCl 0 1.07 121.1 0.993 53.3 0.447 0.975 2 Zn2+ 1mmol/L NaCl 0.1 0.375 476.2 0.998 110.3 0.742 0.980 3 Zn2+ 1mmol/L NaCl 0.5 0.894 588.3 0.981 211.8 0.636 0.972 4 Cd2+ 1mmol/L NaCl 0 2.745 84.7 0.971 37.3 0.596 0.981 5 Cd2+ 1mmol/L NaCl 0.1 0.884 263.2 0.980 61.6 0.673 0.984 6 Cd2+ 1mmol/L NaCl 0.5 0.535 434.8 0.993 85.1 0.777 0.983 -
[1] Li Y J, Yang Z M, Chen Y C, et al. Adsorption, recovery, and regeneration of Cd by magnetic phosphate nanoparticles[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(17): 17321-17332. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05081-6
[2] Singh P K, Wang W J, Shrivastava A K. Cadmium-mediated morphological, biochemical and physiological tuning in three different Anabaena species[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2018, 202: 36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.06.011
[3] Ding Q F, Huang X L, Hu H J, et al. Impact of pyrene and cadmium co-contamination on prokaryotic community in coastal sediment microcosms[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 188: 320-328. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.124
[4] Jacquet A, Barbeau D, Arnaud J, et al. Impact of maternal low-level cadmium exposure on glucose and lipid metabolism of the litter at different ages after weaning[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 219: 109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.137
[5] Jain C K, Singhal D C, Sharma M K. Adsorption of zinc on bed sediment of River Hindon: Adsorption models and kinetics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2004, 114: 231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.09.001
[6] Fu F, Wang Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 407-418. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
[7] 李璇, 张敏, 李秋叶, 等. 二氧化钛表面处理研究进展[J]. 化学研究, 2017, 28(5): 537-547. doi: 10.14002/j.hxya.2017.05.001
Li X, Zhang M, Li Q Y, et al. Research progress of surface treatment of titanium dioxide[J]. Chemical Research, 2017, 28(5): 537-547. doi: 10.14002/j.hxya.2017.05.001
[8] 申书昌, 冷茉含, 彭程, 等. 二氧化钛表面键合配位体固相萃取填料的制备及其吸附性能研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(1): 21-29. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706080096 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706080096
Shen S H, Leng M H, Peng C, et al. The preparation and performance of SPE packing of bonded ligand on the surface of nanometer titanium dioxide[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(1): 21-29. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706080096 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706080096
[9] Kumar R, Chawla J. Removal of cadmium ion from water/wastewater by nano-metal oxides: A review[J]. Water Quality Exposure and Health, 2014, 5: 215-226. doi: 10.1007/s12403-013-0100-8
[10] Yang Y, Zhang C Q, Hu Z. Impact of metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles on wastewater treatment and anaerobic digestion[J]. Environmental Science Processes Impacts, 2013, 15: 39-48. doi: 10.1039/C2EM30655G
[11] 吴莉莉, 曹洪印. 二氧化钛对Cu2+的吸附研究[J]. 化工时刊, 2022, 36(5): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJS202205006.htm
Wu L L, Cao H Y. Research of adsorption of Cu2+ by titanium dioxide[J]. Chemical Industry Times, 2022, 36 (5): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJS202205006.htm
[12] Guan X H, Du J S, Meng X G, et al. Application of titanium dioxide in arsenic removal from water: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 215-216: 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.069
[13] 王文凯, 阎莉, 段晋明, 等. 二氧化钛滤柱对高砷污酸废水的吸附去除[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(3): 1322-1328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201703003.htm
Wang W K, Yan L, Duan J M, et al. Arsenite adsorption removal from acid wastewater using titanium dioxide adsorption filter column[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(3): 1322-1328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201703003.htm
[14] 聂晓, 阎莉, 张建锋. 高指数晶面二氧化钛对砷、锑的共吸附去除[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(2): 318-326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201802016.htm
Nie X, Yan L, Zhang J F. Simultaneous removal of arsenic and antimony on high-index TiO2(HTiO2)[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(2): 318-326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201802016.htm
[15] Hu J X, Shipley H J. Regeneration of spent TiO2 nanoparticles for Pb(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ), and Zn(Ⅱ) removal[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2013, 20(8): 5125-5137. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1502-7
[16] Bozena G, Zakrzewska D, Szymczycha B. Sorption of Cr, Pb, Cu, Zn, Cd, Ni, and Co to nano-TiO2 in seawater[J]. Water Science & Technology, 2018, 77(1): 145-158.
[17] Wagle D, Shipley H J. Adsorption of arsenic(Ⅴ) to titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Effect of particle size, solid concentration, and other metals[J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 2016, 33: 299-305. doi: 10.1089/ees.2016.0014
[18] Wang D X, Wang P F, Wang C, et al. Effects of interactions between humic acid and heavy metal ions on the aggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles in water environment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 248: 834-844. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.084
[19] Vale G, Franco C, Brunnert A M, et al. Adsorption of cadmium on titanium dioxide nanoparticles in freshwater conditions-A chemodynamic study[J]. Electroanalysis, 2015, 27(10): 2439-2447. doi: 10.1002/elan.201500153
[20] Engates K E, Shipley H J. Adsorption of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, and Ni to titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Effect of particle size, solid concentration, and exhaustion[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2011, 18: 386-395. doi: 10.1007/s11356-010-0382-3
[21] Xie X F, Gao L. Effect of crystal structure on adsorption behaviors of nanosized TiO2 for heavy-metal cations[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2009, 9: S185-S188. doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2009.01.035
[22] Xu H C, Li L, Lyu H, et al. pH-dependent phosphatization of ZnO nanoparticles and its influence on subsequent lead sorption[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 208: 723-731. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.10.052
[23] Zhao D, Chen C C, Wang Y F, et al. Surface modification of TiO2 by phosphate: Effect on photocatalytic activity and mechanism implication[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(15): 5993-6001. doi: 10.1021/jp712049c
[24] Moharami S, Jalali M. Effect of TiO2, Al2O3, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles on phosphorus removal from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2014, 33: 1209-1219.
[25] Chen M, Xu N, Cao X D, et al. Facilitated transport of anatase titanium dioxides nanoparticles in the presence of phosphate in saturated sands[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 451: 134-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.04.010
[26] Li M X, Liu J Y, Xu Y F, et al. Phosphate adsorption on metal oxides and metal hydroxides: A comparative review[J]. Environmental Reviews, 2016, 24(3): 319-332. doi: 10.1139/er-2015-0080
[27] Fang J, Shan X Q, Wen B, et al. Stability of titania nanoparticles in soil suspensions and transport in saturated homogeneous soil columns[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(4): 1101-1109.
[28] Zhang X Z, Sun H W, Zhang Z Y, et al. Enhanced bioaccumulation of cadmium in carp in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 67: 160-166.
[29] Fang J, Zhang K K, Sun P D, et al. Co-transport of Pb2+ and TiO2 nanoparticles in repacked homogeneous soil columns under saturation condition: Effect of ionic strength and fulvic acid[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 571(15): 471-478.
[30] Wang K J, Xing B S. Mutual effects of cadmium and phosphate on their adsorption and desorption by goethite[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2004, 127: 13-20.
[31] Mahdavi S, Jalali M, Afkhami A. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4, ZnO, and CuO nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2012, 14(8): 846.
[32] Stietiya M H, Wang J J. Zinc and cadmium adsorption to aluminum oxide nanoparticles affected by naturally occurring ligands[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2014, 43(2): 498-506.
[33] Bosso S T, Enzweiler J. Evaluation of heavy metal removal from aqueous solution onto scolecite[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(19): 4795-4800.
[34] Bitonto L D, Volpe A, Pagano M, et al. Amorphous boron-doped sodium titanates hydrates: Efficient and reusable adsorbents for the removal of Pb2+ from water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 168-177.
[35] Moharami S, Jalali M. Effect of TiO2, Al2O3, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles on phosphorus removal from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2014, 33: 1209-1219.
[36] Kiriukhin M Y, Collins K D. Dynamic hydration numbers for biologically important ions[J]. Biophysical Chemistry, 2002, 99(2): 155-168.
[37] Tansel B. Significance of thermodynamic and physical characteristics on permeation of ions during membrane separation: Hydrated radius, hydration free energy and viscous effects[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2012, 86: 119-126.
[38] Goh K H, Lim T T. Influences of co-existing species on the sorption of toxic oxyanions from aqueous solution by nanocrystalline Mg/Al layered double hydroxide[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 180: 401-408.
-



 下载:
下载: