A Review of Current Status and Analysis Methods of Antibiotic Contamination in Groundwater in China (2012—2021)
-
摘要:
抗生素作为一种新污染物,在不同环境介质中均有检出。未被人类或动物完全吸收和代谢的抗生素会通过废水和废弃物以原型或代谢产物的形式进入环境,并在土壤中积累或淋滤进入地下水。抗生素进入环境可能影响微生物生态, 产生抗性基因,甚至威胁人体健康,而地下水作为重要的饮用水源,其抗生素污染问题不容忽视。本文从抗生素的危害、使用情况、污染来源、污染现状、定性定量检测方法的优缺点及适应范围和形态分析及环境效应等方面对近十年来(2012—2021)中国地下水中抗生素的研究现状进行总结。经调查,中国常用28种抗生素检出浓度在0.1~1000ng/L以上,检出频率较高的抗生素为诺氟沙星、氧氟沙星、磺胺甲恶唑、恩诺沙星、磺胺嘧啶、红霉素等。从空间分布来看,对地下水中抗生素的研究主要集中在华北、西南地区,而对西北地区中地下水抗生素研究程度较低。目前为止受到分析方法检出限及检出种类的限制,对地下水中抗生素的调查及评价还不够全面。通过综述抗生素定性定量分析方法,发现HPLC-MS/MS法因其具有灵敏度高、选择性好和定性定量准确的优点是目前应用最广泛的抗生素定量分析方法,而且可利用该方法对环境中抗生素类型进行初步识别,针对主要类型开展定量分析或长期监测,为抗生素环境效应研究提供数据支撑。而当抗生素以不同的带电形态、络合形态、吸附形态存在时,因其理化性质不同会影响测定的准确性、环境行为和毒理学效应,因而开展抗生素的形态分析对进一步准确测定抗生素和评估其环境效应具有重要意义。本文认为,优化定性定量检测方法、分析抗生素的不同形态、全面调查地下水中抗生素和科学评价抗生素形态与生态毒理学效应的关系,是今后地下水中抗生素污染研究的重点课题。
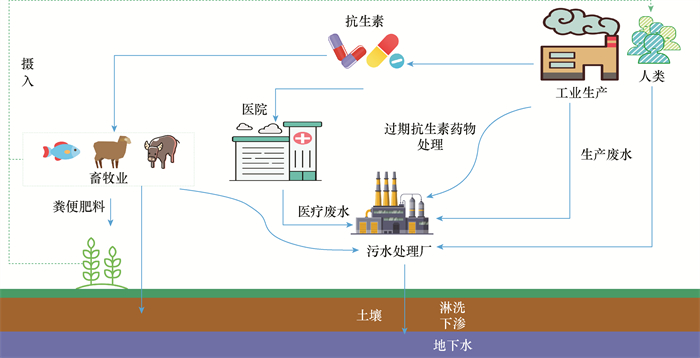
Abstract:As a form of new emerging pollutant, antibiotics have been detected in soil, surface water, groundwater, sediment and other different environmental media. As a major country in the production and usage of antibiotics, China's production and usage are increasing year by year. However, most antibiotics used for humans or animals cannot be fully absorbed and metabolized and will enter the environment in the form of prototypes or metabolites through waste and wastewater accumulating in soil and leaching into groundwater. Antibiotics entering the environment may affect microbial ecology, produce resistance genes, and even threaten human health. Compared with surface water, polluted groundwater is hidden, lagging and difficult to recover. The pollution of antibiotics in groundwater, as the main source of drinking water, has attracted much attention.
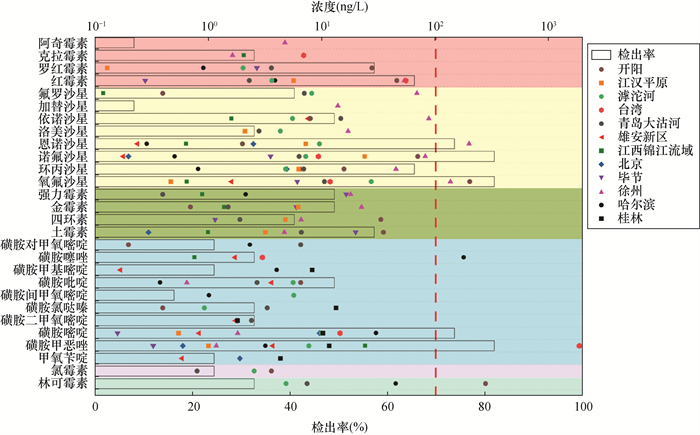
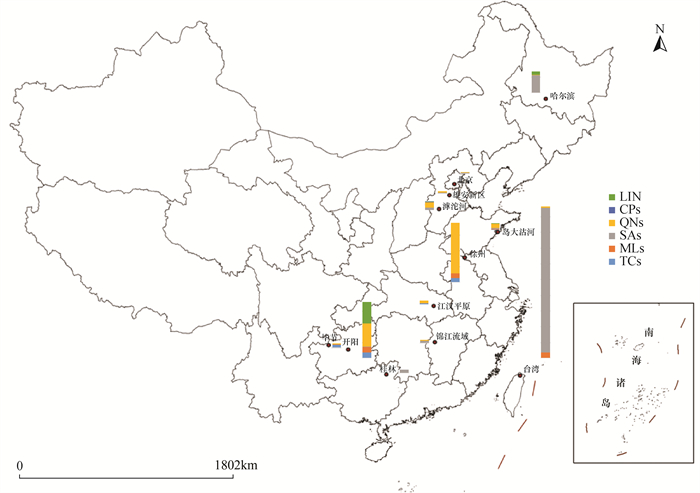
So far, the research on antibiotics in China is still mainly on surface water and soil, and there are few observations on antibiotics in groundwater. In order to systematically grasp the current pollution situation of antibiotics in groundwater in China, relevant literature on antibiotics in groundwater from 2012 to 2021 is reviewed in this paper. Twenty-eight antibiotics detected more than 100 times in environmental media in China were selected as target antibiotics, and the detected concentrations were summarized and analyzed. It was found that the concentrations of 28 antibiotics commonly detected in groundwater varied by more than 4 orders of magnitude, from 0.1ng/L to more than 1000ng/L. The most frequently detected antibiotics were norfloxacin, ofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, enrofloxacin, and erythromycin. Through comparative analysis of the detection of antibiotics in various places, it can be seen that the concentration of antibiotics in groundwater is controlled by the properties of antibiotics, the location of pollution sources, hydrogeological structure and the amount of usage and emissions. From the perspective of spatial distribution, sulfonamide antibiotics are the most detected in northeast China, quinolones are the most detected in North and East China, quinolones and tetracyclines are the most detected in southwest China, and the research on antibiotics in groundwater in northwest China is relatively low. So far, restrained by the detection limits and detection types of the analysis methods, a comprehensive investigation and evaluation of antibiotics in groundwater is not possible.
Due to the wide variety of antibiotics, their different structures lead to different physical andchemical properties. They exist in trace concentrations in the complex environment media, which also affects the accuracy of their qualitative and quantitative analysis. Therefore, the establishment of a sensitive and specific multi-component simultaneous analysis method has been a key issue for antibiotics research. The analysis methods of antibiotics are summarized, which are divided into qualitative analysis methods and quantitative analysis methods. The principle, advantages, disadvantages and application range of several antibiotic analytical methods are presented. These methods include microbial inhibition method (MIT), thin layer chromatography (TLC), gas chromatogram-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), high-performance liquid chromatogram-nuclear magnetic resonance (HPLC-NMR) and liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is the most commonly used method for antibiotic analysis because of its high sensitivity, low detection limit and simultaneous determination of multiple antibiotics. With the rapid development of antibiotic analysis methods, some antibiotics in groundwater can be accurately quantified by using HPLC-MS/MS and other technologies. However, the number of antibiotics that can be analyzed and identified at one time is still limited. The research group of authors has established the qualitative spectrum library of common drugs by UPLC-MS/MS. In the future, the types of antibiotics that can be qualitatively identified in the spectrum library can be expanded by adding the mass spectrum information of antibiotics. Under specific conditions, the spectrum library can be used to carry out semi-qualitative identification of antibiotics in groundwater. At present, the commonly used quantitative detection methods include enzyme-linked immunoassay, capillary electrophoresis, and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Compared with the other two methods, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry has the advantages of high sensitivity, good selectivity and accurate quantitative ability. It is commonly used for the detection of trace antibiotics in reported water samples.
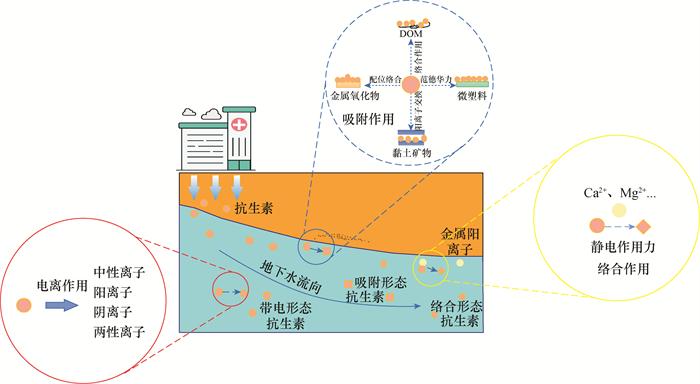
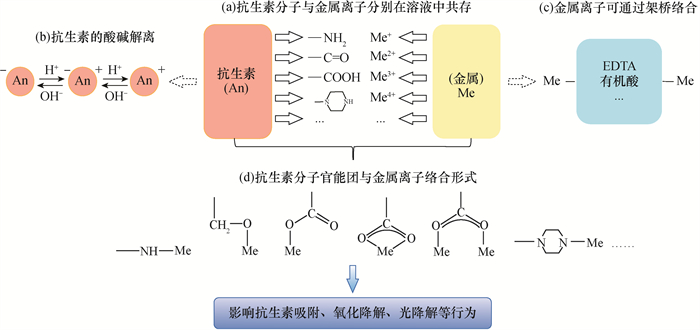
Antibiotics exist in the environment at trace levels and the matrix of environmental samples is complex, so the pretreatment process, including antibiotic separation, purification and concentration, often becomes the key step of determination. For example, the samples to be tested should be adjusted to an appropriate pH to enhance the enrichment of target antibiotics on HLB columns, and Na2EDTA should be added to inhibit its complexation with calcium and magnesium and other metal ions in groundwater. The accuracy of antibiotic determination will be improved, and the detection limit will be lowered for water samples by solid phase extraction and the subsequent concentration process. In addition to the detection limit and recovery rate of antibiotics affected by the analytical instrument, the presence states of antibiotics in water samples will also affect the accuracy and precision.
Antibiotics may exist in the ionized state, complex state, adsorption state and other forms in groundwater. At different pH values, antibiotics may exist in neutral, cationic, anionic, orzwitterionic forms. When it coexists with metal ions, complexation reaction will occur under certain conditions to form antibiotic-metal complex which will reduce the peak area to a certain extent or cause tailing phenomenon on the reverse analytical column. The formation of the complex may also change the environmental behavior (migration, transformation, toxicity, etc.) and ecological effects of antibiotics. In addition, the analysis of antibiotics in different adsorption states can be used to evaluate the differences in microbial killing effects of different adsorption forms, especially the differences in ARG production and spreading. This will be helpful for accurately evaluating the potential effects on the environment or human beings and effectively controlling the risks of antibiotics in environmental media. Therefore, the existing form analysis of antibiotics is of great significance for the further accurate determination of antibiotics and the evaluation of environmental effects.
Up to now, limited by the detection limits and detected types of antibiotics in analytical methods, there has not been a comprehensive national-scale investigation and evaluation of antibiotics in groundwater in China. Only by clarifying the concentration level and spatial distribution of antibiotic pollution in China's groundwater can it help to understand the contents of relevant laws and regulations on new emerging pollutants and support the establishment of a regulatory framework for natural resources and the environment. In conclusion, optimizing qualitative and quantitative detection methods, analyzing different existing forms of antibiotics, comprehensively investigating antibiotics in groundwater, and scientifically evaluating the relationship between antibiotic forms and ecotoxicological effects are the main contents of antibiotics research in groundwater in the future.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- antibiotics /
- pollution status /
- environmental behavior /
- speciation analysis /
- HPLC-MS/MS
-

-
表 1 抗生素定性方法
Table 1. Qualitative methods for antibiotics analysis
抗生素定性方法 方法原理 方法优缺点 方法适用范围 微生物抑制法
(Microbial Inhibition Technique,MIT)传统的测定方法,利用抗生素对微生物的生理机能、代谢的抑制作用,与阴性对照进行对比,判断是否存在抗生素[60] 操作简单,但灵敏度低,特异性差,且相似抗生素之间干扰性大[61] 动物性食品中抗生素残留[62] 薄层色谱法
(Thin Layer Chromatography,TLC)利用各成分对同一吸附剂吸附能力不同,从而达到各成分相互分离的目的 具有设备简单、操作简便等优点[63],但样品处理复杂,且灵敏度低[64] 可用于快速分离和定性少量分析物质 气相色谱-质谱联用
(Gas Cluomatography- Mass Spectrometry,GC-MS)利用样品在色谱柱中气相和固定相间分配系数的不同,经过反复多次分配从而实现分离[65] 具有稳定性好、重复性强、操作简单和扩容性强及普适性大等优点,但不适用于极性大、难挥发的有机污染物[59] 应用于农药和易挥发性有机污染物的定性检测 高效液相色谱-核磁共振联用
(HPLC-NMR)利用HPLC分离复杂化合物,NMR波谱确证未知化合物的结构[66] 该方法相较于质谱检测技术,灵敏度较低,且分析成本高 可用于分析化合物的组成、结构及其变化规律,被广泛应用于化学、医学等行业[67] 表 2 常见抗生素的酸解离常数及存在形式
Table 2. Acid dissociation constants and existing forms of common antibiotics
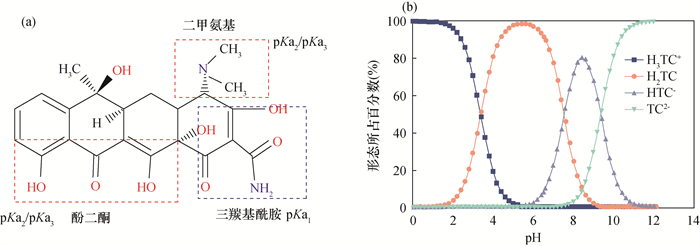
抗生素类别 抗生素名称 pKa pH范围 抗生素形式 参考文献 四环素类 四环素
(TC)pKa1=3.3 <3.30 H3TC+ [94] pKa2=7.7 3.30~7.70 HTC-/TC2- pKa3=9.7 >7.70 HTC-/TC2- 磺胺类 磺胺噻唑
(STZ)pKa1=2.0
pKa2=7.24<2.00 STZ+ [95] 2.00~7.24 STZ0 >7.24 STZ- 大环内酯类 罗红霉素
(ROX)pKa1=9.08
pKa2=12.45<9.08 ROX+ [96] 9.08~12.45 ROX0 >12.45 ROX- β-内酰胺类 头孢拉定
(CED)pKa1=2.63
pKa2=7.27<2.63 CED+ [97] 2.63~7.27 CED0 >7.27 CED- 喹诺酮类 环丙沙星
(CIP)pKa1=6.1
pKa2=8.7<6.10 CIP+ [98] 6.10~8.70 CIP0 >8.70 CIP- -
[1] Zhang Q Q, Ying G G, Pan C G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6772-6782.
[2] 苏建强, 黄福义, 朱永官. 环境抗生素抗性基因研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(4): 481-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDY201304011.htm
Su J Q, Huang F Y, Zhu Y G. Antibiotic resistance genes in the environment[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(4): 481-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDY201304011.htm
[3] Qiao M, Ying G G, Singer A C, et al. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment[J]. Environment International, 2018, 110: 160-172. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.10.016
[4] Wang J, Zhou A, Zhang Y, et al. Research on the adsorption and migration of sulfa antibiotics in underground environment[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(18): 1252. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6056-9
[5] Polianciuc S I, Gurzau A E, Kiss B, et al. Antibiotics in the environment: Causes and consequences[J]. Medicine and Pharmacy Reports, 2020, 93(3): 231-240.
[6] Zeng Y B, Chang F Q, Liu Q, et al. Recent advances and perspectives on the sources and detection of antibiotics in aquatic environments[J]. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry, 2022, doi. org/10.1155/2022/5091181.
[7] 毛娜, 孙志洪, 张丽. HPLC-MS/MS法测定养殖场土壤中6种常见抗生素微量残留[J]. 化学试剂, 2021, 43(7): 945-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSJ202107014.htm
Mao N, Sun Z H, Zhang L. Determination of 6 antibiotics residues in farm soil by HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2021, 43(7): 945-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSJ202107014.htm
[8] 史晓, 卜庆伟, 吴东奎, 等. 地表水中10种抗生素SPE-HPLC-MS/MS检测方法的建立[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1075-1083. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202004024.htm
Shi X, Bu Q W, Wu D K, et al. Simultaneous determination of 10 antibiotic residues in surface water by SPE-HPLC-MS/MS in surface water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1075-1083. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202004024.htm
[9] Xue Q, Qi Y J, Liu F. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of antibiotic residues in environmental waters[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(21): 16857-16867. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4900-1
[10] 剧泽佳, 付雨, 赵鑫宇, 等. 喹诺酮类抗生素在城市典型水环境中的分配系数及其主要环境影响因子[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(9): 4543-4555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202209014.htm
Ju Z J, Fu Y, Zhao X Y, et al. Distribution coefficient of QNs in urban typical water and its main environmental influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(9): 4543-4555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202209014.htm
[11] 张泽宇, 王鑫, 李丽君, 等. 薄膜梯度扩散(DGT)-UPLC-MS/MS法测量地下水中26种抗生素[J]. 地质与资源, 2022, 31(2): 235-242. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2022.02.015
Zhang Z Y, Wang X, Li L J, et al. Determination of 26 antibiotics in groundwater by diffusive gradients in thin films technique combined with UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Geology and Resources, 2022, 31(2): 235-242. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2022.02.015
[12] 于婉柔. 南水北调中线干渠抗生素污染分布特征及环境行为研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021.
Yu W R. Study on the occurrence and environmental behavior of antibiotics in the mid route of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021.
[13] Oberoi A S, Jia Y Y, Zhang H Q, et al. Insights into the fate and removal of antibiotics in engineered biological treatment systems: A critical review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(13): 7234-7264.
[14] 祁彦洁, 刘菲. 地下水中抗生素污染检测分析研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(1): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.002 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/219a9a71-edb5-4da4-bf01-ee19b6961b6b
Qi Y J, Liu F. Analysis of antibiotics in groundwater: A review[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(1): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.002 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/219a9a71-edb5-4da4-bf01-ee19b6961b6b
[15] 杜鹃. 黄渤海部分区域近岸海域中抗生素的分布、分配及释放动力学[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021.
Du J. Occurrence, distribution and desorption kinetics of antibiotics in regional coastal area of the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2021.
[16] 耿嘉璐. 抗性基因和药物的多介质环境分布特征与生态风险评价[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.
Geng J L. Multi-mediat distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of antibiotic resistance genes and pharmaceuticals[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020.
[17] Pruden A, Pei R T, Storteboom H, et al. Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: Studies in northern Colorado[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(23): 7445-7450.
[18] 李金梅, 梁威, 张洪勋, 等. 典型淡水环境中抗生素抗性基因的分布及其溯源[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(5): 2329-2336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ202105061.htm
Li J M, Liang W, Zhang H X, et al. Distribution and origin of antibiotic resistance genes in typical freshwater environments[J]. Chinese Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(5): 2329-2336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ202105061.htm
[19] 高盼盼, 罗义, 周启星, 等. 水产养殖环境中抗生素抗性基因(ARGs)的研究及进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2009, 4(6): 770-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL200906002.htm
Gao P P, Luo Y, Zhou Q X, et al. Research advancement of antibiotics resistance genes(ARGs) in aquaculture environment[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2009, 4(6): 770-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL200906002.htm
[20] 朱永官, 欧阳纬莹, 吴楠, 等. 抗生素耐药性的来源与控制对策[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2015, 30(4): 509-516. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2015.04.010
Zhu Y G, Ouyang W Y, Wu N, et al. Antibiotic resistance: Sources and mitigation[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015, 30(4): 509-516. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2015.04.010
[21] 张焕军, 王席席, 李轶. 水体中抗生素污染现状及其对氮转化过程的影响研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4): 1168-1181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202204007.htm
Zhang H J, Wang X X, Li Y. Progress in current pollution status of antibiotics and their influences on the nitrogen transformation in water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 1168-1181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202204007.htm
[22] 郭子宁, 王旭升, 向师正, 等. 再生水入渗区典型抗生素分布特征与地下水微生物群落影响因素研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(3): 451-462. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111040163 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111040163
Guo Z N, Wang X S, Xiang S Z, et al. Distribution characteristics of typical antibiotics in reclaimed water infiltration area and influencing factors of groundwater microbial community[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3): 451-462. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111040163 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111040163
[23] 王阳. 不同吸附态的左氧氟沙星对大肠杆菌的毒理学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Wang Y. The toxicological study of different adsorbed levofloxacin on escherichia coli[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
[24] 陈淋鹏, 黄福杨, 张冲, 等. 诺氟沙星对地下水中反硝化过程的影响: 反硝化酶活性的证据[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(7): 2496-2501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202007020.htm
Chen L P, Huang F Y, Zhang C, et al. Effect of norfloxacin on denitrification process in groundwater: Evidence for denitrifying enzyme activity[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(7): 2496-2501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202007020.htm
[25] 杨蕾. 地下水中抗生素类污染风险因子筛选及典型抗生素检测方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Yang L. Screening of risk factors for antibiotics contamination in groundwater and study on typical antibiotics detection methods[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
[26] Li S, Shi W Z, Liu W, et al. A duodecennial national synthesis of antibiotics in China's major rivers and seas (2005-2016)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 615: 906-917. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.328
[27] Ben Y J, Hu M, Zhang X Y, et al. Efficient detection and assessment of human exposure to trace antibiotic residues in drinking water[J]. Water Research, 2020, 175: 2022, 41(4): 1168-1181.
[28] Hanna N, Sun P, Sun Q, et al. Presence of antibiotic residues in various environmental compartments of Shandong Province in eastern China: Its potential for resistance development and ecological and human risk[J]. Environment International, 2018, 114: 131-142. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.02.003
[29] Huang Z, Pan X D, Huang B F, et al. Determination of 15 beta-lactam antibiotics in pork muscle by matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction (MSPD) and ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Control, 2016, 66: 145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.01.037
[30] Sommer F, Anderson J M, Bharti R, et al. The resilience of the intestinal microbiota influences health and disease[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2017, 15(10): 630-638. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.58
[31] Li J, Cao J, Zhu Y G, et al. Global survey of antibiotic resistance genes in air[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(19): 10975-10984.
[32] 2020年中国兽用抗菌药使用情况报告[N]. 中国畜牧兽医报, 2020.
Report on the use of veterinary antimicrobials in China in 2020[N]. Chinese Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2020.
[33] 胡敏. 南方某城市饮用水中抗生素残留分布及风险评价研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2019.
Hu M. Study on the distribution characteristics of antibiotic residues and risk assessment in drinking water in a southern city[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2019.
[34] 雷雨洋, 李方方, 欧阳洁, 等. 浙江地区抗生素残留的环境分布特征及来源分析[J]. 化学进展, 2021, 33(8): 1414-1425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXJZ202108013.htm
Lei Y Y, Li F F, Ouyang J, et al. Environmental distribution characteristics and source analysis of antibiotics in Zhejiang area[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2021, 33(8): 1414-1425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXJZ202108013.htm
[35] 童蕾, 姚林林, 刘慧, 等. 抗生素在地下水系统中的环境行为及生态效应研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2016, 11(2): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201602005.htm
Tong L, Yao L L, Liu H, et al. Review on the environmental behavior and ecological effect of antibiotics in groundwater system[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2016, 11(2): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201602005.htm
[36] Li X H, Liu C, Chen Y X, et al. Antibiotic residues in liquid manure from swine feedlot and their effects on nearby groundwater in regions of North China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(12): 11565-11575. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1339-1
[37] 姚学文. 抗生素在猪场粪污处理工艺与周边环境的分布及微生物降解特性[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2020.
Yao X W. Study on distribution of antibiotics in swine wastewater and manure treatment process and surrounding environment and its microbial degradation characteristics[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2020.
[38] Zhou L J, Ying G G, Liu S, et al. Excretion masses and environmental occurrence of antibiotics in typical swine and dairy cattle farms in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 444: 183-195. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.087
[39] 张腾云. 基于UPLC-MS-MS的海水中23种抗生素残留分析方法及其应用研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2019.
Zhang T Y. UPLC-MS-MS-based simultaneous determination of 23 antibiotics in seawater samples and its application[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2019.
[40] 余和春. 地表水回灌过程中典型磺胺类抗生素迁移特性及去除研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
Yu H C. Transport characteristics and removal of typical sulfonamide antibiotics during recharge of surface water[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018.
[41] Li Z, Li M, Liu X, et al. Identification of priority organic compounds in groundwater recharge of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 493: 481-486. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.005
[42] Carvalho I T, Santos L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environ-ments: A review of the European scenario[J]. Environment International, 2016, 94: 736-757. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.025
[43] 张智博. 长三角一体化示范区典型药物的环境归趋及氧化降解机理研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2022.
Zhang Z B. Study on environmental tropism and oxidative degradation mechanism of typical drugs in Yangtze River Delta Integrated Demonstration Zone[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2022.
[44] 高源. 我国典型流域抗生素分布与风险评估的文献计量学研究[D]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学, 2020.
Gao Y. Bibliometric study on antibiotics in typical river basins in China: Distribution and risk assessments[D]. Beijing: Capital University of Economics and Business, 2020.
[45] 韦正峥, 向月皎, 郭云, 等. 国内外新污染物环境管理政策分析与建议[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(2): 443-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX202202015.htm
Wei Z Z, Xiang Y J, Guo Y, et al. Analysis and suggestions of environmental management policies of new pollutants at home and abroad[J]. Research of Environmental Science, 2022, 35(2): 443-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX202202015.htm
[46] 卫承芳, 李佳乐, 孙占学, 等. 水-土壤环境中抗生素污染现状及吸附行为研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(3): 385-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL202203033.htm
Wei C F, Li J L, Sun Z X, et al. Research progress of antibiotic pollution and adsorption behavior in water-soil environment[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(3): 385-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL202203033.htm
[47] 黄福杨. 中国不同环境介质中典型抗生素识别及优先控制清单研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.
Huang F Y. Research on the identification of typical antibiotics and list of priority-controlled antibiotics in various environmental compartments in China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2021.
[48] 陈卫平, 彭程伟, 杨阳, 等. 北京市地下水中典型抗生素分布特征与潜在风险[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(12): 5074-5080. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201712022.htm
Chen W P, Peng C W, Yang Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk analysis of antibiotic in the groundwater in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(12): 5074-5080. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201712022.htm
[49] Fu C, Xu B, Chen H, et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in groundwater, surface water, and sediment in Xiong'an New Area, China, and their relationship with antibiotic resistance genes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 807: 151011. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151011
[50] Wang J L, Zhang C, Xiong L, et al. Changes of antibiotic occurrence and hydrochemistry in groundwater under the influence of the South-to-North Water Diversion (the Hutuo River, China)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 832: 154779. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154779
[51] 马健生, 王卓, 张泽宇, 等. 哈尔滨市地下水中29种抗生素分布特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 944-953. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101040001
Ma J S, Wang Z, Zhang Z Y, et al. Distribution character-istics of 29 antibiotics in groundwater in Harbin[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 944-953. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101040001
[52] 李佳乐, 王萌, 胡发旺, 等. 江西锦江流域抗生素污染特征与生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(8): 4064-4073. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202208017.htm
Li J L, Wang M, Hu F W, et al. Antibiotic pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment in Jinjiang River Basin, Jiangxi Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(8): 4064-4073. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202208017.htm
[53] Gu D M, Feng Q Y, Guo C S, et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in manure, soil, wastewater, groundwater from livestock and poultry farms in Xuzhou, China[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2019, 103(4): 590-596.
[54] Yao L, Wang Y, Tong L, et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers: A case study at Jianghan Plain, central China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 135: 236-242.
[55] Qin L T, Pang X R, Zeng H H, et al. Ecological and human health risk of sulfonamides in surface water and groundwater of Huixian karst wetland in Guilin, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 708: 134552.
[56] 戴刚, 徐浩, 杨琼, 等. 毕节垃圾场周边水源中抗生素污染特征[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(S2): 263-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS2015S2052.htm
Dai G, Xu H, Yang Q, et al. Pollution characteristics of antibiotics in water source of the surrounding of health garbage's landfill, Bijie[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(S2): 263-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS2015S2052.htm
[57] Zou S, Huang F, Chen L, et al. The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the karst river system in Kaiyang, southwest China[J]. Water Science and Technology-Water Supply, 2018, 18(6): 2044-2052.
[58] Lin Y C, Lai W W P, Tung H H, et al. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals, hormones, and perfluorinated compounds in groundwater in Taiwan[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(5): 256.
[59] 郎杭. 地下水中典型药物定性识别及抗生素定量的方法研究与应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
Lang H. The research and application of typical pharmaceutical identification and antibiotics detection in groundwater[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020.
[60] 南琼, 唐景春, 胡羽成, 等. 不同环境介质中抗生素检测方法研究进展[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2017, 29(11): 1609-1621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYJ201711001.htm
Nan Q, Tang J C, Hu Y C, et al. Advances in detection of antibiotics in different environmental matrix[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2017, 29(11): 1609-1621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYJ201711001.htm
[61] 陈宏霞. 基于MOF荧光探针对四环素类抗生素特异识别[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学(北京), 2021.
Chen H X. Fluorescence detector based on MOF conditions for specific recognition of tetracycline antibiotics[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University (Beijing), 2021.
[62] 王珂. 两种微生物抑制法检测抗生素残留优化与改良的研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2020.
Wang K. Research on optimization and improvement of two kinds of microbial inhibition methods to detect antibiotic residues[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2020.
[63] 吕长淮. 薄层色谱法在药物分析中的应用进展[J]. 中国药房, 2006(22): 1748-1749. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYA200622029.htm
Lyu C H. Application progress of thin-layer chroma-tography in drug analysis[J]. Chinese Pharmacy, 2006(22): 1748-1749. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYA200622029.htm
[64] 王婷. 基于化学计量学法的禽肉中典型抗生素残留的SERS快速鉴别研究[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2021.
Wang T. Study on SERS rapid identification of typical antibiotic residues in poultry meat based on stoichiometry[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2021.
[65] 刘明仁. 气相色谱-质谱联用技术在环境有机污染物检测中的应用[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2010.
Liu M R. Application of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in the determination of environmental organic pollutants[D]. Jinan: Jinan University, 2010.
[66] 潘瑞花, 陈建华, 张剑锋. HPLC-NMR在化学品检测中的应用前景[J]. 化学分析计量, 2007(6): 71-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXFJ200706030.htm
Pan R H, Chen J H, Zhang J F. Application prospect of HPLC-NMR in chemical detections[J]. Chemical Analysis and Metrology, 2007(6): 71-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXFJ200706030.htm
[67] 孙余娟. 核磁共振技术检测乳制品中兽药残留的研究[D]. 天津: 天津理工大学, 2021.
Sun Y J. Detection of veterinary drug residues in dairy products by nuclear magnetic resonance[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Technology, 2021.
[68] 任娇阳. 北京市潮白河流域抗生素污染分布与风险评估[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021.
Ren J Y. Distribution and risk assessment of antibiotic contamination in Chaobai River Basin, Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021.
[69] Ahmed S, Ning J, Peng D, et al. Current advances in immunoassays for the detection of antibiotics residues: A review[J]. Food and Agricultural Immunology, 2020, 31(1): 268-290.
[70] 耿建暖. 酶联免疫法及其在食品中的应用研究进展[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2021(19): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJX202119008.htm
Geng J N. Research progress of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and its application in food processing[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2021(19): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJX202119008.htm
[71] 范素素, 方烨渟, 蔡萌, 等. 水环境中磺胺类抗生素固相萃取-液质联用检测方法的建立及效果评估[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(8): 2764-2774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ202208031.htm
Fan S S, Fang Y T, Cai M, et al. Establishment of solid phase extraction-liquid mass spectrometry method for detection of sulfa antibiotics in water environment and its effect evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2022, 16(8): 2764-2774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ202208031.htm
[72] 马建国. 水中抗生素高通量免疫检测技术研究及应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019.
Ma J G. Research and application of high-throughput immunoassay technology for antibiotics in water[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2019.
[73] 王莉. 毛细管电泳对环境水体中典型抗生素的高灵敏度分析方法研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2018.
Wang L. Study of high sensitivity analysis method of typical antibiotics in waters by capillary electrophoresis[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2018.
[74] 袁越. 钙镁离子对四环素在水-腐殖酸间分配的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
Yuan Y. Effects of calcium and magnesium ions on the partition of tetracycline between water and humic acid[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020.
[75] Beccaria M, Cabooter D. Simultaneous determination of antibiotics in seawater samples using solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Analyst, 2020, 145(4): 1129-1157.
[76] 孙晓杰, 李兆新, 董晓, 等. 固相萃取-液相色谱-串联质谱法同时检测海水中抗生素多残留[J]. 分析科学学报, 2016, 32(5): 639-643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKX201605009.htm
Sun X J, Li Z X, Dong X, et al. Determination of antibiotic residues in seawater by solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Sciences, 2016, 32(5): 639-643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKX201605009.htm
[77] 陈永艳, 吕佳, 邢方潇, 等. 饮用水检测中抗生素类标准物质稳定性研究[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2019, 44(6): 758-763. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKSS201906020.htm
Chen Y Y, Lyu J, Xing F X, et al. Study on the stability of antibiotic standard substances in drinking water[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2019, 44(6): 758-763. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKSS201906020.htm
[78] 营娇龙, 秦晓鹏, 郎杭, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定水体中37种典型抗生素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(3): 394-403. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111060168
Ying J L, Qin X P, Lang H, et al. Determination of 37 typical antibiotics by liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3): 394-403. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111060168
[79] 杨聪, 童蕾, 马乃进, 等. 洪湖水体和沉积物中抗生素的分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(5): 78-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ202205011.htm
Yang C, Tong L, Ma N J, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of antibiotics in water and sediments of Honghu Lake[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(5): 78-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ202205011.htm
[80] 赵军杰, 程林丽, 陈亚南, 等. 动物源食品中抗生素残留检测方法进展[J]. 饲料工业, 2022, 43(20): 53-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FEED202220009.htm
Zhao J J, Cheng L L, Chen Y N, et al. Research status of antibiotic residues detection in animal-derived foods[J]. Feed Industry, 2022, 43(20): 53-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FEED202220009.htm
[81] 邓冬冬. 地下水中五种农药液相色谱串联三重四极杆质谱方法的建立与应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
Deng D D. Establishment and application of LC-MS/MS method for five pesticides in groundwater[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019.
[82] 张涛. 三重四极杆质谱仪开发平台的设计、实现与应用[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2020.
Zhang T. Design, implementation and application of development platform for triple quadrupole mass spectrometer[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020.
[83] Junza A, Amatya R, Barron D, et al. Comparative study of the LC-MS/MS and UPLC-MS/MS for the multi-residue analysis of quinolones, penicillins and cephalosporins in cow milk, and validation according to the regulation 2002/657/EC[J]. Journal of Chromatography B-Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 2011, 879(25): 2601-2610.
[84] 宋焕杰, 谢卫民, 王俊, 等. SPE-UPLC-MS/MS同时测定水环境中4大类15种抗生素[J]. 分析试验室, 2022, 41(1): 50-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY202201010.htm
Song H J, Xie W M, Wang J, et al. Simultaneous determination of 15 antibiotics in 4 categories in water environment by SPE-UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Laboratory, 2022, 41(1): 50-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY202201010.htm
[85] 祁彦洁. 水中抗生素的检测方法与非生物衰减行为研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Qi Y J. Determination and abiotic attenuation of antibiotics in water[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
[86] Holton E, Kasprzyk-Hordern B. Multiresidue antibiotic-metabolite quantification method using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry for environmental and public exposure estimation[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2021, 413(23): 5901-5920.
[87] Seifrtova M, Novakova L, Lino C, et al. An overview of analytical methodologies for the determination of antibiotics in environmental waters[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2009, 649(2): 158-179.
[88] Gros M, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Barcelo D. Rapid analysis of multiclass antibiotic residues and some of their metabolites in hospital, urban wastewater and river water by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1292: 173-188.
[89] Boy-Roura M, Mas-Pla J, Petrovic M, et al. Towards the understanding of antibiotic occurrence and transport in groundwater: Findings from the Baix Fluvia alluvial aquifer (NE Catalonia, Spain)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 612: 1387-1406.
[90] 秦晓鹏, 刘菲, 王广才, 等. 抗生素在土壤/沉积物中吸附行为的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015, 42(3): 142-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201503026.htm
Qin X P, Liu F, Wang G C, et al. Adsorption of antibiotics in soils/sediments: A review[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(3): 142-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201503026.htm
[91] 仲小飞, 秦晓鹏, 杜平, 等. 高效液相色谱法同时测定水体中氧氟沙星及其手性异构体[J]. 色谱, 2018, 36(11): 1167-1172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPZZ201811012.htm
Zhong X F, Qin X P, Du P, et al. Simultaneous determination of ofloxacin enantiomers in water by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2018, 36(11): 1167-1172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPZZ201811012.htm
[92] 陈小燕, 牛玉玲, 朱敏, 等. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱法测定牛奶中四环素类抗生素[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2017, 42(2): 129-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKSS201702009.htm
Chen X Y, Niu Y L, Zhu M, et al. Determination of tetra-cycline antibiotics in milk by solid phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2017, 42(2): 129-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKSS201702009.htm
[93] 付浩. 水中典型喹诺酮类抗生素的活性炭吸附特性研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2017.
Fu H. Activated carbon adsorption of quinolone antibiotics in water[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2017.
[94] Chang P H, Li Z, Yu T L, et al. Sorptive removal of tetracycline from water by palygorskite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1-3): 148-155.
[95] Pei Z, Yang S, Li L, et al. Effects of copper and alumi-num on the adsorption of sulfathiazole and tylosin on peat and soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 184: 579-585.
[96] 张洪丹. 水环境中不同粒径的典型黏土矿物吸附罗红霉素的特征分析[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2016.
Zhang H D. Analysis of characteristics on the adsorption relationship between different size typical clay minerals and roxithromycin in the water[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2016.
[97] 侯卓. 头孢类抗生素的固相萃取-高效毛细管电泳方法建立与研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018.
Hou Z. Establishment and research of solid-phase extraction-capillary electrophoresis method for cephalo-sporins[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018.
[98] Wu Q, Li Z, Hong H, et al. Adsorption and intercalation of ciprofloxacin on montmorillonite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2010, 50(2): 204-211.
[99] 欧阳卓智. 复合污染下金属离子对抗生素氧化及光降解的影响机制[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020.
Ouyang Z Z. The mechanism of metal ions affecting the oxidation and photolysis of antibiotics under combined pollution[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020.
[100] Zhang Y, Boyd S A, Teppen B J, et al. Role of tetracycline speciation in the bioavailability to escherichia coli for uptake and expression of antibiotic resistance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(9): 4893-4900.
[101] 王娅南, 彭洁, 谢双, 等. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定地表水中40种抗生素[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(1): 188-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202001021.htm
Wang Y N, Peng J, Xie S, et al. Determination of 40 antibiotics in surface water by solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(1): 188-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202001021.htm
[102] 徐舟影, 孟发科, 吕意超, 等. 抗生素与重金属复合污染废水处理的研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(11): 2686-2695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX202111017.htm
Xu Z Y, Meng F K, Lyu Y C, et al. Research progress in treatment of antibiotics and heavy metals compound polluted wastewater[J]. Research of Environmental Science, 2021, 34(11): 2686-2695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX202111017.htm
[103] 黄翔峰, 熊永娇, 彭开铭, 等. 金属离子络合对抗生素去除特性的影响研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(1): 133-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201601017.htm
Huang X F, Xiong Y J, Peng K M, et al. The progress of antibiotics removal performance under the complexion effect of metal ions[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(1): 133-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201601017.htm
[104] Zhang Y, Cai X, Lang X, et al. Insights into aquatic toxicities of the antibiotics oxytetracycline and ciprofloxacin in the presence of metal: Complexation versus mixture[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 166: 48-56.
[105] 张雨. 抗生素-金属复合物水生毒理及选择性吸附去除[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2013.
Zhang Y. Aquatic toxicity and selective adsorption removal of antibiotic and metal complex[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2013.
[106] Pulicharla R, Hegde K, Brar S K, et al. Tetracyclines metal complexation: Significance and fate of mutual existence in the environment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 221: 1-14.
[107] 汤贝贝. 铜-四环素络合对植物根系吸附和转移四环素的影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2018.
Tang B B. The adsorption and transport of tetracycline by roots of macrophyte under the influence of copper complexation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[108] 马江雄, 周欣, 赵超, 等. 水体中痕量四环素类抗生素分析方法研究进展[J]. 化学通报, 2022, 85(11): 1336-1345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXTB202211008.htm
Ma J X, Zhou X, Zhao C, et al. Advances in analytical methods for trace tetracycline antibiotics in water[J]. Chemistry, 2022, 85(11): 1336-1345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXTB202211008.htm
[109] 周志洪, 黄卓尔, 吴清柱, 等. 在线固相萃取-液相色谱-串联质谱法测定环境水体中抗生素[J]. 分析试验室, 2016, 35(9): 1092-1098. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201609024.htm
Zhou Z H, Huang Z E, Wu Q Z, et al. Determination of antibiotics in surface water with liquid qhromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after online solid phase extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Laboratory, 2016, 35(9): 1092-1098. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201609024.htm
[110] 李硕. 微塑料-抗生素在地下水中的迁移行为及降解机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.
Li S. Migration behavior and degradation mechanism of microplasties-antibiotics in groundwater[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021.
[111] 王婷. 针铁矿和赤铁矿对氧四环素的吸附研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
Wang T. Study on adsorption of oxytetracycline onto goethite and hematite[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020.
[112] 秦晓鹏. 左氧氟沙星在针铁矿上的吸附: 磷酸盐和腐殖酸的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Qin X P. Adsorption of levofloxacin to goethite: Effects of phosphate and humic acid[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
[113] Xu H Z, Qu X L, Li H, et al. Sorption of tetracycline to varying-sized montmorillonite fractions[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2014, 43(6): 2079-2085.
[114] Wang C J, Li Z, Jiang W T, et al. Cation exchange interaction between antibiotic ciprofloxacin and montmorillonite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 183(1-3): 309-314.
[115] 韦世平. 恩诺沙星在水体-蒙脱石体系中的光解和吸附过程及Cu(Ⅱ)的影响机制[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2022.
Wei S P. Photolysis and adsorption of enrofloxacin in water-montmorillonite system and the mechanism of Cu(Ⅱ) effect[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2022.
[116] Guo X, Yang C, Dang Z, et al. Sorption thermodynamics and kinetics properties of tylosin and sulfamethazine on goethite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 223: 59-67.
[117] 盛峰. 青霉素在天然水体及土壤矿物上的转化机理及毒性研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2019.
Sheng F. Transformation and the associated toxicity of penicillin antibiotics in natural water and soil mineral environments[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019.
[118] 王一飞. 微塑料对氟喹诺酮类抗生素的吸附作用[D]. 杭州: 浙江师范大学, 2021.
Wang Y F. Adsorption of fluoroquinolones by microplastics[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Normal University, 2021.
[119] Kim I, Kim H D, Jeong T Y, et al. Sorption and toxicity reduction of pharmaceutically active compounds and endocrine disrupting chemicals in the presence of colloidal humic acid[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2016, 74(4): 904-913.
[120] 李艳丹. 典型氟喹诺酮类抗生素在高岭土上吸附特征的实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
Li Y D. Sorption behavior of typical fluoroquinolone antibiotics on kaolinite: Batch experiments[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017.
[121] 蔡学巍. 水体中溶解性有机质与典型药物的相互作用及其对典型药物光降解的影响研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021.
Cai X W. The study on the interaction of dissolved organic matter with typical pharmaceuticals and its effects on the photodegradation of typical pharma-ceuticals in aqueous environment[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021.
[122] 杨波, 张永丽, 郭洪光. 腐植酸与环丙沙星结合机制的多维光谱学解析研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1494-1501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXXB202112008.htm
Yang B, Zhang Y L, Guo H G. Multi-spectroscopic investigation on mechanism of binding interaction between humic acid and ciprofloxacin enhanced publishing[J]. Acta Chemica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1494-1501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXXB202112008.htm
[123] Huang F, An Z, Moran M J, et al. Recognition of typical antibiotic residues in environmental media related to groundwater in China (2009-2019)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 399: 122813.
-



 下载:
下载: