Laser-based Green and Efficient Sample Preparation Procurement for Geological Samples with Complex Matrices
-
摘要:
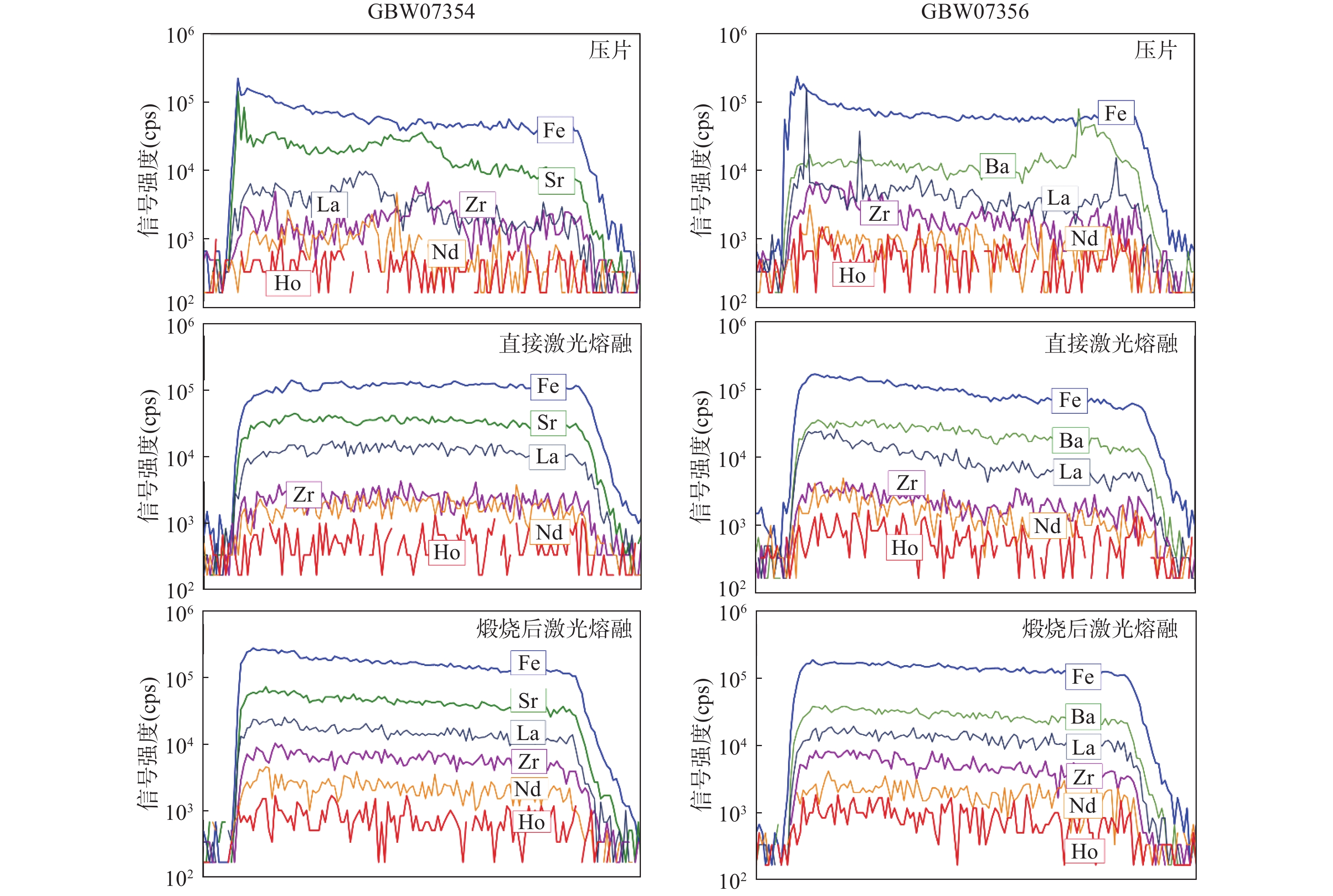
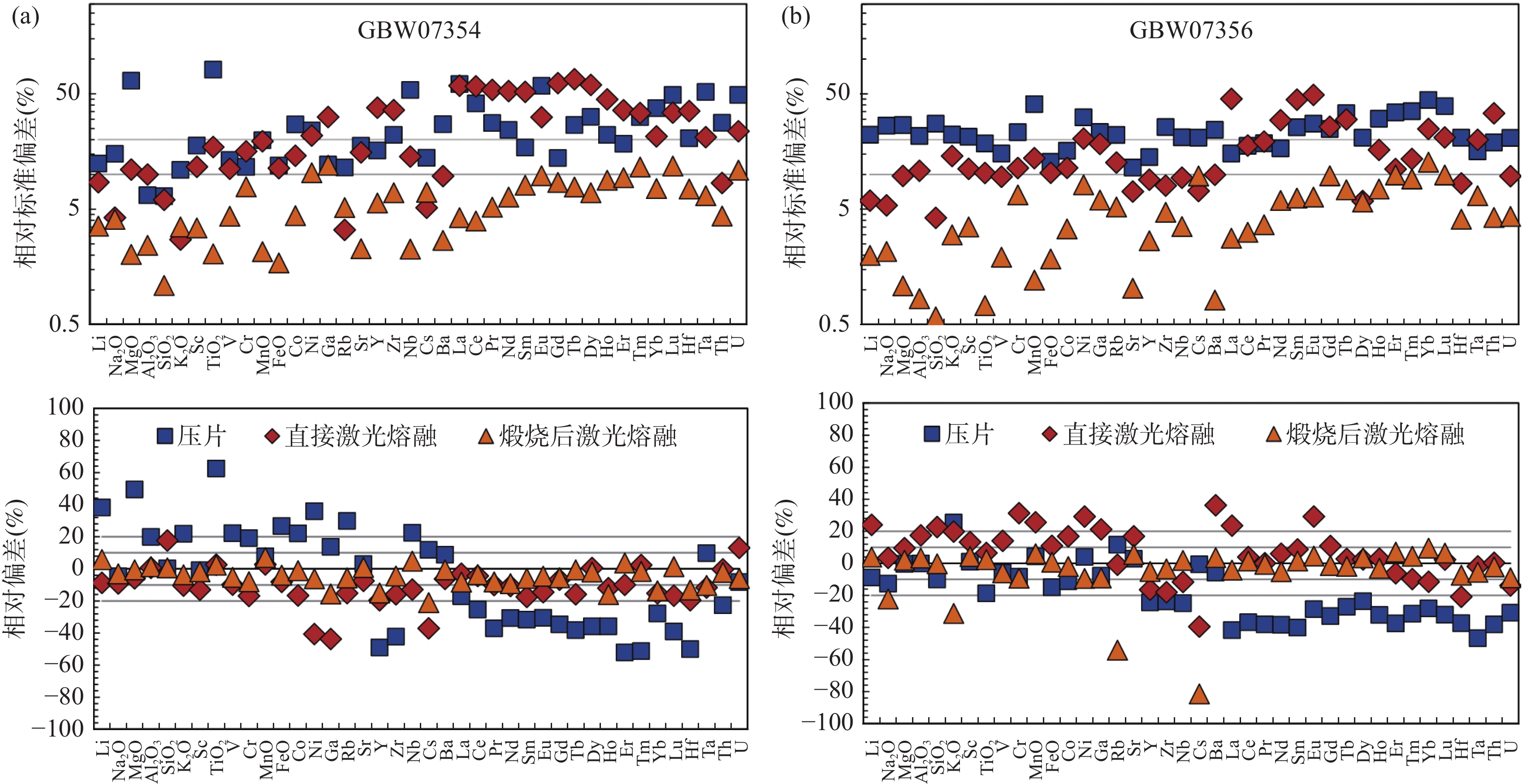
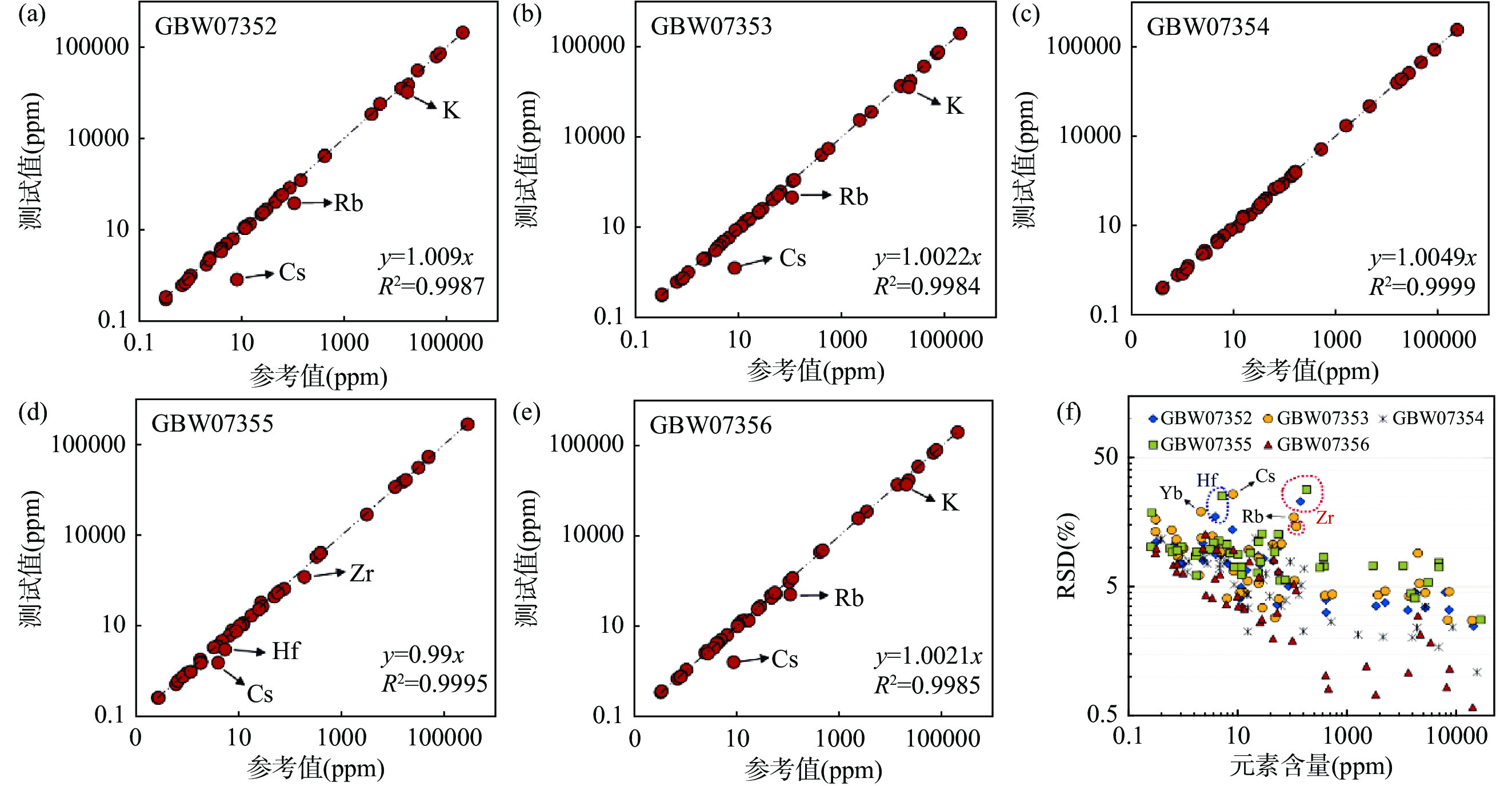
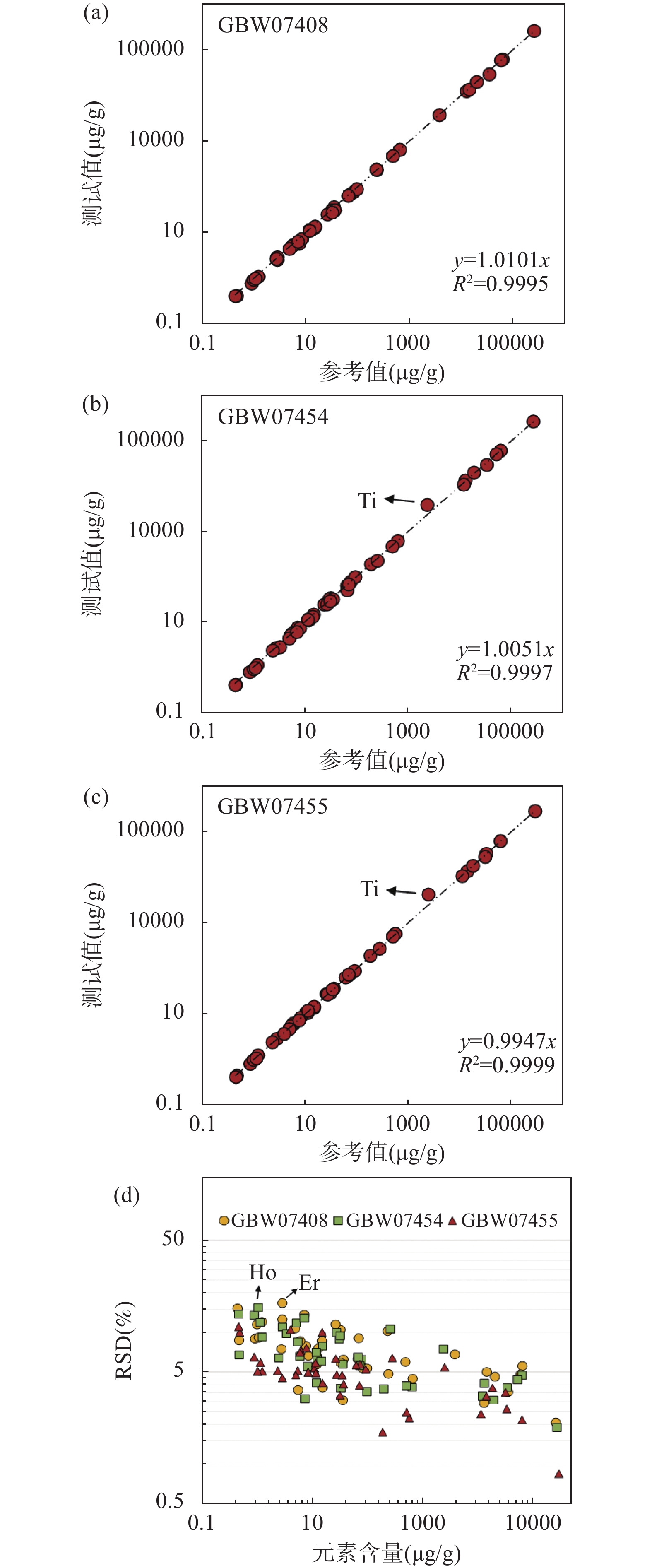
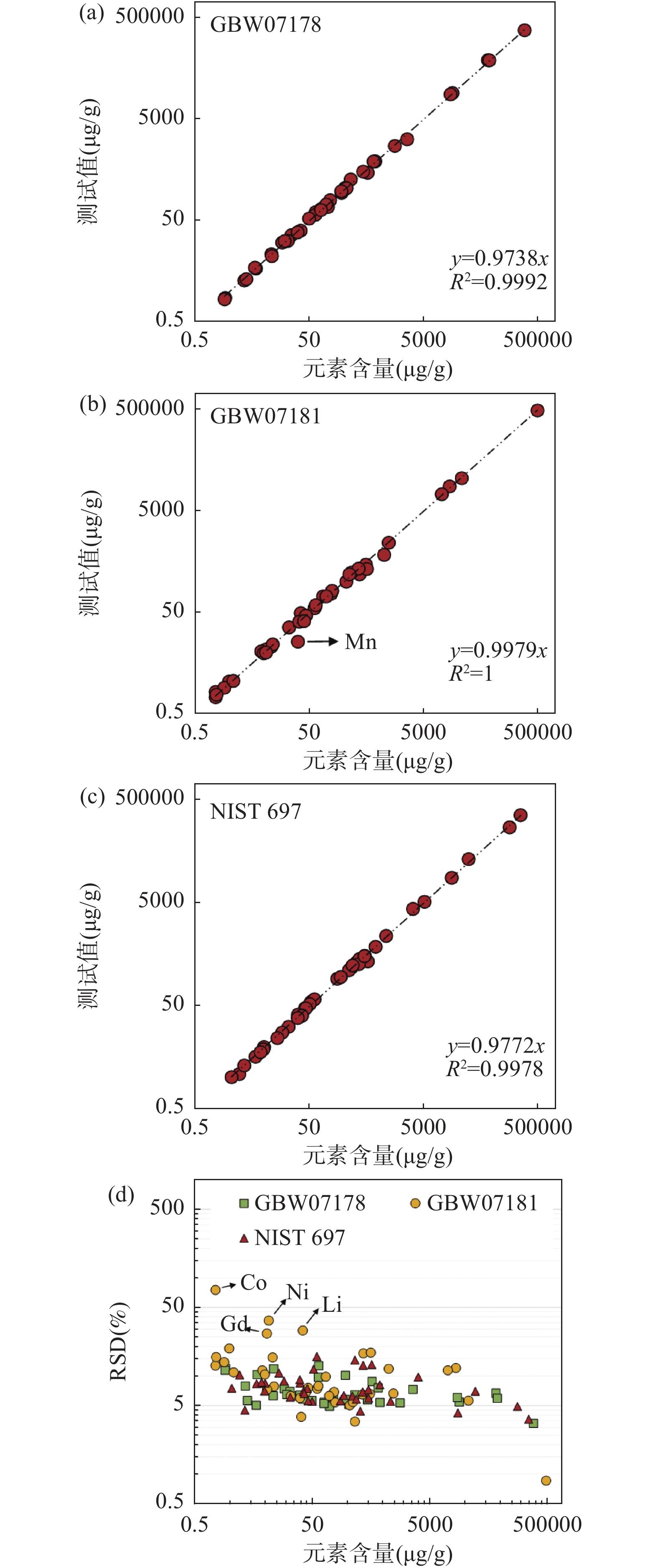
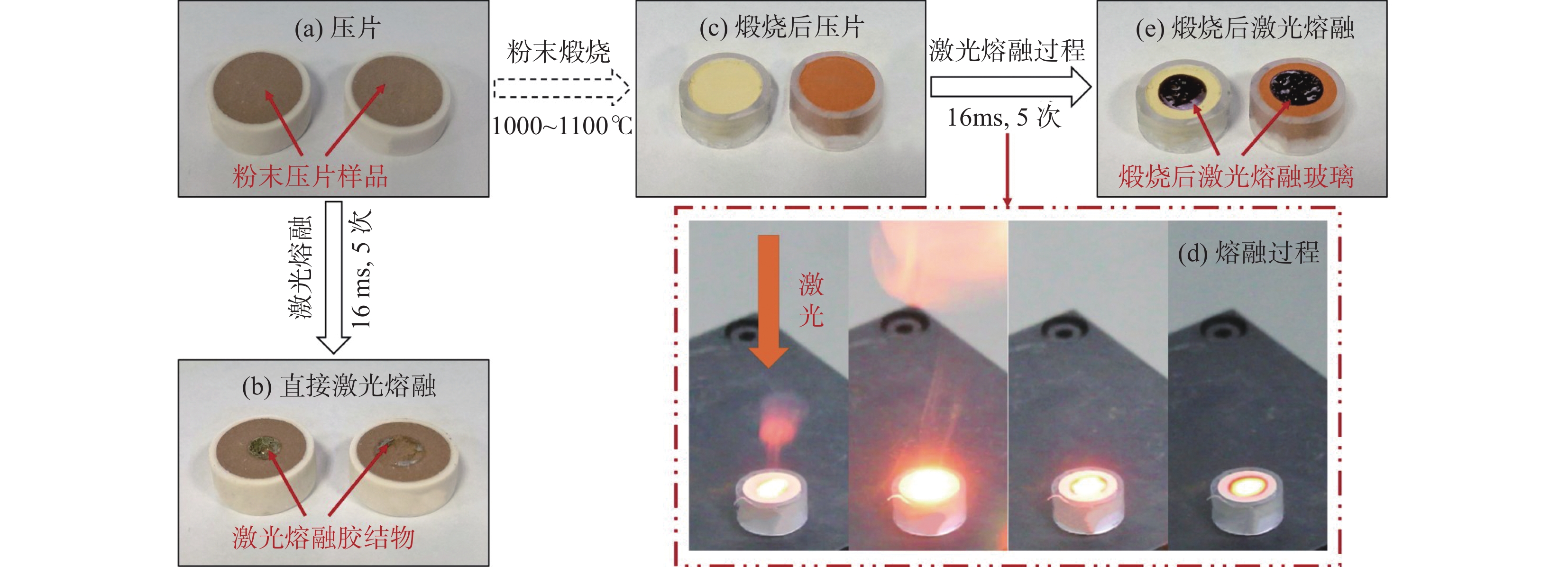
全岩地质样品主微量元素组成分析可为研究地球演化、矿床成因、矿产资源分布等地球科学问题提供重要的基础数据。激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)技术可以直接固体进样,避免了传统分析技术繁琐的湿化学消解流程,不仅低污染、低消耗,而且分析速度快,已经成为最有力的元素分析手段之一。但激光剥蚀进样量小,采样无法代表复杂、不均一样品的化学组成,阻碍了其在全岩主、微量元素分析中的应用。将复杂地质样品制备成均一、稳定的样品靶,是开发LA-ICP-MS全岩地质样品分析方法的关键。本文建立了针对复杂地质样品LA-ICP-MS全岩分析的绿色、高效前处理技术。首先将样品在1000~1100℃下煅烧去除挥发份,压制成片后用高能量、宽脉宽红外激光照射熔融,最终得到均一、稳定的样品玻璃。相比直接粉末压片的样品,该技术将海洋沉积物标准物质GBW07354和GBW07356中各元素的平均分析精密度分别提高了7.7倍和3.9倍。优化后的前处理技术已应用于海洋沉积物、土壤和铝土矿标准物质中主微量元素的快速准确分析。海洋沉积物标准物质中大部分元素的测试值与参考值的相对偏差都在10%以内;土壤成分标准物质中大部分主量元素、稀土元素(REEs)、其他微量元素的测试值与参考值的相对偏差分别在5%、20%和15%以内;铝土矿标准样品中测试元素达到40个,首次给出了Sc和W元素的参考值。本文建立的样品前处理技术可快速将海洋沉积物、土壤和铝土矿标准样品制备成均一稳定的玻璃,使LA-ICP-MS技术可直接较好地应用于复杂地质全岩样品(海洋沉积物、土壤和铝土矿)元素分析中,进一步提高了地质样品主微量元素的测试效率。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Knowledge of the chemical composition of whole-rock geological samples is the basic work of geochemical research. Laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) has become the most powerful tools of elemental analysis as its advantages of direct solid sampling, avoiding the cumbersome wet chemical digestion process of traditional analytical techniques, low-pollution and low-consumption and high-efficiency. However, the small sample volume of laser ablation cannot represent the chemical composition of complex and inhomogeneous samples, resulting in poor analytical precision and accuracy, which hinders its application in whole-rock bulk analysis. It is critical to prepare complex whole-rock geological samples into homogeneous and stable sample targets.
OBJECTIVES To establish a green and efficient pretreatment technique for LA-ICP-MS whole rock analysis of complex geological samples.
METHODS The samples were first calcined at 1000-1100℃ to remove volatiles, pressed into pellets, and then melted by high-energy wide pulse width infrared laser irradiation to finally obtain a homogeneous and stable sample glass.
RESULTS Compared with pressed powder pellets, the new sample preparation procurement improved the analytical precision of each element in marine sediments GBW07354 and GBW07356 by an average of 7.7 times and 3.9 times, respectively. The deviation between the measured values and reference values of most elements in marine sediment samples was within 10%; the deviation between the measured values and reference values of most major elements, REEs, and other trace elements in soil composition standards was within 5%, 20%, and 15%, respectively; the number of elements measured in bauxite samples reached 40, and the compositions of Sc and W elements were given for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS Rapid and accurate analysis of major and trace elements in marine sediment, soil, and bauxite standard samples has been determined through the optimized pretreatment technique. The sample preparation procurement established in this paper allows the LA-ICP-MS technique to be directly and better applied to the elemental analysis of complex geological whole rock samples, further improving the efficiency of major and trace element analysis in geological samples.
-

-
表 1 仪器设备及测试参数
Table 1. Instrumental operating conditions.
高能量红外激光 激光剥蚀系统 ICP-MS 工作条件 参数 工作条件 参数 工作条件 参数 激光类型 Nd:YAG 激光类型 ArF 准分子激光 射频功率 1350W 波长 1.064μm 波长 193nm 等离子体气流量 14.0L/min 脉冲宽度 0.1~20ms 脉冲宽度 15ns 辅助气流量 1.0L/min 激光频率 2Hz 能量密度 8.0J/cm2 载气类型 氩气 操作电流 300A 束斑大小 44μm 载气气流 0.88L/min 控制系统 PCL 激光频率 8Hz 采样深度 5mm 电源 AC220V±10%,50Hz 载气类型 氦气 同位素测定 7Li,23Na,25Mg,27Al,29Si,31P,39K,42Ca,45Sc,49Ti,51V,52Cr,55Mn,57Fe,59Co,60Ni,65Cu,66Zn,71Ga,85Rb,88Sr,89Y,90Zr,93Nb,133Cs,137Ba,139La,140Ce,141Pr,143Nd,147Sm,151Eu,157Gd,159Tb,163Dy,165Ho,166Er,169Tm,173Yb,175Lu,179Hf,181Ta,182W,195Pt,197Au,205Tl,208Pb,209Bi,232Th,238U 冷却系统 内部循环水 载气流量 0.63L/min 驻留时间/元素 10ms 检测器模式 双模式 表 2 待测标准物质的烧失量和氧化物总量
Table 2. Loss on ignition and total oxides of the standard materials to be measured.
标准物质类型 标准物质编号 烧失量
(%)氧化物总量
(%)海洋沉积物标准物质 GBW07352 16.98 83.02 GBW07353 16.60 83.40 GBW07354 8.37 91.63 GBW07355 7.92 92.08 GBW07356 16.30 83.70 土壤成分分析标准物质 GBW07408 9.25 90.75 GBW07454 8.64 91.36 GBW07455 6.85 93.15 铝土矿标准物质 NIST697 22.17 77.83 GBW 07178 14.91 85.09 GBW 07181 0.12 99.88 -
[1] Moreda P A, Barciela A D C, Dominguez G R, et al. Alternative solid sample pretreatment methods in green analytical atomic spectrometry[J]. Spectroscopy Letters, 2009, 42(6-7): 394−417. doi: 10.1080/00387010903187393
[2] Arroyo L, Trejos T, Hosick T, et al. Analysis of soils and sediments by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS): An innovative tool for environmental forensics[J]. Environmental Forensics, 2010, 11(4): 315−327. doi: 10.1080/15275922.2010.494949
[3] Vannoorenberghe M, van Acker T, Belza J, et al. Multi-element LA-ICP-MS analysis of the clay fraction of archaeological pottery in provenance studies: A methodological investigation[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2020, 35(11): 26810−2696.
[4] Jantzi S C, Dutton C L, Saha A, et al. Novel “filter pellet” sample preparation strategy for quantitative LA-ICP-MS analysis of filter-bound sediments: A “green chemistry” alternative to sediment fingerprinting in Tanzania’s Ruvu River Basin[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2019, 19(1): 478−490. doi: 10.1007/s11368-018-2076-2
[5] Susset M, Leduc-Gauthier A, Humbert A C, et al. Comparison of the fluctuations of the signals measured by ICP-MS after laser ablation of powdered geological materials prepared by four methods[J]. Analytical Sciences, 2023, 39(6): 999−1014. doi: 10.1007/s44211-023-00309-5
[6] Hu Z C, Qi L. Sample Digestion Methods[M]//Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), 2014: 87-109.
[7] 张晨西, 苗琦, 倪倩. 地质全岩样品LA-ICP-MS整体分析的前处理方法[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(3): 479−486. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.03.011
Zhang C X, Miao Q, Ni Q. Sample preparation methods for bulk analysis of geological materials by using LA-ICP-MS[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2016, 35(3): 479−486. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.03.011
[8] Zhang W, Hu Z C, Liu Y, et al. Quantitative analysis of major and trace elements in NH4HF2-modified silicate rock powders by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2017, 983: 149−159. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.06.039
[9] Pakiela M, Wojciechowski M, Wagner B, et al. A novel procedure of powdered samples immobilization and multi-point calibration of LA-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(7): 1539−1543. doi: 10.1039/c0ja00201a
[10] Zhu Y B, Hioki A, Chiba K. Quantitative analysis of the elements in powder samples by LA-ICP-MS with PMMA powder as the binder and Cs as the internal standard[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2013, 28(2): 301−306. doi: 10.1039/c2ja30279a
[11] Bao Z A, Zhang H F, Yuan H L, et al. Flux-free fusion technique using a boron nitride vessel and rapid acid digestion for determination of trace elements by ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31(11): 2261−2271. doi: 10.1039/C6JA00269B
[12] Mukherjee P K, Khanna P P, Saini N K. Rapid determination of trace and ultra trace level elements in diverse silicate rocks in pressed powder pellet targets by LA-ICP-MS using a matrix-independent protocol[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2014, 38(3): 363−379. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2013.012015.x
[13] Wu S T, Karius V, Schmidt B C, et al. Comparison of ultrafine powder pellet and flux-free fusion glass for bulk analysis of granitoids by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2018, 42(4): 575−591. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12230
[14] Horner N S, Beauchemin D. The use of sol-gels as solid calibration standards for the analysis of soil samples by laser ablation coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(4): 715−720. doi: 10.1039/C3JA50374G
[15] Klemm W, Bombach G. A simple method of target preparation for the bulk analysis of powder samples by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)[J]. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 370(5): 641−646. doi: 10.1007/s002160100848
[16] Hubová I, Holá M, Pinkas J, et al. Examination of sol-gel technique applicability for preparation of pellets for soil analysis by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2007, 22(10): 1238−1243. doi: 10.1039/b701555k
[17] Zhang S Y, Zhang H L, Hou Z, et al. Rapid determination of trace element compositions in peridotites by LA‐ICP‐MS using an albite fusion method[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2018, 43(1): 93−111.
[18] Monsels D A, van Bergen M J, Mason P R D. Determination of trace elements in bauxite using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry on lithium borate glass beads[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2018, 42(2): 239−251. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12206
[19] Malherbe J, Claverie F, Alvarez A, et al. Elemental analyses of soil and sediment fused with lithium borate using isotope dilution laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2013, 793: 72−78. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.07.031
[20] Carvalho A A C, Alves V C, Silvestre D M, et al. Comparison of fused glass beads and pressed powder pellets for the quantitative measurement of Al, Fe, Si and Ti in bauxite by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2017, 41(4): 585−592. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12173
[21] Aguilera J A, Aragon C. Analysis of rocks by CSigma laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with fused glass sample preparation[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(1): 144−152. doi: 10.1039/C6JA00360E
[22] Zhang C X, Hu Z C, Zhang W, et al. Green and fast laser fusion technique for bulk silicate rock analysis by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistriy, 2016, 88(20): 10088−10094. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02471
[23] He Z W, Huang F, Yu H M, et al. A flux-free fusion technique for rapid determination of major and trace elements in silicate rocks by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2016, 40(1): 5−21. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2015.00352.x
[24] Zhu L Y, Liu Y S, Hu Z C, et al. Simultaneous determination of major and trace elements in fused volcanic rock powders using a hermetic vessel heater and LA-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2013, 37(2): 207−229. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2012.00181.x
[25] Arroyo L, Trejos T, Gardinali P R, et al. Optimization and validation of a laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry method for the routine analysis of soils and sediments[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2009, 64(1): 16−25. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.10.027
[26] Zeng L W, Wu M F, Chen S, et al. Direct and sensitive determination of Cu, Pb, Cr and Ag in soil by laser ablation microwave plasma torch optical emission spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2022, 246: 123516. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123516
[27] 王佳翰, 李正鹤, 杨峰, 等. 偏硼酸锂碱熔-电感耦合等离子体质谱法同时测定海洋沉积物中48种元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(2): 306−315.
Wang J H, Li Z H, Yang F, et al. Simultaneous determination of 48 elements in marine sediments by ICP-MS with lithium metaborate fusion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(2): 306−315.
[28] 李迎春, 张磊, 尚文郁. 粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法分析富硒土壤样品中的硒及主次量元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 145−152.
Li Y C, Zhang L, Shang W Y. Determination of selenium, major and minor eleements in selenium-rich soil samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with powder pellet preparation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1): 145−152.
[29] Shaheen M E, Fryer B J. A simple solution to expanding available reference materials for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry analysis: Applications to sedimentary materials[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2011, 66(8): 627−636. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2011.06.010
[30] Duodu G O, Goonetillkek A, Allen C, et al. Determination of refractive and volatile elements in sediment using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2015, 898: 19−27. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.09.033
[31] Byers H L, Mchenry L J, Grundl T J. Forty-nine major and trace element concentrations measured in soil reference materials NISTSRM2586, 2587, 2709a, 2710a and 2711a using ICP-MS and wavelength dispersive-XRF[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2016, 40(3): 433−445. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2016.00376.x
[32] 王娜, 徐铁民, 魏双, 等. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定超细粒度岩石和土壤样品中的稀土元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(1): 68−76.
Wang N, Xu T M, Wei S, et al. Determination of rare earth elements in ultra-fine rock and soil samples by ICP-MS using microwave digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(1): 68−76.
[33] 张颖, 汪虹敏, 王小静, 等. 深海沉积物元素现场测定及方法对比研究[J]. 分析化学, 2018, 46(4): 570−577.
Zhang Y, Wang H M, Wang X J, et al. On-site determination of element concentrations in marine sediments and comparative study of analytical methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(4): 570−577.
[34] Prasad A D, Rastogi L, Thangavel S, et al. A single step acid assisted microwave digestion method for the complete dissolution of bauxite and quantitation of its composition (Al2O3, Fe2O3, SiO2, TiO2, Cr2O3, MgO, MnO and V2O5) by ICP-AES[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2023, 47(2): 403−413. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12481
[35] Maslennikova A V, Artemyev D A, Shtenberg M V, et al. Express multi‐element determination in lake sediments by laser ablation mass‐spectrometry (LA‐ICP‐MS)[J]. Limnol Oceanogr Methods, 2020, 18(8): 411−243. doi: 10.1002/lom3.10372
[36] Hattendorf B, Latkoczy C, Günther D. Peer reviewed: Laser ablation-ICPMS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2003, 75(15): 341A−347A. doi: 10.1021/ac031283r
[37] Košler J, Wiedenbeck M, Wirth R, et al. Chemical and phase composition of particles produced by laser ablation of silicate glass and zircon-implications for elemental fractionation during ICP-MS analysis[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2005, 20(5): 402−409. doi: 10.1039/B416269B
[38] Luo T, Wang Y, Hu Z C, et al. Further investigation into ICP-induced elemental fractionation in LA-ICP-MS using a local aerosol extraction strategy[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(4): 941−949. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00483C
[39] 王毅民, 王晓红, 高玉淑, 等. 中国海及大陆架沉积物标准物质系列评介[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(5): 1145−1153.
Wang Y M, Wang X H, Gao Y S, et al. A review on the reference material series for China Sea and continental shelf sediments[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(5): 1145−1153.
[40] 王毅民, 高玉淑, 韩慧明, 等. 实用地质分析标准物质手册(中-英文对照版)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003: 206.
Wang Y M, Gao Y S, Han H M, et al. Practical reference material for ceoanalysis (Chinese-English)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003: 206.
[41] Zhang W, Qi L, Hu Z C, et al. An investigation of digestion methods for trace elements in bauxite and their determination in ten bauxite reference materials using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2016, 40(2): 195−216. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2015.00356.x
-



 下载:
下载: