Analyzing the Reproductive Characteristics of
-
摘要:
青海湖裸鲤是中国重要的内陆珍稀鱼种,在青海湖湖泊生态系统中起着核心作用。繁殖环境是鱼类种群延续的关键因素,能获取青海湖裸鲤的繁殖环境参数和明确最佳产卵场,对于保护和扩大其渔业资源量也非常重要。本文尝试利用耳石的微区原位氧同位素组成分析青海湖裸鲤的繁殖特征,利用SHRIMP Ⅱ离子探针测定5尾青海湖裸鲤耳石微区原位δ18O组成,沿着最长生长轴到边缘打点,束斑直径大约25μm,束斑深度约2~3μm。分析结果表明,裸鲤耳石的δ18O值变动范围分别是−4.88‰~3.46‰、−0.28‰~3.91‰、−1.43‰~2.94‰、−1.81‰~3.35‰,并且耳石间歇带的δ18O值高于成长带。耳石间歇带是裸鲤在湖水中形成,而成长带是在河水中形成,上述结果与青海湖湖水的δ18O值显著高于河水的δ18O值一致,因此记录了裸鲤的洄游行为。核心区域差异性的δ18O值则反映了裸鲤的产卵地和水温状况,表明有的裸鲤在水温较低的河口产卵孵化,有的在水温较高的河流上游产卵孵化。与其他样品不同的是,其中1尾裸鲤耳石的δ18O变动范围是−9.36‰~−5.21‰,表明该裸鲤固定在河流里生长繁殖,不发生洄游行为。这一发现为进一步优化青海湖裸鲤的人工繁殖和利用耳石化石探究青海湖水环境演变提供了研究基础。
Abstract:BACKGROUND It is of great significance to study the breeding environment of the naked carp in Qinghai Lake for the conservation and restoration of natural habitat. The naked carp is the only economic species in Qinghai Lake, colloquially called “Huang Yu”, and plays a core role in the lake ecosystem. As an anadromous species, the naked cap migrates between Qinghai Lake and major rivers to spawn such as the Buha, Shaliu, Quanji, Heima, and Hargai rivers from April to August every year. Due to intensive fishing, arid climate, and the lack of spawning rivers, the amount of the naked carp’s resources has dropped sharply, from 28000 tons in the 1960s to 2263 tons in the 1990s. In view of its important ecological status, it is urgent to restore and protect the resources of naked carp in Qinghai Lake. Since 1982, Qinghai Province has forbidden fishing to restore and protect the fish resources. At the same time, it has established fish conservation bases and artificial breeding and releasing stations around Qinghai Lake. By 2022, the fish resources of the naked carp had increased to 108500 tons, 42 times as many as in the early stages of protection. The breeding environment is the key factor for the continuation of the fish population, and different fish require different parameters of the spawning ground, such as river, light, sediment and water temperature. It is also very important to obtain the reproductive environmental parameters and determine the optimal spawning ground for the protection and expansion of the fish resources. At present, only Zhou et al.[3] have discussed the environmental requirements of natural reproduction of the naked carp by indoor artificial simulation. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the breeding environment of the naked carp for the conservation and restoration of natural habitat. Otolith δ18O provides a method for fish population identification, migration and environment exploration of spawning ground. Otolith, a calcium carbonate mineral in bony fish, has both auditory and balancing functions and is known as the “recorder” of time and water environment. Microchemical analysis of otolith can reveal the life history and water environment changes of fish. Especially, the core area of otolith is formed at the early stage of incubation, and its microchemical composition can reflect the hydrochemical characteristics of the habitat and solve the problem of fish identification. The otolith δ18O is closely related to water temperature. Under normal salinity conditions, the δ18O change of 1‰ corresponds to the seawater temperature change of about 5℃. For example, the higher otolith δ18O values of Pacific bluefin tuna, which migrated across the Pacific from the Western Pacific (WPO) to the Eastern Pacific (EPO), reflected the cold-water temperatures encountered during migration. Similarly, the lower δ18O value in otolith core of Oncorhynchus keta, which migrated between freshwater and marine environments, indicated that Chinese salmon were also anadrotic spawning fish, returned to the ocean after hatching. Yuan et al.[12] analyzed the δ13C and δ18O values in the otolith of small yellow croaker in the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea, the population of southern Yellow Sea was subdivided into offshore and coastal populations for the first time, and no station crossing between the two populations was recorded. The overall successful rate of discrimination was recorded to be 82.6% by cluster analysis. Tatsuya et al.[13] conducted otolith δ18O and microstructure analyses to investigate nursery habitat temperatures and early life growth rates. In conclusion, the otolith δ18O provides a method for fish population identification, migration, and environment exploration of spawning ground. In this study, the SHRIMP Ⅱ ion probe was used to determine the otolith δ18O of the naked carp in Qinghai Lake. Combined with the hydrochemical composition of lake water and river water in Qinghai Lake, the optimal migration and spawning sites and environmental conditions of the naked carp were investigated to provide effective information for further revealing its life history.
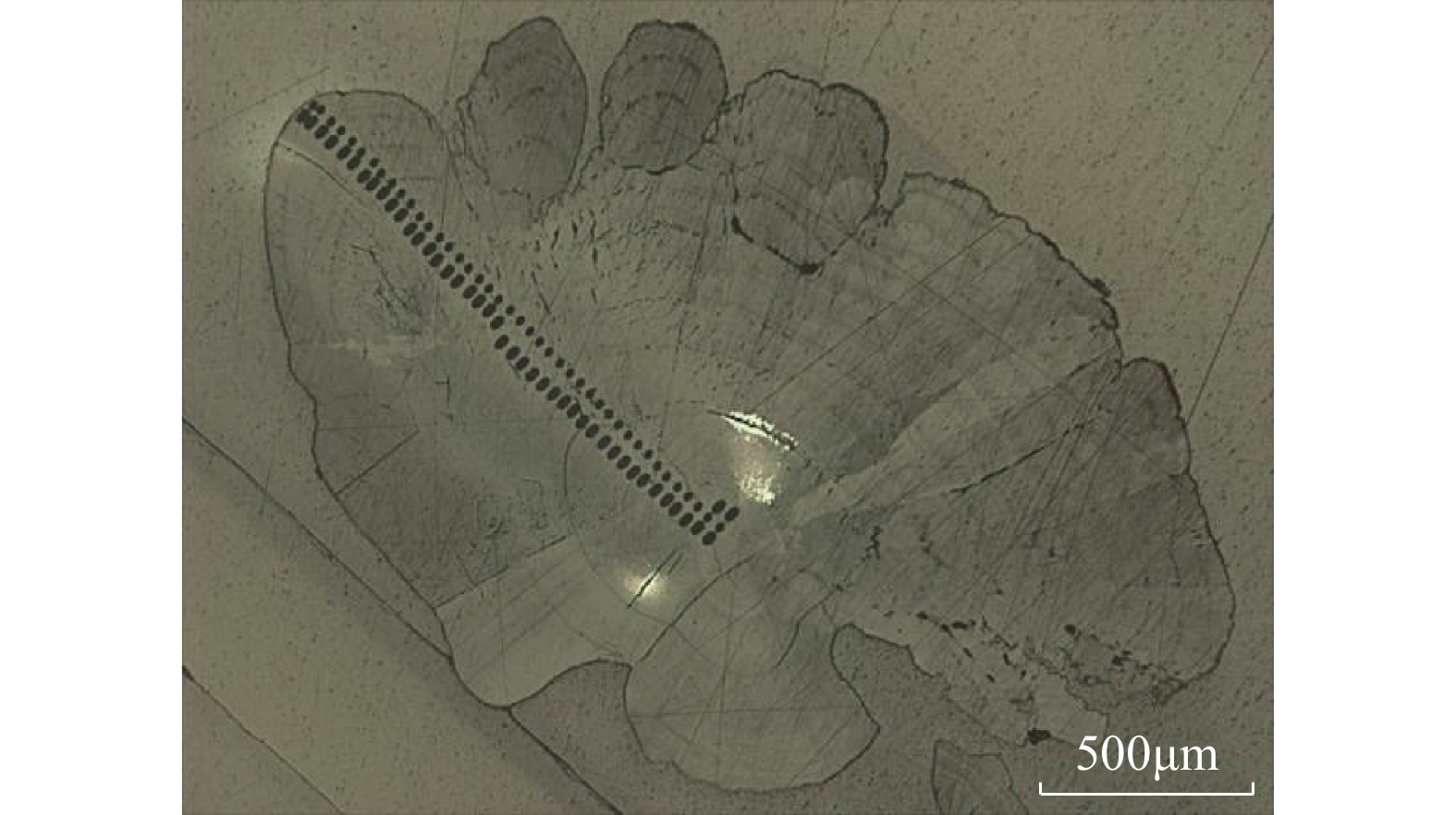
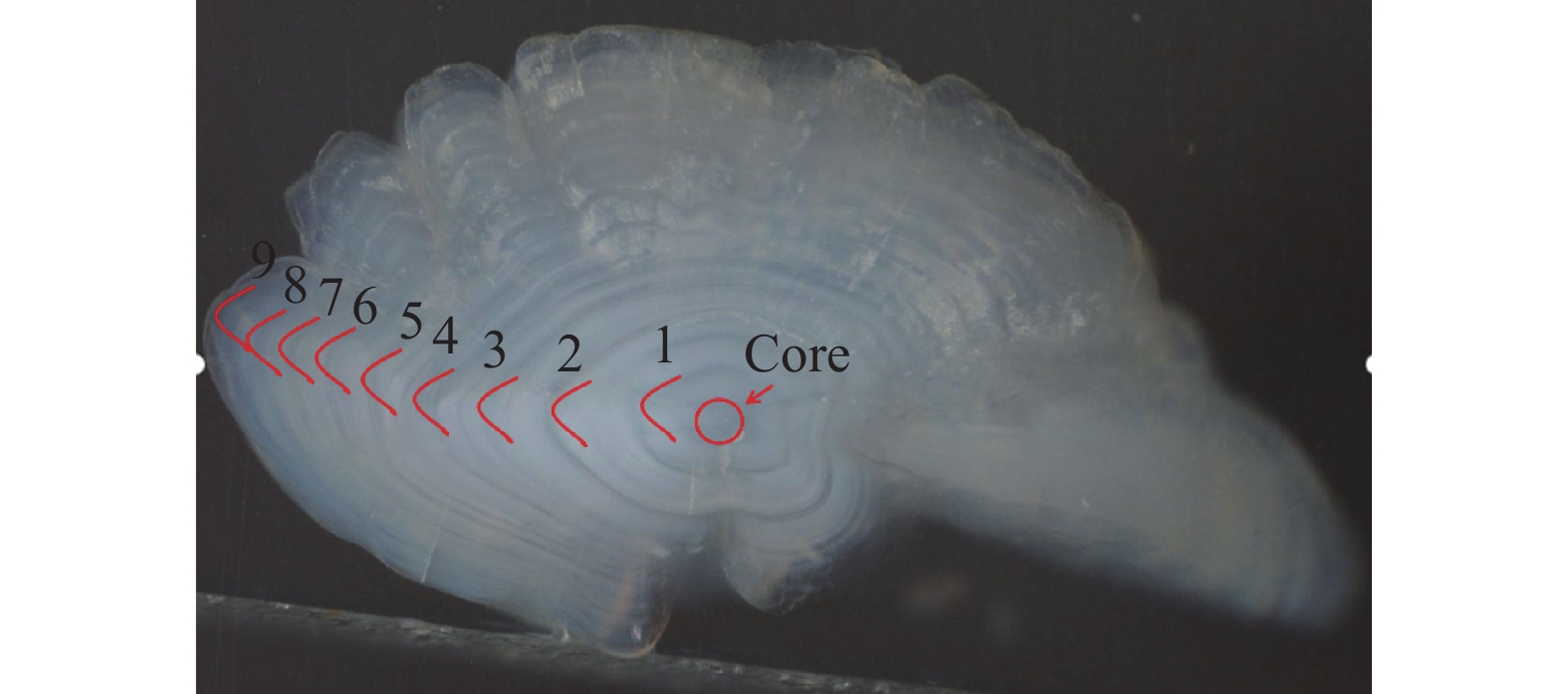
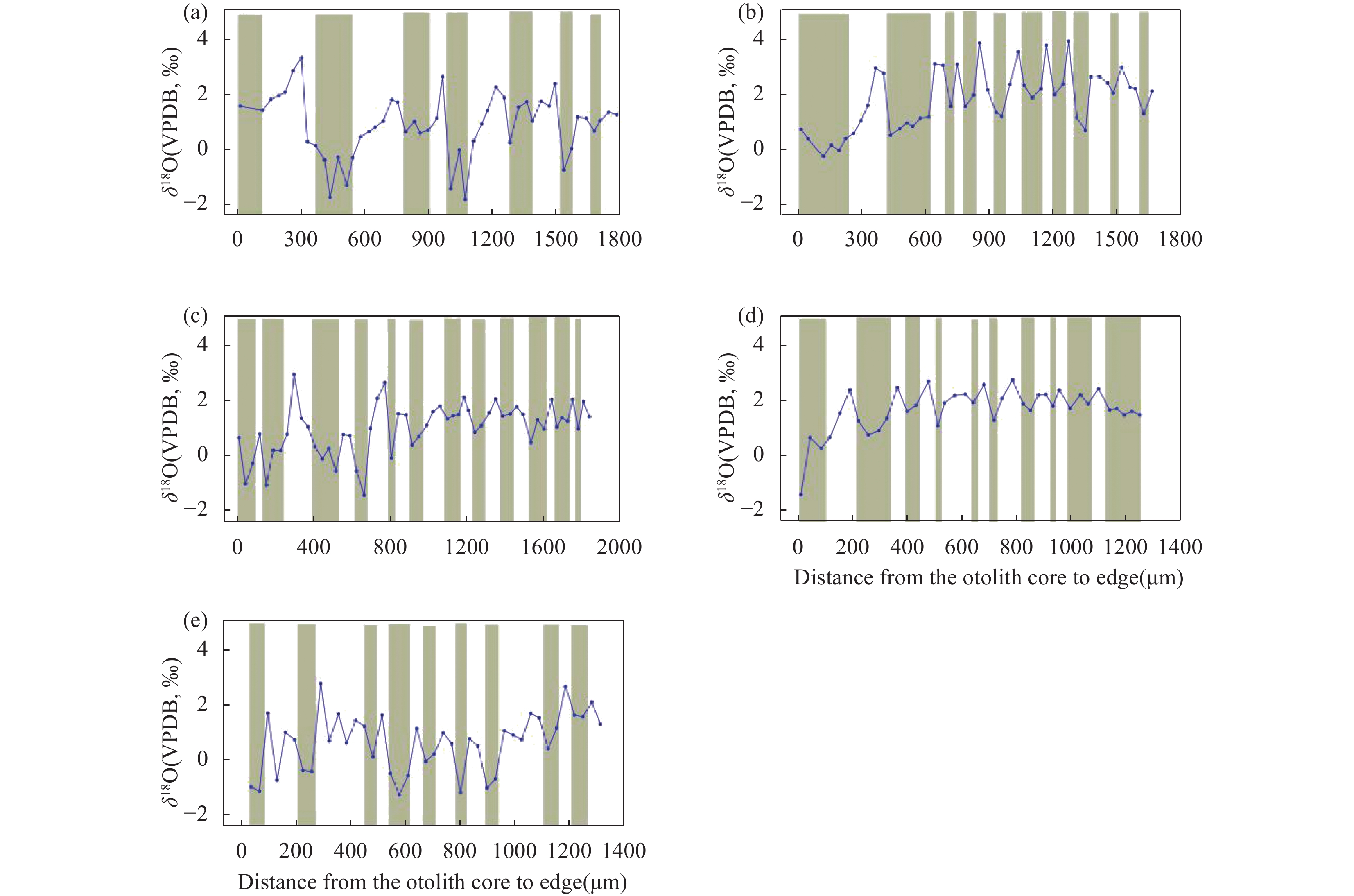
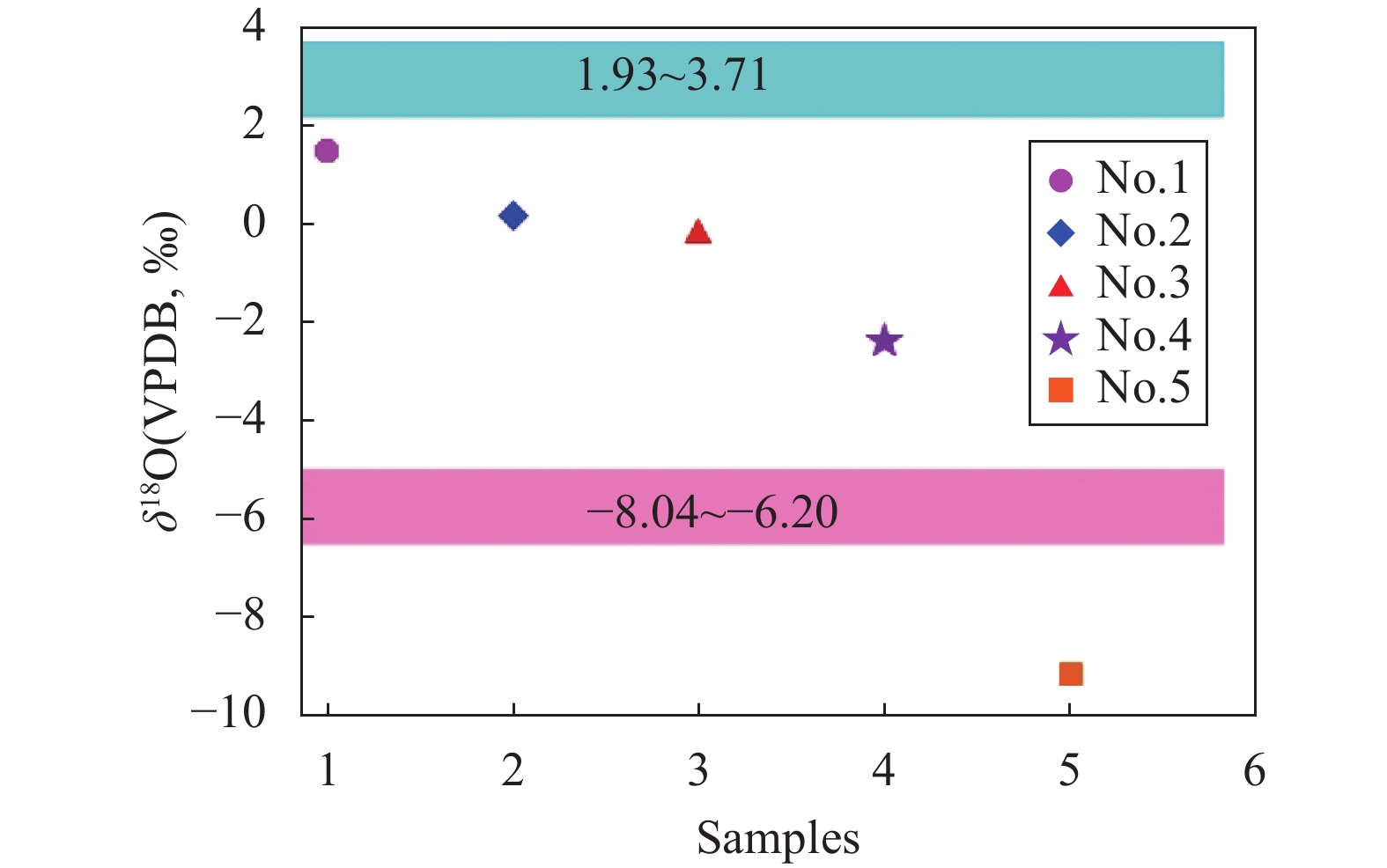
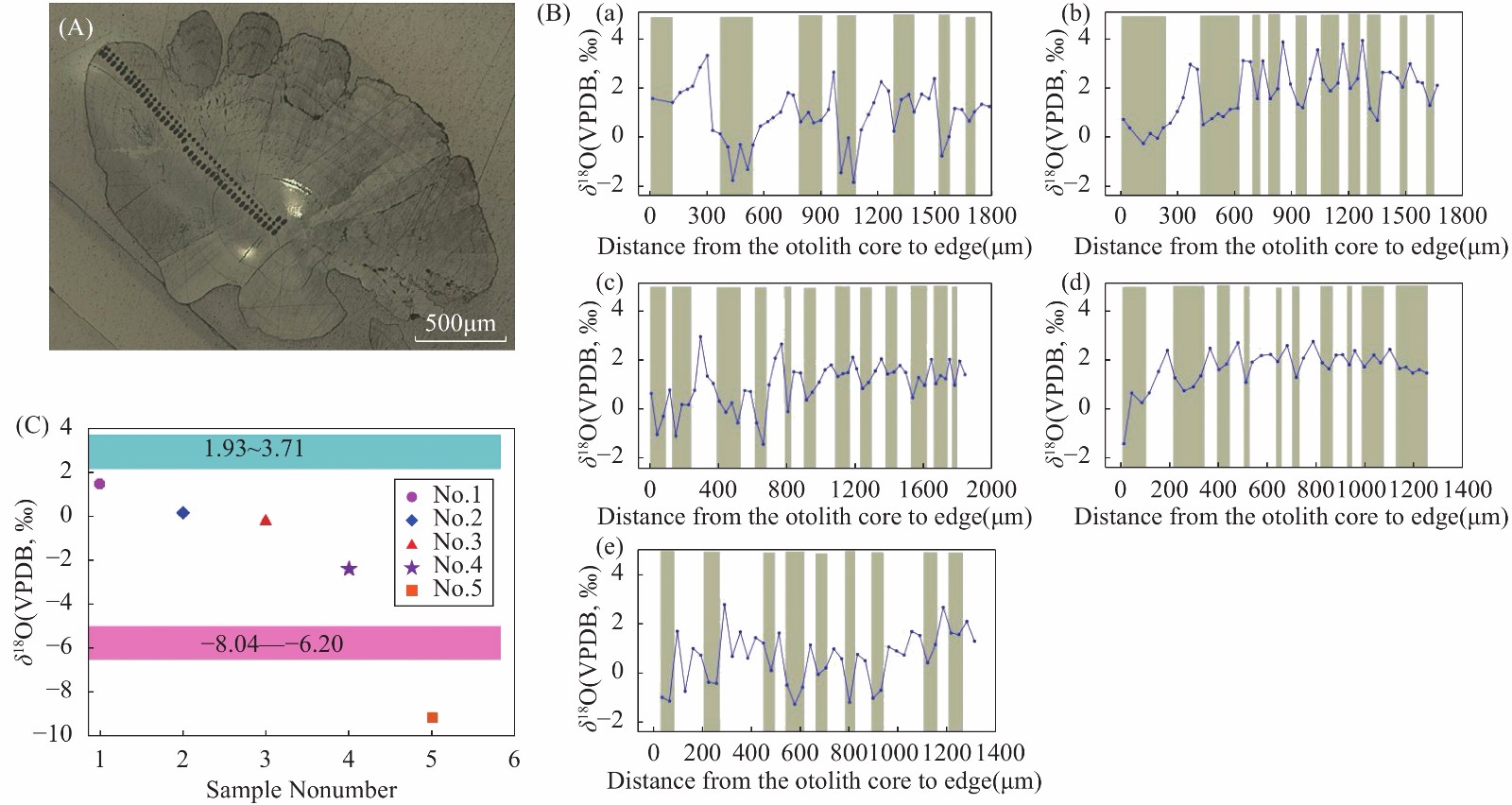
RESULTS The SHRIMP Ⅱ ion probe was used to determine the in-situ δ18O composition of the otolith microregion of five naked carp in Qinghai Lake. The in-situ oxygen isotope analysis of otolith was performed by SHRIMP Ⅱ ion probe at the School of Earth Sciences, Australian National University. Sectioned otoliths were prepared for SHRIMP analysis by casting them in epoxy resin, with NBS 18 and 19 reference calcites, to form a 35 mm diameter mount. After being documented by optical photomicroscopy, the samples were coated with high purity Al and transferred to the ANU SHRIMP Ⅱ for analysis using procedures based on those described in detail by Long et al.[21-22]. In brief, the SHRIMP Ⅱ was operated in multi-collector, negative ion mode. A 15kV, ~3nA Cs+ primary ion beam was focused to a 25mm diameter spot on the Al-coated target, producing 200−250pA of secondary 16O−. 16O− and 18O− were measured simultaneously on Faraday cups using Keithley 642 electrometers. Each analysis consisted of a pre-burn of about 3 min to allow the secondary ion isotopic composition to stabilise, followed by 10 or 14 times (10s/time) estimates of the 18O/16O ratio. The accuracy was 0.1‰−0.2‰, and the standard deviation was about 0.3‰. The reference material was measured once every 5 samples completed during analysis. The spot starting position of the ion probe was the core of the otolith, along the longest growth axis to the edge. The spot diameter of the ion probe was about 25μm, and the spot depth was about 2−3μm. The spot test was shown in Fig.E.1A. (2) The δ18O composition along the growth axis of the otolith. The δ18O ratios along the growth axis of 5 naked carp otoliths were shown in Fig.E.1B. The mean values of otolith δ18O from No.1 to No.5 were 1.29‰, 1.79‰, 0.99‰, 0.93‰, −7.41‰ respectively, and their interval range were −4.88‰−3.46‰, −0.28‰−3.91‰, −1.43‰−2.94‰, −1.81‰−3.35‰, −9.36‰−5.21‰, respectively. The otolith δ18O in individual juvenile plaice ranged from 0.2‰ to 1.9‰, when they were reared at two temperatures (11℃ and 17℃), which indicated that the otolith δ18O ratios were significantly affected by water temperature, but not by feeding level, and there were no significant synergistic effects. The δ18O ratios of plaice are close to the higher δ18O ratios of samples 1 to 4 in this study, which is the result of the fact that naked carp lived in the lake with high salinity and low water temperature for part of the time. The Schizothorax kozlovi and the naked carp belong to the subfamily Schizostomus. The average otolith δ18O ratios of the Schizothorax kozlovi cultured in fresh water is −9.4‰, which is very close to the δ18O ratios of the naked carp No.5, indicating that sample No.5 has been living in fresh water. The gray bands are the incremental zones of otolith, and the interval zones between the incremental zones are discontinuous zones. The δ18O ratios of the naked carp in samples 1 to 5 show a trend of lower incremental zones and higher discontinuous zones, because the δ18O ratios of otolith is inversely correlated with water temperature. The incremental zones of otolith are formed in spring and summer, while the discontinuous zones in autumn and winter, and the water temperature in spring and summer is significantly higher than that in autumn and winter. The otolith δ18O ratios of the five samples were analyzed by one-way variance analysis. The δ18O ratios of the No.1, No.3 and No.4 naked carp were not significantly different (P>0.05), while the δ18O ratios of the No.2 and No.5 naked carp were significantly different from the other three samples (P<0.05). The δ18O ratios of Qinghai Lake ranged from 1.93‰ to 3.71‰, with an average value of 2.43‰, and that of surrounding rivers ranged from −8.04‰ to −6.20‰. The average δ18O ratios of Buha River, Shaliu River, Quanji River and Heima River were −6.15‰, −7.21‰, −5.98‰, and −7.31‰, respectively. This is because the δ18O ratios of different types of water bodies vary greatly, and the δ18O ratios of lake water are obviously higher than that of surface river water due to strong evaporation. Comparing the δ18O ratios of lake water and river water with that of 5 samples, it can be seen that the δ18O signals of lake water and river water are recorded in the otolith of No.1-No.4, indicating that they migrated between lake water and river water, however, the δ18O signal of river water was only recorded in the otolith of No.5, which indicated that the No.5 naked carp had been living in river water, that is, “sitting water fish”. (3) Composition of δ18O in otolith cores of the naked carp. The average δ18O ratios of otoliths from No.1 to No.5 were 1.51‰, 0.20‰, −0.22‰, −2.38‰, and −9.14‰, respectively, and their interval range were 1.43‰−1.59‰, 0.28‰−0.7‰, 1.02‰−0.64‰, 4.88‰−0.74‰, 9.36‰−8.96‰. The average δ18O ratios of otolith cores were compared with the δ18O composition of lakes and rivers, as shown in Fig.E.1C. Since the core area of otolith was formed in the early incubation period of naked carp, the water environment at birth was recorded. From the distribution, the δ18O ratios of the core area of naked carp No.1-No.3 were closer to the lake water, which indicated that their spawning place was near the estuary. The water body was mixed with lake and river water, and having lower water temperature, which indicated the migration and spawning may have started in late May. The δ18O ratios of the core area of the No.4 naked carp was closer to the river water, which indicated that the spawning area was far away from the lake and the water temperature was higher, while the No.5 naked carp lived in the river all the time and the water temperature was higher when spawning. In conclusion, the habits of the naked carp are not fixed. Some breed in estuaries, some in upstream rivers, and some migrate between rivers and lakes to spawn, and a small part of the naked carp breed in rivers, which may be related to the local rivers’ cutout in autumn and winter. Some fish that migrate to the upper reaches of rivers to spawn have stayed in rivers for breeding due to the cutout of rivers. Similarly, the otolith cores of Pacific herring born in the Strait of Georgia have lower δ18O ratios (−8.2‰ to −2.0‰), while the otolith cores of the southern Puget Sound samples have higher δ18O ratios (−3.9‰ to −0.9‰).
DISSCUSION (1) The relationship between δ18O ratios of otolith and water temperature. The otolith of the naked carp can record not only the age, but also the water environment and the life history of the fish. The otolith δ18O ratios of fish is determined by the δ18O ratios of water body and the water temperature. The δ18O ratios of the water body are related to the ratio of precipitation to evaporation, runoff and precipitation, while there is an inverse correlation between temperature and otolith δ18O ratios. The living environment of fish can be inferred from the δ18O ratios value on the otolith of fish, and the isotopic balance between the surrounding water environment and aragonite minerals is reached or almost reached, therefore, the fractionation of 16O/18O isotopes is closely related to the temperature of the water body, generally showing a negative correlation. For marine fish, the variation of δ18O ratios at 1‰ corresponds to the variation of sea temperature at about 5℃ under normal salinity conditions. The relationship between temperature variation and otolith δ18O ratios of freshwater fish at 1‰ has not been established. (2) Experimental research about temperature control on otolith δ18O ratios. Water temperature, water flow, water depth, riverbed quality and light are the most important environmental parameters in fish breeding. In general, the reproductive activities of fish are not determined by a single environmental factor, and their specific reproductive needs are often multiple environmental factors. When the water temperature of the freshwater tributaries around Qinghai Lake reaches the threshold of 6−16℃, the naked carp will start to migrate, on the one hand, due to the different composition of δ18O ratios in different spawning sites, and on the other hand, due to the different spawning time, the difference of water temperature is recorded in the otolith δ18O.The contribution of the δ18O composition and the change of water temperature to the δ18O ratios in the otolith of the naked carp cannot be quantified, and needs to be further verified by the artificial control experiment. For example, Nakamura et al.[31] cultured mackerel larvae at six different temperatures (16.3℃, 17.6℃, 18.3℃, 20.0℃, 24.0℃ and 26.5℃) and determined the δ18O ratios, the linear relationship between the water temperature and the otolith δ18O of mackerel was determined. Willmes et al.[32] reared male oversea fish for 360 days at different salinity (8.75‰, 5.28‰ and 4.06‰) and water temperature (16.4℃, 16.7℃, 18.7℃ and 20.5℃), and then reconstructed the thermal life history of the fish. Wang et al.[33] evaluated whether cooking behavior would lead to further isotopic fractionation of carbonate in otolith and showed that the otolith δ18O ratios were highly consistent between cooked and uncooked, which indicated the cooking process has no or little effect on the otolith isotope value. (3) Fossil otolith is a good carrier to study the paleoclimate environment. Otoliths are well preserved in sediment, so the fossil otoliths are often used in paleoclimate, palaeoecology and palaeogeography. For example, Wurster et al.[34] analyzed high-resolution δ18O ratios of Aplodinotus grunniens from the Easterman archeological site to infer climate change in the eastern continental United States during the Holocene. Andrus et al.[35] used the otolith δ18O ratios of a well-preserved Peruvian catfish fossil to calculate the sea surface temperature of the Peruvian Sea in the Middle Holocene. Surge et al.[36] analyzed the δ18O ratios of modern and circa 2nd−3rd century AD fossil otoliths of the Mexican sea catfish, and the recovered winter temperatures were very similar to those of modern times. Long et al.[21] analysed the δ18O ratios of otolith in the sediment of Mungo Lake, Australia, and the variation of the δ18O ratios indicates an early flood in the lake, a subsequent increase in the δ18O by 4‰ indicating increasing evaporation of the lake. At the same time, because there is no “Reservoir effect”, the otolith preserved in the sediment is also a good material to measure radioactive carbon. Therefore, fossil otoliths preserved in sediments are not only one of the ideal materials to determine the age of sediments, but also a good carrier to study the paleoclimate environment. (4) Relationship between δ18O ratios of otolith and fish breeding population. The naked carp in Qinghai Lake is one of the second-class national protected animals in China. Since 1982, Qinghai Province has implemented the closure of the lake to breed fish, covering Qinghai Lake and all the rivers entering the lake. Currently, the sixth closure period in 10 years will end on December 31, 2030. At the same time, the original species preservation bases and artificial breeding and releasing stations have been established around Qinghai Lake. Since 2002, artificial breeding and releasing work has been carried out, and 105 million large-size naked carp fry have been released into the Shaliu and Quanji rivers. Therefore, there should be two populations of natural reproduction and artificial reproduction in Qinghai Lake, and it is difficult to distinguish the two populations only by the otolith δ18O ratios. (5) In order to identify fish populations more accurately and understand fish life history, many scholars combine the δ18O and δ13C ratios of otolith for analysis, because the change of otolith δ13C ratios can record the maturity of fish and the change in the food chain. For example, Gao et al.[38] analyzed the δ18O and δ13C ratios of the otolith core and the second summer season round of Pacific herring in Pikew Bay, Washington, and concluded that there are two types of herring. Ashford et al.[39] tested the δ18O and δ13C ratios of cod otolith located on the Patagonia continental shelf and Patagonia in southern Georgia, and found that the δ18O ratios reflected the sea water temperature in the surrounding environment where the fish lived, so that the different population could be identified. The source of metabolic carbon and the δ13C ratios of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in seawater affect the δ13C ratios of otolith. For the first time, Jiang Tao et al.[40] analyzed otolith stable isotope ratios of δ18O and δ13C using an isotope ratio mass spectrometry on Coilia nasus juveniles collected from the Changjiang River Estuary. The different environments with different water temperature and food organism composition might be experienced by the two groups of C. nasus fish. He Yongfeng et al.[25] took Sichuan schizostomus of different age groups as the research object to explore the relationship between stable isotopes and environment. The results showed that δ18O and δ13C ratios of Schizothorax kozlovi at age 1t were not significantly correlated with otolith mass, but both were significantly different between lapillus and asteriscus. There was no significant difference of lapillus δ18O and δ13C between the sexes, but with significant difference among different ages. The correlation of δ18O with δ13C was an effective method in identification of different culture stocks of S. kozlovi, which indicates that the isotopic signatures of otolith could be used as a method to identify freshwater fish stocks.
-
Key words:
- Qinghai Lake naked carp /
- spawning grounds /
- otolith /
- oxygen isotope /
- SHRIMP /
- water temperature
-

-
表 1 5尾裸鲤的体长、体重和耳石年轮统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of body length, weight and otolith rings of 5 naked carp.
样品编号
Sample No.裸鲤体长
Length (cm)裸鲤体重
Weight (g)年轮计数
Annual ring count1 30.0 302 7 2 35.0 450 10 3 42.0 590 12 4 33.0 440 10 5 32.0 350 9 -
[1] 张信,陈大庆,严莉,等. 青海湖裸鲤资源保护面临的问题与对策[J]. 淡水渔业,2005,35(4):57−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2005.04.021
Zhang X,Chen D Q,Yan L,et al. Problems and countermeasures in the conservation of naked carp resources in Qinghai Lake[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2005, 35(4):57−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2005.04.021
[2] 史建全,祁洪芳. 青海湖裸鲤增殖放流技术集成及示范[J]. 青海科技,2018,25(1):24−28.
Shi J Q,Qi H F. Integration and demonstration of breeding and releasing technology of Naked carp in Qinghai Lake[J]. Qinghai Science and Technology, 2018, 25(1):24−28.
[3] 周杨浩,荣义峰,周卫国,等. 人工模拟条件下青海湖裸鲤自然繁殖环境条件需求研究[J]. 水生生物学报,2022,46(6):779−787.
Zhou Y H,Rong Y F,Zhou W G,et al. Environmental requirements of natural reproduction of Gymnocypris przewalskii under artificial simulated conditions[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2022, 46(6):779−787.
[4] Davoren G K,Woloschiniwsky C S,Halden N M. Does otolith chemistry indicate the natal habitat of Newfoundland capelin Mallotus villosus?[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2015, 464:88−95. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2014.10.025
[5] Tripp A,Morrison S,Loeppky A R,et al. Water strontium concentrations influence strontium concentrations in the pre-hatch otolith region of capelin (Mallotus villosus)[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2022, 547:151667. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2021.151667
[6] Gonzalvo S,Kawakami T,Tanoue H,et al. Estuarine dependency of Lates japonicus in Shimanto Estuary,Japan,inferred from otolith Sr:Ca[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2021, 252:107269. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2021.107269
[7] 丛旭日,李秀启,董贯仓,等. 基于耳石微化学的黄河垦利段刀鲚生活史初步研究[J]. 渔业科学进展,2022,43(1):31−37.
Cong X R,Li X Q,Dong G C,et al. Preliminary investigations on Coilia nasus from the Kenli section of the Huanghe River based on otolith microchemistry[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2022, 43(1):31−37.
[8] Geffen A J. Otolith oxygen and carbon stable isotopes in wild and laboratory reared plaice (Pleuronectesplatessa)[J]. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 2012, 95:419−430. doi: 10.1007/s10641-012-0033-2
[9] Degens E T,Deuser W G,Haedrich R L. Molecular structure and composition of fish otoliths[J]. Marine Biology, 1969, 2(2):105−113. doi: 10.1007/BF00347005
[10] Kawazu M,Tawa A,Ishihara T,et al. Discrimination of eastward trans-Pacific migration of the Pacific bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis through otolith δ13C and δ18O analyses[J]. Marine Biology, 2020, 167:110. doi: 10.1007/s00227-020-03723-9
[11] Wang J,Gao Y,Liu W,et al. The life history and populations of chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) in China:An otolith isotopic investigation[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2021, 127:104903. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.104903
[12] 袁威,王玉堃,张廷廷,等. 基于耳石δ13C和δ18O的黄、渤海秋季小黄鱼补充群体的种群划分[J]. 渔业科学进展,2019,40(5):11−18.
Yuan W,Wang Y K,Zhang T T,et al. Investigating the population structure of Larimichthys polyactis from the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea using stable isotope mass spectrometry[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(5):11−18.
[13] Tatsuya S, Van D, Kotaro S, et al. Otolith δ18O and microstructure analyses provide further evidence of population structure in sardine Sardinops sagax around South Africa[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 2020, doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsaa130.
[14] Liu W G,Yang H,Ning Y F,et al. Contribution of inherent organic carbon to the bulk δ13C signal in loess deposits from the arid western Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2007, 38(9):1571−1579. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2007.05.004
[15] An Z S,Colman S M,Zhou W J,et al. Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32ka[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2:619. doi: 10.1038/srep00619
[16] 陈大庆,张信,熊飞,等. 青海湖裸鲤生长特征的研究[J]. 水生生物学报,2006,30(2):173−179.
Chen D Q,Zhang X,Xiong F,et al. Studies on growth characteristics of Gymnocypris przewalskii[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2006, 30(2):173−179.
[17] 史建全,祁洪芳,杨建新,等. 青海湖裸鲤人工繁殖及鱼苗培育技术的研究[J]. 淡水渔业,2000,30(2):3−6.
Shi J Q,Qi H F,Yang J X,et al. Study on artificial breeding and fry breeding techniques of naked carp in Qinghai Lake[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2000, 30(2):3−6.
[18] 史建全,杨建新,祁洪芳,等. 青海湖裸鲤形态特征与遗传性状[J]. 青海科技,2000,7(2):16−18.
Shi J Q,Yang J X,Qi H F,et al. Morphologic characristics and genetic properties of Gymnocypris przewalskii[J]. Qinghai Science and Technology, 2000, 7(2):16−18.
[19] Zhou L,Jin Z D,Li F C. Mineralogy of the otoliths of naked carp Gymnocypris przewalskii (Kessler) from Lake Qinghai and its Sr/Ca potential implications for migratory pattern[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(6):983−990.
[20] 吴恒飞,陈克龙,张乐乐,等. 气候变化下青海湖流域生态健康评价研究[J]. 生态科学,2022,41(4):41−48.
Wu H F,Chen K L,Zhang L L,et al. Study on ecological health evaluation of Qinghai Lake Basin under climate change[J]. Ecological Science, 2022, 41(4):41−48.
[21] Long K,Wood R,Williams I S,et al. Fish otolith microchemistry:Snapshots of lake conditions during early human occupation of Lake Mungo,Australia[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 463:29−43.
[22] Long K,Stern N,Williams I S,et al. Fish otolith geochemistry,environmental conditions and human occupation at Lake Mungo,Australia[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 88:82−95. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.01.012
[23] 胡志中,晏雄,王坤阳,等. 碳酸盐碳氧同位素标准物质性状对分析和保存的影响[J]. 岩矿测试,2021,40(4):476−490.
Hu Z Z,Yan X,Wang K Y,et al. Characteristics of carbon and oxygen isotope standard materials of carbonates and their effect on isotope analysis and standard preservation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(4):476−490.
[24] 熊飞,陈大庆,刘绍平,等. 青海湖裸鲤不同年龄鉴定材料的年轮特征[J]. 水生生物学报,2006,30(2):185−191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2006.02.010
Xiong F,Chen D Q,Liu S P,et al. Annuli characteristics of the different ageing materials of Gymnocypris Przewalskii (Kessler)[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2006, 30(2):185−191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2006.02.010
[25] 何勇凤,吴兴兵,王旭歌,等. 四川裂腹鱼耳石碳、氧稳定同位素特征[J]. 应用生态学报,2017,28(7):2339−2343.
He Y F,Wu X B,Wang X G,et al. Otolith carbon and oxygen stable isotopes in laboratory-reared Schizothorax kozlovi[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(7):2339−2343.
[26] Cui B L,Li X Y. Characteristics of stable isotope and hydrochemistry of the groundwater around Qinghai Lake,NE Qinghai—Xizang Plateau,China[J]. Environmental Earth Science, 2014, 71:1159−1167. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2520-y
[27] Liu W G,Li X Z,Zhang L,et al. Evaluation of oxygen isotopes in carbonate as an indicator of lake evolution in arid areas:The modern Qinghai Lake,Qinghai—Xizang Plateau[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268:126−136. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.08.004
[28] 高娟琴,于扬,王登红,等. 新疆阿勒泰地区地表水体氢氧同位素组成及空间分布特征[J]. 岩矿测试,2021,40(3):397−407.
Gao J Q,Yu Y,Wang D H,et al. Composition and spatial distribution characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of surface water in Altay,Xinjiang Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3):397−407.
[29] Martino J C, Doubleday Z A, Chung M T, et al. Experimental support towards a metabolic proxy in fish using otolith carbon isotopes[J]. The Company of Biologists, 2020, 223(6):jeb217091.
[30] Shirai K,Otake T,Amano Y,et al. Temperature and depth distribution of Japanese eel eggs estimated using otolith oxygen stable isotopes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 236:373−383. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.03.006
[31] Nakamura M,Yoneda M,Ishimura T,et al. Temperature dependency equation for chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) identified by a laboratory rearing experiment and microscale analysis[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 2020, 71:1384−1389. doi: 10.1071/MF19313
[32] Willmes M,Lewis L S,Davis B E,et al. Calibrating temperature reconstructions from fish otolith oxygen isotope analysis for California’s critically endangered Delta Smelt[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2019, 33(14):1207−1220. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8464
[33] Wang P, Shiao J, Wang Y, et al. Evaluation of cooking effects on otolith stable carbon and oxygen isotope values of teleostean fish Pomadasys kaakan (Cuvier, 1830)[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2022, 36(4): e9233.
[34] Wurster C M,Patterson W P. Late Holocene climate change for the eastern interior United States:evidence from high-resolution δ18O values of sagittal otoliths[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology, 2001, 170(1):81−100.
[35] Andrus C F T,Crowe D E,Sandweiss D H. Otolith δ18O record of mid-Holocene sea surface temperatures in Peru[J]. Science, 2002, 295(5559):1508−1511. doi: 10.1126/science.1062004
[36] Surge A D,Walker K J. Oxygen isotope composition of modern and archaeological otoliths from the estuarine hardhead catfish ( Ariopsis felis ) and their potential to record low-latitude climate change[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology, 2005, 228:179−191.
[37] 王玉娇,金章东,周玲,等. 青海湖裸鲤(湟鱼)鱼骨产出层位及其耳石微化学对明朝青海湖水位的指示[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2014,44(8):1833−1843.
[38] Gao Y W,Joner S H,Bargmann G G. Stable isotopic composition of otoliths in identification of spawning stocks of Pacific herring (Clupea pallasi) in Puget Sound[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 2001, 58:2113−2120. doi: 10.1139/f01-146
[39] Ashford J,Jones C. Oxygen and carbon stable isotopes in otoliths record spatial isolation of Patagonian toothfish (Dissostichus eleginoides)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71:87−94. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.08.030
[40] 姜涛,刘洪波,杨健. 长江口刀鲚幼鱼耳石碳,氧同位素特征初报[J]. 海洋科学,2015,39(6):48−53.
Jiang T,Liu H B,Yang J. Characteristics of C and O stable isotope in otolith of juvenile Coilia nasus from the Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(6):48−53.
-




 下载:
下载: