WATER EXCHANGE AND BIOGEOCHEMICAL EFFECTS OF SUBTERRANEAN ESTUARY WITH TIDE
-
摘要:
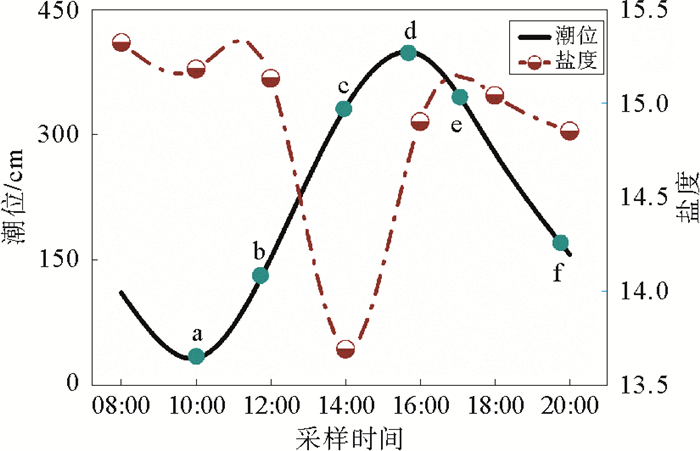
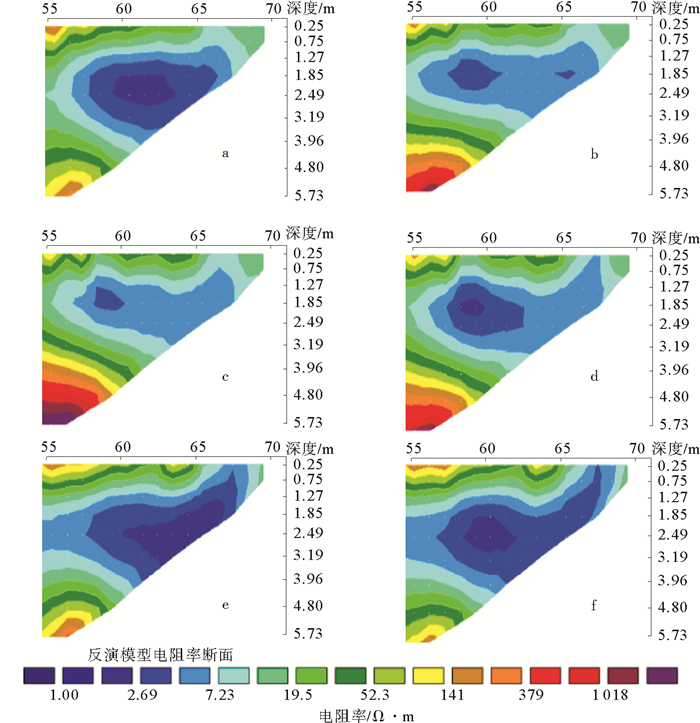
海岸带地下河口中的生物地球化学过程是一种重要的陆海相互作用驱动力,对于海洋中的物质收支至关重要。以青岛金沙滩为典型研究区域,借助电阻率成像、同位素示踪等技术手段对潮汐影响下的地下河口的生物地球化学特征进行刻画,发现地下水体的电阻率、盐度、pH、镭氡同位素及营养盐含量等各种理化参数的周日变化均表现出明显的潮汐规律,但较同步潮汐信号滞后2~4 h。研究结果表明,在涨落潮过程中,海水在地下河口发生倒灌排放,并显著地改变了含水层的生物地球化学背景场。
Abstract:The biogeochemical process in the subterranean estuary of a coastal zone is an important driving force to the interaction between land and sea, which is critical for the research of material budget. In this study, the Qingdao Golden Beach was chosen as a typical case for research. Using resistivity imaging and isotopic tracing technology as means, we tried to understand the biogeochemical changes of the subterranean estuary on a tidal scale. It is found that in a typical tidal cycle, various physical and chemical parameters of groundwater, such as resistivity, salinity, pH, radium/radon isotopes and nutrients, are all significantly influenced by the changing tide. Tidal signals in the subterranean estuary are usually delayed for about 2-4 hours. In the cycle of flood and ebb tides, seawater will be recharged into and discharged out of the subterranean estuary, and thus the biogeochemical background of the aquifer will be significantly changed.
-
Key words:
- coastal zone /
- subterranean estuary /
- resistivity imaging /
- radium/radon isotopes /
- Qingdao Golden Beach
-

-
[1] 彭晓彤, 周怀阳.海岸带营养盐生物地球化学研究评述[J].海洋通报, 2002, 21(3):69-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.03.011
[2] Zone L O I I, Kremer H H, Tissier M D A L, et al. Land-Ocean Interactions in the Coastal Zone: Science Plan and Implementation Strategy[J]. Environmental Policy Collection, 2005, 20(11): 1262-1268. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=027a9bf69efd027ba3d8c348bf96ca99&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] Moore W S. The subterranean estuary: a reaction zone of ground water and sea water [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1999, 65(1/2): 111-125. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e58275a6c8bfbcf90c2b7d717b97bb97&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] Burnett W C, Bokuniewicz H, Huettel M, et al. Groundwater and Pore Water Inputs to the Coastal Zone[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2003, 66 (1/2): 3-33. doi: 10.1023/B:BIOG.0000006066.21240.53
[5] Smith C G, Cable J E, Martin J B, et al. Evaluating the source and seasonality of submarine groundwater discharge using a radon-222 pore water transport model [J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 273(3/4): 312-322. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4dc65ba644bc1ea022e5bc1feb18a628
[6] Swarzenski P W, Burnett W C, Greenwood W J, et al. Combined time-series resistivity and geochemical tracer techniques to examine submarine groundwater discharge at Dor Beach, Israel [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33 (24): L24405. doi: 10.1029/2006GL028282
[7] 沈焕庭, 朱建荣.论我国海岸带陆海相互作用研究[J].海洋通报, 1999, 18(6):11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.1999.06.002
[8] 苏永军, 范剑, 刘宏伟, 等.高密度电阻率法探测海水入侵咸淡水界限初步调查研究——以莱州湾为例[J].地质调查与研究, 2014, 37(3):177-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2014.03.003
[9] Sun Y, Torgersen T. The effects of water content and Mn-fiber surface conditions on 224Ra measurement by 220Rn emanation [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1998, 62(3/4): 299-306.
[10] Moore W S, Arnold R. Measurement of 223Ra and 224Ra in coastal waters using a delayed coincidence counter [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 1996, 101(C1):1321-1329. doi: 10.1029/95JC03139
[11] Waska H, KIM S, Kim G, et al. An efficient and simple method for measuring 226Ra using the scintillation cell in a delayed coincidence counting system (RaDeCC) [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2008, 99(12): 1859-1862. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.08.008
[12] Peterson R N, Burnett W C, Dimova N, et al. Comparison of measurement methods for radium-226 on manganese-fiber [J]. Limnology & Oceanography Methods, 2009, 7(2): 196-205.
[13] Mulligan A E, Charette M A. Intercomparison of submarine groundwater discharge estimates from a sandy unconfined aquifer [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2006, 327(3/4): 411-425. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a896b35c5c74f0f47b08268f0a219b21
[14] Grasshoff K, Almgreen T. Methods of seawater analysis [M]. Weinheim, New York: Wiley-Vch, 1976.
-




 下载:
下载: