FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF MICRO-SEEPAGE IN HYDRATE-BEARING QUARTZ SANDS BASED ON DIGITAL CORES
-
摘要:
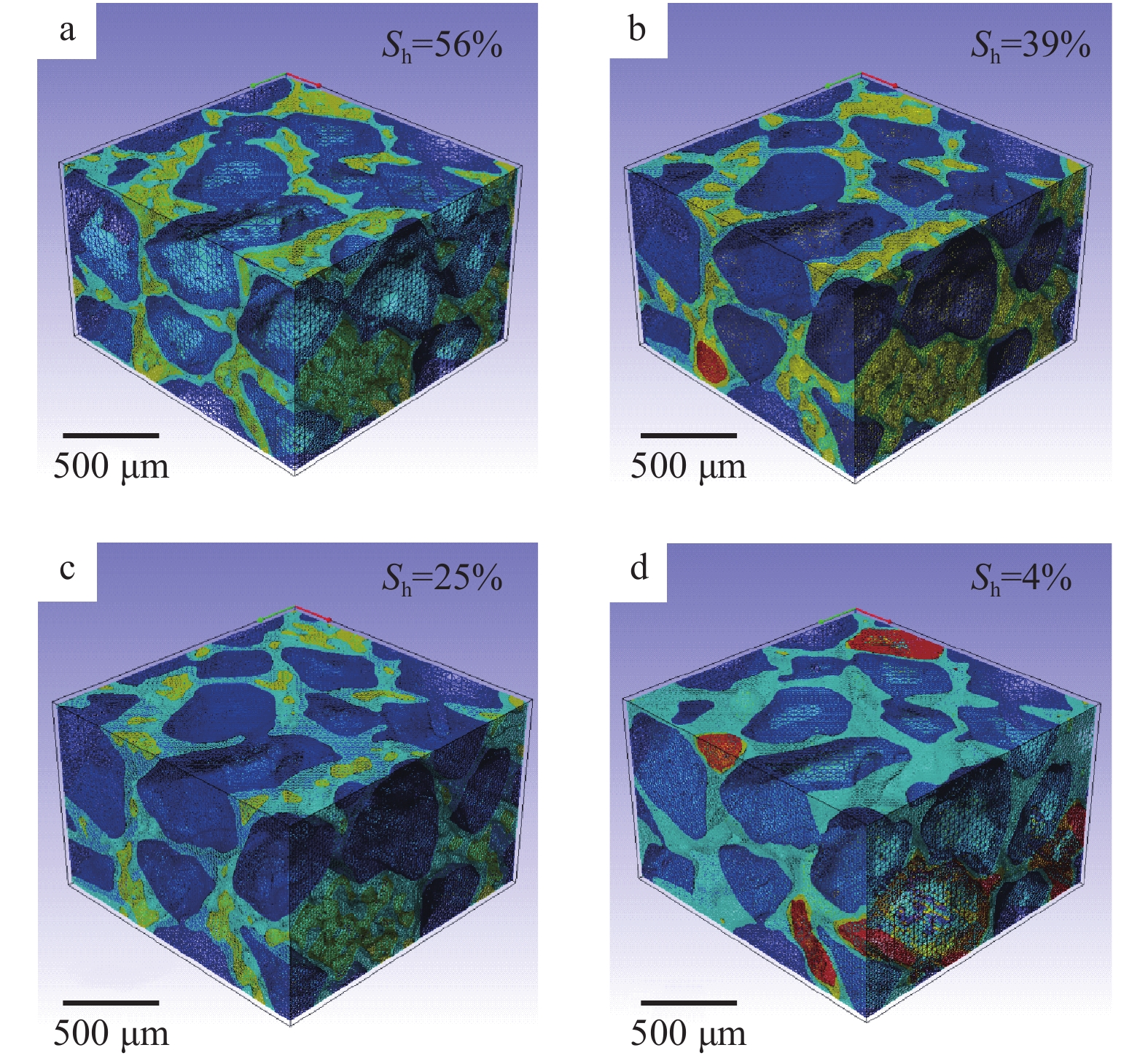
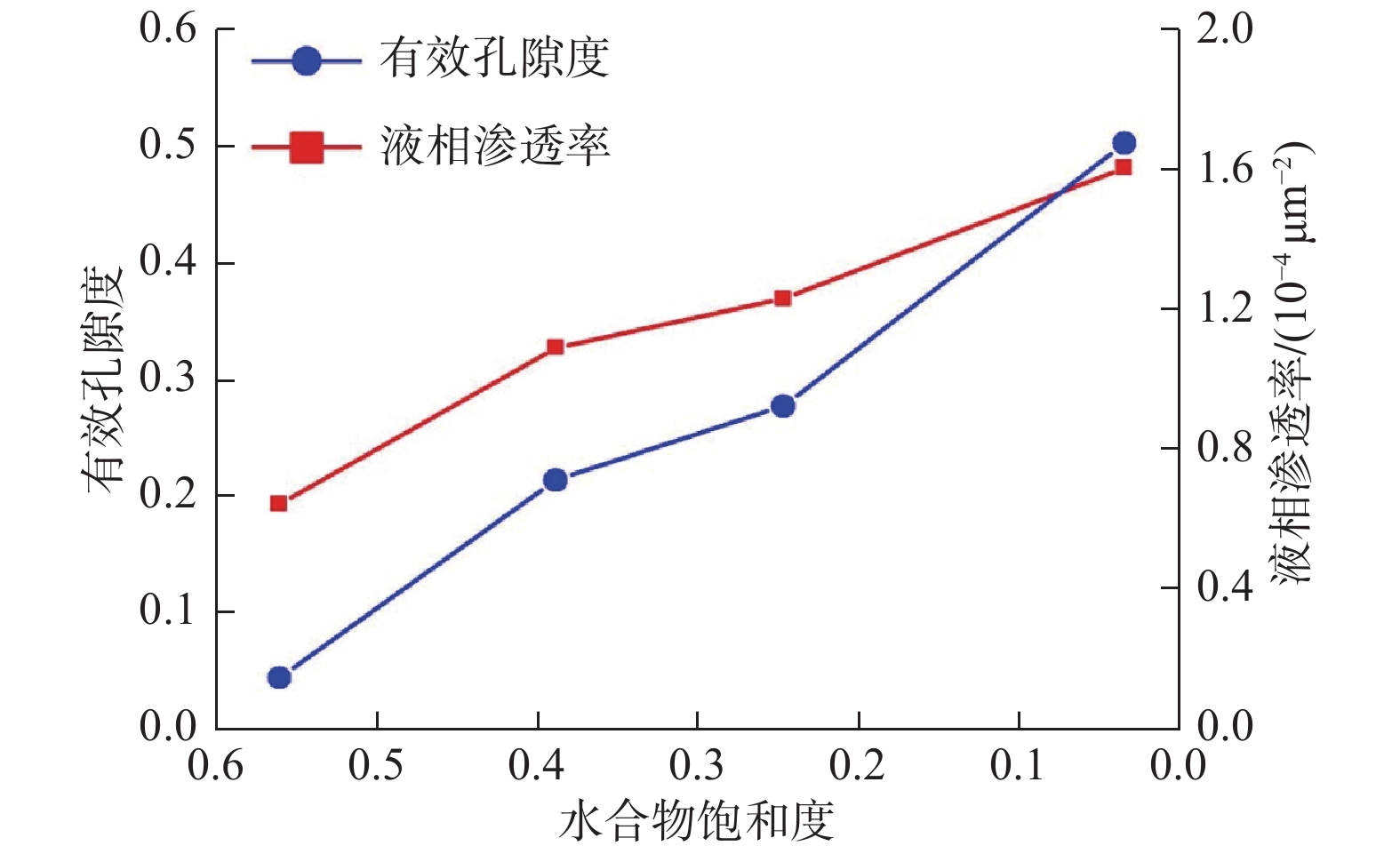
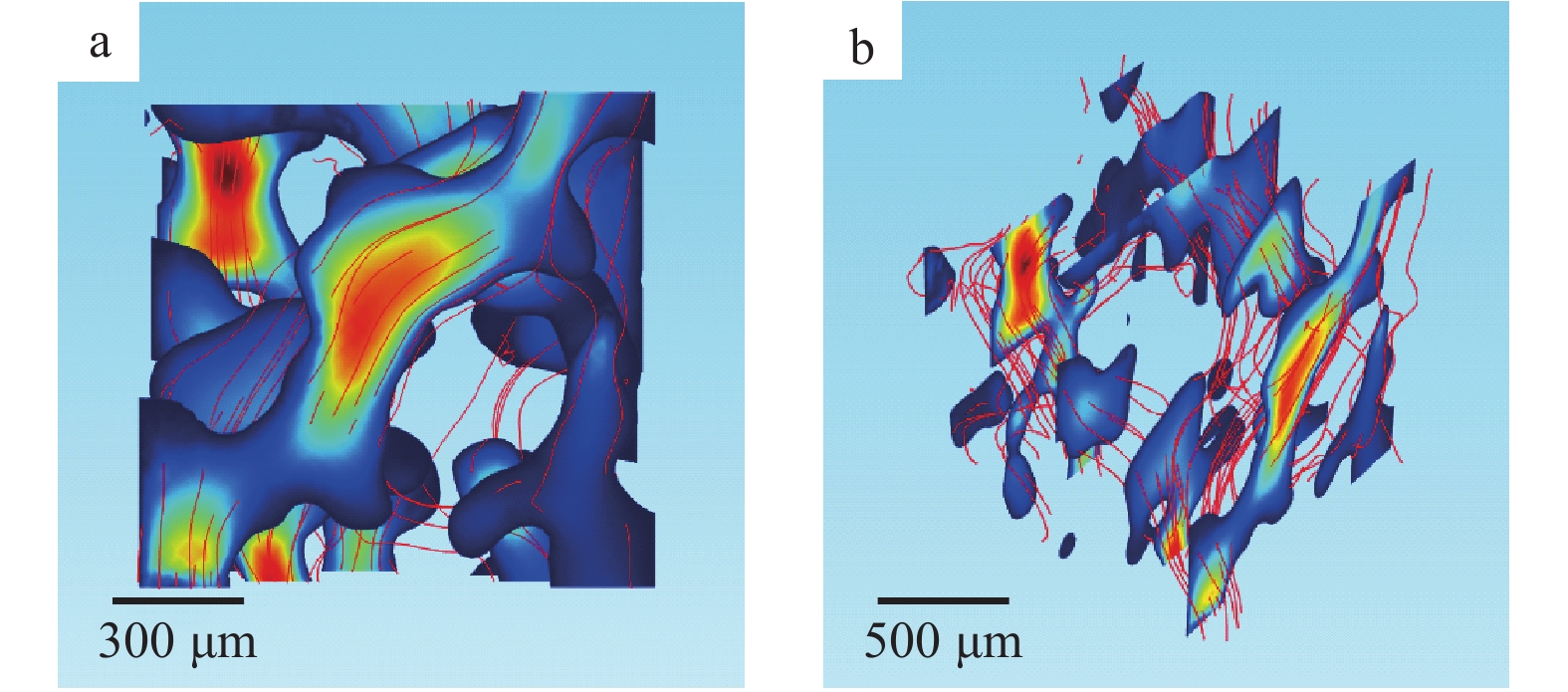
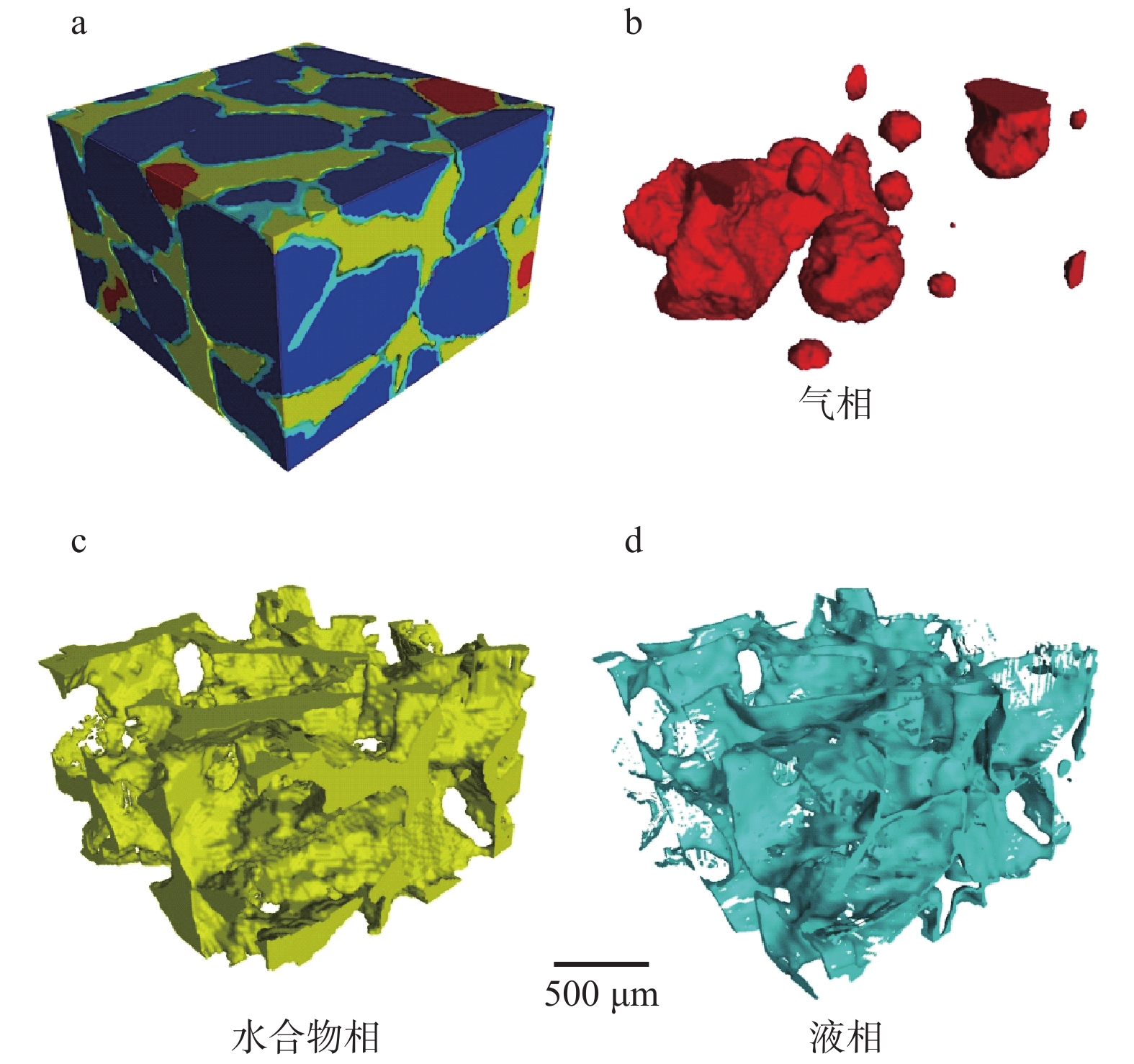
利用X射线计算机断层扫描系统(CT)获得不同饱和度下含水合物石英砂内部气、水、水合物各相态分布特征,通过有限元方法计算了不同水合物饱和度下石英砂液相渗透率变化,并模拟了流体在孔隙内的流动情况,获得了假定边界条件下孔隙流体的三维流速分布。研究结果表明,随着水合物饱和度的降低,渗透率逐渐增大,其中当水合物饱和度从56%下降到39%时,液相渗透率值增速最大;水合物分解末期,液相渗透率并未随着有效孔隙度的增大而快速升高,通过CT扫描图像显示,部分石英砂孔隙和喉道可见甲烷气泡滞留,由于气体的贾敏效应在一定程度上阻碍了液体的流动,从而导致液相渗透率增速降低。本研究建立了一种基于石英砂内部真实孔隙特征的液相渗透率和液体流速计算方法,可为水合物开采过程中储层微观渗流演化机理研究提供参考。
Abstract:In this study, the distribution characteristics of gas, water and hydrate in hydrate-bearing quartz sands under different saturation are acquired by X-ray computed tomography (CT). The change of liquid phase permeability is calculated using the finite element method. The flow of fluid in the pores is simulated and the three-dimensional velocity distribution of the pore fluid under the assumed boundary conditions is obtained. The results show that the liquid phase permeability in quartz sand increases gradually with the decrease of hydrate saturation. When the hydrate saturation decreases from 56% to 39%, the liquid phase permeability value of quartz sand increases to the maximum. At the end of hydrate decomposition, the permeability does not increase rapidly with the increase in effective porosity. The CT scan image shows that some methane bubbles are trapped in quartz sand pores and throat. Due to the Jamin effect, the flow of liquid is hindered to a certain extent, which leads to the decrease of liquid phase permeability growth rate. In this study, a calculation method of liquid phase permeability and liquid velocity based on the real pore characteristics of the hydrate-bearing quartz sand is established, which can provide a reference for the study of the evolution mechanism of micro seepage in the process of hydrate exploitation.
-
Key words:
- methane hydrate /
- digital core /
- finite element /
- liquid phase permeability /
- velocity
-

-
[1] Nimblett J,Ruppel C. Permeability evolution during the formation of gas hydrates in marine sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2003,108(B9):2420.
[2] Priest J A,Druce M,Roberts J,et al. PCATS Triaxial:A new geotechnical apparatus for characterizing pressure cores from the Nankai Trough,Japan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2015,66:460-470. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.12.005
[3] 李彦龙,刘乐乐,刘昌岭,等. 天然气水合物开采过程中的出砂与防砂问题[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2016,32(7):36-43.
[4] 蔡建超,夏宇轩,徐 赛,等. 含水合物沉积物多相渗流特性研究进展[J]. 力学学报,2020,52(1):208-223. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-362
[5] 林承焰,吴玉其,任丽华,等. 数字岩心建模方法研究现状及展望[J]. 地球物理学进展,2018,33(2):679-689. doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0335
[6] Dai S,Seol Y. Water permeability in hydrate-bearing sediments:A pore-scale study[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2014,41(12):4176-4184. doi: 10.1002/2014GL060535
[7] 张思勤,汪志明,洪 凯,等. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的3D数字岩心渗流特征分析[J]. 测井技术,2016,40(1):12-22.
[8] 闫国亮,孙建孟,刘学锋,等. 储层岩石微观孔隙结构特征及其对渗透率影响[J]. 测井技术,2014,38(1):28-32.
[9] 王平全,陶 鹏,刘建仪,等. 基于数字岩心的低渗透率储层微观渗流和电传导数值模拟[J]. 测井技术,2017,41(4):389-393.
[10] 曹廷宽,刘成川,曾 焱,等. 基于CT扫描的低渗砂岩分形特征及孔渗参数预测[J]. 断块油气田,2017,24(5):657-661.
[11] 姜黎明,刘宁静,孙建孟,等. 利用CT图像与压汞核磁共振构建高精度三维数字岩心[J]. 测井技术,2016,40(4):404-407.
[12] Wang J Q,Zhao J F,Yang M J,et al. Permeability of laboratory-formed porous media containing methane hydrate:Observations using X-ray computed tomography and simulations with pore network models[J]. Fuel,2015,145:170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.12.079
[13] Wang D G,Wang C C,Li C F,et al. Effect of gas hydrate formation and decomposition on flow properties of fine-grained quartz sand sediments using X-ray CT based pore network model simulation[J]. Fuel,2018,226:516-526. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.04.042
[14] 喻西崇,刘 瑜,宋永臣,等. 基于LBM方法的天然气水合物沉积物中多相流动规律研究[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2011,35(5):99-103.
[15] Chen X Y,Verma R,Espinoza D N,et al. Pore-scale determination of gas relative permeability in hydrate-bearing sediments using X-ray computed micro-tomography and lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Water Resources Research,2018,54(1):600-608. doi: 10.1002/2017WR021851
[16] Li C F,Liu C L,Hu G W,et al. Investigation on the multi-parameter of hydrate-bearing sands using nano-focus X-ray computed tomography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2019,124(3):2286-2296. doi: 10.1029/2018JB015849
[17] 刘乐乐,张 准,宁伏龙,等. 含水合物沉积物渗透率分形模型[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学,2019,49:034614.
[18] Zhang Z,Li C F,Ning F L,et al. Pore fractal characteristics of hydrate‐bearing sands and implications to the saturated water permeability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2020,125:e2019JB018721.
[19] Liu L L,Zhang Z,Li C F,et al. Hydrate growth in quartzitic sands and implication of pore fractal characteristics to hydraulic,mechanical,and electrical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2020,75:103-109.
[20] 李承峰,胡高伟,业渝光,等. X射线计算机断层扫描测定沉积物中水合物微观分布[J]. 光电子·激光,2013,24(3):551-557.
-



 下载:
下载: