Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Typical Soil Profiles of Muchuan County, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
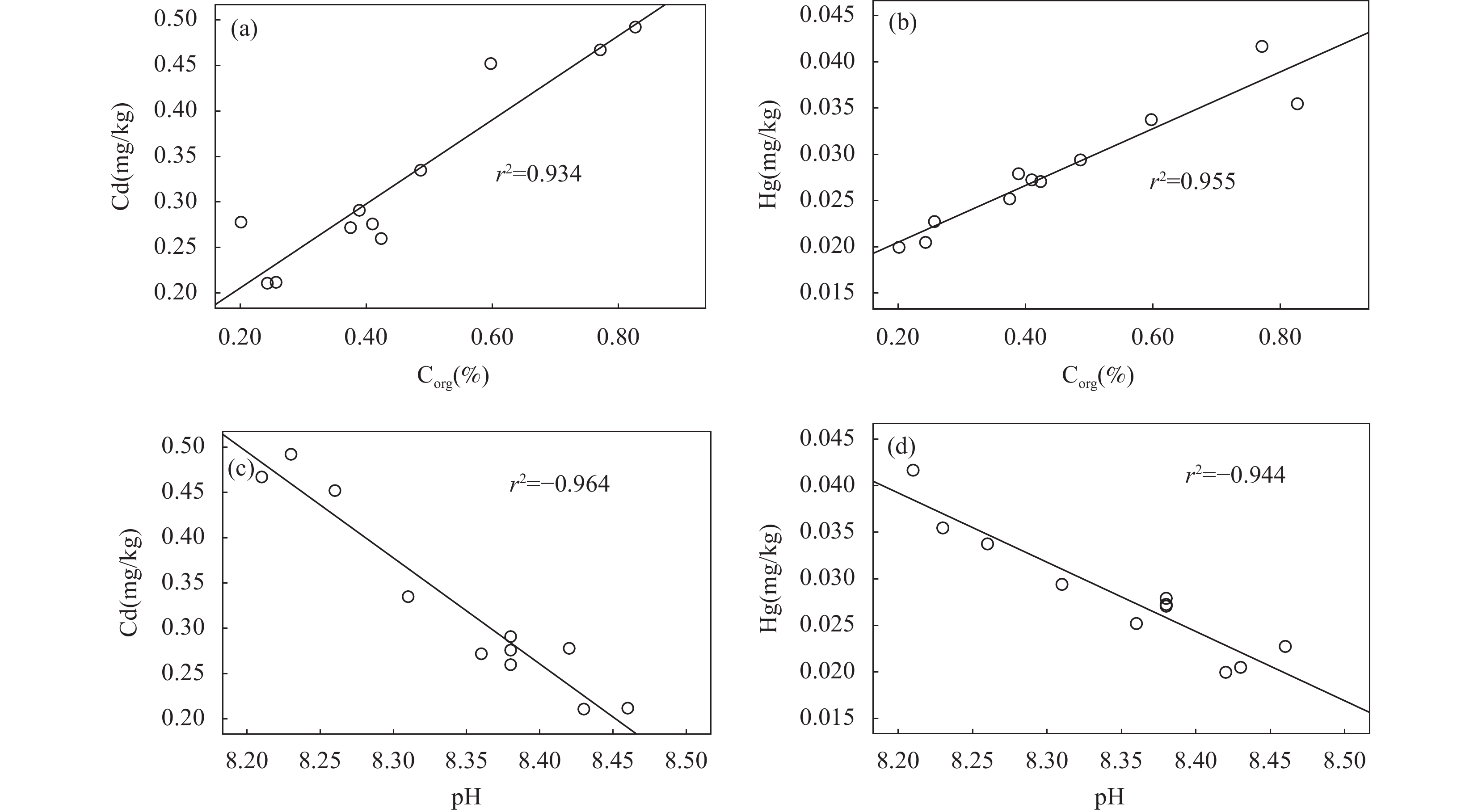
根据全国土壤污染状况调查显示,全国土壤的环境状况总体不容乐观,耕地土壤环境质量令人担忧,已对粮食安全构成威胁。已有的研究工作多集中于土壤重金属的空间分布特征及污染源分析、重金属污染风险评估以及评估方法,但对于不同土壤深度重金属在耕地中的积累与剖面分布的变化及其生态风险分析相对较少。为研究四川省沐川县土壤剖面重金属分布特征和生态风险,本文在研究区选择三个不同地质背景区采集了土柱剖面样品开展相关工作。结果表明:样品中As、Cd、Hg、Pb、Ni、Cu、Zn七项指标中,除了Cu外,其余重金属元素含量都高于国家和四川省土壤背景值,表明这些元素在土壤中呈现不同程度地富集。土壤中7种重金属的浓度与土壤养分(氮、磷、钾),土壤有机碳和pH值存在相关性,如在玉米地剖面中,氮和磷与Cd呈显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.845、0.747。大量研究表明,磷肥中含有一定量的重金属。磷肥中重金属含量高低与磷矿及其来源有关,磷肥能够增加土壤 Cd 含量。土壤有机碳与Cd呈显著正相关,相关系数为0.934,其原因是土壤有机质对重金属的吸附作用,有机碳对土壤中重金属的保留起了重要作用。pH值与Cd呈显著负相关,相关系数为-0.964,随着pH值的增加,土壤对重金属离子的吸附会增加,从而导致土壤中活性重金属离子减少。土壤重金属之间存在显著的正相关关系,表明它们普遍存在同源性。采用地质积累指数($ {I}_{\mathrm{g}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{o}} $)评价土壤重金属污染程度,并选取潜在生态风险指数($ RI $)评价其潜在生态风险,结果表明土壤中主要污染元素为Cd。生态风险指数显示,玉米地的潜在生态风险较大,其中Cd、Hg的生态风险较高,潜在生态风险指数($ RI $)随着剖面深度的增加而降低。当地应采取适当措施,加强对该地区污染的防治工作,避免对人体健康造成危害。
-
关键词:
- 土壤 /
- 重金属 /
- 含量分布 /
- 污染评价 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUND Soil is a precious resource for human survival and social development. The quality of the soil environment is impacted by a variety of issues due to the social economy’s rapid expansion, and the issue of heavy metal contamination in farmed land has garnered great attention globally. Heavy metals in soil pose a severe risk to the security of agricultural products and public health due to their persistence, latency, and ease of entry into the food chain. In recent years, many scholars have carried out research on soil heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment under different conditions such as natural conditions, industrial and mining industries and developed transportation in different regions. Zhou et al.[11] found that Xiong’an New Area was affected by the production activities of surrounding enterprises. The contents of As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in some root soil samples exceeded the screening value standard for soil pollution risk of agricultural land (GB 15618—2018), and the exceeding ratios were 23.33%, 96.67%, 33.33%, 33.33% and 10.00%, respectively. Song et al.[12] evaluated the characteristics of heavy metal pollution in the surface soil of Fuping County, Hebei Province, and found that As and Cd exceeded the acceptable carcinogenic risk level (As is 10−5, Cd is 10−6). Kumar et al.[10] collected data on heavy metal-contaminated soils in India from 1991 to 2018. The average Cd content of all soil types exceeded the limit values, and the potential ecological risk values of Cd were greater than 320, reflecting a higher ecological risk. For the heavily polluted soil, according to the different pollution situation in our country, the remediation measures are taken according to local conditions. However, due to the wide area of contaminated soil and the complex composition of pollution sources, the current soil remediation work still faces huge problems.
OBJECTIVES To study the vertical distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soil, the relationship between soil heavy metals and soil nutrient elements, as well as the degree of pollution and potential ecological risks.
METHODS The contents of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn were measured using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS); As content was determined by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HG-AFS); P and K2O contents were determined by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF); N content was determined by oxidation combustion gas chromatography (GC); Hg content was determined by cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry (CV-AFS); Organic carbon content was determined by high-frequency combustion infrared absorption method (IR); potentiometric method (POT) was used to measure soil pH value. Statistical analysis and calculation of soil heavy metal content, pollution index, and ecological risk index were conducted using Excel 2016. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted using SPSS 26, and the degree of soil heavy metal pollution was evaluated using the geoaccumulation index (Igeo). Potential ecological risk index (RI) values were selected to evaluate potential ecological risks.
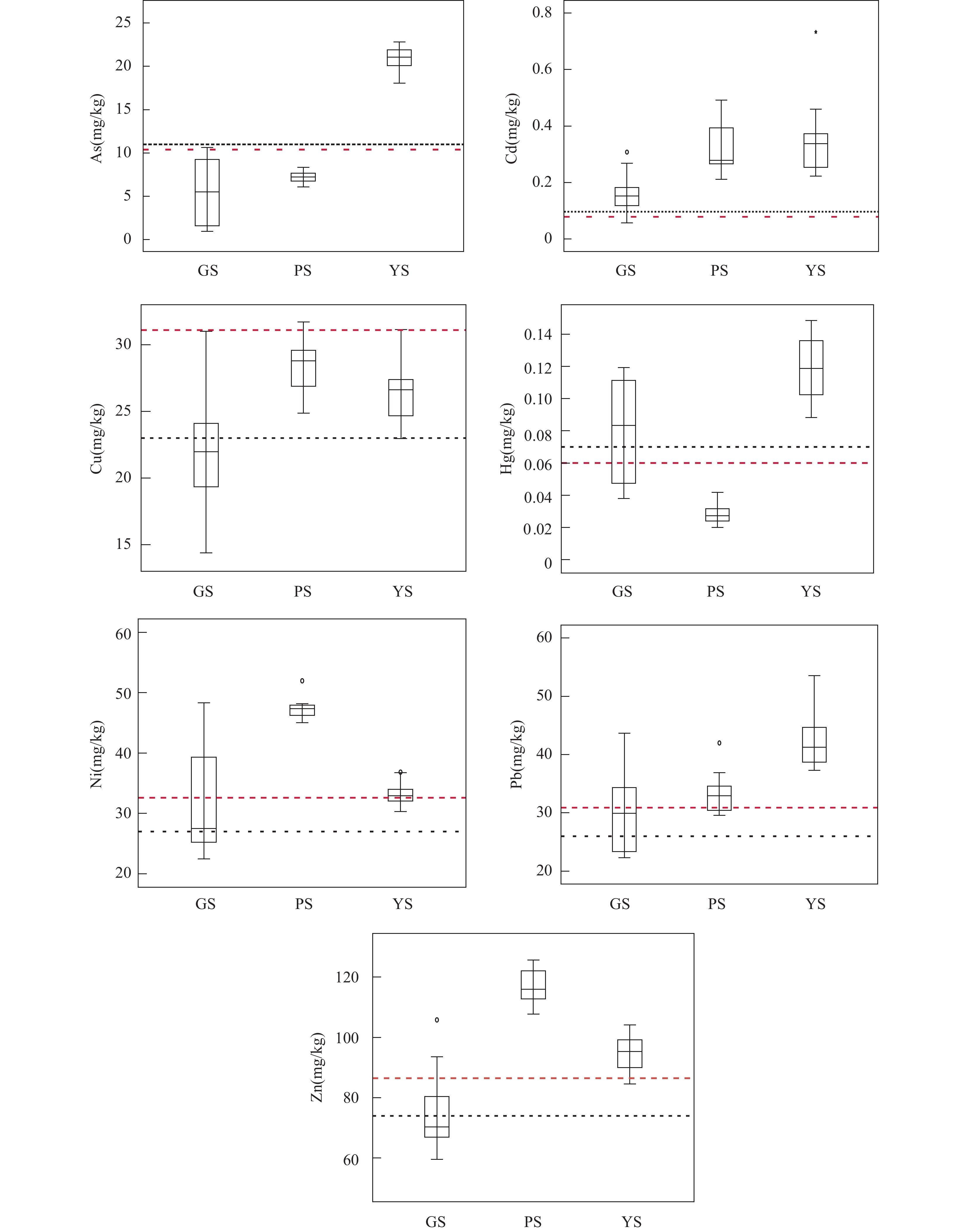
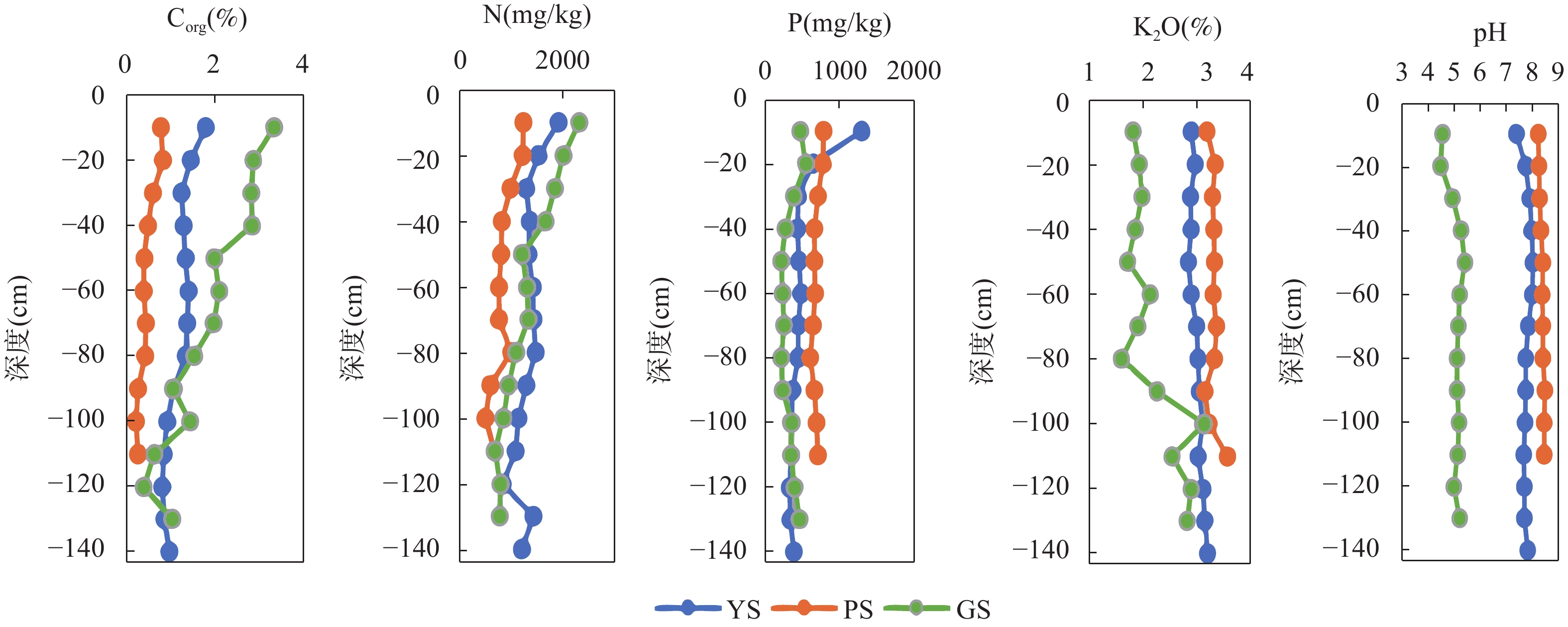
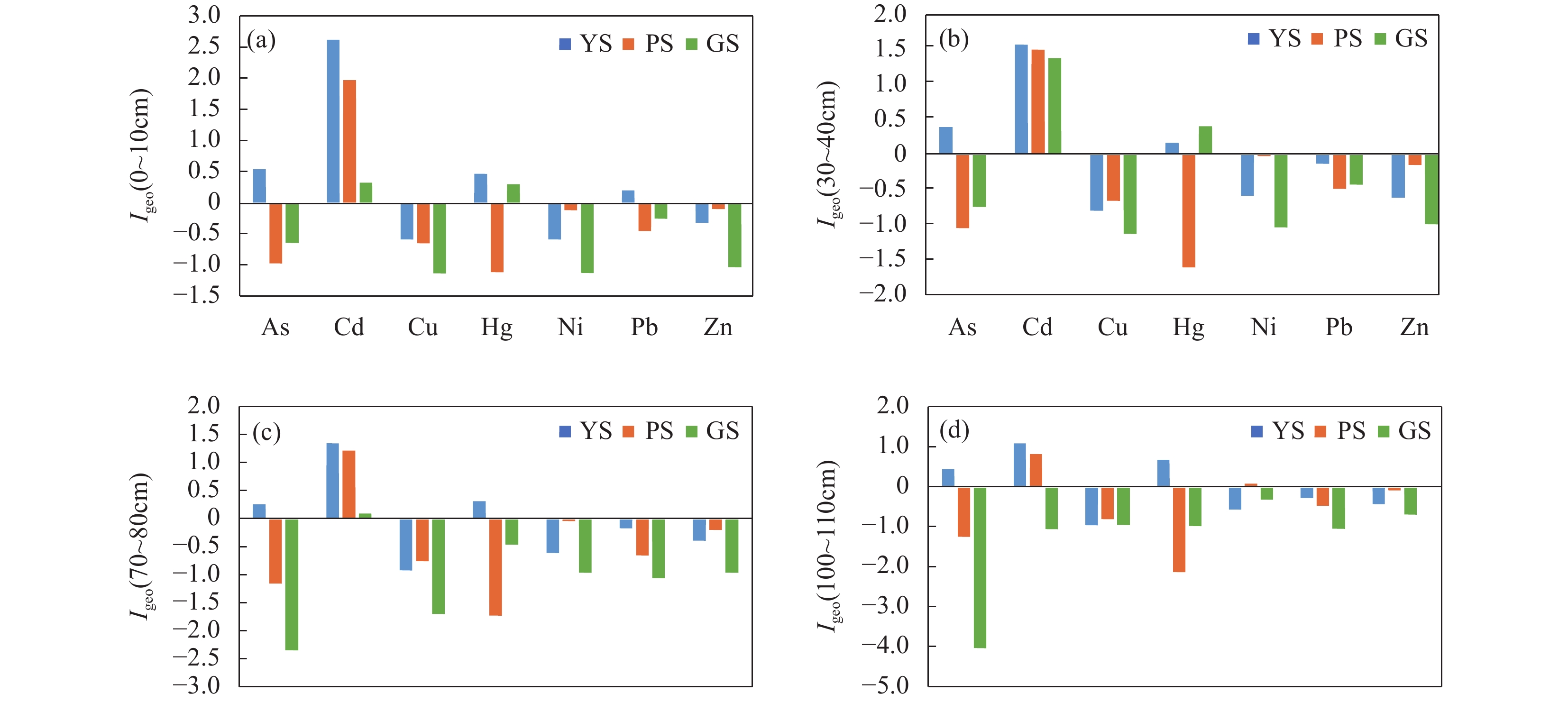
RESULTS The average contents of As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the soil of YS plot were 20.8mg/kg, 0.35mg/kg, 26.38mg/kg, 0.121mg/kg, 33.29mg/kg, 42.37mg/kg, and 94.47mg/kg, respectively; The average contents of As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the soil of PS plot were 7.21mg/kg, 0.32mg/kg, 28.32mg/kg, 0.028mg/kg, 47.34mg/kg, 33.29mg/kg, and 116.45mg/kg, respectively; The average contents of As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the soil of GS plot were 5.42mg/kg, 0.16mg/kg, 22.38mg/kg, 0.08mg/kg, 31.8mg/kg, 30mg/kg, and 75.03mg/kg, respectively. The concentrations of As, Cd, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn were higher than the national and Sichuan soil background values, indicating that these metals were relatively enriched in the soil of Muchuan County. The relationship between seven heavy metals at different soil depths was evaluated through Pearson correlation analysis (seen in Table 4). There was a significant positive correlation between heavy metals, indicating their widespread homology. In the PS profile, the correlation between Cd, Hg and organic carbon was very high, with correlation coefficients of 0.934 and 0.955, respectively (Fig.5); As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Zn showed a highly significant negative correlation with pH, and the correlation between Cd, Hg content and soil pH was shown in Fig.5, with correlation coefficients of −0.964 and −0.944, respectively. The content of heavy metals in soil was closely related to organic carbon and pH value, which should be attributed to the adsorption of organic matter and the fact that pH not only affected the electrostatic adsorption of heavy metals by soil particles, but also damaged the inert part of the parent material. Soil organic matter and pH value are important factors affecting the migration of heavy metals in soil. The surface soil had a high content of organic matter, multiple adsorption sites, and a high soil pH value, which reduced the solubility of heavy metals and thus the metal migration rate. Soil pollution assessment results. The Igeo values of Cu and Zn in all soil profiles were less than 0, indicating that the soil in the study area was not contaminated by these heavy metals. The Igeo value of Cd at four depths was significantly reduced. Except that the Igeo value at GS point was less than 1, YS and PS were greater than 1, indicating that the Cd pollution degree of corn land (YS, PS) was more serious than that of tea garden land (GS). This may be due to the difference of tillage conditions, and the Igeo value of surface soil at YS point was between 2 and 3, showing moderate-strong pollution. The Igeo values of As, Hg, Ni and Pb at four depths were all less than 1 and close to 0, indicating that the soil pollution was slight, which may be caused by human input or natural changes. In general, conventional agricultural practices lead to the enrichment of heavy metals in soils due to excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides, wastewater irrigation and atmospheric deposition. Zhao et al.[42] found that use of fertilizers and manure increased the content of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) by approximately 3% per year. The order of heavy metal pollution degree from high to low is Cd>Hg>As>Pb>Ni. Potential ecological risk assessment. According to the description of risk level, the YS plot had the highest potential risk index for Cd and Hg, and there was a significant ecological risk of Cd and Hg at depths of 0-140cm (80≤Ei<160), among which the surface soil Cd had a strong ecological risk (160≤Ei<320). It indicates that Cd pollution sources in the region may be affected by past agricultural activities, including fertilizers and pesticides. The soil Cd of PS plot exhibited strong ecological hazards (160≤Ei<320) at the depth of 0-30cm while exhibiting strong ecological hazards (80≤Ei<160) at 60-110cm. The Cd and Hg in surface soil at the GS plot site had moderate ecological risks (40≤Ei<80). The value of RI showed a strong ecological risk (300≤RI<600) at 0-10cm of the YS plot, and a moderate ecological risk (150≤RI<300) at 30-140cm. Moderate ecological hazards (150≤RI<300) were present in the PS plot, while mild ecological hazards (RI<150) were present at 60-110cm. The ecological hazards of GS plot at 0-130cm were relatively weak. The Ei values of heavy metals in soil decreased with the increase of depth, which was consistent with the evaluation results of Igeo pollution. The Ei values of Cd in the three profiles were relatively high, indicating that special attention should be paid to the control of heavy metal pollution.
CONCLUSIONS According to the results of soil vertical profile data, it can be concluded that heavy metal content tends to accumulate in the surface soil, and its content decreases with increasing depth. The Igeo value and Ei value also decrease with the increase of formation depth. The geoaccumulation index and potential ecological risk analysis indicate that Cd poses significant ecological risks to the local soil, and appropriate measures should be taken to strengthen pollution prevention and control in the area to avoid harm to human health. The content of heavy metals is closely related to soil nutrients and physicochemical properties, positively correlated with organic carbon content, and negatively correlated with pH value. According to the research results, it is suggested to carry out further research on the accumulation of heavy metals in soil, rationally assess its ecological harm, and ensure the safe use of land.
-

-
表 1 研究区不同类型土柱剖面取样点概况
Table 1. Sampling points of different types of soil column profiles in the study area.
采样地点 采样深度(cm) 土地利用类型 土壤类型 地质背景 可见特征描述 剖面YS 140 山坡旱地,
种植玉米黄色黏质土 三叠系雷口坡组(T2l),岩性为粉砂岩与白云岩、泥质灰岩互层,夹黑色碳质页岩 0~50cm灰黄色黏质土,50~140cm黄色黏质土 剖面PS 110 山坡旱地,
种植玉米紫色黏质土 侏罗系蓬莱镇组(J3p)岩性
以泥岩、砂岩和粉砂岩为主0~80cm紫色黏质土,80~110cm紫色黏质土,
土壤水分降低剖面GS 130 茶园地 灰色黏质土 三叠系须家河组(T3x) ,岩性主要为砂岩、粉砂岩、泥岩及煤层组成的沉积旋回 0~40cm,灰色黏质土,有机质较丰富;40~70cm,土壤颜色变黄,细砂成分增多;80~90cm,青灰色淤泥,水分增多;90~100cm,土壤变灰黑色,水分变少;100~120cm,青灰色黏质土;120~130cm,灰绿色,底部为页岩、泥岩 表 2 各指标分析测试检出限
Table 2. Detection limit of each index analysis.
分析项目 检出限 分析项目 检出限 As 0.5 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kgZn 4 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kgCd 0.03 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kgP 10 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kgCu 1. $ 0\mathrm{ } $ mg/kgCorg 0.10% Hg 0.0005 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kgK2O 0.05% Pb 2 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kgpH 0.1 Ni 2 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kgN 20 $ \mathrm{m} $ g/kg表 3 三个采样点土壤剖面重金属与土壤养分指标的Pearson相关性
Table 3. Pearson correlation between heavy metals in soil profiles and soil nutrient indicators at three sampling points.
采样地点 养分元素 As Cd Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 剖面YS N 0.186 0.813** 0.706** −0.419 −0.147 0.724** 0.135 P 0.401 0.947** 0.758** −0.188 −0.120 0.828** 0.307 K2O 0.155 −0.399 −0.486 0.795** 0.526 −0.669** 0.638* Corg 0.003 0.759** 0.764** −0.721** −0.340 0.861** −0.150 pH −0.492 −0.455 −0.120 −0.627* −0.088 −0.265 −0.836** 剖面PS N 0.814** 0.845** 0.828** 0.924** −0.160 −0.072 0.724* P 0.458 0.747** 0.504 0.632* −0.209 0.481 0.695* K2O −0.113 −0.266 0.047 −0.295 0.924** −0.121 0.424 Corg 0.865** 0.934** 0.865** 0.955** −0.283 0.065 0.717* pH −0.897** −0.964** −0.884** −0.944** 0.287 −0.223 −0.735** 剖面GS N 0.934** 0.448 −0.262 0.899** −0.765** 0.897** −0.612* P 0.186 0.144 0.661* 0.084 0.265 0.485 0.425 K2O −0.713** −0.237 0.801** −0.721** 0.937** −0.366 0.863** Corg 0.947** 0.552 −0.303 0.953** −0.824** 0.893** −0.673* pH −0.451 −0.039 −0.054 −0.358 0.227 −0.649* 0.110 注:“**”表示在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著;“*”表示在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 4 土壤剖面重金属之间的Pearson相关性
Table 4. Pearson correlation between heavy metals in soil profiles.
元素 As Cd Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn As 1 Cd 0.546** 1 Cu 0.187 0.644** 1 Hg 0.772** 0.141 −0.288 1 Ni −0.369* 0.141 0.683** −0.769** 1 Pb 0.822** 0.672** 0.310 0.566** −0.311 1 Zn 0.029 0.500** 0.783** −0.484** 0.864** 0.065 1 注:“**”表示在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著;“*”表示在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 5 三个采样点土壤剖面重金属潜在生态风险指数
Table 5. Potential ecological risk index of heavy metals in soil profiles of three sampling points.
采样地点 采样深度
(cm)$ {E}_{i} $ RI As Cd Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 剖面YS 10 21.9 278.4 5.0 83.3 5.0 8.7 1.2 403.5 30 21.1 141.6 4.3 72.9 4.9 7.8 1.0 253.6 60 20.0 125.3 4.5 66.7 5.1 6.9 1.0 229.6 90 18.0 95.7 3.7 88.6 4.7 6.4 1.1 218.1 110 20.6 96.5 3.8 96.9 5.1 6.2 1.1 230.1 140 20.7 146.6 4.3 90.5 5.6 6.0 1.2 274.9 剖面PS 10 7.7 177.3 4.8 27.8 6.9 5.5 1.4 231.4 30 8.0 171.6 5.0 22.5 7.2 6.0 1.4 221.7 60 7.0 103.3 4.7 16.8 7.4 5.0 1.3 145.5 90 6.3 80.5 4.1 15.2 7.0 4.8 1.3 147.6 110 6.3 80.1 4.3 13.7 8.0 5.4 1.4 119.2 剖面GS 10 9.6 56.6 3.4 74.2 3.4 6.3 0.7 154.3 30 9.7 101.8 3.8 78.6 3.9 6.2 0.8 204.8 60 6.9 33.8 3.5 64.8 4.2 5.0 0.8 119.1 90 2.3 64.2 3.0 31.6 5.2 3.9 0.9 111.0 110 0.9 21.6 3.9 30.4 6.0 3.6 0.9 67.5 130 1.5 85.1 5.0 25.7 7.4 3.8 1.2 129.7 -
[1] Chai L, Wang Y, Wang X, et al. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 125: 107507. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107507
[2] Zhang L X, Zhu G Y, Ge X, et al. Novel insights into heavy metal pollution of farmland based on reactive heavy metals (RHMs): Pollution characteristics, predictive models, and quantitative source apportionment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 360: 32−42. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.075
[3] Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, et al. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(1): 84−91. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.019
[4] Zhuo H, Wang X, Liu H, et al. Source analysis and risk assessment of heavy metals in development zones: A case study in Rizhao, China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2019, 42: 135−146.
[5] Pecina V, Brtnický M, Baltazár T, et al. Human health and ecological risk assessment of trace elements in urban soils of 101 cities in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 267: 129215.
[6] Yunus K, Zuraidah M A, John A. A review on the accumulation of heavy metals in coastal sediment of Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Ecofeminism and Climate Change, 2020, 1(1): 21−35. doi: 10.1108/EFCC-03-2020-0003
[7] 贺灵, 吴超, 曾道明, 等. 中国西南典型地质背景区土壤重金属分布及生态风险特征 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 384-396.
He L, Wu C, Zeng D M, et al. Soil heavy metal distribution and ecological risk characteristics in typical geological background areas of Southwestern China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 384-396.
[8] Zhang Q, Han G, Liu M, et al. Distribution and contamination assessment of soil heavy metals in the Jiulongjiang River catchment, Southeast China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16: 4674. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16234674
[9] Frišták V, Pipíška M, Lesný J, et al. Utilization of biochar sorbents for Cd2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+ ions separation from aqueous solutions: Comparative study[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 187(1): 4093.
[10] Kumar V, Sharma A, Kaur P, et al. Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: A state-of-the-art[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 216: 449−462. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.066
[11] 周亚龙, 王乔林, 王成文, 等. 雄安新区企业周边农田土壤-作物系统重金属污染风险及累积效应[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(12): 5977-5987.
Zhou Y L, Wang Q L, Wang C W, et al. Risk and cumulative effect of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil crop system around enterprises in Xiong’an[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42 (12): 5977-5987.
[12] 宋绵, 龚磊, 王艳, 等. 河北阜平县表层土壤重金属对人体健康的风险评估[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 133-144.
Song M, Gong L, Wang Y, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in surface soil of Fuping County, Hebei Province on human health[J]. Rock and Mineral Testing, 2022, 41(1): 133-144.
[13] Huang H B, Lin C Q, Yu R L, et al. Contamination assessment, source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in paddy soils of Jiulong River Basin, Southeast China[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9: 14736−14744. doi: 10.1039/C9RA02333J
[14] Barrena-González J, Contador J F L, Fernández M P. Mapping soil properties at a regional scale: Assessing deterministic vs. geostatistical interpolation methods at different soil depths[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14: 10049. doi: 10.3390/su141610049
[15] 谢龙涛, 潘剑君, 白浩然, 等. 基于GIS的农田土壤重金属空间分布及污染评价——以南京市江宁区某乡镇为例[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(2): 316-325.
Xie L T, Pan J J, Bai H R, et al. GIS based spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil—Taking a township in Jiangning District of Nanjing as an example[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 57 (2): 316-325.
[16] Ye X, Li H, Ma Y, et al. The bioaccumulation of Cd in rice grains in paddy soils as affected and predicted by soil properties[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2014, 14: 1407−1416. doi: 10.1007/s11368-014-0901-9
[17] 成晓梦, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等. 四川省沐川县西部地区土壤硒含量特征及影响因素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 808-819.
Cheng X M, Sun B B, He L, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium content in Western Muchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 808-819.
[18] 韩伟, 王乔林, 宋云涛, 等. 四川省沐川县北部土壤硒地球化学特征与成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1): 215-222.
Han W, Wang Q L, Song Y T, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of soil selenium in Northern Muchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 215-222.
[19] Müller G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2: 108−118.
[20] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control—A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975−1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[21] 魏复盛, 陈静生, 吴燕玉, 等. 中国土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 1991(4): 12−19,94.
Wei F S, Chen J S, Wu Y Y, et al. Study on the background values of soil environment in China[J]. Environmental Science, 1991(4): 12−19,94.
[22] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 21(2): 112-115.
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Tuo X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metal toxicity coefficient in potential ecological hazard index evaluation[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2008, 21(2): 112-115.
[23] 成杭新, 彭敏, 赵传冬, 等. 表生地球化学动力学与中国西南土壤中化学元素分布模式的驱动机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6): 159-191.
Cheng H X, Peng M, Zhao C D, et al. The driving mechanism of supergene chemical kinetics and the distribution pattern of chemical elements in soils in Southwest China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 159-191.
[24] Huang Y, Li T, Wu C, et al. An integrated approach to assess heavy metal source apportionment in peri-urban agricultural soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 299: 540−549. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.041
[25] Sun C, Liu J, Wang Y, et al. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(5): 517−523. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.063
[26] Pan L B, Ma J, Wang X L, et al. Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: Levels, sources and spatial distribution[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 148: 248−254. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.049
[27] Dumat C, Quenea K, Bermond A, et al. Study of the trace metal ion influence on the turnover of soil organic matter in cultivated contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 142(3): 521−529. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.027
[28] Huang B, Li Z, Li D, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metal(loid)s in aggregates of different size fractions along contaminated paddy soil profile[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(30): 23939−23952. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0012-4
[29] Kelepertzis E, Paraskevopoulou V, Argyraki A, et al. Evaluation of single extraction procedures for the assessment of heavy metal extractability in citrus agricultural soil of a typical Mediterranean environment (Argolida, Greece)[J]. 2015, 15(11): 2275.
[30] Sun R, Yang J, Xia P, et al. Contamination features and ecological risks of heavy metals in the farmland along shoreline of Caohai Plateau wetland, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 254: 126828. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126828
[31] 王美, 李书田. 肥料重金属含量状况及施肥对土壤和作物重金属富集的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(2): 466−480.
Wang M, Li S T. The status of heavy metal content in fertilizers and the impact of fertilization on heavy metal enrichment in soil and crops[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2014, 20(2): 466−480.
[32] Jiang B, Adebayo A, Jia J, et al. Impacts of heavy metals and soil properties at a Nigerian e-waste site on soil microbial community[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 362: 187−195. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.060
[33] Khaledian Y, Pereira P, Brevik E C, et al. The influence of organic carbon and pH on heavy metals, potassium, and magnesium levels in lithuanian podzols[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2017, 28(1): 345−354.
[34] Xu J, Kleja D B, Biester H, et al. Influence of particle size distribution, organic carbon, pH and chlorides on washing of mercury contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 109: 99−105. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.058
[35] Ahmad M, Soo lee S, Yang J E, et al. Effects of soil dilution and amendments (mussel shell, cow bone, and biochar) on Pb availability and phytotoxicity in military shooting range soil[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2012, 79: 225−231. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.01.003
[36] Huang B, Li Z, Huang J, et al. Aging effect on the leaching behavior of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, and Cd) in red paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(15): 11467−11477. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4386-x
[37] Zhang H, Luo Y, Makino T, et al. The heavy metal partition in size-fractions of the fine particles in agricultural soils contaminated by waste water and smelter dust[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 248: 303−312.
[38] Li X P, Feng L. Multivariate and geostatistical analyzes of metals in urban soil of Weinan industrial areas, northwest of China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 47: 58−65. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.11.041
[39] Li X, Yang H, Zhang C, et al. Spatial distribution and transport characteristics of heavy metals around an antimony mine area in Central China[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 170: 17−24. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.011
[40] Wang X P, Wang L Q, Zhang Q, et al. Integrated assessment of the impact of land use types on soil pollution by potentially toxic elements and the associated ecological and human health risk[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 299: 118911.1−118911.9.
[41] Novara A, Ruehl J, la Mantia T, et al. Litter contribution to soil organic carbon in the processes of agriculture abandon[J]. Solid Earth, 2015, 6(2): 425−432. doi: 10.5194/se-6-425-2015
[42] Zhao S, Qiu S, He P. Changes of heavy metals in soil and wheat grain under long-term environmental impact and fertilization practices in North China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2018, 41(15): 1970−1979. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2018.1485158
[43] 陈文轩, 李茜, 王珍, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833.
Chen W X, Li Q, Wang Z, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833.
[44] Yang Q, Li Z, Lu X, et al. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642: 690−700. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.068
[45] Wei M, Pan A, Ma R, et al. Distribution characteristics, source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil in Shiquan County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 171: 225−237. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.12.089
[46] 张小敏, 张秀英, 钟太洋, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属富集状况及其空间分布研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(2): 692−703. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.02.047
Zhang X M, Zhang X Y, Zhong T Y, et al. Study on the enrichment and spatial distribution of heavy metals in farmland soils in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(2): 692−703. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.02.047
-




 下载:
下载: