GRAIN-SIZE DISTRIBUTION PATTERNS OF THE CORE SEDIMENTS FROM BHS01 OF BOHAI STRAIT AND THEIR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPLICATIONS
-
摘要:
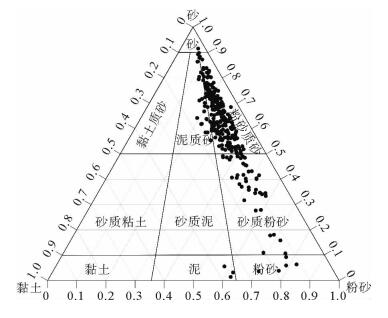
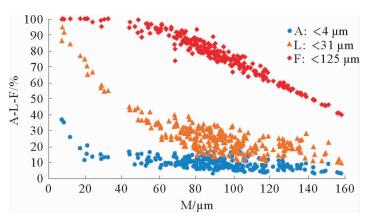
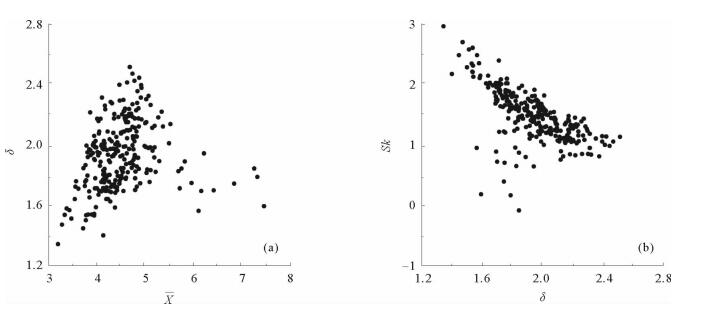
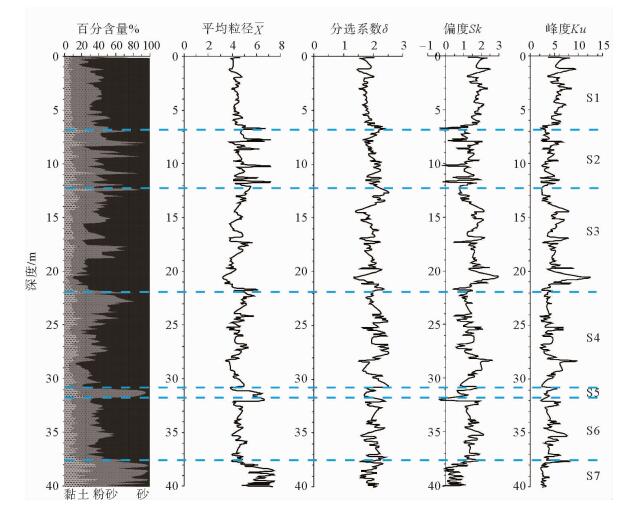
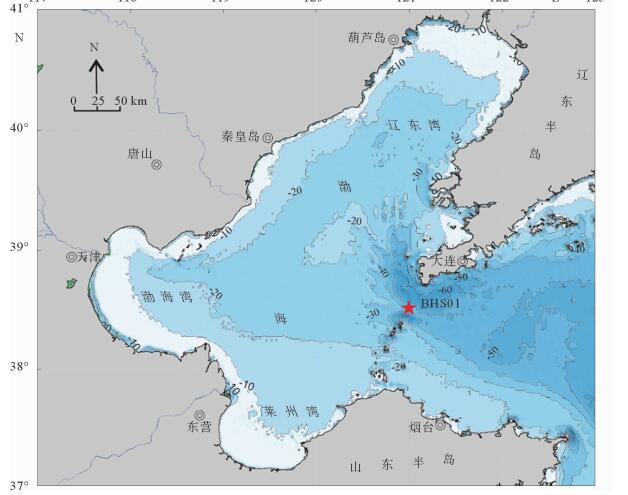
通过对渤海海峡BHS01孔上部40 m沉积物样品进行粒度测试分析,探讨渤海海峡地区的沉积环境变化。结果表明,渤海海峡BHS01孔上部沉积物平均粒径(X)介于3.2Φ~7.5Φ,以粉砂质砂、砂质粉砂为主;分选系数(δ)介于1.3~2.5,分选较差—差;偏度(Sk)为-0.4~3.0,以正偏、极正偏为主;峰度(Ku)1.9~12.4,表现为尖锐—正态。通过对沉积物粒级组成、粒度结构以及粒度参数随深度变化等特征进行分析,揭示了渤海海峡地区水动力条件较强,波动频繁的环境变化信息,据此将BHS01孔上部沉积物自下而上划分为7个沉积层段,反映渤海海峡地区中更新世以来经历了从浅海相-河流相-浅海相的沉积变化过程。
Abstract:Grain-size distribution patterns of the upper 40m of sediments of the core BHS01 are studied to detect the evolutional course of depositional environment of the Bohai Strait. Results show that the mean grain size of the sediments varies from 3.2Φ to 7.5Φ, indicating mixed sediments of silty sand and sandy silt. The sorting of the sediments ranges from 1.3 to 2.5, indicating poor sorting deposits. The skewness of the sediments are mostly dropped in the range of -0.4~3.0, showing a positive and super-positive skewness, while the kurtosis of the sediments varies from 1.9 to 12.4, showing an acute normal distribution. Based on the integrated analysis of grain size parameters, C-M diagrams, scatter diagrams and the changes in grain size with depth, it is concluded that the Bohai Strait was once a high-energy environment. Seven sedimentary units are recognized for the upper part of BHS01, which indicate the evolutional history of the region since Middle Pleistocene from shallow sea facies to fluvial facies, to shallow sea facies again.
-
Key words:
- the Bohai Strait /
- BHS01 core /
- marine-terrigenous sediments /
- grain-size
-

-
[1] Visher G S. Grain size distributions and depositional processes [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1969, 39(3):1074-1106. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0226056781/
[2] Saito Y, Yang Z, Hori K. The Huanghe (Yellow River) and Changjiang (Yangtze River) deltas: a review on their characteristics, evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene [J]. Geomorphology, 2001, 41(2):219-231. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0169-555X(01)00118-0/
[3] Yang S Y, Jung H S, Lim D I, et al. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2003, 63(1):93-120. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9692c64055ede8f886a2a97ba93984b3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] Liu Z, Tuo S, Colin C, et al. Detrital fine-grained sediment contribution from Taiwan to the northern South China Sea and its relation to regional ocean circulation[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 255(3/4): 149-155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3c70f15b2d54be4783aa8b6db264f74b
[5] 蒋东辉, 高 抒. 渤海海峡潮流底应力与沉积物分布的关系[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(4): 663-667. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.021
[6] 高 抒. 沉积物粒径趋势分析:原理与应用条件[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5): 826-836. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb200206014
[7] 乔淑卿, 石学法, 王国庆, 等. 渤海底质沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(4):139-147. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201004014
[8] 孙有斌, 高 抒, 李 军. 边缘海陆源物质中环境敏感粒度组分的初步分析[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(1):83-86. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.01.021
[9] Cheng P, Gao S, Bokuniewicz H. Net sediment transport patterns over the Bohai Strait based on grain size trend analysis[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 60(2): 203-212. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2003.12.009
[10] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 渤海地质[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 1985: 1-233.
[11] 陈中亚, 马妍妍, 李广雪. 中国东部陆架海区粒度分析研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(4):18-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201604003
[12] 姚政权, 石学法. 渤海湾沿岸第四纪海侵研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿.2015, 31(2): 9-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201502002
[13] 姚菁. 渤海南岸LZ908孔海陆交互相地层气候代用指标及沉积环境研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80068-1014308947.htm [14] 杨旭辉, 冯秀丽, 褚忠信, 等.中国东部陆架表层沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境浅析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 42(7/8):126-134. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qdhydxxb201207019
[15] 李 艳, 刘艳, 李安春, 等. 大连湾附近海域表层沉积物粒度特征及水动力环境指示[J]. 海洋通报, 2014, 33(5): 552-558. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hytb201405010
[16] 刘成, 胡日军, 朱龙海,等. 庙岛群岛海域沉积动力环境分区及沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(8): 24-33. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201808004
[17] 张剑, 李日辉, 王中波, 等. 渤海东部与黄海北部表层沉积物的粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5): 1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201605001
[18] 蓝先洪, 李日辉, 张志珣, 等. 渤海东部与黄海北部表层沉积物的元素地球化学记录[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(6):718-728. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201506004
[19] 王 双. 黄渤海表层沉积物磁学特征及其环境指示意义[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10423-1014329216.htm [20] 李日辉, 孙荣涛, 徐兆凯, 等. 黄海与渤海交界区附近表层沉积物中的底栖有孔虫分布与环境因素制约[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(3):93-103. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201403011
[21] 王 庆, 仲少云, 刘建华, 等. 山东庙岛海峡的峡道动力地貌[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(2):17-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200602003
[22] 乔淑卿, 石学法, 王国庆, 等. 渤海底质沉积物的粒度特征及输运趋势探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2009,32 (4) :139-146. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC201004014.htm
[23] 陈义兰, 吴永亭, 刘晓瑜, 等.渤海海底地形特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2013, 31(1):75-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2013.01.009
[24] 蔡 锋,曹超, 周兴华, 等. 中国近海海洋-海底地形地貌[M]. 北京:海洋出版社, 2013: 46-55.
[25] 陈晓辉, 张训华, 李日辉, 等. 渤海海峡海域灾害地质研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2014, 34(1):11-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7627231
[26] 刘建华, 王 庆, 仲少云, 等. 渤海海峡老铁山水道动力地貌及演变研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2008, 27(1):68-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2008.01.010
[27] 赵铁虎, 齐君, 梅赛, 等. 渤海海峡跨海通道地质条件调查与分析[J]. 科技导报, 2016, 34(21): 39-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kjdb201621008
[28] Folk R L, Andrews P B, Lewis D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand journal of geology and geophysics, 1970, 13(4): 937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[29] Wentworth, Chester K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1922, 30(5): 377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910
[30] McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation [J]. Techniques in sedimentology, 1988: 63-85. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0227211167/
[31] 李 琰,于洪军, 易 亮, 等. 渤海南部Lz908孔海陆交互沉积的粒度特征及其对沉积环境的指示[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(5):107-113. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hykx201405016
[32] 吕文哲, 易 亮,付腾飞,等.渤海南部早-中更新统湖相沉积的粒度特征及其对沉积环境的指示[J]. 海岸工程, 2017, 36(1):34-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2017.01.004
[33] Passega R. Texture as Characteristic of Clastic Deposition[J]. Bull amer assoc petrol geol, 1957, 41:1952-1984. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=548da65c8633bd39ebec32127d3b44d6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[34] Passega R. Grain size representation by CM patterns as a geologic tool [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1964, 34(4):830-847. doi: 10.1306/74D711A4-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[35] 李 勇, 李海燕, 赵应权. 沉积物粒度特征及其对环境的指示意义——以濠河为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(3): 918-925. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201503025
[36] 孙 军,杨慧良,何 磊,等.渤海海峡BHS01孔沉积物磁性地层学研究[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(02):315-324. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201902008
-



 下载:
下载: