LOGGING DATA INTERPRETATION OF THE MUDDY RESERVOIR IN E1f2 OF SUBEI BASIN
-
摘要:
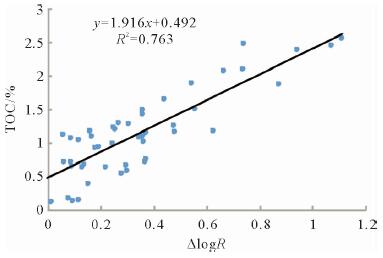
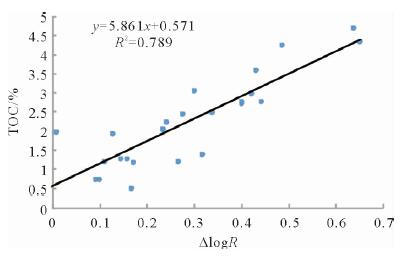
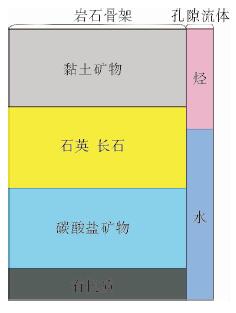
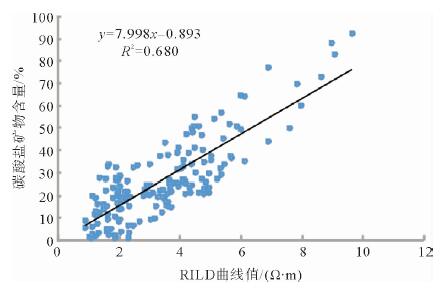
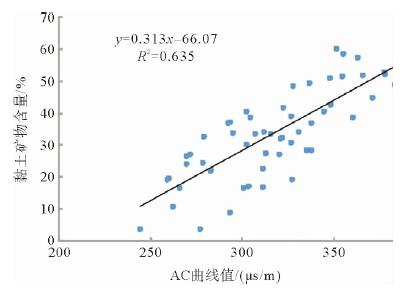
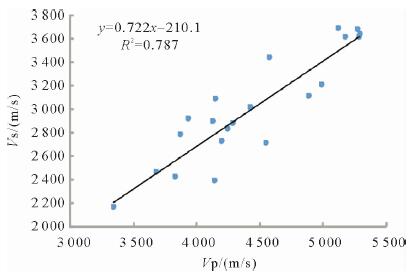
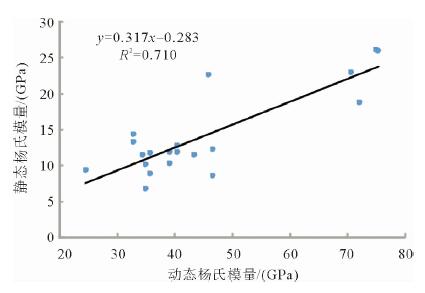
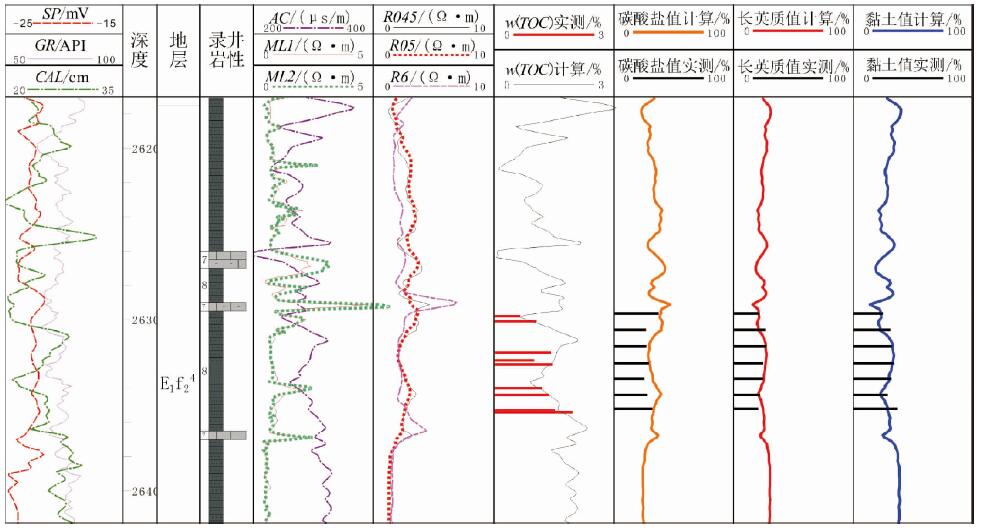
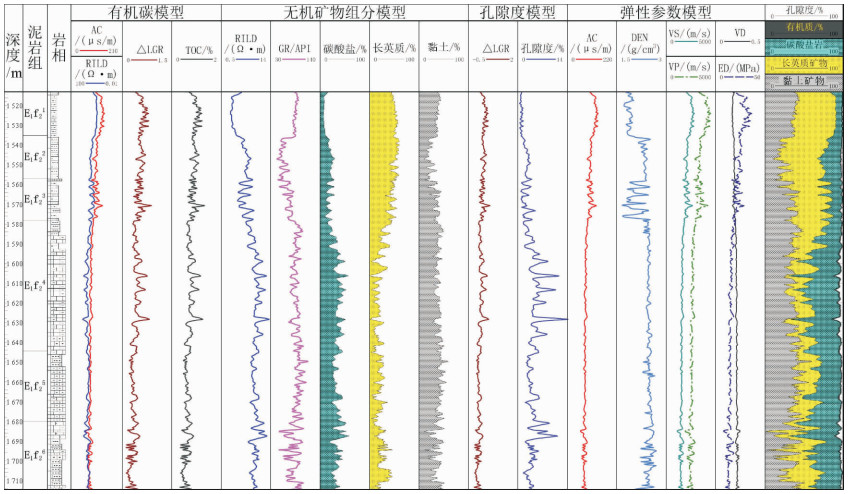
利用测井数据、岩心观察、铸体薄片、扫描电镜、三轴应力测试、全岩分析测试、有机地化测试等资料,在完成测井曲线标准化的基础上优选出影响研究区泥页岩储层质量的几个主要参数,分别建立了有机碳及无机矿物含量测井解释模型、孔隙度模型、弹性参数模型等,并基于相关模型将各参数归一化到同一岩石体积模型中,完成对单井的综合解释。结果表明:所建模型具有较高的准确性,依据测井解释结果能够有效划分出有利岩相段及易压裂层段,继而实现对苏北盆地阜二段泥页岩储层特征及可压裂性的研究,用于指导下一步泥页岩油气勘探。
Abstract:Integrated interpretation is made for the data of logging, core observation, casting thin section examination, SEM analysis, triaxial shear test, bulk rock analysis and organic geochemistry. After pre-processing and standardization of logging data, some key parameters that affect the quality of the shale reservoir in E1f2 of the Subei Basin are extracted. Upon the basis, four basic models related to organic carbon, inorganic minerals, porosity and elastic parameters respectively are established. All the results after normalization are put into the physical model of bulk-volume rock for interpretation of target well. The research results prove that the above models are effective in the Subei Basin. Both favorable lithofacies and fracturing layers can be predicted via compressive interpretation of logging data. The research results may have some significance for reservoir evaluation and fracture prediction in the E1f2 of the Subei Basin.
-

-
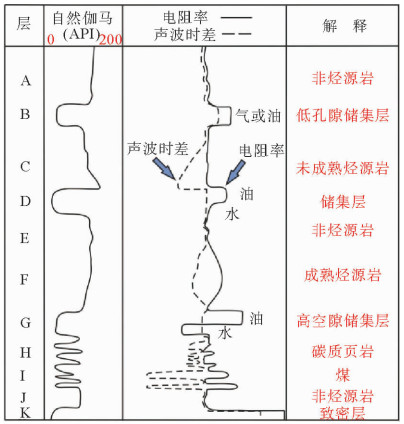
图 2 ΔlogR法理论模型解释示意图(据文献[5])
Figure 2.
-
[1] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等.中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J].石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641-653. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201006001
[2] 张善文, 张林晔, 李政, 等.济阳坳陷古近系页岩油气形成条件[J].油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.001
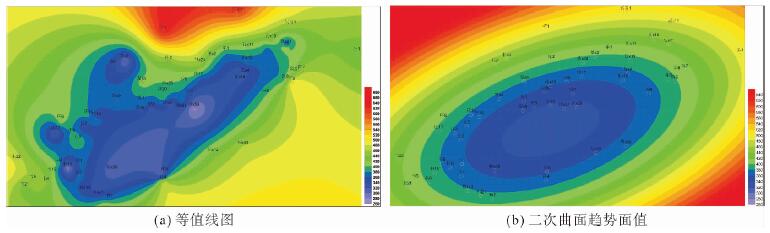
[3] 张启锐.地质趋势面分析[M].北京:科学出版社, 1990:26-28.
[4] 耿生臣.罗家地区泥页岩矿物组分含量解释模型构建方法[J].油气地质与采收率, 2013, 20(1):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2013.01.006
[5] Passey Q R, Creaney S, Kulla J B.A practical modal for organic richness from porosity and resistivity logs[J].AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(12):1777-1794. http://archives.datapages.com/data/bulletns/1990-91/images/pg/00740012/0000/17770.pdf
[6] 顾红英.测井曲线标定有机碳方法在苏北盆地的应用[J].江苏地质, 2004, 28(3):166-169. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsdz200403009
[7] 赵铭海, 傅爱兵, 关丽, 等.罗家地区页岩油气测井评价方法[J].油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6):20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.005
[8] Chalmers G R, Bustin R M, Power I M. Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses: Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doig units[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1099-1119. doi: 10.1306/10171111052
[9] Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett Shale[J]. Journal of sedimentary research, 2009, 79(12): 848-861. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2009.092
[10] Heath J E, Dewers T A, Mcpherson B J, et al. Pore networks in continental and marine mudstones: characteristics and controls on sealing behavior[J]. Geosphere, 2011, 7(2): 429-454. doi: 10.1130/GES00619.1
[11] Slatt R M, O'Brien N R. Pore types in the Barnett and Woodford gas shales: Contribution to understanding gas storage and migration pathways in fine-grained rocks[J]. AAPG Bulletin. 2011, 95(12): 2017-2030. doi: 10.1306/03301110145
[12] Aplin A C, Macquaker J H S. Mudstone diversity: Origin and implications for source, seal, and reservoir properties in petroleum systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin. 2011, 95(12): 2031-2059. doi: 10.1306/03281110162
[13] Mastalerz M, Schimmelmann A, Drobniak A, et al. Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany Shale across a maturation gradient: Insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. AAPG bulletin, 2013, 97(10): 1621-1643. doi: 10.1306/04011312194
[14] 罗红梅, 罗晓容, 刘书会, 等.东营凹陷北部陡坡带致密砂砾岩体物性特征及弹性波速影响因素[J].油气地质与采收率, 2014, 21(2):91-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2014.02.023
[15] 尹帅, 丁文龙, 王濡岳, 等.陆相致密砂岩及泥页岩储层纵横波波速比与岩石物理参数的关系及表征方法[J].油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(3):22-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.03.004
[16] 刘惠民, 张守鹏, 王朴, 等.沾化凹陷罗家地区沙三段下亚段页岩岩石学特征[J].油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6):11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.003
[17] 聂昕, 邹长春, 杨玉卿, 等.测井技术在页岩气储层力学性质评价中的应用[J].工程地球物理学报, 2012, 9(4):433-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2012.04.012
[18] 杨建, 付永强, 陈鸿飞, 等.页岩储层的岩石力学特性[J].天然气工业, 2012, 32(7):12-14. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2012.07.003
[19] 袁俊亮, 邓金根, 张定宇, 等.页岩气储层可压裂性评价技术[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(3):523-527. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201303015
[20] Rickman R, Mullen M, Petre E, et al. A practical Use of Shale Petrophysics for Stimulation Design Optimization: All Shale Plays Are Not Clones of the Barnett Shale[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Denver, Colorado: 2008.
[21] Tissot B P, Welte D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence: A new approach to oil and gas exploration [M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1978: 1-362.
-



 下载:
下载: