Research progress of the Meso-Cenozoic sedimentary evolution in eastern Pakistan sea
-
摘要:
巴基斯坦海域地处全球三大板块交汇区域,地质历史时期经历过复杂的构造-沉积演化;新生代以来,印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞导致喜马拉雅快速隆升,并在巴基斯坦东部海域发育世界第2大深水扇−印度扇;此外,还位于亚洲两大季风区之一的印度季风区,是研究“构造-沉积-气候”耦合问题的天然有利场所。通过归纳总结前人研究成果,对巴基斯坦东部海域中—新生代沉积研究现状进行了综述,提出了该区尚存争议的主要问题和下一步研究方向。目前,针对巴基斯坦东部海域沉积研究主要有4大方向:中新世以来印度扇沉积研究现状;中—新生代其他典型地质体沉积研究现状;晚第四纪末次浊流沉积研究现状;构造-沉积-气候耦合研究现状。相比较而言,对于德干玄武岩之下的中生代沉积、典型沉积体系之外的区域沉积演化、陆域-海域沉积体系对比等方面报道较少,尚需更加深入地研究。
Abstract:The East Pakistan sea area, located in the junction of three major plates of the world, has experienced complex tectonic-sedimentary evolution in history. Since Cenozoic era, the collision between the Indian plate and the Eurasian plate has been accelerated, that led to the rapid uplifting of the Himalaya, the form of the Indus deep-water fan, the second largest in the world, and the development of the sea off the Pakistan land. In addition to it, the area is heavily influenced by Indian monsoon as one of the two major monsoon regions in Asia. It is indeed the unique place in the world for study of the coupling relationship and interaction among the tectonic, sedimentary and climatic factors. Upon the basis of previous research results, we summarized in this paper the current research status of sedimentary evolution of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic basins in the Eastern Pakistan sea, put forward some main problems remained in controversy and made suggestions for future researches. Four main research interests and directions are put in front of us, i.e, the Indus fan since Miocene; the typical Meso-Cenozoic sedimentary geological bodies; the latest Quaternary turbidite sedimentology and the interaction of tectonic, sedimentation and climate. So far, few reports are available concerning the Mesozoic sediments beneath the Deccan basalt, the regional sedimentary evolution out of the depositional system, and the correlation of continental-marine sedimentary systems. Further investigations should be accelerated.
-
Key words:
- eastern Pakistan sea /
- sedimentary evolution /
- Indus Fan /
- coupling relationship
-

-
图 2 中生代以来印度板块关键构造事件[3]
Figure 2.
图 3 巴基斯坦海域-陆地地层对比柱状图[2]
Figure 3.
图 5 古近纪以来印度扇(上部)沉积速率演化[34]
Figure 5.
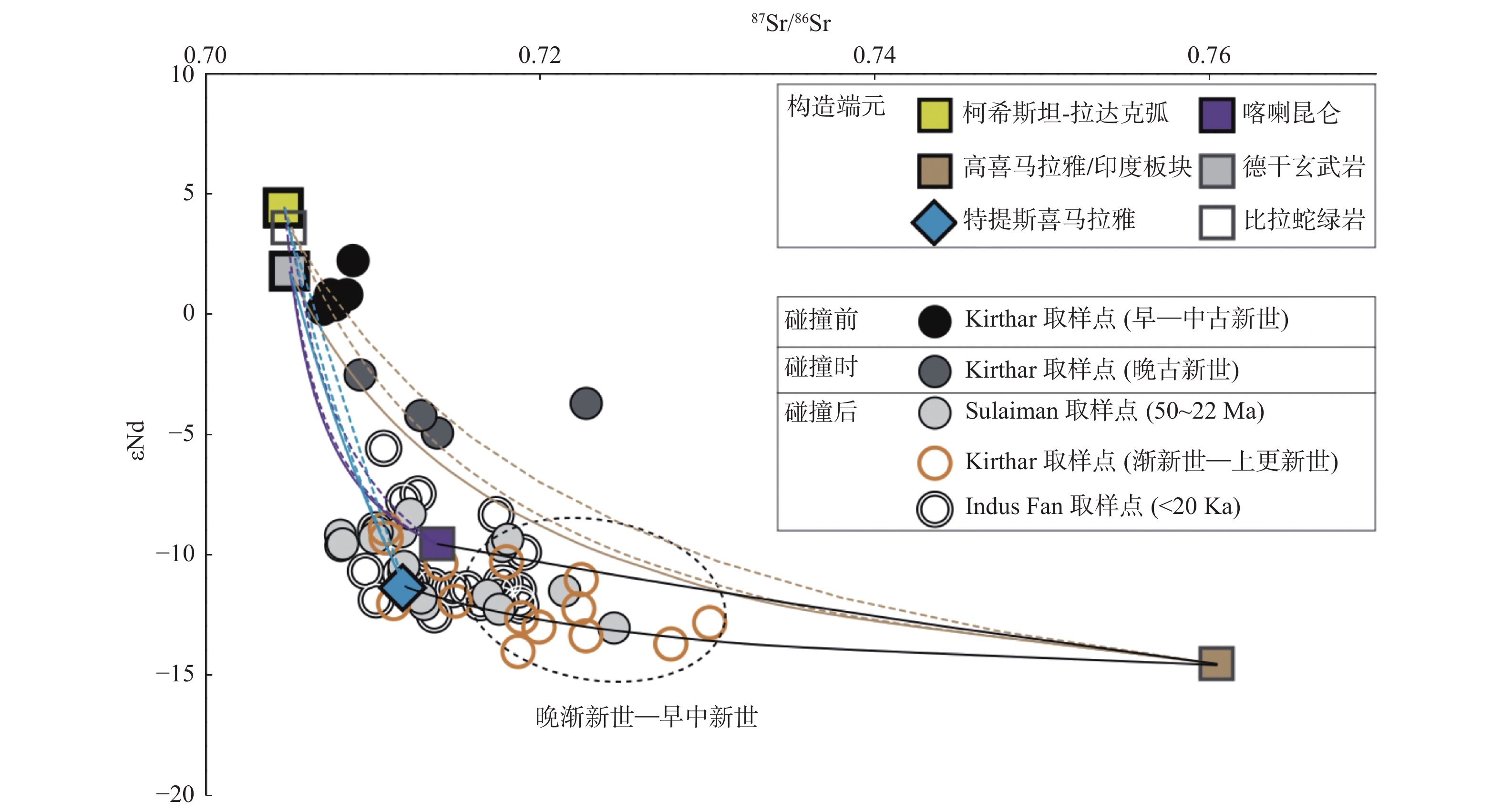
图 7 εNd-87Sr/86Sr同位素交汇图显示下印度河与印度扇物源输入信号演化[36]
Figure 7.
图 8 典型碳酸盐岩台地地震反射特征[24]
Figure 8.
图 9 晚第四纪印度扇浊流沉积演化模式[41]
Figure 9.
图 10 中-新生代南亚和印度洋地区构造-沉积-气候耦合分析[35]
Figure 10.
-
[1] SCOTESE C R,GAHAGAN L M AND LARSON R L. Plate tectonic reconstructions of the Cretaceous and Cenozoic ocean basins[J]. Tectonophysics,1988,155(1/4):27-48. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(88)90259-4
[2] CARMICHAEL S M,AKHTER S,BENNETT J K,et al. Geology and hydrocarbon potential of the offshore Indus Basin,Pakistan[J]. Petroleum Geoscience,2009,15(2):107-116. doi: 10.1144/1354-079309-826
[3] CHATTERJEE S,GOSWAMI A,SCOTESE C R. The longest voyage:tectonic,magmatic,and paleoclimatic evolution of the Indian plate during its northward flight from Gondwana to Asia[J]. Gondwana Research,2013,23(1):238-267. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.07.001
[4] GAINA C,VAN HINSBERGEN D J J,SPAKMAN W. Tectonic interactions between India and Arabia since the Jurassic reconstructed from marine geophysics,ophiolite geology,and seismic tomography[J]. Tectonics,2015,34:875-906. doi: 10.1002/2014TC003780
[5] GAEDICKE C,PREXL A,SCHLÜTER H U,et al. Seismic stratigraphy and correlation of major regional unconformities in the northern Arabian Sea[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,2002,195(1):25-36. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2002.195.01.03
[6] SOLANGI S H,NAZEER A,ABBASI S A,et al. Morphological features of shelf margin:Examples from the Pakistan Offshore[J]. Geodesy and Geodynamics,2019,10:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2018.09.004
[7] MCHARGUE T R,WEBB J E. Internal geometry,seismic facies,and petroleum potential of canyons and inner fan channels of the Indus submarine fan[J]. AAPG bulletin,1986,70(2):161-180.
[8] CLIFT P,SHIMIZU N,LAYNE G,et al. Fifty-five million years of Xizang evolution recorded in the Indus Fan[J]. Eos,Transactions American Geophysical Union,2000,81(25):277-281.
[9] CLIFT P,CALVES G,GIOSAN L,et al. Climate and Tectonic Signals Preserved in the Indus Submarine Fan,Arabian Sea[J]. AGUFM,2007,2007:OS33A-0995.
[10] KHIM B K,LEE J,HA S,et al. Variations in δ13C values of sedimentary organic matter since late Miocene time in the Indus Fan (IODP Site 1457) of the eastern Arabian Sea[J]. Geological Magazine,2020,157(6):1012-1021. doi: 10.1017/S0016756818000870
[11] GOMBOS A M,POWELL W G,NORTON I O. The tectonic evolution of western India and its impact on hydrocarbon occurrences:an overview[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1995,96:119-129. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(94)00129-I
[12] MINSHULL T A,LANE C I,COLLIER J S,et al. The relationship between rifting and magmatism in the northeastern Arabian Sea[J]. Nature Geoscience,2008,1(7):463-467. doi: 10.1038/ngeo228
[13] KHAN M,LIU Y. Geodynamic evolution of the offshore Indus Basin Pakistan:the western Indian plate passive continental margin[J]. Geophysical Journal International,2019,217(2):1366-1386. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggz091
[14] KHAN M,ABDELMAKSOUD A. Unfolding impacts of freaky tectonics on sedimentary sequences along passive margins:Pioneer findings from western Indian continental margin (Offshore Indus Basin)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020:104499.
[15] KOLLA V,COUMES F. Morphology,internal structure,seismic stratigraphy,and sedimentation of Indus Fan[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1987,71(6):650-677.
[16] KOLLA V, SCHWAB A M. Indus Fan: multi-channel seismic reflection images of channel-levee-overbank complexes[M]//Atlas of Deep Water Environments. Springer, Dordrecht, 1995: 100-104.
[17] CLIFT P D,SHIMIZU N,LAYNE G D,et al. Development of the Indus Fan and its significance for the erosional history of the Western Himalaya and Karakoram[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,2001,113(8):1039-1051. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2001)113<1039:DOTIFA>2.0.CO;2
[18] GAEDICKE C,SCHLÜTER H U,ROESER H A,et al. Origin of the northern Indus Fan and Murray Ridge,Northern Arabian Sea:interpretation from seismic and magnetic imaging[J]. Tectonophysics,2002,355(1/4):127-143. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00137-3
[19] CLIFT P,GAEDICKE C. Accelerated mass flux to the Arabian Sea during the middle to late Miocene[J]. Geology,2002,30(3):207-210. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0207:AMFTTA>2.0.CO;2
[20] CLIFT P,GAEDICKE C,EDWARDS R,et al. The stratigraphic evolution of the Indus Fan and the history of sedimentation in the Arabian Sea[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches,2002,23(3):223-245. doi: 10.1023/A:1023627123093
[21] INAM A, TAHIR M. Channel-levee system-the major controlling mechanism for the sediment deposition on the Indus Fan[C]//Joint International Conference and First Annual Meeting of IGCP-475 DeltaMAP and APN project on the Mega-Deltas of Asia. 2004: 15-20.
[22] KHAN N,REHMAN K,AHMAD S,et al. Sequence stratigraphic analysis of Eocene Rock Strata,Offshore Indus,southwest Pakistan[J]. Marine Geophysical Research,2016,37(3):207-228. doi: 10.1007/s11001-016-9280-5
[23] SHAHZAD K,BETZLER C,AHMED N,et al. Growth and demise of a Paleogene isolated carbonate platform of the Offshore Indus Basin,Pakistan:effects of regional and local controlling factors[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2018,107(2):481-504. doi: 10.1007/s00531-017-1504-7
[24] SHAHZAD K,BETZLER C,QAYYUM F. Controls on the Paleogene carbonate platform growth under greenhouse climate conditions (Offshore Indus Basin)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,101:519-539. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.025
[25] CLIFT P D. Controls on the erosion of Cenozoic Asia and the flux of clastic sediment to the ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2006,241(3/4):571-580. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.11.028
[26] PANDEY D K,CLIFT P D,KULHANEK D K,et al. Expedition 355 summary[J]. Proceedings of the International Ocean Discovery Program,2016:355.
[27] 刘瑞璇,鹿化煜,王珧,等. 东阿拉伯海拉克希米盆地浊流沉积序列的粒度变化及其对中更新世气候转型的响应[J]. 第四纪研究,2018,38(5):1120-1129. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.05.07
[28] 龚建明,廖晶,梁杰,等. 巴基斯坦海域油气勘探方向探讨[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(11):1-6.
[29] 江凯禧,姚长华,郭清正,等. 印度扇深水区古—始新统烃源岩特征及发育模式[J]. 沉积学报,2016,34(4):785-793.
[30] QAYYUM M,LAWRENCE R D,NIEM A R. Discovery of the palaeo-Indus delta-fan complex[J]. Journal of the Geological Society,1997,154(5):753-756. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.154.5.0753
[31] GARZANTI E,CRITELLI S,INGERSOLL R V. Paleogeographic and paleotectonic evolution of the Himalayan Range as reflected by detrital modes of Tertiary sandstones and modern sands (Indus transect,India and Pakistan)[J]. Geological society of america bulletin,1996,108(6):631-642. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1996)108<0631:PAPEOT>2.3.CO;2
[32] BASTIA R, RADHAKRISHNA M. Sedimentation history and development of fan system along the continental margins of India[M]//Developments in Petroleum Science. Elsevier, 2012, 59: 127-160.
[33] ELLOUZ-ZIMMERMANN N, LALLEMANT S J, CASTILLA R, et al. Offshore frontal part of the Makran Accretionary prism: The Chamak survey (Pakistan)[M]//Thrust belts and foreland basins. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007: 351-366.
[34] MÉTIVIER F,GAUDEMER Y,TAPPONNIER P,et al. Mass accumulation rates in Asia during the Cenozoic[J]. Geophysical Journal International,1999,137(2):280-318.
[35] CALVÈS G. Tectono-stratigraphic and climatic record of the NE Arabian Sea[D]. Aberdeen: University of Aberdeen, 2009.
[36] ZHUANG G,NAJMAN Y,GUILLOT S,et al. Constraints on the collision and the pre-collision tectonic configuration between India and Asia from detrital geochronology,thermochronology,and geochemistry studies in the lower Indus basin,Pakistan[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2015,432:363-373. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.10.026
[37] CALVÈS G, SCHWAB A M, HUUSE M, et al. Seismic volcanostratigraphy of the western Indian rifted margin: the pre‐Deccan igneous province[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2011, 116(B1).
[38] PRINS M A,POSTMA G,CLEVERINGA J,et al. Controls on terrigenous sediment supply to the Arabian Sea during the late Quaternary:the Indus Fan[J]. Marine Geology,2000,169(3/4):327-349. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00086-4
[39] GOVIL P,NAIDU P D. Late Quaternary changes in depositional processes along the western margin of the Indus Fan[J]. Geo-Marine Letters,2008,28(1):1-6. doi: 10.1007/s00367-007-0083-1
[40] LIMMER D R,HENSTOCK T J,GIOSAN L,et al. Impacts of sediment supply and local tectonics on clinoform distribution:the seismic stratigraphy of the mid Pleistocene-Holocene Indus Shelf[J]. Marine Geophysical Research,2012,33(3):251-267. doi: 10.1007/s11001-012-9160-6
[41] BOURGET J,ZARAGOSI S,RODRIGUEZ M,et al. Late Quaternary megaturbidites of the Indus Fan:Origin and stratigraphic significance[J]. Marine Geology,2013,336:10-23. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.11.011
[42] CLIFT P D,GIOSAN L,HENSTOCK T J,et al. Sediment storage and reworking on the shelf and in the canyon of the Indus River‐fan system since the last glacial maximum[J]. Basin Research,2014,26(1):183-202. doi: 10.1111/bre.12041
[43] CLIFT P D,HODGES K V,HESLOP D,et al. Correlation of Himalayan exhumation rates and Asian monsoon intensity[J]. Nature geoscience,2008,1(12):875-880. doi: 10.1038/ngeo351
[44] NAJMAN Y. The detrital record of orogenesis:a review of approaches and techniques used in the Himalayan sedimentary basins[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2006,74(1/2):1-72.
[45] CURRAY J R. Sediment volume and mass beneath the Bay of Bengal[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1994,125(1/4):371-383. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90227-5
[46] KITOH A. Effects of mountain uplift on East Asian summer climate investigated by a coupled atmosphere-ocean GCM[J]. Journal of Climate,2004,17(4):783-802. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0783:EOMUOE>2.0.CO;2
[47] ZHISHENG A,KUTZBACH J E,PRELL W L,et al. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Xizang plateau since Late Miocene times[J]. Nature,2001,411(6833):62-66. doi: 10.1038/35075035
[48] CLEMENS S,PRELL W,MURRAY D,et al. Forcing mechanisms of the Indian Ocean monsoon[J]. Nature,1991,353(6346):720-725. doi: 10.1038/353720a0
[49] RUDDIMAN W F. What is the timing of orbital-scale monsoon changes?[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2006,25(7/8):657-658. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.02.004
[50] CLEMENS S C,Murray D W,Prell W L. Nonstationary phase of the Plio-Pleistocene Asian monsoon[J]. Science,1996,274(5289):943-948. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5289.943
[51] 孙国洪,田丽艳,李小虎,等. 西南印度洋中脊岩石地球化学特征及其岩浆作用研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(5):126-138.
[52] 王小杰,颜中辉,刘俊,等. 基于模型优化的广义自由表面多次波压制技术在印度洋深水海域的应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(5):221-230.
[53] 廖晶,龚建明,陈建文,等. 印度扇近海盆地重力滑动构造新发现[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(6):76-79.
[54] 韩宗珠,孙苑高,王传,等. 西南印度洋中脊玄武岩地球化学特征及其对岩浆过程的指示意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(1):11-19.
-




 下载:
下载: