TECTONIC FEATURES OF THE MALAY BASIN AND THEIR CONTROL OVER HYDROCARBON ACCUMULATION
-
摘要:
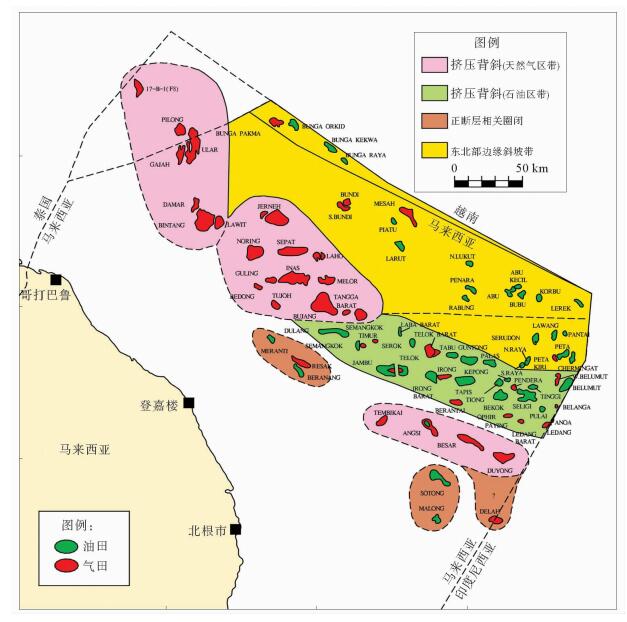
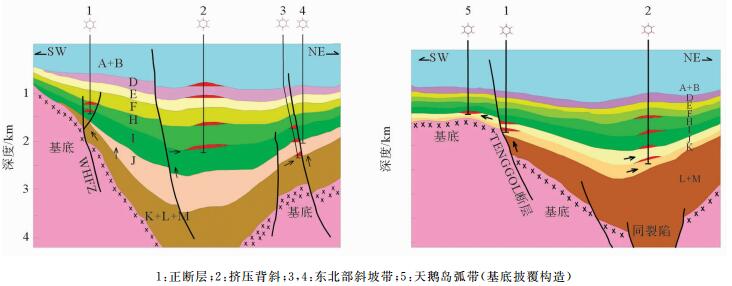
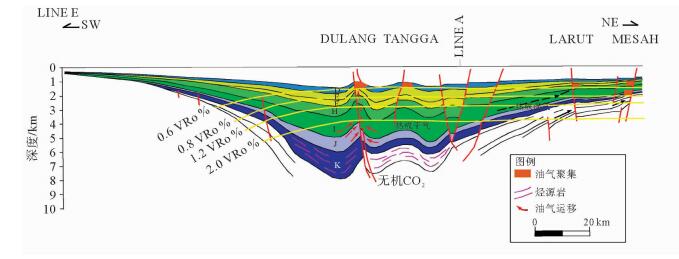
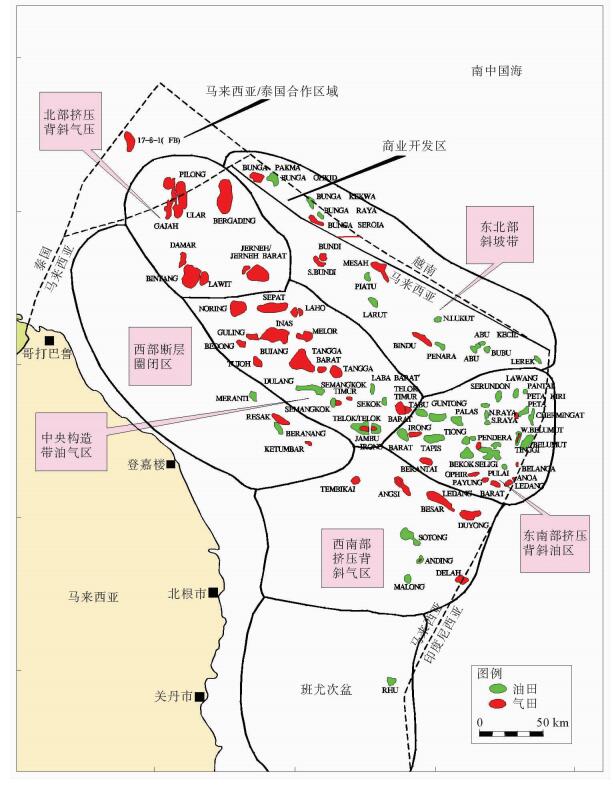
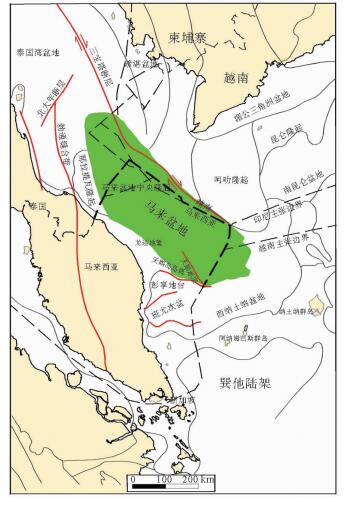
马来盆地为新生代断陷盆地,经历始新世断陷期、渐新世凹陷期、中新世构造反转期3个演化阶段。中-晚中新世发生正反转构造,构造反转导致区域左行旋转逐渐变换为右行,中部和东南部反转作用强烈。马来盆地南部圈闭形成时间早,北部圈闭形成时间晚;早期生成的油在南部聚集,北部逸散;后期生成的气在北部有效聚集。北部烃源岩沉积、沉降快,埋深大,有利于成熟生烃,目前多数烃源岩已经进入生气阶段;由于后期东南部的抬升生烃受到抑制,生气量较少。马来盆地油气分布具有东部和南部以油藏为主,北部以气藏为主的特点。马来盆地划分了六大勘探区域,其中东南挤压背斜油区是油气最为富集的区域,也是主力油气产区。该区未来勘探重点主要位于深部H和J组超压带下的气藏和凝析油藏。通过对马来盆地构造特征、构造成因机制等方面的研究,厘清了构造对油气成藏的控制作用,并指出了下一步勘探的方向。
Abstract:The Malay Basin is a Cenozoic fault basin. The structural characteristics and tectonic mechanism of the Basin are studied in this paper in order to understand the control of structure over hydrocarbon accumulation. The basin has experienced three evolutionary stages: the Eocene fault depression stage, the Oligocene depression stage, and the Miocene tectonic inversion stage. In Middle-Late Miocene, a positive inverted structure is observed with a gradual change from left lateral rotation to right lateral rotation. The inverse is stronger in the center and southeastern parts of the Basin. The trap formation time is earlier in the southern part of the Basin. Oil accumulated in the south and escapes to the north in the early stage; and gas generated in the later stage and effectively accumulated in the north. The source rocks in the north were formed under a rapid sedimentation rate in a large depth and conducive to a mature and gas phase. Due to the later uplifting of the southeast part of the basin, hydrocarbon generation is suppressed and there is less gas accumulation. Oil fields are mainly distributed in the southeast, and gas field in the north. In this paper, the Malay Basin is divided into six exploration areas, and the southeast, the main producing area extruded anticline oil area is the richest one. The deep H and J groups located in the overpressure belts are recommended as future exploration targets.
-
Key words:
- tectonic inversion /
- genetic mechanism /
- control effect /
- Malay Basin /
- exploration direction
-

-
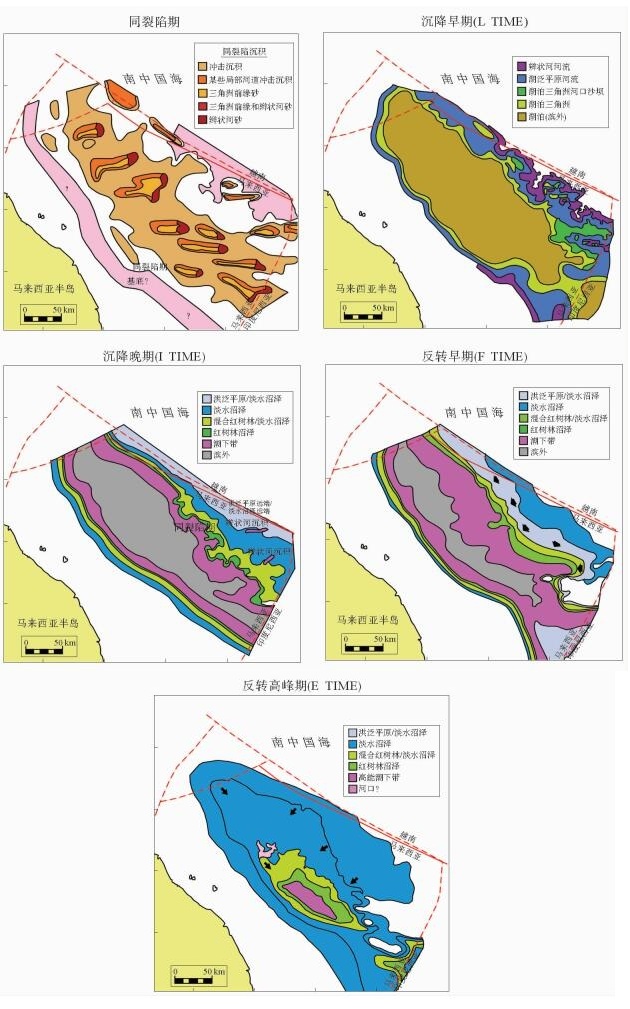
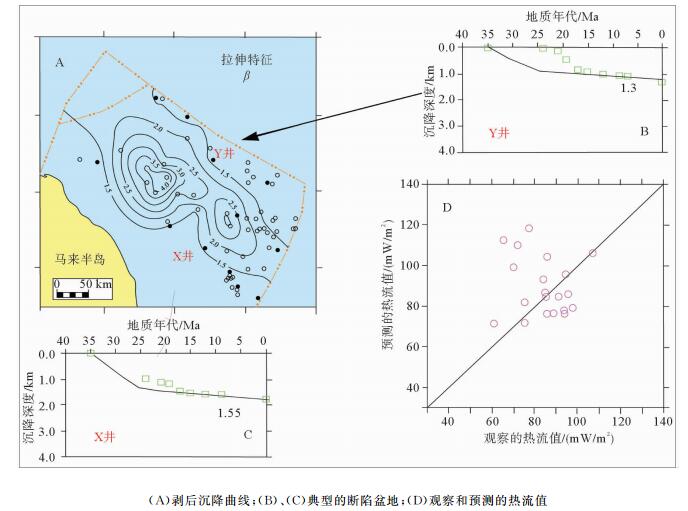
图 2 马来盆地沉积古环境重建(据文献[2])
Figure 2.
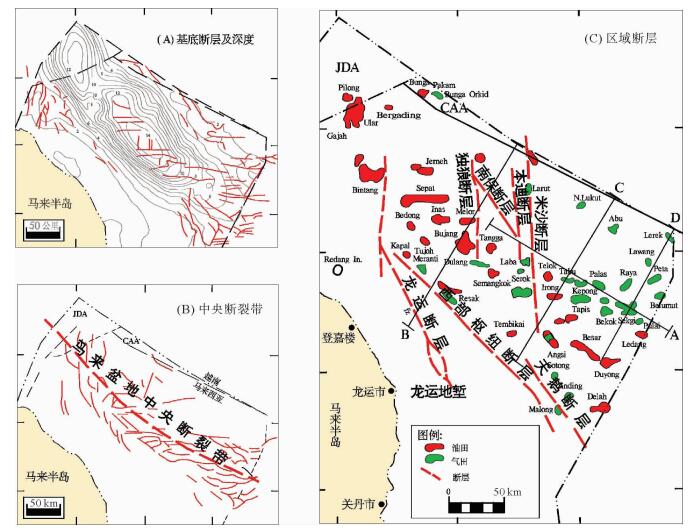
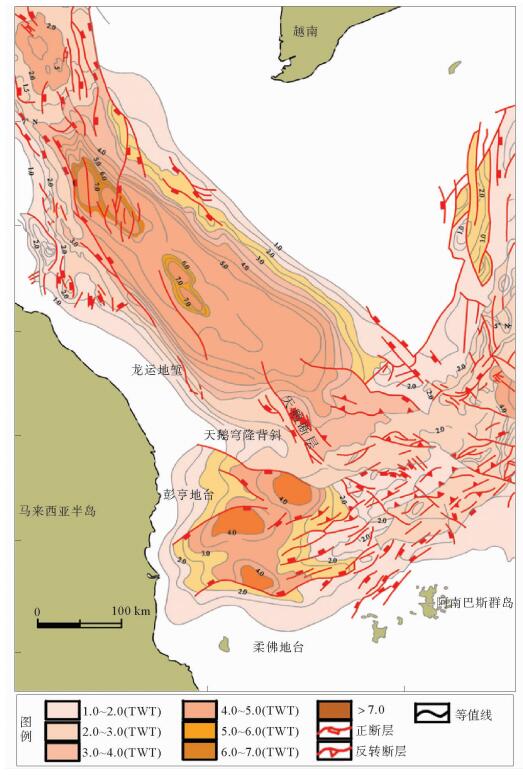
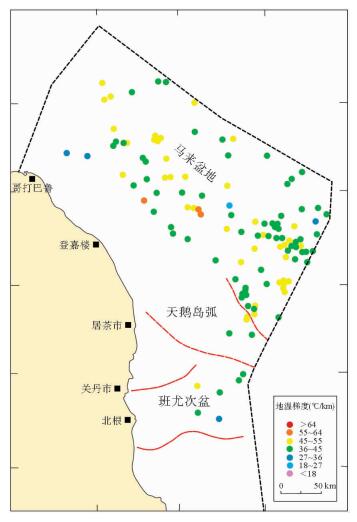
图 4 马来盆地的构造因素(据文献[6])
Figure 4.
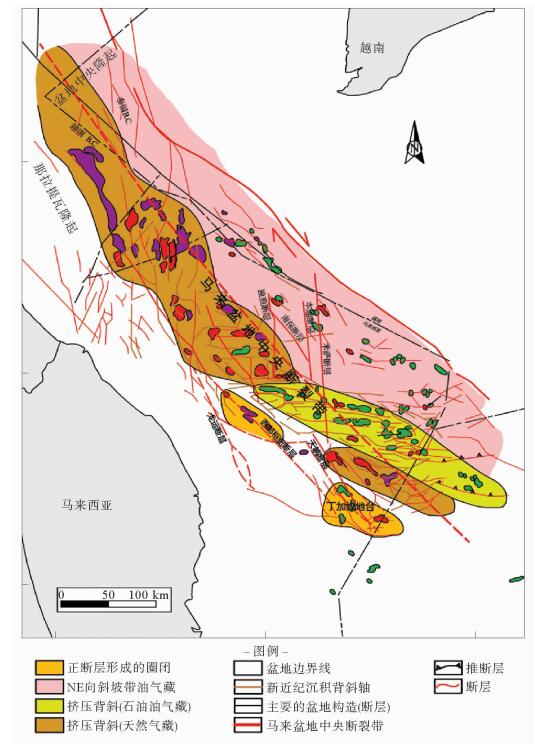
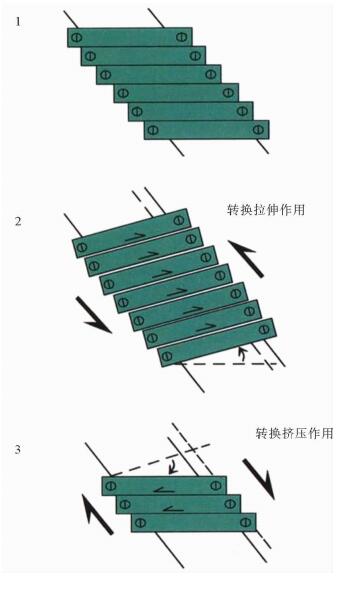
图 9 马来盆地构造反转机制模型(据文献[16])
Figure 9.
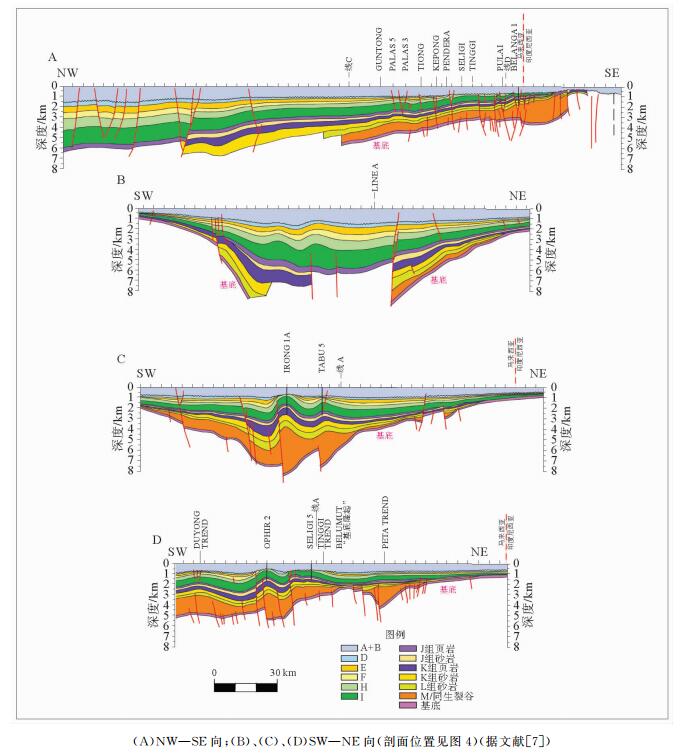
图 12 马来盆地圈闭类型剖面图(据文献[21])
Figure 12.
-
[1] Ginger D C, Ardjakusuma W O, Hedley R J, et al. Inversion history of the West Natuna Basin: examples from the Cumi Cum PSC[C]//Proceedings of the Indonesia. Petroleum Association 22nd Annual Convention, 1993: 635-658.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/292024311_Inversion_history_of_the_West_Natuna_Basin_Examples_from_the_Cumi-Cumi_PSC [2] EPIC. Regional study of the Malay Basin-Final Portfolios[R]. Esso-PETRONAS Integrated Colla-Borative Study, Esso Production Malaysia Inc, 1994.
[3] Tjia H D. Inversion tectonics in the Malay Basin:evidence and timing of events[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 1994, 36: 119-126. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281603831_Inversion_tectonics_in_the_Malay_Basin_Evidence_and_timing_of_events
[4] Madon N, Tjia H D. Role of pre-tertiary fractures in formation and development of the Malay and Penyu basins[C]. Hall R, Blundell D I. Tectonic Evolution of Southeast Asia. London: Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1996, 106: 281-289.
[5] Ngah T S. Trap styles of the Tenggol Arch and the southern part of the Malay Basin[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 1987, 21: 177-193. doi: 10.7186/bgsm21198710
[6] Liew K K. Structural development at the west-central margin of the Malay Basin[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 1994, 36: 67-80. http://archives.datapages.com/data/geological-society-of-malaysia/bulletins/036/036001/pdfs/67.htm
[7] Madon, M B H. Depositional setting and origin of berthierine oolitic ironstones in the lower Miocene Terengganu shale, Tenggol Arch, offshore Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1992, 62(5): 899-916. https://www.crossref.org/iPage?doi=10.1306%2FD4267A0A-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[8] 杨福忠, 薛良清.南亚太地区盆地类型及油气分布特征[J].海外勘探, 2006(5):65-70 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsykt200605013
[9] Kingston D R, Dishroon C P, Williams P A. Global basin classification system[J].American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1983, 67(12): 2175-2193. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ028861568/
[10] Ismail M T, Amar S, Rudolph K W. Structural and sedimentary evolution of the Malay Basin[C]. Abstracts of AAPG international Conference & Exhibition, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. 1994: 2l-24.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255146880_Structural_and_sedimentary_evolution_of_the_Malay_Basin [11] Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y, et al. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: new insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology, 1982, 10(12): 611-616. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<611:PETIAN>2.0.CO;2
[12] White J M Jr, Wing R S. Structural development of the South China Sea with particular reference to Indonesia[C]//Proceedings of the Indonesian Petroleum Association 7th Annual Convention, Jakarta. 1978: 159-178.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323053264_Structural_Development_of_the_South_China_Sea_with_Particular_Reference_to_Indonesia [13] Yusoff W I. Heat flow in offshore Malaysian basins[J]. CCOP Technical Publication, 1990, 21: 39-54.
[14] Watts M. Gravity anomalies, subsidence history, and the tectonic evolution of the Malay and Penyu basins[J], Basin Research, 1998, 10(4): 375-392. DOI: 10.1046/j. 1365-2117. 1998. 00074.x.
[15] Zhang Q M, Zhang Q X. A distinctive hydrocarbon basin-Yinggehai Basin South China Sea[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1991, 8(6): 69-74. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0743-9547(91)90097-H/
[16] Madon M B H. The kinematics of extension and inversion in the Malay Basin offshore Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 1997, 41: 127-138. doi: 10.7186/bgsm41199711
[17] Ramli N. Depositional model of a Miocene barred wave-and storm-dominated shoreface and shelf, Southeastern Malay Basin, offshore West Malaysia[C]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1986, 70: 34-47.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/239915101_Depositional_Model_of_a_Miocene_Barred_Wave-_and_Storm-Dominated_Shoreface_and_Shelf_Southeastern_Malay_Basin_Offshore_West_Malaysia [18] Yusoff W I. Geothermics of the Malay Basin, offshore Malaysia[D]. Durham: University of Durham, 1993: 213.
http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/5537/ [19] Yusoff W I. Heat flow study in the Malay Basin[C]. CCOP Technical Publication, 1984, 15: 77-87.
[20] Yusoff W I. Heat flow in offshore Malaysian basins[C]. CCOP Technical Publication, 1990, 21: 39-54.
[21] Ngah T S. Trap styles of the Tenggol Arch and the southern part of the Malay Basin[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 1987, 21: 177-193. doi: 10.7186/bgsm21198710
[22] 叶德燎.东南亚与南亚油气资源及其评价[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2004.
-



 下载:
下载: