Determination of Phenolic Compounds from Lignin Decomposition Products in Marine Sediments by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
-
摘要:
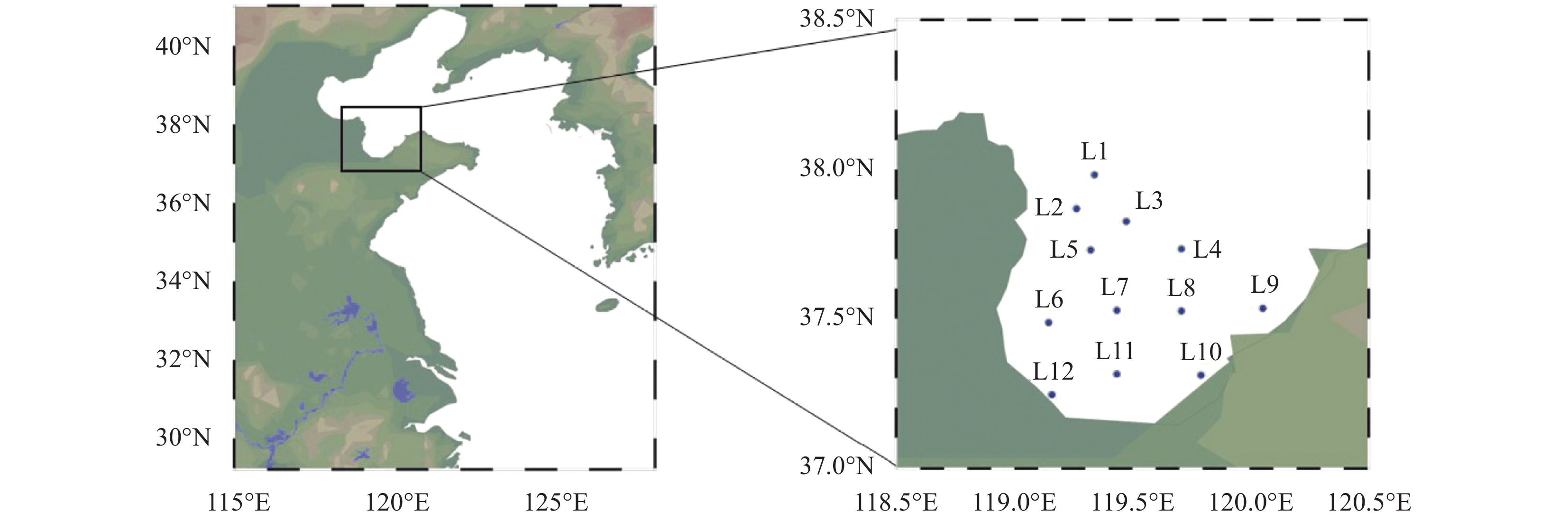
木质素分解产物酚类化合物是指示海洋环境中陆源有机碳来源的重要生物标志物,因此,开发检测海洋沉积物中木质素分解产物酚类化合物的简便方法,对研究海洋有机碳的来源及生物地球化学循环过程具有重要意义。本文采用固相萃取(SPE)和超高效液相色谱-飞行时间质谱技术(UHPLC-TOF/MS),建立了一种同步测定海洋沉积物中木质素分解产物酚类化合物(11种)的方法。首先对海洋沉积物样品进行氧化铜氧化碱分解和SPE净化处理,再采用填料粒径为1.8μm的反相C18柱进行分离,电喷雾TOF/MS全扫描模式检测,内标法定量。结果表明:沉积物中木质素的11种主要分解产物酚类化合物在20min内分离良好;方法具有良好的精密度(相对标准偏差RSD均小于9.0%),在线性范围内相关系数(R2)均不小于0.9989,加标回收率在86.8%~93.2%之间。应用该方法对莱州湾表层沉积物中木质素分解产物酚类化合物进行测定,12个表层沉积物样品中11种目标化合物的检出率均为100%;相关诊断比值:肉桂基酚系列单体总量与香草基酚系列单体总量的比值C/V在0.18~0.81之间,均值为0.38;丁香基酚系列单体总量与香草基酚系列单体总量的比值S/V在0.18~0.45之间,均值为0.26;对羟基酚系列单体中酮的量与对羟基酚系列单体总量的比值PON/P在0.01~0.07之间,均值为0.03;P系列单体总量与V和S系列单体总量之和的比值P/(V+S)在0.55~3.77之间,均值为1.44;V系列中酸类单体与醛类单体的比值(Ad/Al)v在0.12~1.07之间,均值为0.49;S系列单体中酸类单体与醛类单体的比值(Ad/Al)s在0.15~1.26之间,均值为1.02。表明莱州湾表层沉积物中的木质素主要来源于被子植物草本组织,并且具有中等或偏高程度的降解,但仍有少量新鲜植物有机质。本研究也表明UHPLC-TOF/MS是测定海洋沉积物中木质素分解产物酚类化合物的高效方法,能对沉积物中木质素含量和有机质来源进行有效指示。
-
关键词:
- 电喷雾飞行时间质谱法 /
- 木质素 /
- 酚类化合物 /
- 有机碳 /
- 莱州湾
Abstract:BACKGROUND Lignin is an important component of marine organic carbon. It is also an important biomarker for extracting information on the evolution of the land and marine environment and tracking the source of organic marine matter. However, the existing analytical techniques are difficult to determine lignin directly. So, the content of phenolic compounds in the decomposition products of lignin in marine sediments were generally determined to indicate the content of lignin and the source of organic matter. The content of phenolic compounds in the decomposition products of lignin in marine sediments is often used to reflect the content of lignin. In addition, by calculating the diagnostic ratio of individual phenolic compounds, it also provides important information about the classification, source, and diagenesis of terrestrial organic matter in marine sediments. However, phenolic compounds in the decomposition products of lignin have the characteristics of strong polarity and low volatility, so they cannot be directly detected by gas chromatography and need to be derivatized first, which makes the sample processing complicated and often results in incomplete derivatization. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop a simple and reliable method for determination of phenolic compounds of the lignin decomposition products in marine sediments to explore the source of organic matter and understand the environmental evolution process.
OBJECTIVES To establish a simple and reliable method for the determination of phenolic compounds of lignin decomposition products in marine sediments using solid phase extraction (SPE) combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry, and to trace the content level and source of lignin in the sediments of Laizhou Bay in China.
METHODS Marine sediment samples were first decomposed with oxidative-alkaline CuO and extracted by solid phase extraction. Briefly, the oxidation was carried out in a polytetrafluoroethylene digestion tank. 1.00g of sediment sample, 500mg of copper oxide, and 100mg of ammonium ferrous sulfate were accurately weighed and placed in the tank. The components were thoroughly mixed with the sample and then the digestion tank was transferred to a glove box filled with nitrogen. 8.0mL of aqueous sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 8.0% (bubbled with N2 to remove dissolved oxygen) was added to the tank. The digestion tank was covered tightly and transferred to an oven heating to 150℃ for reaction, which was terminated after 3h. After the digestion tank cooled to room temperature, it was carefully unscrewed, and an internal standard (ethyl vanillin) solution was added. Subsequently, the hydrolysate was transferred to a centrifuge tube, spun at 8000r/min for 10min, and the supernatant and reaction residue was separated. 2.0mL of 1.0% sodium hydroxide solution was added to rinse the residue, and centrifuged at 8000r/min for 10min. Combining the centrifuged supernatant obtained twice, the solution was acidified to pH=1 with hydrochloric acid. After the solution was left to stand for 30 minutes, solid phase extraction was performed. The SPE procedure was as follows: A hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) SPE cartridge (200mg, 6mL) was conditioned with 5mL of methanol and 5mL of ultrapure water. Sample solution was passed through the cartridge in a flow rate 1.0mL/min, and then the cartridges were rinsed with 10mL water, and dried under vacuum for about 3min. Phenolic compounds were eluted with 10mL ethyl acetate, and were evaporated by a rotary evaporator, reconstituted with sample solvent. Then, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography using ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 column with packing particle size of 1.8μm was used to directly separate all target compounds at 28℃, with gradient elution. The mobile phase was composed of ultrapure water with 0.1% formic acid (V/V) and acetonitrile/methanol (9:1, V/V) , and the flow rate was set to 0.25mL/min. Electrospray ionization (in positive) time of flight mass spectrometry was applied to detect target compounds in full scan mode, and quantification was performed using an internal standard determination.
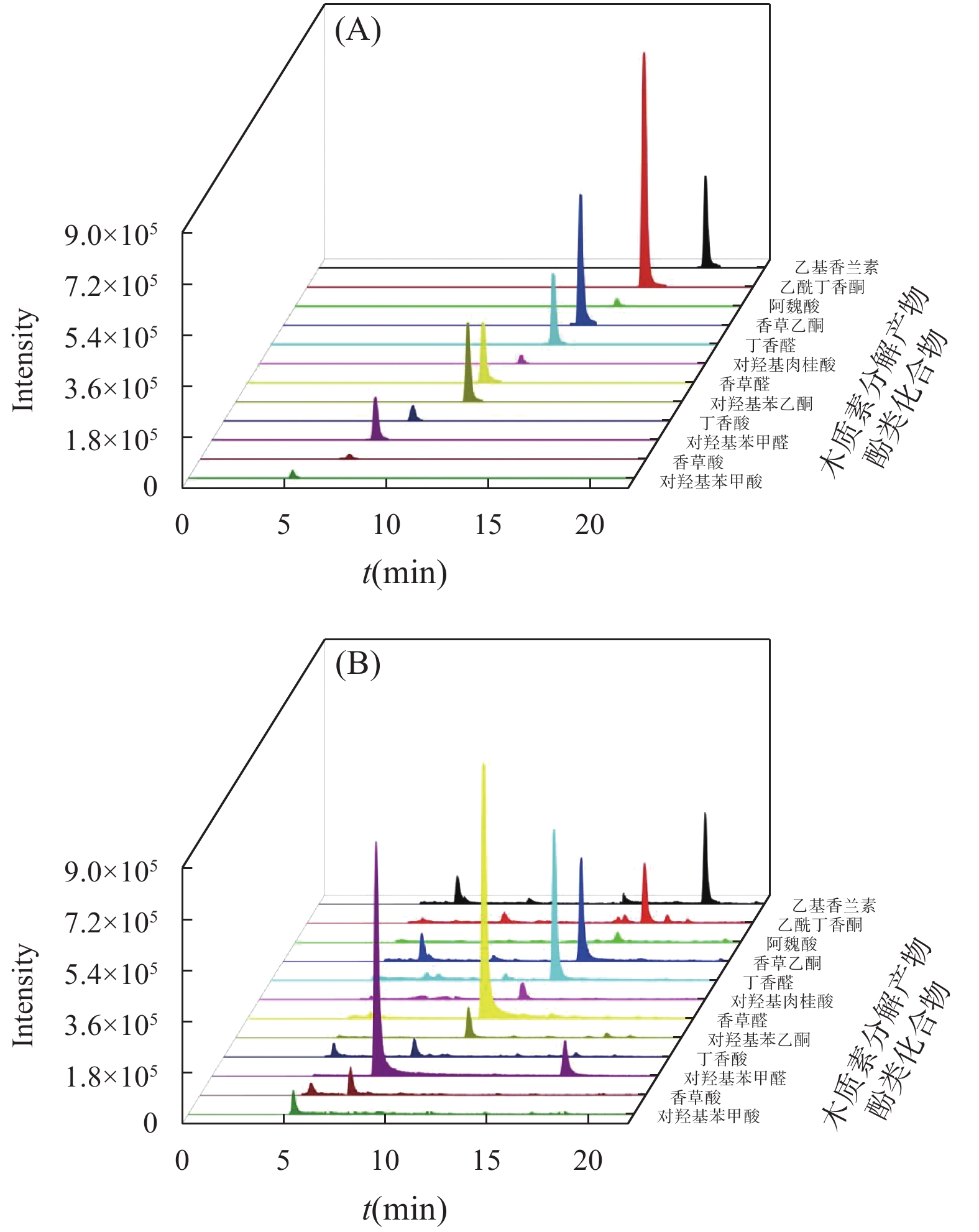
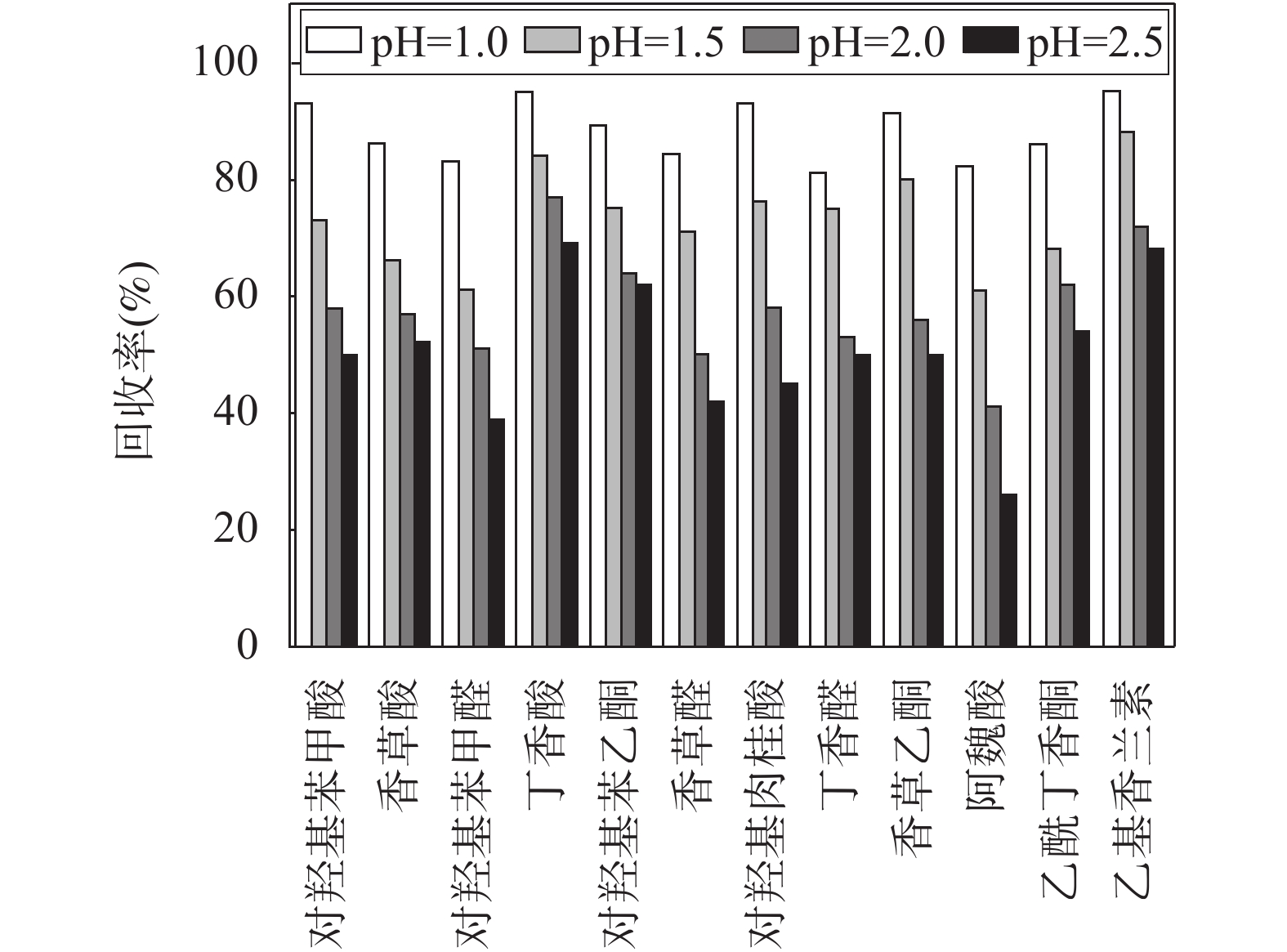
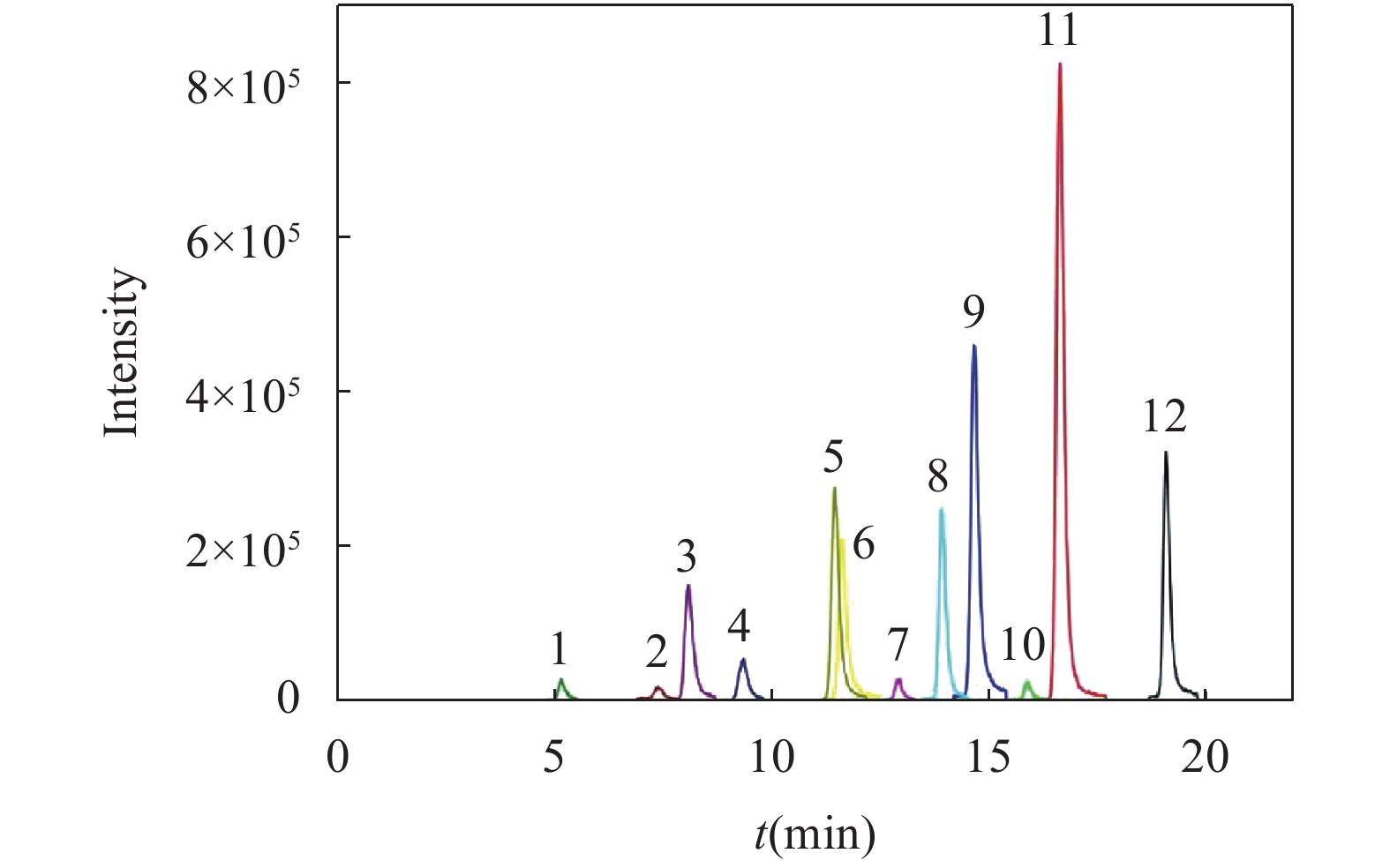
RESULTS Firstly, chromatographic conditions and solid phase extraction conditions were systematically optimized. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography was used for the chromatographic separation of phenolic compounds from lignin decomposition products in marine sediments. The separation effects of three mobile phase systems, namely, water-acetonitrile, water- methanol, and water-methanol-acetonitrile, were compared. When using a water-methanol -acetonitrile ternary mobile phase system, the resolution of various phenolic compounds was superior to the commonly used water-acetonitrile or water-methanol binary mobile phase systems in the literature. In addition, the effects of mobile phase acidity (trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid, and acetic acid were added into the mobile phase) on the separation of various phenolic compounds were investigated. The results showed that adding a certain concentration of all three acids to the mobile phase provided better separation results. Considering the compatibility with mass spectrometry, it was finally determined that adding 0.1% formic acid into the mobile phase achieved good peak patterns and resolution. In order to determine the ionization mode suitable for the analysis of phenolic compounds from lignin decomposition products in marine sediment, electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry was performed on each target phenolic compound in ESI+ and ESI− mode, respectively. Under ESI+ mode, various target phenolic compounds were less affected by interfering substances in the sample matrix, and the MS response value for most of the phenolic compounds was higher than that found in ESI− mode. Hence, ESI-TOF/MS in positive mode was selected to determine phenolic compounds of lignin decomposition products in marine sediment. Subsequently, the fragmentation voltage was optimized to obtain the highest sensitivity for all target phenolic compounds, which was the main mass spectrometric condition that affected the quantification accuracy and sensitivity. The effect of fragmentation voltage on the MS response signal of each target phenolic compound was investigated in the range of 80V to 200V. Overall, considering the detection sensitivity of the [M+H]+ ion peak of each target compound, 130V was selected as the optimal fragmentation voltage to determine phenolic compounds of lignin decomposition products in marine sediment. The effect of pH (1.0-2.5) of the loading solution for solid phase extraction on the extraction efficiency of various target phenolic compounds was systematically investigated, to ensure that the phenolic compounds of lignin decomposition products in marine sediments have a good recovery rate during the SPE process. When the pH of the loading solution was 1.0 and 1.5, the recovery rate of various phenolic compounds by using HLB solid phase extraction column was significantly higher than that of the loading solution adjusted pH to 2.0 and 2.5. When the pH of the sample solution was 1.0 and 1.5, although the recoveries of syringaldehyde and acetovanillone were relatively similar, the recoveries of other phenolic compounds were the highest at a pH of 1.0. Considering the recovery rate of all the target phenolic compounds and applicability of the method, the pH of the sample solution was confirmed to adjust to 1.0. In this study, HLB SPE column with 200mg of packing material was used to enrich phenolic compounds in sample extraction solution. Generally, 5-10mL of eluting solvent can ensure the full elution of all target phenolic compounds adsorbed on the SPE column. Therefore, based on the results of literature research, ethyl acetate was finally selected as the eluting solvent, with a dosage of 10mL. Under the optimum experimental conditions, the 11 main decomposition phenol compounds of lignin in marine sediments were well separated within 20 minutes. The proposed method had good precision (RSD was less than 9.0%), the correlation coefficient (R2) was not less than 0.9989 in the linear range, and the recovery rate of all spiked phenol compounds in blank marine sediment was in the range of 86.8%-93.2%, thereby indicating that the developed method would be suitable to determine the target decomposition phenol compounds of lignin in marine sediment. Subsequently, the method was used to determine the phenolic compounds of lignin decomposition products in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay. The detection rate of 11 target phenolic compounds in 12 surface sediment samples was 100%, and the concentration of Σ8 in 12 surface sediment samples ranged from 0.001mg/10gds to 0.019mg/10gds. The value of C/V was between 0.18 and 0.81, with an average of 0.38; the value of S/V was between 0.18 and 0.45, with an average of 0.26; PON/P value was between 0.01 and 0.07, with an average of 0.03; P/(V+S) value was between 0.55 and 3.77, with an average of 1.44; (Ad/Al)v value was between 0.12 and 1.07, with an average of 0.48; the value of (Ad/Al)s was between 0.15 and 1.26, with an average of 1.02.
CONCLUSIONS The above diagnostic ratios indicate that the lignin in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay originate mainly from the herbaceous tissue of angiosperms, while the proportion of organic matter in vascular plants is relatively low. The degradation degree of terrestrial organic matter in most sampling stations is medium or high, but there is still a small amount of fresh plant debris. The proposed method has the advantages of high efficiency, simple for sample pretreatment, and is a powerful technique for the determination of main decomposition product phenolic compounds of lignin in marine sediments.
-

-
表 1 超高效液相色谱-飞行时间质谱分析木质素主要分解产物酚类化合物和内标物的分子式、保留时间及精确分子质量
Table 1. Molecular formulas, retention times and exact molecular mass of the main decomposition products of lignin (phenolic compounds) and the internal standard analyzed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-TOF/MS).
序号 酚类化合物 分子式 保留时间(min) 精确分子量[M+H]+ 精确分子量[M-H]- 1 对羟基苯甲酸 C7H6O3 5.14 139.0395 137.0244 2 香草酸 C8H8O4 7.37 169.0495 167.0272 3 对羟基苯甲醛 C7H6O2 8.08 123.0441 121.0295 4 丁香酸 C9H10O5 9.35 199.0601 197.0455 5 对羟基苯乙酮 C8H8O2 11.46 137.0597 135.0452 6 香草醛 C8H8O3 11.61 153.0546 151.0401 7 对羟基肉桂酸 C9H8O3 12.90 165.0546 163.0401 8 丁香醛 C9H10O4 13.91 183.0652 181.0506 9 香草乙酮 C9H10O4 14.65 167.0703 165.0557 10 阿魏酸 C10H10O4 15.89 195.0652 193.0506 11 乙酰丁香酮 C10H12O4 16.68 197.0808 195.0663 12 乙基香兰素 C9H10O3 19.08 167.0703 165.0557 表 2 最佳实验条件下 11种目标化合物的线性方程相关系数及方法的检出限和定量限
Table 2. Correlation coefficients for linear analysis, detection limits and quantification limits of the method for UHPLC-TOF/MS determination of 11 target compounds under the optimal experimental conditions.
序号 酚类化合物 R2 方法检出限
(ng/g)方法定量限
(ng/g)1 对羟基苯甲酸 0.9989 5.34 17.80 2 香草酸 0.9989 7.27 24.23 3 对羟基苯甲醛 0.9991 0.67 2.13 4 丁香酸 0.9996 1.79 5.98 5 对羟基苯乙酮 0.9991 0.38 1.25 6 香草醛 0.9997 0.49 1.64 7 对羟基肉桂酸 0.9989 4.16 13.95 8 丁香醛 0.9993 0.47 1.58 9 香草乙酮 0.9994 0.23 0.76 10 阿魏酸 0.9994 5.13 17.1 11 乙酰丁香酮 0.9997 0.13 0.42 表 3 三种不同添加浓度水平下11种目标化合物的回收率和回收率的RSD(n=6)
Table 3. The recovery rate and its RSD of 11 target compounds under three different spiked levels (50.0ng/g, 100.0ng/g, 400.0ng/g) in the spiked recovery experiment with blank marine sediment (n=6).
酚类化合物 不同加标浓度水平下目标化合物回收率(%)(n=6) 不同加标浓度水平下目标化合物回收率的RSD(%)(n=6) 加标50.0ng/g 加标100.0ng/g 加标400.0ng/g 加标50.0ng/g 加标100.0ng/g 加标400.0ng/g 对羟基苯甲酸 87.8 90.1 91.9 8.4 7.0 5.8 香草酸 89.3 87.7 87.4 6.4 6.0 6.1 对羟基苯甲醛 86.8 90.0 88.9 7.0 7.2 6.3 丁香酸 88.7 88.1 89.4 8.3 6.3 7.5 对羟基苯乙酮 89.5 91.1 92.3 7.3 6.5 5.5 香草醛 87.4 88.5 87.8 5.2 5.5 4.6 对羟基肉桂酸 88.9 89.3 89.6 6.2 6.5 4.6 丁香醛 89.1 90.7 91.5 8.2 8.5 6.5 香草乙酮 87.5 88.9 89.5 7.4 5.3 5.5 阿魏酸 86.9 89.9 91.0 6.1 8.1 6.2 乙酰丁香酮 90.8 91.2 93.2 8.8 6.2 4.1 表 4 莱州湾表层沉积物中11种木质素主要分解产物酚类化合物的含量
Table 4. Content of 11 main phenolic compounds from lignin decomposition products of the surface sediment samples collected from the Laizhou Bay, China.
站位 酚类化合物含量(ng/g)(ds) 对羟基苯甲酸 香草酸 对羟基苯甲醛 丁香酸 对羟基苯乙酮 香草醛 对羟基肉桂酸 丁香醛 香草乙酮 阿魏酸 乙酰丁香酮 L1 62.33 26.08 136.41 5.98 3.48 20.65 17.75 5.60 2.33 22.17 0.50 L2 324.43 100.31 425.50 108.50 53.58 671.40 243.67 265.19 110.36 113.53 25.96 L3 350.21 507.56 511.59 119.13 39.5 481.33 297.51 233.46 79.82 122.80 26.18 L4 101.58 204.40 254.26 7.73 16.47 195.19 86.06 64.19 31.78 20.14 7.76 L5 176.82 326.83 425.68 46.14 25.88 317.00 74.67 99.34 46.57 50.57 9.33 L6 223.73 408.17 381.33 86.76 39.31 393.35 249.20 176.55 77.37 112.05 29.02 L7 114.31 73.84 297.40 9.86 5.17 69.67 39.80 22.06 7.27 34.99 2.23 L8 214.02 414.12 419.47 62.57 22.06 303.95 135.91 127.37 48.75 34.99 11.52 L9 180.05 195.33 421.15 29.25 14.86 188.62 110.52 70.42 22.43 32.43 6.37 L10 193.59 255.99 401.93 26.20 15.22 256.06 79.62 67.27 37.39 32.44 5.40 L11 156.60 57.41 325.48 5.83 5.39 47.84 33.30 12.90 4.06 28.22 1.42 L12 147.93 101.40 317.60 13.95 5.56 96.48 26.98 25.10 9.89 31.64 2.66 表 5 莱州湾表层沉积物样品中11种木质素的分解产物酚类化合物的各项特征参数
Table 5. Characteristic parameters of 11 phenolic compounds from lignin decomposition products in surface sediment samples of the Laizhou Bay, China.
站位 木质素不同分解产物酚类化合物的各项特征参数 C(ng/g) S(ng/g) V(ng/g) P(ng/g) C/V S/V P/(V+S) PON/P (Ad/Al)v (Ad/Al)s Σ8(mg/10g ds) L1 39.92 12.08 49.06 202.23 0.81 0.25 3.31 0.02 1.07 1.26 0.0010 L2 357.19 399.65 882.06 803.50 0.40 0.45 0.63 0.07 0.41 0.15 0.016 L3 420.31 378.76 1068.71 901.30 0.39 0.35 0.62 0.04 0.51 1.05 0.019 L4 106.20 79.68 431.38 372.31 0.25 0.18 0.73 0.04 0.12 1.05 0.0062 L5 125.24 154.82 690.40 628.38 0.18 0.22 0.74 0.04 0.46 1.03 0.0097 L6 361.24 292.34 878.88 644.37 0.41 0.33 0.55 0.06 0.49 1.04 0.015 L7 74.79 34.14 150.78 416.88 0.50 0.23 2.25 0.01 0.45 1.06 0.0026 L8 170.90 201.47 766.82 655.54 0.22 0.26 0.68 0.03 0.49 1.36 0.011 L9 142.95 106.03 406.39 616.06 0.35 0.26 1.20 0.02 0.42 1.04 0.0066 L10 112.06 98.87 549.43 610.75 0.20 0.18 0.94 0.02 0.39 1.00 0.0076 L11 61.51 20.16 109.31 487.46 0.56 0.18 3.77 0.01 0.45 1.20 0.0019 L12 58.61 41.72 207.77 471.09 0.28 0.20 1.89 0.01 0.56 1.05 0.0031 平均值 169.24 151.64 515.92 567.49 0.38 0.26 1.44 0.03 0.49 1.02 0.0083 -
[1] Zhang T,Li X G,Sun S W,et al. Determination of lignin in marine sediment using alkaline cupric oxide oxidation-solid phase extraction-on-column derivatization-gas chromatography[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2013, 12(1):63−69. doi: 10.1007/s11802-011-1936-z
[2] Jex C N,Pate G H,Blyth A J,et al. Lignin biogeochemistry:From modern processes to Quaternary archives[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 87:46−59. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.12.028
[3] Sun S,Schefuß E,Mulitza S,et al. Origin and processing of terrestrial organic carbon in the Amazon system:Lignin phenols in river,shelf,and fan sediments[J]. Biogeosciences, 2017, 14:2495−2512. doi: 10.5194/bg-14-2495-2017
[4] 王映辉,许云平. 黄河下游—河口—邻近海域表层沉积物中木质素的特征及其示踪意义[J]. 海洋科学,2016,40(2):55−64.
Wang Y H,Xu Y P. Characteristics and environmental implications of lignin in surface sediments from the lower Yellow River—estuary—adjacent sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(2):55−64.
[5] 巩菲,刘月,张大海,等. 黄河济南段柱状沉积物中木质素的分布特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2017,156(3):53−59.
Gong F,Liu Y,Zhang D H,et al. Distribution characteristics of lignin from the core in Jinan section of the Yellow River[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2017, 156(3):53−59.
[6] Yang B,Ljung K,Nielsen A B,et al. Impacts of long-term land use on terrestrial organic matter input to lakes based on lignin phenols in sediment records from a Swedish forest lake[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 774:145517. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145517
[7] Gordon E G,Goni M A. Sources and distribution of terrigenous organic matter delivered by the Atchafalaya River to sediments in the northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(13):2359−2375. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01412-6
[8] 王心怡,李中乔,金海燕,等. 应用木质素示踪楚科奇海表层沉积物中有机碳的来源和降解程度[J]. 海洋学报,2017,39(10):19−31.
Wang X Y,Li Z Q,Jin H Y,et al. Sources and degradation of orgnic carbon in the surface sediments across the Chukchi Sea,insighes from lignin phenols[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(10):19−31.
[9] Tolu J,Gerber L,Boily J F,et al. High-throughput characterization of sediment organic matter by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and multivariate curve resolution:A promising analytical tool in (paleo) limnology[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2015, 880:93−102. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.03.043
[10] 刘月,王敏,张婷,等. 杭州湾外泥质区柱状沉积物中木质素的分布特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 海洋环境科学,2017,36(1):8−14.
Liu Y,Wang M,Zhang T,et al. Distribution characteristics of lignin in sediment cores from the mud area off Hangzhou Bay and the implication for regional sedimentary environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(1):8−14.
[11] 凌媛,王永,王淑贤,等. 生物标志物在海洋和湖泊古生态系统和生产力重建中的应用[J]. 地学前缘,2022,29(2):327−342.
Ling Y,Wang Y,Wang S X,et al. Application of biomarkers in reconstructing marine and lacustrine paleoecosystems and paleoproductivity:A review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(2):327−342.
[12] Hedges J I,Ertel J R. Characterization of lignin by gas capillary chromatography of cupric oxide oxidation products[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1982, 54(2):174−178. doi: 10.1021/ac00239a007
[13] 叶君,胡利民,石学法,等. 基于木质素示踪北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积有机碳的来源、输运与埋藏[J]. 第四纪研究,2021,41(3):752−765.
Ye J,Hu L M,Shi X F,et al. Sources,transport and burial of terrestrial organic carbon in the surface sediments across the East Siberian Arctic Shelf,insights from lignin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(3):752−765.
[14] 江智婧,朱均均,李鑫,等. 反相高效液相色谱法定量分析木质素的主要降解产物[J]. 色谱,2011,29(1):59−62. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2011.00059
Jiang Z J,Zhu J J,Li X,et al. Determination of main degradation products of lignin using reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2011, 29(1):59−62. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2011.00059
[15] Sun L,Spencer R G M,Hernes P J,et al. A comparison of a simplified cupric oxide oxidation HPLC method with the traditional GC-MS method for characterization of lignin phenolics in environmental samples[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods, 2015, 13:1−8.
[16] Owen B C,Haupert L,Jarrell T M,et al. High-performance liquid chromatography/high-resolution multiple stage tandem mass spectrometry using negative-ion-mode hydroxide-doped electrospray ionization for the characterization of lignin degradation products[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84:6000−6007. doi: 10.1021/ac300762y
[17] 欧阳新平,陈子龙,邱学青. 超高效液相色谱/高分辨质谱法测定木质素氧化降解产物中单酚类化合物[J]. 分析化学,2014,42(5):723−728.
Ouyang X P,Chen Z L,Qiu X Q. Determination of monophenolic compounds from lignin oxidative degradation using ultra performance liquid chromatography/high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 42(5):723−728.
[18] 营娇龙,秦晓鹏,郎杭,等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定水体中37种典型抗生素[J]. 岩矿测试,2022,41(3):394−403.
Ying J L,Qin X P,Lang H,et al. Determination of 37 typical antibiotics by liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3):394−403.
[19] 莫力佳,石勇,高建华,等. 辽东半岛东岸泥区有机碳来源及其对流域和海岸环境变化的响应[J]. 地球化学,2021,50(2):199−210.
Mo L J,Shi Y,Gao J H,et al. Source and distribution of lignin in mud deposits along the southeastern coast of Liaodong Peninsula and its response to environmental changes of the catchment[J]. Geochimica, 2021, 50(2):199−210.
[20] 朱帅,沈亚婷,贾静,等. 环境介质中典型新型有机污染物分析技术研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试,2018,37(5):586−606.
Zhu S,Shen Y T,Jia J,et al. Review on the analytical methods of typical emerging organic pollutants in the environment[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(5):586−606.
[21] Heidke I,Scholz D,Hoffmann T. Quantification of lignin oxidation products as vegetation biomarkers in speleothems and cave drip water[J]. Biogeosciences, 2018, 15:5831−5845. doi: 10.5194/bg-15-5831-2018
[22] 王全成,胡丹阳,杨柳明,等. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱法测定森林土壤中木质素[J]. 实验室科学,2021,24(5):40−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4305.2021.05.010
Wang Q C,Hu D Y,Yang L M,et al. Determination of lignin in forest soil by solid phase extraction/high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Laboratory Science, 2021, 24(5):40−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4305.2021.05.010
[23] 于雅晨,李坤兰,马英冲,等. 反气相色谱法测定有机溶剂型木质素的溶解度参数[J]. 色谱,2013,31(2):143−146.
Yu Y C,Li K L,Ma Y C,et al. Determination of the solubility parameter of organosolv lignin by inverse gas chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2013, 31(2):143−146.
[24] 李鹏辉,蒋政伟,李家全,等. 木质素降解产物酚羟基测定方法研究进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2022,42(9):2666−2671.
Li P H,Jiang Z W,Li J Q,et al. Research progress in quantitative determination of phenolic hydroxyl groups in lignin[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022, 42(9):2666−2671.
[25] Heinonen J,Tamper J,Laatikainen M,et al. Chromatographic recovery of monosaccharides and lignin from lignocellulosic hydrolysates[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2018, 41(12):2402−2410.
[26] Wang Y L,Chen J H,Gao L Y,et al. Determination of eight typical lipophilic algae toxins in particles suspended in seawater by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 44(3):335−341. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(16)60911-8
[27] Tsutsuki K,Esaki I,Kuwatsuka S. CuO-oxidation products of peat as a key to the analysis of the paleo-environmental changes in a wetland[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1994, 40(1):107−116. doi: 10.1080/00380768.1994.10414283
[28] 戴群英,邹立,彭燕. 黄河口潮间带沉积物中木质素的分布以及降解特征[J]. 海洋环境科学,2017,36(2):210−215.
Dai Q Y,Zou L,Peng Y. Distribution and degradation of lignin in the sediment of intertidal mudflat of Yellow River Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(2):210−215.
[29] 冯朝军,潘建明,王红群,等. 微波消解-气相色谱法测定沉积物中的木质素[J]. 岩矿测试,2011,30(1):23−26.
Feng C J,Pan J M,Wang H Q,et al. Gas chromatographic determination of lignin in sediment samples assisted with microwave digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(1):23−26.
[30] Kaiser K,Benner R. Characterization of lignin by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry a simplified CuO oxidation method[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 84:459−464.
[31] Yan G,Kaiser K. A rapid and sensitive method for the analysis of lignin phenols in environmental samples using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry with multiple reaction monitoring[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2018, 1023:74−80. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.03.054
[32] 谢秀风,郗敏,孔范龙,等. 木质素作为湿地陆源性溶解性有机质(DOM)示踪剂的研究进展[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2015, 37(3):125−129.
Xie X F,Xi M,Kong F L,et al. Proceedings in the application of wetland lignin to tracing terrestrial organic mattes[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015, 37(3):125−129.
[33] 李先国,杜培瑞,孙书文,等. 山东半岛东北岸近海表层沉积物中木质素的分布特征及有机物来源[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2013(2):81−88.
Li X G,Du P R,Sun S W,et al. Distribution characteristics of lignin and sources of organic matter in surface sediments offshore of north eastern Shandong Peninsula[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013(2):81−88.
[34] 黄佳埼,林昕,汪福顺,等. 乌江流域下游梯级水库沉积物中木质素的特征及有机碳来源辨析[J]. 上海大学学报(自然科学版),2021,27(2):271−279.
Huang J Q,Lin X,Wang F S,et al. Characteristics of lignin in sediment cores from cascade reservoirs downstream of the Wujiang River and source analysis of organic carbon[J]. Journal of Shanghai University (Natural Science), 2021, 27(2):271−279.
[35] 李先国,王敏,孙书文,等. 渤海表层沉积物中木质素的分布特征及其对陆源有机物来源的示踪意义[J]. 海洋环境科学,2013,32(3):327−332.
Li X G,Wang M,Sun S W,et al. Distribution of lignin in the surface sediments of Bohai Sea and its implication for tracing terrigenous organic matter[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2013, 32(3):327−332.
[36] 尚文郁, 孙青, 谢曼曼, 等. 中国东北干旱-半干旱地区湖泊沉积物木质素酚类化合物特征及其气候指示意义[J]. 岩矿测试, 2023,42(2): 346-360.
Shang W Y, Sun Q, Xie M M, et al. Characteristics and climatic implications of lignin-derived phenolic compounds in Arid Lake, northeastern China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2023,42(2): 346-360.
-



 下载:
下载: