Residual Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Hexabromocyclododecane in Humans from 2010 to 2018 in Beijing
-
摘要:
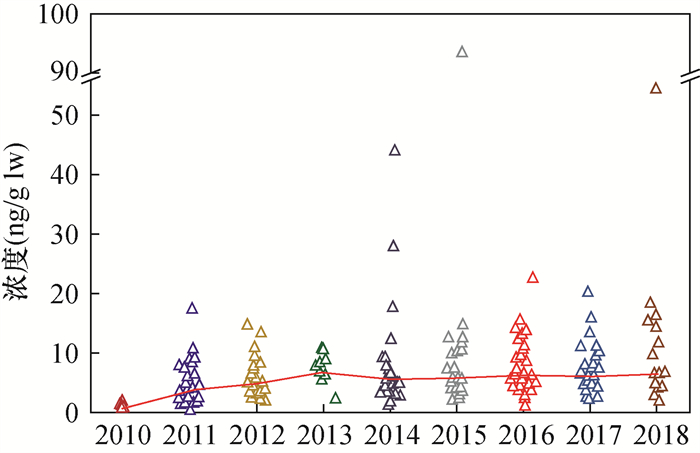
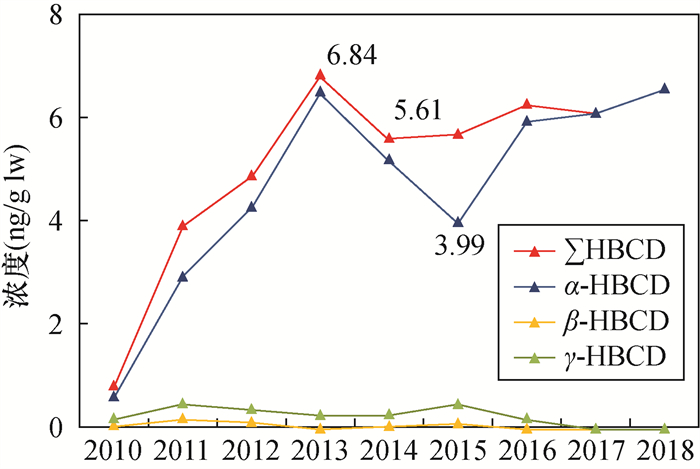
六溴环十二烷(HBCDs)作为一种持久性有机污染物,具有生物累积性及多种生物毒性,以母乳、血清、头发及脂肪组织为介质,评价人体HBCDs的残留特征和健康风险受到广泛关注。本文以北京地区为研究区域,连续采集和分析2010—2018年母乳样品中的HBCDs,探究北京人体中HBCDs的残留特征与变化趋势,同时评估婴幼儿通过母乳喂养摄入HBCDs是否存在健康风险。研究共招募85名志愿者采集233份母乳样品,采用液液萃取-多级净化法进行样品处理,高效液相色谱-串联质谱法(LC-MS/MS)测定样品中HBCDs及其异构体含量。样品的测定结果显示:① HBCDs的检出率为100%,浓度范围为0.46~93.5ng/g lw(脂重),均值和中值分别为7.27ng/g lw和5.77ng/g lw,高端暴露量第95百分位值为15.6ng/g lw;② α-HBCD为主要异构体,3种非对映异构体的含量占比大小为:α-HBCD>γ-HBCD>β-HBCD;③婴幼儿HBCDs的每日估计摄入量EDI中值为20.5ng/kg bw/day,第95百分位值为71.4ng/kg bw/day,高于日本、加纳及中国的其他城市。2010—2018年北京地区母乳中HBCDs浓度与北京地区以往的研究数据相比较接近,与国内外其他地区相比水平较高,且存在个体差异。HBCDs总量从2010—2013年持续上升,而后小幅度下降并趋于平缓,可能与中国及全球HBCDs的使用及禁用有关。健康风险评估结果显示,99%的母乳样品的非致癌风险危害系数(HQ)小于1,表明婴幼儿通过母乳喂养摄入HBCDs不会带来显著的健康风险,但1%母乳样品HQ值大于1,表明研究区域存在高风险暴露婴幼儿个体。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) have been identified as organic pollutants with the properties of persistence, long-distance migration, bioaccumulation, and biological toxicity. HBCDs have been detected in all kinds of biological and abiotic samples around the world, and have adverse effects on the environment and human body. As a non-invasive biological sample, human milk is a good medium for evaluating the exposure of HBCDs in the human body, and is widely used in the study of the exposure level of HBCDs in various countries, especially in nursing infants and young children. According to the survey, the production and use of HBCDs in Beijing has continued to rise since the use and production restriction of HBCDs in 2016, and the total use of HBCDs in 2019 increased by 60.8% compared with 2018. Therefore, in recent years in Beijing, especially before and after the use and production restriction of HBCDs, the residual characteristics and change trend of HBCDs in breast milk have attracted much attention.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the residual characteristics and trends of HBCDs in breast milk in Beijing from 2010 to 2018, evaluate the health risks for infants to intake HBCDs via breastfeeding, and provide basic data support for the scientific use, management, control, and human exposure risk assessment of HBCDs.
METHODS Breast milk samples (n=233) were obtained from 85 volunteer donors living in Beijing from 2010 to 2018. All volunteers have been living in Beijing for more than 5 years, are healthy, and do not directly engage in HBCDs production, processing, and other related occupations. Each sample was about 30mL, which was manually collected by volunteers into a 30mL clean glass bottle with a Teflon lined screw cap, and then transferred to a laboratory refrigerator for cryopreservation at -20℃. All volunteers were informed of the objective of this study. Pretreatment was conducted by liquid-liquid extraction and ammonia, ethanol, ether and n-hexane were added in turn. After liquid-liquid extraction, concentrated sulfuric acid sulfonation was combined with solid phase extraction (SPE) to purify the samples. Finally, 200μL methanol was added for constant volume. After centrifugation, the upper layer solution was transferred to a brown sample bottle (including lined tube) for storage. The qualitative and quantitative analysis of HBCDs was performed by Waters UPLC CLASS ultra-high performance liquid phase tandem API 4000 triple quadrupole mass spectrometry(LC-MS/MS). The isotope internal standard method was used for quantitative analysis to reduce the matrix effect.
RESULTS The detection rate of HBCDs in breast milk was 100%, indicating that HBCDs have been widespread in the human body. The concentration range of HBCDs was 0.46-93.5ng/g lw (lipid weight), with the average and median values of 7.27ng/g lw and 5.77ng/g lw, respectively. The 95th percentile of high-end exposure was 15.6ng/g lw. There were individual differences in the milk samples. The detection rates of α, β and γ-HBCD in all breast milk samples were 100%, 35.6% and 70.8%, respectively. α-HBCD had the most abundant diastereomers in breast milk samples, accounting for 80.1%, followed by γ-HBCD and β-HBCD in order. There were also a small number of breast milk samples that were dominated by γ-HBCD, accounting for 52.2%-83.5%. Even samples taken by the same volunteer in different months had different major diastereomers. The median EDI of HBCDs via human milk for infant was 20.5ng/kg bw/day, and the 95th percentile value was 71.4ng/kg bw/day, which was comparable to the previous research in Beijing, but higher than Japan, Ghana and other cities in China.
CONCLUSIONS Compared with the HBCDs in breast milk from other regions at home and abroad, the level of HBCDs in breast milk in this study is close to the previous research data in Beijing, but higher than that of Shanghai, Shenzhen and other cities in China, as well as higher than the results of recent studies in Japan, the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, India, the Philippines and some African countries, which may be related to the continuous use of HBCDs in China and the large amount of use. In human breast milk, α-HBCD is the main diastereomers, while in a small number of samples, γ-HBCD is the main diastereomers. The differences in the distribution characteristics of these diastereomers may be due to the differences in the absorption, metabolism and excretion mechanisms among individuals, and the transformation of HBCDs among different isomers in vivo, and the differences in the main external exposure pathways. The level of HBCDs showed an obvious upward trend from 2010 to 2013, reached the highest value of 6.84ng/g lw in 2013, and then decreased slightly and remained constant, which may be related to the production, use and prohibition of HBCDs globally and domestically. The time trend of α-HBCD and HBCDs is basically the same, while the content of β-HBCD and γ-HBCD in breast milk is low, and the change trend is stable with time. The concentration of HBCDs in breast milk changed slowly from 2014 to 2018 but did not show a significant downward trend after the initial ban of HBCDs in China in 2016, which may indicate that there are still a large number of HBCDs in production and use on the market, and human intake of HBCDs through air, dust, diet and other ways does not decrease. The risk assessment results indicate that the Hazard Quotient (HQ) of 99% breast milk samples is less than 1, which indicates that the intake of HBCDs through breast-feeding during lactation would not bring significant health risk to infants, but the HQ value of 1% breast milk samples is greater than 1, which suggests that breastfeeding may bring health risks to infants. More research is needed to further investigate the major sources of exposure and the effect of each potential factor.
-
Key words:
- hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) /
- breast milk /
- liquid-liquid extraction /
- HPLC-MS/MS /
- residue levels /
- time trend
-

-
表 1 志愿者与母乳样品数量信息
Table 1. Main information of the donors and samples
采样年份 志愿者人数 样品个数 志愿者平均年龄 2010 7 8 29 2011 14 32 31 2012 7 25 29 2013 3 13 29 2014 12 26 30 2015 7 28 31 2016 17 44 32 2017 9 42 32 2018 9 15 35 表 2 液相色谱梯度洗脱程序
Table 2. Gradient elution procedure of HPLC for separation
时间
(min)A相
(%)B相
(%)流速
(μL/min)0.00 60.0 40.0 500 11.0 92.0 8.0 500 14.0 100 0.0 500 16.0 60.0 40.0 500 20.0 60.0 40.0 500 表 3 质谱条件与参数
Table 3. Main parameters of mass spectrometer
质谱条件 参数 雾化温度(Temperature,TEM) 300℃ 离子喷射电压(Ion Spray Voltage,IS) -4500V 气帘气压力(Curtain Gas,CUR) 10psi 雾化气(Ion Source Gas1,GS1) 60psi 辅助气(Ion Source Gas2,GS2) 50psi 碰撞气压力(Collision Gas,CAD) 8psi 去簇电压(Declustering Potential,DP) -40V 入口电压(Entrance Potential,EP) -10V 碰撞能量(Collision Energy,CE) -40eV 碰撞出口电压(Collision Cell Exit Potential,CXP) -6V 表 4 北京市2010—2018母乳中HBCDs及其非对映异构体浓度
Table 4. Levels of HBCDs and diastereoisomers in breast milk in Beijing from 2010 to 2018
HBCDs异构体 检出率
(%)最小值
(ng/g lw)P5
(ng/g lw)平均值
(ng/g lw)中值
(ng/g lw)P95
(ng/g lw)最大值
(ng/g lw)占比
(%)α-HBCD 100 0.12 1.24 5.83 5.09 13.6 48.3 80.1 β-HBCD 35.6 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.00 1.35 13.4 3.60 γ-HBCD 70.8 0.00 0.00 1.18 0.24 3.22 73.1 16.3 HBCDs 100 0.46 1.84 7.27 5.77 15.6 93.5 - 注:浓度低于检出限取0值;P5、P95分别表示第5、第95百分位值。 表 5 婴幼儿对HBCDs每日估计摄入量
Table 5. Estimated daily intake (EDI) of HBCDs for infants
HBCDs
异构体最小值
(ng/kg bw/day)P5
(ng/kg bw/day)平均值
(ng/kg bw/day)中值
(ng/kg bw/day)P95
(ng/kg bw/day)最大值
(ng/kg bw/day)α-HBCD 0.35 4.28 23.5 17.6 55.6 236.3 β-HBCD 0.00 0.00 0.76 0.00 2.57 27.1 γ-HBCD 0.00 0.00 3.89 0.97 12.1 168.9 HBCDs 1.38 5.76 28.2 20.5 71.4 267.3 注:P5、P95分别表示第5、第95百分位值。 -
[1] Huang X M, Chen C, Shang Y, et al. In vitro study on the biotransformation and cytotoxicity of three hexabromo-cyclododecane diastereoisomers in liver cells[J]. Chemosphere: Environmental Toxicology and Risk Assessment, 2016, 161: 251-258.
[2] Zhao Y H, Li Q Q, Miao X, et al. Determination of hexabromocyclododecanes in sediments from the Haihe River in China by an optimized HPLC-MS-MS method[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 55: 174-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.07.013
[3] Tavoloni T, Stecconi T, Galarini R, et al. BFRs (PBDEs and HBCDs) in freshwater species from Lake Trasimeno (Italy): The singular case of HBCDs in red swamp crayfish[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 758: 143585. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143585
[4] 田亚静. 六溴环十二烷修正案对我国的影响及对策建议[J]. 生态经济, 2017, 33(12): 180-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STJJ201712037.htm
Tian Y J. The influence of hexabromocyclododecane amendment on China and its countermeasures[J]. Ecological Economy, 2017, 33(12): 180-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STJJ201712037.htm
[5] Shi X L, Zha J M, Wen B, et al. Diastereoisomer-specific neurotoxicity of hexabromocyclododecane in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 686: 893-902. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.008
[6] 刘芳, 冀秀玲, 唐蔚, 等. 发育期六溴环十二烷染毒对雌性大鼠脑组织中乙酰胆碱含量及其相关酶活力的影响[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2011(11): 947-949. doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2011.11.019
Liu F, Ji X L, Tang W, et al. Effects of hexabro-mocyclododecane on acetylcholinecontents and related enzymes activities of brain in female rats in growth and development period[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2011(11): 947-949. doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2011.11.019
[7] Darnerud P O. Toxic effects of brominated flame retardants in man and in wildlife[J]. Environment International, 2003, 29(6): 841-853. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00107-7
[8] 刘小燕, 刘珊, 张丽娟, 等. 六溴环十二烷对斑马鱼的甲状腺激素干扰效应研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(11): 2192-2198. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-0509
Liu X Y, Liu S, Zhang L J, et al. Thyroid hormone-disrupting effects of hexabromocyclododecane in Zebrafish(Danio rerio)[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(11): 2192-2198. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-0509
[9] 李鹏, 杨从巧, 金军, 等. 生产源区人血清中六溴环十二烷水平与甲状腺激素相关性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(10): 3970-3976. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.10.046
Li P, Yang C Q, Jin J, et al. Correlation between serum levels of hexabromocyclododecane and thyroid hormones in the production area[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(10): 3970-3976. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.10.046
[10] Ema M, Fujii S, Hirata-Koizumi M, et al. Two-genera-tion reproductive toxicity study of the flame retardant hexabromocyclododecane in rats[J]. Reproductive Toxicology, 2008, 25(3): 335-351. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.12.004
[11] 王馨蕾. 六溴环十二烷及其异构体分析方法与分布规律研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019.
Wang X L. The analytical methods establishment and distribution of hexabromocyclododecane and its diastereisomer[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2019.
[12] 王亚韡, 曾力希, 杨瑞强, 等. 新型有机污染物的环境行为[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.
Wang Y W, Zeng L X, Yang R Q, et al. Environmental behavior of emerging organic pollutants[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018.
[13] Huang M R, Li J, Xiao Z X, et al. Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane isomers in breast milk from the general population in Beijing, China: Contamination levels, temporal trends, nursing infant's daily intake, and risk assessment[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 244: 1-8.
[14] Shi Z X, Wu Y N, Li J G, et al. Dietary exposure assessment of chinese adults and nursing infants to tetrabromobisphenol-A and hexabromocyclododecanes: Occurrence measurements in foods and human milk[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(12): 4314-4319.
[15] Shi Z X, Zhang L, Zhao Y, et al. A national survey of tetrabromobisphenol-A, hexabromocyclododecane and decabrominated diphenyl ether in human milk from China: Occurrence and exposure assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599-600: 237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.237
[16] Shi Z X, Yang J, Yue H, et al. Levels of tetrabromobi-sphenol A, hexabromocyclododecanes and polybro-minated diphenyl ethers in human milk from the general population in Beijing, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 452-453: 10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.038
[17] 王力明, 王宝成, 李晓斌. 北京市持久性有机污染物统计调查与分析[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2021, 29(3): 1-3. doi: 10.19482/j.cn11-3237.2021.03.01
Wang L M, Wang B C, Li X B. Statistical investigation and analysis of persistent organic pollutants in Beijing[J]. Fine and Specialty Chemicals, 2021, 29(3): 1-3. doi: 10.19482/j.cn11-3237.2021.03.01
[18] 田芹, 佟玲, 宋淑玲, 等. 手性高效液相色谱-同位素稀释串联质谱法测定土壤及蚯蚓中的六溴环十二烷对映体[J]. 分析化学, 2015, 43(9): 1383-1388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201509025.htm
Tian Q, Tong L, Song S L, et al. Determination of hexabro-mocyclododecanes enantiomers in earthworm and soil by chiral high performance liquid chromatography-isotopic dilution-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(9): 1383-1388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201509025.htm
[19] 宋淑玲, 潘萌, 马晓东. 北京女性两个相邻哺乳期体内p, p'-DDE排泄速度与富集速度研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 954-961. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202108020091
Song S L, Pan M, Ma X D. Excretionrate and accumulating rate of p, p'-DDE in Beijing resident during consecutive lactation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 954-961. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202108020091
[20] 施致雄, 封锦芳, 李敬光, 等. 超高效液相色谱-电喷雾质谱法结合同位素稀释技术检测动物源性食品中的六溴环十二烷异构体[J]. 色谱, 2008, 26(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.01.001
Shi Z X, Feng J F, Li J G, et al. Analysis of hexabromocyclododecane diastereo isomers in foods of animal origin using ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and isotope dilution[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2008, 26(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.01.001
[21] Zhao X Z, Shi Z X. Legacy brominated flame retardants in human milk from the general population in Beijing, China: Biomonitoring, temporal trends from 2011 to 2018, and nursing infant's exposure assessment[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 285: 131533. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131533
[22] 丁问微, 田英, 金军, 等. 上海某医院产妇乳汁中六溴环十二烷水平及新生儿经母乳日摄入量的监测分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2011, 45(6): 498-501. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2011.06.006
Ding W W, Tian Y, Jin J, et al. Monitoring and analysis of the level of hexabromocyclododecane in maternal milk and the daily intake of newborn through breast milk in a hospital in Shanghai[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2011, 45(6): 498-501. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2011.06.006
[23] Lu S, Tan Z, Jiang Y, et al. Hexabromocyclododecanes in breast milk from residents in Shenzhen, China: Implications for infant exposure[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622-623: 1090-1097. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.277
[24] Eljarrat E, Guerra P, Martínez E, et al. Hexabromo-cyclododecane in human breast milk: Levels and enantiomeric patterns[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(6): 1940-1946.
[25] Kakimoto K, Akutsu K, Konishi Y, et al. Time trend of hexabromocyclododecane in the breast milk of Japanese women[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 71(6): 1110-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.035
[26] Fujii Y, Kato Y, Masuda N, et al. Contamination trends and factors affecting the transfer of hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers, tetrabromobisphenol A, and 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol to breast milk in Japan[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 936-943. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.015
[27] Abdallah A E, Harrad S. Tetrabromobisphenol-A, hexabromocyclododecane and its degradation products in UK human milk: Relationship to external exposure[J]. Environment International, 2011, 37(2): 443-448. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2010.11.008
[28] Harrad S, Abdallah A E. Concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol-A in breast milk from United Kingdom women do not decrease over twelve months of lactation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(23): 13899-13903.
[29] Tao F, Abdallah A E, Ashworth D C, et al. Emerging and legacy flame retardants in UK human milk and food suggest slow response to restrictions on use of PBDEs and HBCDD[J]. Environment International, 2017, 105: 95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.05.010
[30] Ryan J J, Rawn D F K. The brominated flame retardants, PBDEs and HBCD, in Canadian human milk samples collected from 1992 to 2005;concentrations and trends[J]. Environment International, 2014, 70: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.04.020
[31] Carignan C C, Abdallah A E, Wu N, et al. Predictors of tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBP-A) and hexabromo-cyclododecanes (HBCD) in milk from Boston mothers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(21): 12146-12153.
[32] Devanathan G, Subramanian A, Sudaryanto A, et al. Brominated flame retardants and polychlorinated biphenyls in human breast milk from several locations in India: Potential contaminant sources in a municipal dumping site[J]. Environment International, 2012, 39(1): 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.10.005
[33] Malarvannan G, Isobe T, Covaci A, et al. Accumulation of brominated flame retardants and polychlorinated biphenyls in human breast milk and scalp hair from the Philippines: Levels, distribution and profiles[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 442: 366-379. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.10.005
[34] Darnerud P O, Aune M, Larsson L, et al. Levels of brominated flame retardants and other pesistent organic pollutants in breast milk samples from Limpopo Province, South Africa[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(19): 4048-4053. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.054
[35] Asante K A, Adu-Kumi S, Nakahiro K, et al. Human exposure to PCBs, PBDEs and HBCDs in Ghana: Temporal variation, sources of exposure and estimation of daily intakes by infants[J]. Environment International, 2011, 37(5): 921-928. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.03.011
[36] Müller M H B, Polder A, Brynildsrud O B, et al. Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in breast milk and associated health risks to nursing infants in northern Tanzania[J]. Environment International, 2016, 89-90: 38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.12.032
[37] Ryan J J, Wainman B C, Schecter A, et al. Trends of the brominated flame retardants, PBDEs and HBCD, in human milks from North America[J]. Organohalogen Compounds, 2006, 68: 778-781.
[38] Du M M, Lin L, Yan C, et al. Diastereoisomer-and enantiomer-specific accumulation, depuration, and bioisomerization of hexabromocyclododecanes in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(20): 11040-11104.
[39] Roosens L, Abdallah M A, Harrad S, et al. Exposure to hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) via dust ingestion, but not diet, correlates with concentrations in human serum: Preliminary results[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2009, 117(11): 1707-1712. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0900869
[40] 程鑫. 六溴环十二烷异构体在鱼体内的污染分布特征及其选择性代谢规律研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2018.
Cheng X. Distribution characteristics and selective metabolism of hexabromocyclododecane isomers in fish[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2018.
[41] Kim U J, Oh J E. Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabro-mocyclododecane flame retardants in infant-mother paired serum samples, and their relationships with thyroid hormones and environmental factors[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 184: 193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.034
[42] Barghi M, Shin E S, Choi S D, et al. HBCD and TBBPA in human scalp hair: Evidence of internal exposure[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 207: 70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.032
[43] Johnson-Restrepo B, Adams D H, Kannan K. Tetrabromo-bisphenol A (TBBPA) and hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in tissues of humans, dolphins, and sharks from the United States[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 70(11): 1935-1944. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.002
[44] Isobe T, Oda H, Takayanagi N, et al. Hexabro-mocyclodo-decanes in human adipose tissue from Japan[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2009, 6(4): 328-333.
[45] 朱秀华, 李岩, 白皓, 等. 环境空气中六溴环十二烷研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(12): 2469-2481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201612003.htm
Zhu X H, Li Y, Bai H, et al. Research progress on hexabromocyclododecanes in environmental air[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(12): 2469-2481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201612003.htm
[46] Li L, Weber R, Liu J, et al. Long-term emissions of hexa-bromocyclododecane as a chemical of concern in products in China[J]. Environment International, 2016, 91: 291-300.
[47] 李玉芳, 潘萌, 顾涛, 等. 北京哺乳期女性及婴幼儿多环芳烃暴露风险变化特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(4): 578-586. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201912040167
Li Y F, Pan M, Gu T, et al. Exposure of mother and infants to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during lactation, Beijing[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(4): 578-586. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201912040167
[48] 张倩. 广州市居民食用水产品中PBDEs和HBCDs的富集特征和暴露风险评估[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2020.
Zhang Q. Enrichment characteristics and exposure risk assessment of PBDEs and HBCDs in edible aquatic products of Guangzhou residents[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2020.
-



 下载:
下载: