Discussion on Pretreatment Method for Extracting Rare Earth Elements from Weathered Crust Elution-deposited Rare Earth Ores
-
摘要:
传统观点认为,风化壳淋积型稀土矿床(即离子吸附型稀土矿床)中,稀土主要以吸附态赋存于风化壳黏土矿物表面,其他赋存形式占比较少。但近年来的同步辐射研究显示,稀土元素也同时以内层络合物形式存在,而内层络合物的存在可能会抑制稀土元素的离子交换。如何将风化壳淋积型稀土矿中各种形态的稀土元素有效地溶出,对于提高稀土资源利用率十分重要。本文选取南岭地区风化壳淋积型稀土矿石样品,选择混合酸(五酸)消解、盐酸消解、硝酸消解、硫酸铵浸提的前处理方式,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)测定,探讨样品中稀土元素的溶出情况。结果表明,采用混合酸(五酸)能够溶出样品中的全相稀土;盐酸或硝酸能够溶出以离子状态吸附于黏土矿物或铁锰氧化物中的稀土元素,以及以碳酸盐、磷酸盐等形式存在的稀土元素;硫酸铵浸提则只能将离子相的稀土元素置换出来。采用硝酸、盐酸溶出的稀土量,占混合酸(五酸)消解溶出稀土量(全相稀土)的71.7%~97.5%,硫酸铵浸提溶出的稀土量(离子相稀土)最低,仅是全相稀土量的9.1%~75.5%。Sc3+的离子半径明显小于其他稀土元素,其提取率也明显低于其他稀土元素;铈(Ce)不同于其他稀土元素的分异-富集特性,使其在硫酸铵浸提中提取率与其他稀土元素不一致。
-
关键词:
- 风化壳淋积型稀土矿 /
- 样品处理 /
- 稀土元素(REEs) /
- 酸溶 /
- 硫酸铵浸提 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUND Weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores are the dominant mineral resources in China[1-5]. The occurrence of rare earth elements (REEs) in weathering crust elution-deposited is very complicated. At present, the “ionic” rare earth extraction process can only use the “exchangeable adsorption state” rare earth elements, that is, the “ionic phase” rare earth elements, and other phase rare earth elements cannot be effectively recycled[6]. How to effectively dissolve various forms of rare earth elements in ion-adsorbed rare earth ore is very important to improve the utilization rate of rare earth resources.
OBJECTIVES To compare the extraction efficiency of REEs in weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores by different pretreatment methods and discuss the influencing factors.
METHODS Five pretreatment methods, being open mixed acid digestion (HCl+HNO3+HF+HClO4+H2SO4), nitric acid digestion with or without hydrogen peroxide, hydrochloric acid digestion with hydrogen peroxide and ammonium sulfate leaching, were used to extract REEs in six rare earth samples from the Nanling area. The content of REEs in samples was determined by ICP-MS. For ion-adsorbed rare earth minerals, the open digestion method of five acids can replace the complicated alkali melting method for the determination of REEs in samples under certain conditions. Nitric acid, hydrochloric acid digestion or ammonium sulfate leaching can only dissolve part of REEs in ion-adsorbed rare earth samples.
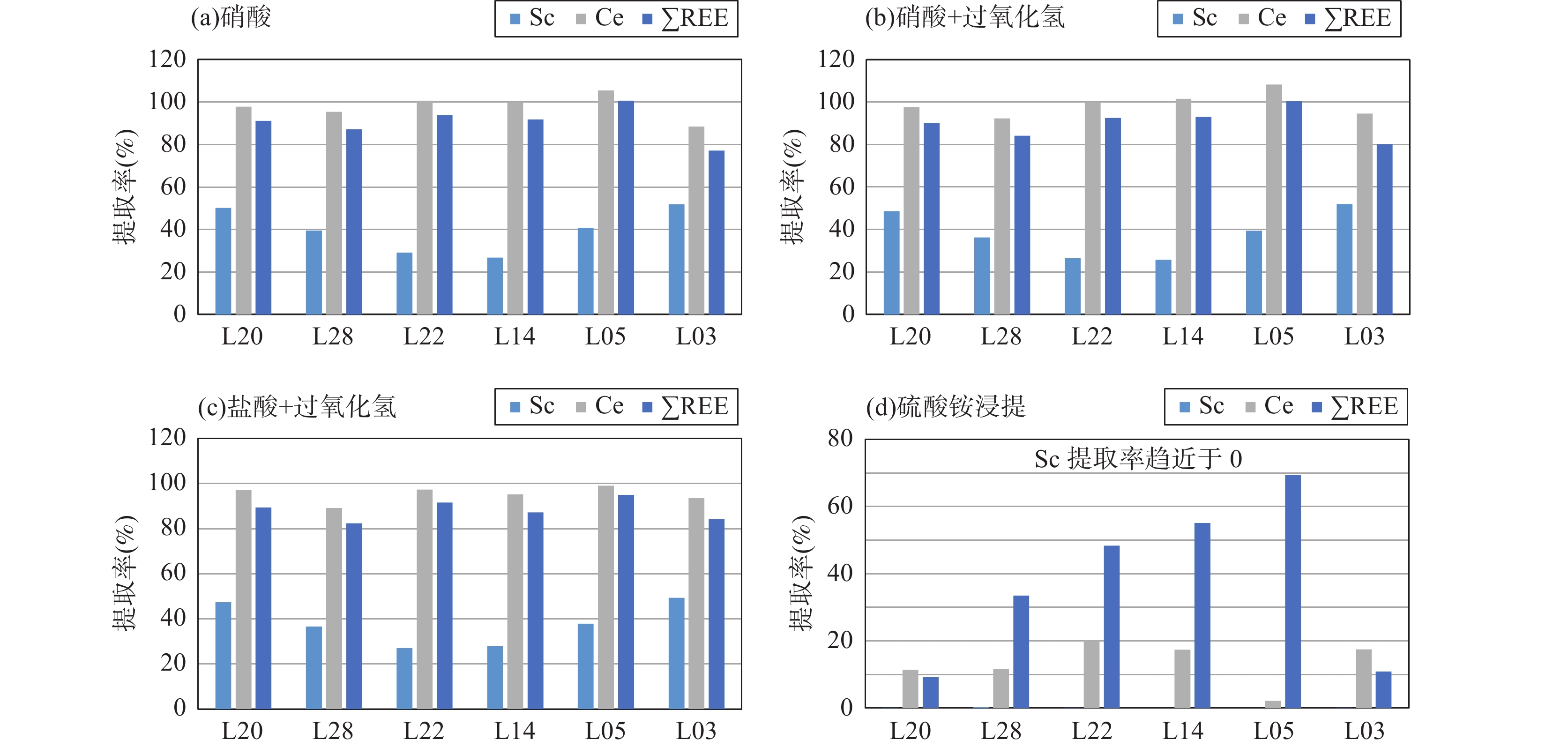
RESULTS The amount of REE extracted by different pretreatment methods is quite different. The results of mixed acid digestion (five acids) are the highest; the results of nitric acid with or without hydrogen peroxide digestion, hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide digestion are similar. The amount of REEs dissolved by nitric acid or hydrochloric acid digestion is slightly lower than mixed acid digestion. The amount of REEs dissolved by ammonium sulfate leaching is the lowest. The amount of REEs dissolved by 50% nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and other digestion methods accounts for 75.3%-91.7% of the total phase REEs, and the amount of REEs dissolved by ammonium sulfate leaching (ionic phase rare earth) only accounts for 9.1%-5.5% of the total phase REEs. The extraction rate of scandium (Sc) is much lower than that of total REEs in nitric acid and hydrochloric acid digestion, and Sc can not be dissolved by ammonium sulfate leaching. There is no correlation between the extraction rate of cerium (Ce) and other REE, the total extraction rate of light REE or the total extraction rate of REEs. The difference of the results by different pretreatments is closely related to the occurrence state of REEs in the samples. Mixed acid digestion can completely destroy the structure of the sample, and all the REEs in the sample can be dissolved. The REEs are differentiated and enriched in weathering crust layers. Some REEs still exist in the form of mineral facies after weathering. The content of REEs in ionic phase is closely related to weathering degree and mineral composition of each layer of weathering crust. Proportion of REEs content in different parts of weathering crust is not the same. Hydrochloric acid or nitric acid can dissolve REEs in the ionic state adsorbed in clay minerals or iron and manganese oxides, as well as REEs in the form of carbonates, phosphates, etc. Some REEs exist stably in silicate mineral lattices that cannot be completely dissolved by nitric or hydrochloric acid. Ammonium sulfate leaching can only dissolve the ionic REEs in the sample, so the digestion result of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid is lower than that of the whole phase REEs, and higher than that of ammonium sulfate leaching.
CONCLUTIONS The differences and influencing factors of REEs extracted from ion-adsorbed rare earth samples by different pretreatment methods are discussed, which can provide reference for further research on the extraction methods of REEs from elution-deposited rare earth ores. Mixed acid digestion can extract the full phase REEs in the weathered crust eluviated rare earth ore sample, which can be used to evaluate the total amount of REEs in the weathered crust eluviated rare earth ore. Nitric acid digestion, nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide digestion, hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide digestion cannot dissolve REEs in the silicate structure completely. Therefore, this method is suitable for evaluating the content of REEs in the form of ionic states, oxides, carbonates and phosphates in samples. Ammonium sulfate leaching can be used to evaluate the content of ionic phase REEs in weathering crust leaching type rare earth ores. The extraction rate of REEs is greatly affected by the chemical characteristics and occurrence state of REEs. Because the ionic radius of Sc3+ is obviously smaller than that of other REEs, Sc3+ can enter the crystal lattices of many rock-forming minerals in the form of homogeneity, which results in that ammonium sulfate leaching cannot dissolve Sc. Only a small amount of Sc can be dissolved by hydrochloric or nitric acid digestion. The different enrichment-differentiation characteristics of Ce and other REEs also make the extraction rate of Ce by ammonium sulfate leaching inconsistent with other REEs. The REEs with similar ionic radii often have similar extraction efficiency in the same pretreatment.
-

-
表 1 电感耦合等离子体质谱仪工作条件
Table 1. Operating parameters for ICP-MS measurements.
工作参数 设定值 工作参数 设定值 ICP功率 1300W 跳峰 1点/质量 冷却气流速 13.0L/min 停留时间 10ms/点 辅助气流速 1.2L/min 扫描次数 40次 雾化气流速 0.9L/min 测量时间 31s 取样锥孔径 1.0mm 截取锥孔径 0.9mm 超锥孔径 1.1mm 表 2 GBW07160和GBW07161采用混合酸(五酸)消解测定结果(n=3)
Table 2. Analytical results of GBW07160 and GBW07161 determined by open mixed acid digestion (n=3).
稀土
元素GBW07160 GBW07161 五酸消解结果
(μg/g)标准值
(μg/g)五酸消解结果
(μg/g)标准值
(μg/g)Sc 6.22 5.67~6.98 8.29 7.69±0.59 Y 2383 2386±205 965 976±47 La 85.3 93.8±8.5 2271 2362±145 Ce 24.7 28.3±4.1 178 187±8.1 Pr 33.8 37.2 440 447±24.8 Nd 170 189±17 1568 1595±86 Sm 115 129±17 286 285±25.9 Eu 1.10 1.55±0.26 62.3 64.8±3.63 Gd 210 234 234 226±26 Tb 46.4 49.1±5.1 31.6 34.6±2.2 Dy 315 314±44 182 183±17 Ho 68.1 65.5±5.4 31.9 35.7±4.0 Er 207 192±26 90.1 96±9 Tm 26.8 27.7±3.1 12.3 13.2±1.1 Yb 184 193±26 78.1 87.8±11 Lu 24.9 26.7±2.6 11.24 12.0±0.88 表 3 加标试验回收率 (n=3)
Table 3. Recovery rates of added standard tests (n=3).
样品
L04硝酸消解 硝酸+双氧水消解 盐酸+双氧水消解 硫酸铵浸提 加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)Sc 6.00 6.48 108 6.00 5.96 99.4 6.00 5.43 90.5 200 215.4 108 Y 6.00 6.50 108 6.00 5.72 95.3 6.00 6.19 103 200 183.2 91.6 La 6.00 6.84 114 6.00 6.86 114 6.00 5.99 100 200 212.9 106 Ce 6.00 6.29 105 6.00 6.53 109 6.00 6.60 110 200 208.1 104 Pr 6.00 5.75 96 6.00 6.08 101 6.00 7.12 119 200 192.0 96.0 Nd 6.00 5.66 94 6.00 5.92 98.7 6.00 6.40 107 200 177.9 89.0 Sm 6.00 6.43 107 6.00 6.57 109 6.00 6.49 108 200 203.4 102 Eu 6.00 6.14 102 6.00 6.28 105 6.00 6.18 103 200 200.6 100 Gd 1.50 1.44 96 1.50 1.70 113 1.50 1.61 107 80.0 80.4 100 Tb 1.50 1.62 108 1.50 1.68 112 1.50 1.63 109 80.0 80.2 100 Dy 1.50 1.45 96 1.50 1.67 111 1.50 1.64 109 80.0 80.1 100 Ho 1.50 1.61 108 1.50 1.61 107 1.50 1.57 105 80.0 82.8 103 Er 1.50 1.62 108 1.50 1.67 111 1.50 1.37 91.6 80.0 84.3 105 Tm 1.50 1.55 103 1.50 1.57 105 1.50 1.57 104 80.0 80.9 101 Yb 1.50 1.60 106 1.50 1.63 109 1.50 1.60 106 80.0 77.7 97.1 Lu 1.50 1.50 100 1.50 1.56 104 1.50 1.58 105 80.0 83.7 105 样品
L28硝酸消解 硝酸+双氧水消解 盐酸+双氧水消解 硫酸铵浸提 加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)加标量
(μg)回收量
(μg)回收率
(%)Sc 6.00 6.55 109 6.00 6.55 109 6.00 5.87 97.9 100 106.6 107 Y 6.00 6.10 102 6.00 6.27 104 6.00 5.92 98.6 100 105.1 105 La 6.00 6.76 113 6.00 6.88 115 6.00 4.93 82.1 100 107.6 108 Ce 6.00 6.18 103 6.00 6.56 109 6.00 6.14 102 100 106.8 107 Pr 6.00 6.16 103 6.00 6.10 102 6.00 6.68 111 100 110.9 111 Nd 6.00 6.13 102 6.00 6.19 103 6.00 5.04 84.0 100 116.6 117 Sm 6.00 6.55 109 6.00 6.45 107 6.00 5.95 99.2 100 98.9 98.9 Eu 6.00 6.35 106 6.00 6.31 105 6.00 6.17 103 100 118.4 118 Gd 1.50 1.64 109 1.50 1.79 119 1.50 1.75 116 4.00 4.09 102 Tb 1.50 1.61 108 1.50 1.54 103 1.50 1.56 104 4.00 3.88 96.9 Dy 1.50 1.44 96.0 1.50 1.70 114 1.50 1.57 104 4.00 4.31 108 Ho 1.50 1.61 107 1.50 1.57 105 1.50 1.55 103 4.00 4.17 104 Er 1.50 1.56 104 1.50 1.69 113 1.50 1.46 97.1 4.00 3.92 98.0 Tm 1.50 1.52 102 1.50 1.49 100 1.50 1.53 102 4.00 4.03 101 Yb 1.50 1.51 100 1.50 1.56 104 1.50 1.50 100 4.00 3.61 90.3 Lu 1.50 1.52 102 1.50 1.55 103 1.50 1.52 102 4.00 4.01 100 表 4 不同前处理方法测得稀土总量与提取率 (n=3)
Table 4. Content and extraction rates of REEs by different pretreatment methods (n=3).
样品前处理方式 六个离子吸附型稀土样品稀土总量测定结果(μg/g) L20 L28 L22 L14 L05 L03 混合酸 208 344 310 511 771 152 硝酸 178 275 276 439 752 109 硝酸+过氧化氢 176 265 272 444 737 113 盐酸+过氧化氢 175 259 267 419 707 119 硫酸铵浸提 19.0 106 160 308 581 15.4 样品前处理方式 六个离子吸附型稀土样品稀土总量提取率(%) L20 L28 L22 L14 L05 L03 硝酸 85.6 79.9 89.0 85.9 97.5 71.7 硝酸+过氧化氢 84.6 77.0 87.7 86.9 95.6 74.3 盐酸+过氧化氢 84.1 75.3 86.1 82.0 91.7 78.3 硫酸铵浸提 9.1 30.8 51.7 60.3 75.5 10.2 注:提取率为各种方法提取稀土结果与混合酸(五酸)消解结果(全相稀土)相比的百分数。 -
[1] 池汝安, 田军. 风化壳淋积型稀土矿评述[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2007, 51(6): 641−650. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2007.06.001
Chi R A, Tian J. Review of weathered crust rare earth ore[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2007, 51(6): 641−650. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2007.06.001
[2] 赵芝, 王登红, 陈郑辉, 等. 南岭离子吸附型稀土矿床成矿规律研究新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(12): 2814−2827. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.12.016
Zhao Z, Wang D H, Chen Z H, et al. Progress of research on metallogenic regularity of ion-adsorption type REE deposit in the Nanling Range[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(12): 2814−2827. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.12.016
[3] 赵芝, 王登红, 王成辉, 等. 离子吸附型稀土找矿及研究新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6): 1454−1465. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.021
Zhao Z, Wang D H, Wang C H, et al. Progress in prospecting and research of ion-adsorption type REE deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(6): 1454−1465. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.021
[4] 雒恺, 马金龙. 花岗岩风化过程中稀土元素迁移富集机制研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(7): 692−708. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.7.dqkxjz202207003
Luo K, Ma J L. Recent advances in migration and enrichment of rare earth elements during chemical weathering of granite[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(7): 692−708. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.7.dqkxjz202207003
[5] 池汝安, 张臻悦, 余霞军, 等. 风化淋积型稀土矿研究进展[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(6): 1178−1192.
Chi R A, Zhang Z Y, Yu X J, et al. Research process of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(6): 1178−1192.
[6] 丁嘉榆. 离子型稀土矿开发的历史回顾——纪念赣州有色冶金研究所建所60周年[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2012, 3(4): 14−19.
Ding J Y. Historical review of the ionic rare earth mining: In honor of the 60 anniversary of GNMRI[J]. Nonferrous Metal Science and Engineering, 2012, 3(4): 14−19.
[7] Yang M J, Liang X L, Ma L Y, et al. Adsorption of REEs on kaolinite and halloysite: A link to the REE distribution on clays in the weathering crust of granite[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 525: 210−217. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.07.024
[8] 王臻, 肖仪武, 冯凯. 离子吸附型稀土矿成矿特点及元素赋存形式[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2021(6): 43−51.
Wang Z, Xiao Y W, Feng K. Metallogenic characteristics and occurrence of REE in ion adsorption type rare earth deposits[J]. Nonferrous Metal (Mineral Processing Section), 2021(6): 43−51.
[9] Mukai H, Kon Y, Sanematsu K, et al. Microscopic analyses of weathered granite in ion-absorption rare earth deposit of Jianxi Province, China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 2045−2322. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58985-6
[10] 佘海东, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 稀土元素在热液中的迁移与沉淀[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(12): 3567−3581.
She H D, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al. Migration and precipitation of rare earth elements in the hydrothermal fluids[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(12): 3567−3581.
[11] 吴石头, 王亚平, 孙德忠, 等. 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定稀土矿石中15种稀土元素——四种前处理方法的比较[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(1): 12−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.003
Wu S T, Wang Y P, Sun D Z, et al. Determination of 15 rare earth elements in rare earth ores by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry: A comparison of four different pretreatment methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(1): 12−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.003
[12] 宋旭东, 樊小伟, 陈文, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定离子吸附型稀土矿中全相稀土总量[J]. 冶金分析, 2018, 38(6): 19−24. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.010305
Song X D, Fan X W, Chen W, et al. Determination of total-phase rare earth content in ion-adsorption rare earth ore by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2018, 38(6): 19−24. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.010305
[13] 张磊, 周伟, 朱云, 等. 硫酸铵溶液淋滤-电感耦合等离子体质谱测定离子相稀土分量的方法优化[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(5): 518−525. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712110192
Zhang L, Zhou W, Zhu Y, et al. An optimized method for determination of ionic phase rare earth elements by ICP-MS using ammonium sulfate leaching[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(5): 518−525. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712110192
[14] 池汝安, 田君, 罗仙平, 等. 风化壳淋积型稀土矿的基础研究[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2012, 3(4): 1−13. doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2012.04.010
Chi R A, Tian J, Luo X P, et al. The basic research on the weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2012, 3(4): 1−13. doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2012.04.010
[15] 施意华, 邱丽, 唐碧玉, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定离子型稀土矿中离子相稀土总量及分量[J]. 冶金分析, 2014, 34(9): 14−19. doi: 10.13228/j.issn.1000-7571.2014.09.003
Shi Y H, Qiu L, Tang B Y, et al. Determination of total ionic-phase rare earth and component in ion-adsorption rare earth ore by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2014, 34(9): 14−19. doi: 10.13228/j.issn.1000-7571.2014.09.003
[16] 刘艳珠, 丁正雄, 孔维长, 等. 离子吸附型稀土浸取试剂和富集回收技术的演变——从抑杂浸取到强化浸取及分阶段的选择——强化浸取[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2023, 41(3): 610−622.
Liu Y Z, Ding Z X, Kong W Z, et al. Evolution of leaching reagents and enrichment recovery technology of ion adsorption rare earths: Leaching strategy from impurity suppression to enhancing and selection-enhancing in stages[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2023, 41(3): 610−622.
[17] 白金峰, 张勤, 孙晓玲, 等, 高分辨电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地球化学样品中钪钇和稀土元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2011, 30(1): 17-22.
Bai J F, Zhang Q, Sun X L, et al. Determination of Sc, Y and rare earth elements in geochemical samples by high resolution inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(1): 17-22.
[18] 刘贵磊, 许俊玉, 温宏利, 等. 动态反应池-电感耦合等离子体质谱法精确测定配分差异显著的重稀土元素[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2016, 36(1): 176−183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2016.01.024
Liu G L, Xu J Y, Wen H L, et al. Determination of heavy rare earth elements of special rare earth ores by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with a dynamic reaction cell[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2016, 36(1): 176−183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2016.01.024
[19] 时晓露, 凤海元. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定离子吸附型稀土矿中16种离子吸附型稀土元素的含量[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2016, 52(10): 1230−1233.
Shi X L, Feng H Y. ICP-MS determination of 16 ionic adsorptive rare earth elements in ionic rare earth ores[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2016, 52(10): 1230−1233.
[20] 张磊, 李迎春, 屈文俊, 等. 离子吸附型稀土监控样定值研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 878−885. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202004230058
Zhang L, Li Y C, Qu W J, et al. Preparation of ion-adsorption type REE monitoring samples[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 878−885. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202004230058
[21] 苏春风. 电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定稀土矿中16种稀土元素含量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2020, 10(6): 28−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2020.06.007
Su C F. Determination of 16 rare elements in rare earth ores by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 10(6): 28−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2020.06.007
[22] 罗武平, 李光来, 李成祥, 等. 江西相山下家岭稀土矿物风化壳剖面地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(3): 237−246.
Luo W P, Li G L, Li C X, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the weathered crust profile in the Xiajialing REE deposit of the Xiangshan area, Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2019, 39(3): 237−246.
[23] 黄健, 谭伟, 梁晓亮, 等. 富稀土副矿物的风化特征及其对稀土成矿过程的影响——以广东仁居离子吸附型稀土矿床为例[J]. 地球化学, 2022, 51(6): 684-695. Huang J, Tan W, Liang X L, et al. Weathering characters of REE-bearing accessory minerals and their effects on REE mineralization in Renju regolith-hosted REE deposits in Guangdong Province[J]. 地球化学, 2022, 51(6): 684-695.
[24] 梁晓亮, 谭伟, 马灵涯, 等. 离子吸附型稀土矿床形成的矿物表/界面反应机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(1): 29−41.
Liang X L, Tan W, Ma L Y, et al. Mineral surface reaction constraints on the formation of ion-adsorption rare earth element deposits[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(1): 29−41.
[25] 伍普球, 周靖文, 黄健, 等. 离子吸附型稀土矿床中稀土的富集-分异特征: 铁氧化物-黏土矿物复合体的约束[J]. 地球化学, 2022, 51(3): 271−282.
Wu P Q, Zhou J W, Huang J, et al. Enrichment and fractionation of rare earth elements in ion-adsorption rare earth elements deposits: Constraints of iron oxide-clay mineral composites[J]. Geochimica, 2022, 51(3): 271−282.
[26] 范晨子, 张誉, 陈郑辉, 等. 江西赣南风化淋滤型稀土矿床中粘土矿物研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(5): 803−810.
Fan C Z, Zhang Y, Chen Z H, et al. The study of clay minerals from weathered crust rare earth ores in Southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2015, 34(5): 803−810.
[27] 王长兵, 倪光清, 瞿亮, 等. 花岗岩风化壳中Ce地球化学特征及其找矿意义——以滇西岔河离子吸附型稀土矿床为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 10(5): 1013−1028. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2021.05.008
Wang C B, Ni G Q, Qu L, et al. Ce geochemical characteristics of granite weathering crust and its prospecting significance: A case study of Chahe ion adsorption rare earth deposit in Western Yunnan[J]. Mineral Desposits, 2021, 10(5): 1013−1028. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2021.05.008
[28] Williams-Jones A E, Vasyukova O V. The economic geology of scandium, the runt of the rare earth element litter[J]. Economic Geology, 2018, 113(4): 973−988. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.2018.4579
[29] 陶旭云, 王佳新, 孙嘉, 等. 钪矿床类型与成矿机制[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(5): 1023−1038.
Tao X Y, Wang J X, Sun J, et al. Main types and metallogenic mechanism of scandium deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(5): 1023−1038.
[30] Chakhmouradian A R, Wall F. Rare earth elements: Minerals, mines, magnets (and more)[J]. Elements, 2012, 8(5): 333−340. doi: 10.2113/gselements.8.5.333
-



 下载:
下载:

