CARBON ISOTOPE REVERSAL IN SHALE GAS: ORIGIN AND IMPLICATIONS
-
摘要:
通过对多研究区的页岩气碳同位素倒转现象及成因进行总结,发现目前对页岩气碳同位素倒转成因的主流认识有扩散和吸附/解吸过程中的碳同位素分馏、初次裂解气和二次裂解气的混合以及页岩气与水和过渡金属发生反应。此外,高地温、溶解作用和构造活动也可能会对碳同位素倒转有一定的贡献。碳同位素倒转在预测页岩气高产区及资源量、压裂效果以及页岩气藏的保存条件等方面有着重要的指示意义。但目前还存在一些争议,如扩散作用和吸附/解吸作用哪个占主导地位,初次裂解气和二次裂解气的混合在什么情况下才能导致碳同位素倒转,页岩气与水和过渡金属的反应中反应物和生成物还无法确定。这些争议的解决需要广大学者进一步的研究。
Abstract:Carbon isotopic reversal is a phenomenon often observed in the shale gas in some areas. Studies suggest that the reversal may come from various reasons, such as carbon isotope fractionation by diffusion and adsorption/desorption processes, mixing of primary cracking gas and secondary cracking gas and the reaction of shale gas with water and transition metals. In addition, high temperature, dissolution and tectonic activities may also contribute to some extent to carbon isotope reversal in shale gas. Carbon isotope reversal in shale gas is a significant indicator to prediction of shale gas yield zone and resource potential assessment, as well as fracturing effect and preservation conditions of shale gas reservoirs. However, there are still controversies. The dominant role of diffusion and adsorption/desorption remains uncertain; it is arguable that under what circumstances a mixture of primary cracking gas and secondary cracking gas may lead to carbon isotope reversal; and the reactants and products need to be identified in the reaction of shale gas with water and transition metals. Further studies are needed to settle these disputes.
-
Key words:
- carbon isotope /
- shale gas /
- isotope reversal /
- Kerogen /
- geochemical characteristics
-

-
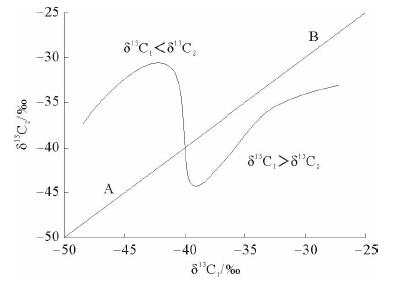
图 1 基于中国、美国和加拿大的典型海相页岩气数据总结的δ13C1与δ13C2关系图(据文献[15]修改)
Figure 1.
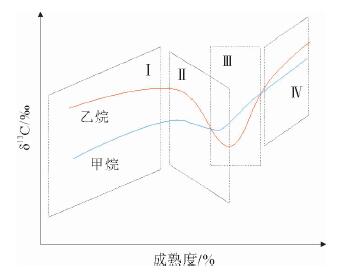
图 2 甲烷和乙烷碳同位素值随成熟度变化模式图(据文献[14])
Figure 2.
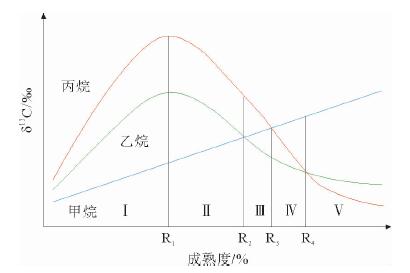
图 3 甲烷、乙烷和丙烷碳同位素值随成熟度变化模式图(据文献[19]修改)
Figure 3.
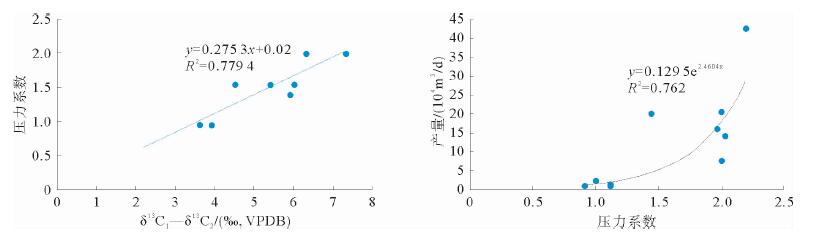
图 4 四川盆地威远、长宁、涪陵区块龙马溪组页岩气压力系数与甲烷和乙烷碳同位素值反转大小、初始产气量关系图(数据来自文献[31])
Figure 4.
-
[1] 蒋有录, 查明.石油天然气地质与勘探[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2016:73-76, 229.
[2] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等.中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J].石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641-653. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201006001
[3] Hill R J, Jarvie D M, Zumberge J, et al. Oil and gas geochemistry and petroleum systems of the Fort Worth Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4): 445-473. doi: 10.1306/11030606014
[4] Curtis J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11): 1921-1938. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a0a945b1e9be609ea86247395927ba7a
[5] Tilley B, McLellan S, Hiebert S, et al. Gas isotope reversals in fractured gas reservoirs of the western Canadian Foothills:mature shale gases in disguise[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(8): 1399-1422. doi: 10.1306/01031110103
[6] Zumberge J, Ferworn K, Brown S. Isotopic reversal (‘rollover’) in shale gases produced from the Mississippian Barnett and Fayetteville formations[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 31(1): 43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.06.009
[7] Slatt R M, Rodriguez N D. Comparative sequence stratigraphy and organic geochemistry of gas shale: commonality or coincidence?[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2012, 8(8): 68-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2012.01.008
[8] 魏祥峰, 郭彤楼, 刘若冰.涪陵页岩气田焦石坝地区页岩气地球化学特征及成因[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3):539-548. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201603017
[9] 秦华, 范小军, 刘明, 等.焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩解吸气地球化学特征及地质意义[J].石油学报, 2016, 37(7):846-854. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201607003
[10] 韩辉, 李大华, 马勇, 等.四川盆地东北地区下寒武统海相页岩气成因:来自气体组分和碳同位素组成的启示[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(3):453-459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2013.03.014
[11] 盖海峰, 肖贤明.页岩气碳同位素倒转:机理与应用[J].煤炭学报, 2013, 38(5):827-833. http://ir.gig.ac.cn:8080/handle/344008/19317
[12] 王香增.陆相页岩气[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2014:2-33.
[13] 戴金星, 倪云燕, 黄士鹏, 等.次生型负碳同位素系列成因[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(1):1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201601001
[14] Xia X Y, James C, Braun R, et al. Isotopic reversals with respect to maturity trends to mixing of primary and secondary products in source rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 339(2): 205-212. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=815b5027056dafd1045afda1251fb918
[15] Dai J X, Zou C N, Liao S M, et al. Geochemistry of the extremely high thermal maturity Longmaxi shale gas, southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 74: 3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.01.018
[16] 戴金星, 倪云燕, 黄士鹏, 等.煤成气研究对中国天然气工业发展的重要意义[J].天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(1):1-22. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.01.0001
[17] 冯子齐, 刘丹, 黄士鹏, 等.四川盆地长宁地区志留系页岩气碳同位素组成[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(5):705-713. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201605005
[18] Tilley B, Muchlenbachs K. Isotope reversals and universal stages and trends to gas maturation in sealed, self-contained petroleum system[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 339(339): 194-204. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c8724289fee560cd268303f8f8d1e0f4
[19] Hao F, Zou H Y. Cause of shale gas geochemical anomalies and mechanisms for gas enrichment and depletion high-maturity shales[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 44(3): 1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=22f3c4f065a727a59fb018bb58153494
[20] 林会喜, 程付启, 金强, 等.天然气成分、同位素分馏机理及实例分析[J].天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(2):195-200.
[21] 戴金星.天然气中烷烃碳同位素研究的意义[J].天然气工业, 2011, 31(12):1-6. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.12.001
[22] Zhang T, Krooss B M. Experimental investigation on the carbon isotope fractionation of methane during gas migration by diffusion through sedimentary rocks at elevated temperature and pressure[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(16): 2723-2742.DOI:10.1016/s0016-7037(01)00601-9
[23] Schloemer S, Krooss B M. Molecular transport of methane, ethane and nitrogen and the influence of diffusion on the chemical and isotopic composition of natural gas accumulations[J]. Geofluids, 2004, 4(1): 81-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-8123.2004.00076.x
[24] Xia X Y, Tang Y C. Isotope fractionation of methane during natural gas flow with coupled diffusion and adsorption/desorption[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 77(1): 489-503. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=816176fa049052789760d8964392e5dd
[25] Hao F, Li S T, Sun Y C, et al. Characteristics and origin of the gas and condensate in the Yinggehai Basin, offshore South China Sea: evidence for effects of overpressure on petroleum generation and migration[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1996, 24(3): 363-375. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(96)00009-5
[26] Burruss R C, Laughrey C D. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic reversals in deep basin gas: evidence for limits to the stability of hydrocarbons[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41(2): 1285-1296. doi: 10.3997/2214-4609.20145393
[27] 吴伟, 罗超, 张鉴, 等.油型气乙烷碳同位素演化规律与成因[J].石油学报, 2016, 37(12):1463-1471. doi: 10.7623/syxb201612002
[28] Vinogradov A P, Galimor E M. Isotopism of carbon and the problem of oil origin[J]. Geochemistry, 1970, 3: 275-296.
[29] Qin S, Tang X, Song Y, et al. Distribution and fractionation mechanmism of stable carbon isotope of coalbed methane[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2006, 49(12): 1252-1258. doi: 10.1007/s11430-006-2036-3
[30] 孟强, 王晓峰, 王香增, 等.页岩气解析过程中烷烃碳同位素组成变化及其地质意义——以鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡东南部长7页岩为例[J].天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(2):333-340. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201502014
[31] 刘飏.高-过成熟页岩中天然气地球化学成因模式与应用[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2017.
[32] 屈振亚, 孙佳楠, 史健婷, 等.页岩气稳定碳同位素特征研究[J].天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(7):1376-1384. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201507017
-



 下载:
下载: