Semi-quantitative restoration of paleobathymetric of Baiyun Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin based on depositional architecture
-
摘要:
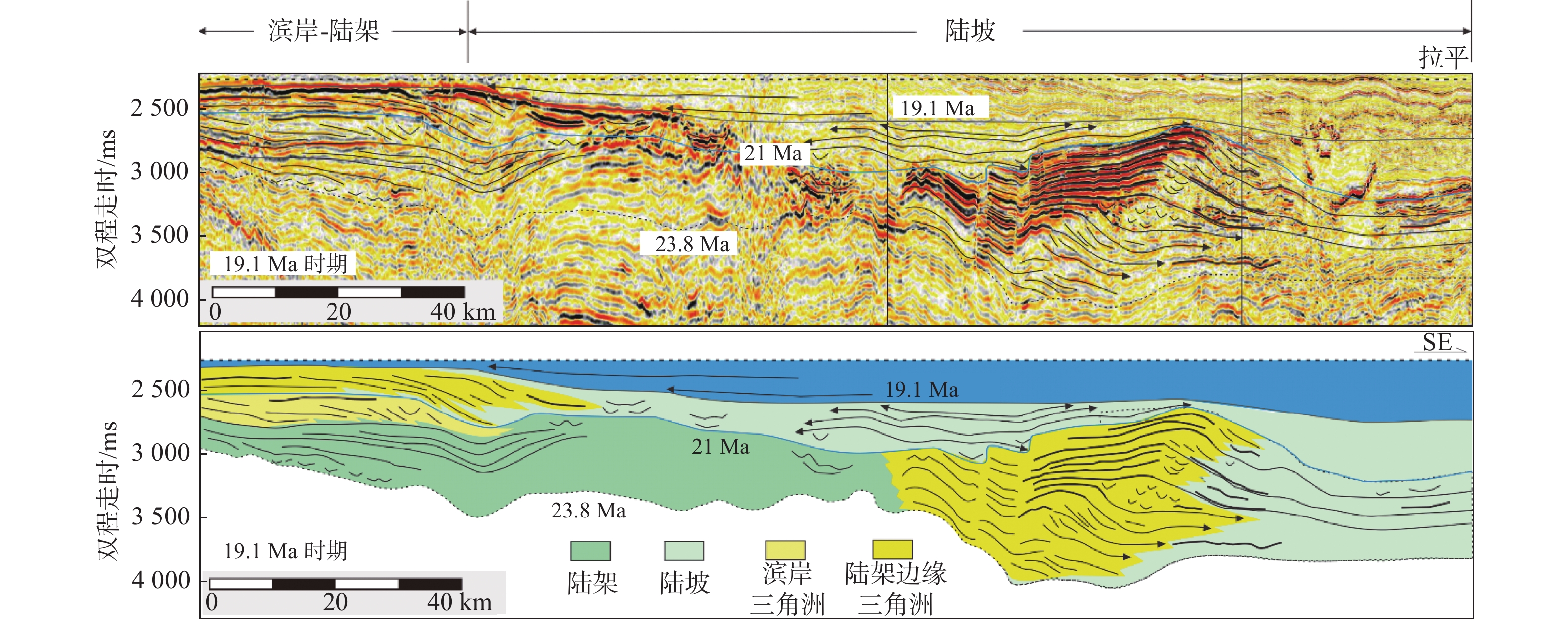
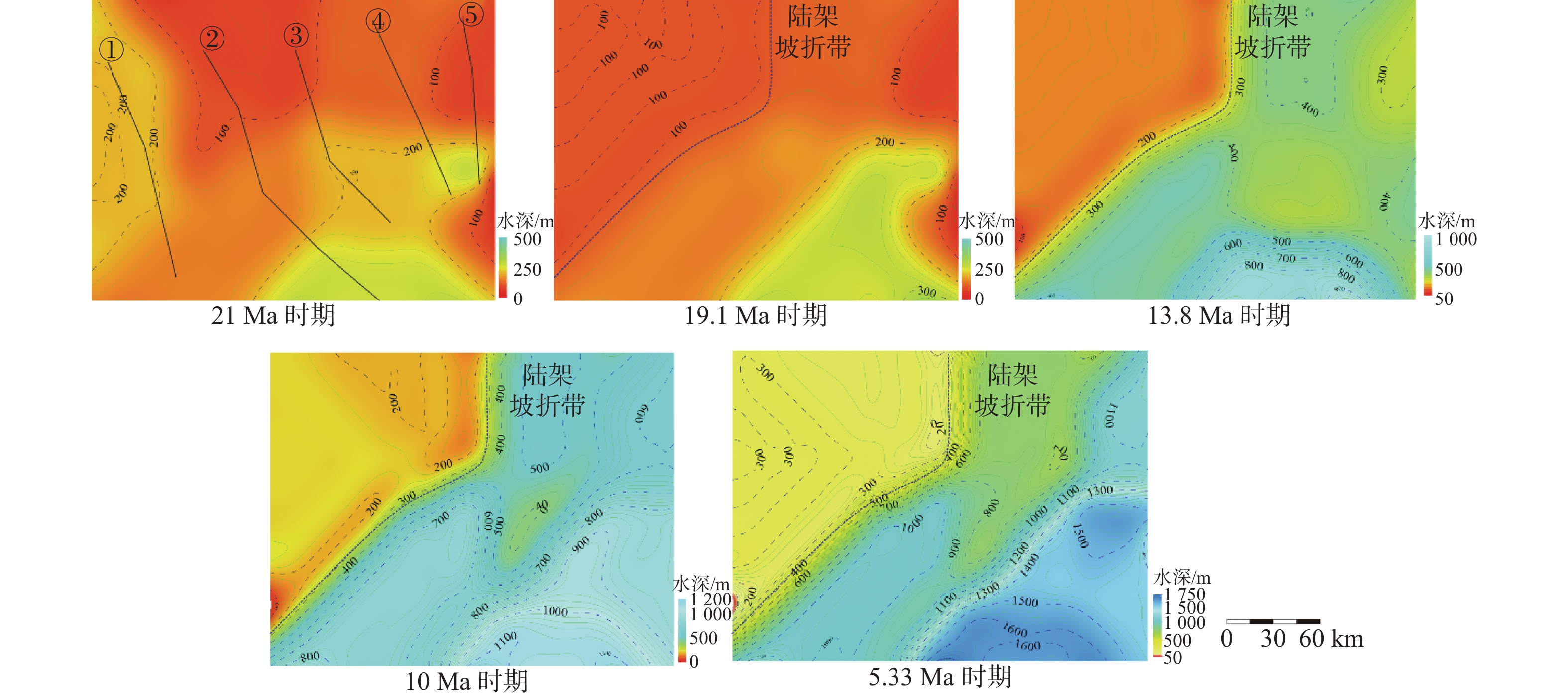
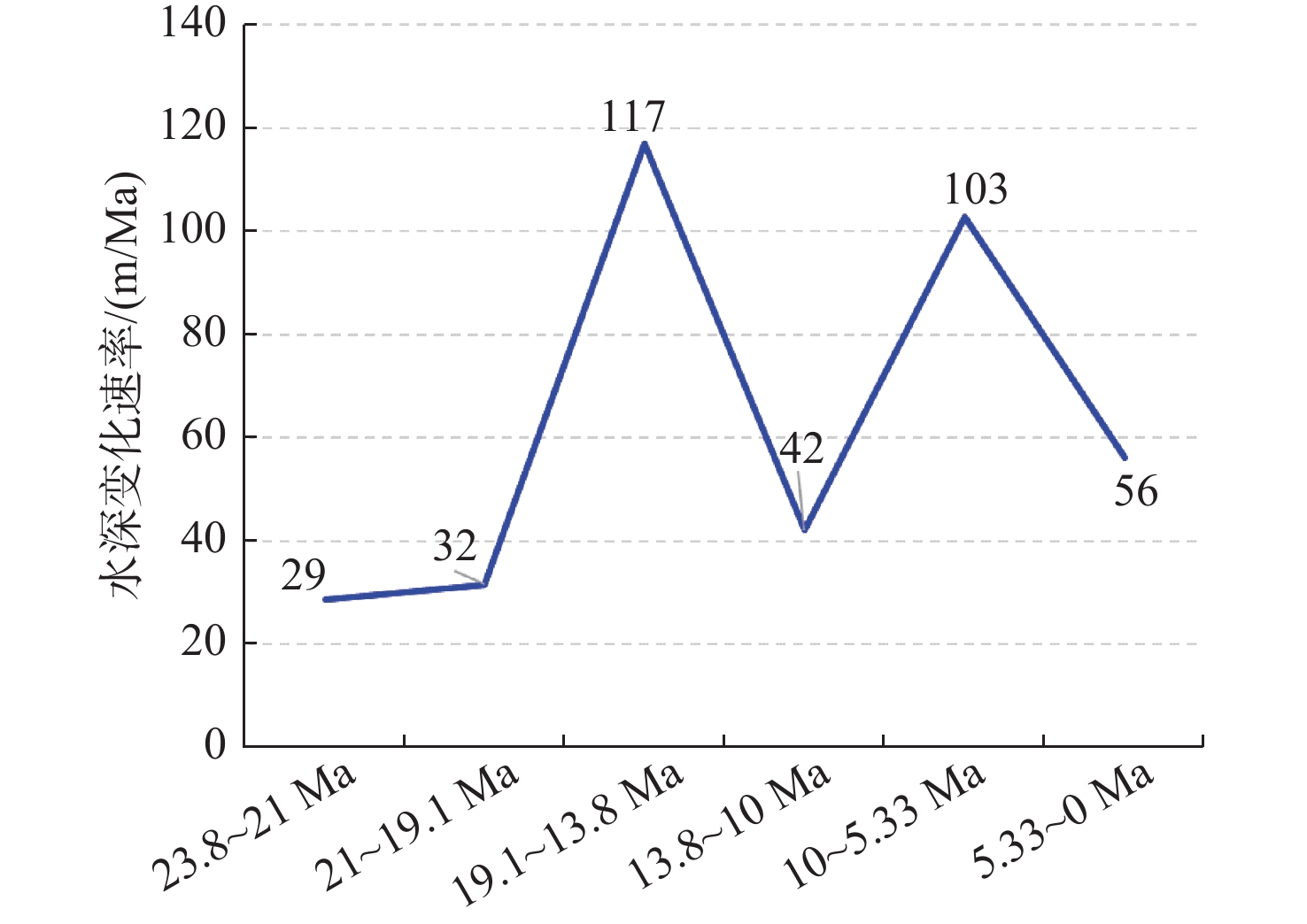
针对南海北部深水沉积盆地的古水深恢复这一难题,以珠江口盆地白云凹陷为例,根据陆架陆坡沉积特征,通过在三级层序格架内精细地震线描和层拉平恢复结合的沉积构型技术对白云凹陷裂后阶段5个关键地质时期(21 Ma、19.1 Ma、13.8 Ma、10 Ma和5.33 Ma)古水深进行研究。结果表明,21 Ma、19.1 Ma时期平均古水深<300 m,之后至13.8 Ma时期最大水深900 m。10 Ma和5.33 Ma时期,水深由1 100 m扩大至1 600 m。从21~5.33 Ma时期,陆架坡折带沿NW-SE向分布在白云北坡,古水深表现为西北陆架区浅,东南陆坡-深海平原区水体深。白云凹陷古水深整体上经历了浅海-半深海-深海的水体持续加深过程,存在2期(13.8 Ma和5.33 Ma)水深速率相对其他时期变快的时期,古水深变化速率分别为117和103 m/Ma,13.8 Ma时期水体加深速率最大。古水深的研究成果对白云凹陷热沉降史和沉积古地貌形态恢复具有重要研究意义。
Abstract:Aiming at reconstruction of paleobathymetric depth in the deep-water sedimentary basins in the northern South China Sea, this paper takes the Baiyun Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin as an example. According to the sedimentary characteristics of the continental shelf and slope, this study is based on depositional architecture by characterization of seismic profile and bedding flattening in third-order sequence in five critical geological stages(21, 19.1, 13.8, 10 and 5.33 Ma) of post-rift stage in Baiyun Sag. The results show that the average paleobathymetric depth in the 21 Ma and 19.1 Ma stages is less than 300 m, from then to 13.8 Ma, the maximum paleobathymetric depth is 900 m. During the 10 Ma and 5.33 Ma stages, the paleobathymetric depth expanded from 1100 m to 1600 m. From 21 Ma to 5.33 Ma, the shelf break belt had spreaded along the northwest-southeast direction on the northern slope of Baiyun Sag. The paleobathymetric depth of northwest shelf area is shallow, and the southeast continental slope and deep sea plain area is deep on the plane. The paleobathymetric depth of the Baiyun Sag had undergone a continuous deepening process of shallow sea to semi-deep sea and finally deep sea, and there were two stages (13.8 Ma and 5.33 Ma) much faster paleobathymetric depth rate than other stage in Baiyun Sag, the paleo-water depth change rate is 117 m/Ma and 103 m/Ma respectively,and the deepening rate of the paleobathymetric depth was the largest in the 13.8 Ma stage. The result of paleobathymetric has important research and guiding significance for the determination of the key parameters of paleobathymetric for thermal depression history research and the restoration of sedimentary paleomorphology.
-
Key words:
- paleobathymetric /
- semi-quantitative /
- sedimentary architecture /
- Baiyun Sag /
- Pearl River Mouth Basin
-

-
[1] AZMY K,VEIZER J,JIN J,et al. Paleobathymetry of a Silurian shelf based on brachiopod assemblages:an oxygen isotope test[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences,2006,43(3):281-293. doi: 10.1139/e05-109
[2] CLIFTON H E. Sedimentologic approaches to paleobathymetry,with applications to the Merced Formation of Central California[J]. Palaios,1988,3(5):507-522. doi: 10.2307/3514723
[3] PLINT A G,TYAGI A,HAY M J,et al. Clinoforms,paleobathymetry,and mud dispersal across the Western Canada Cretaceous foreland basin:evidence from the Cenomanian Dunvegan Formation and contiguous strata[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2009,79(3):144-161. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2009.020
[4] TAYLOR P D,KUKLINSKI P,GORDON D P. Branch diameter and depositional depth in cyclostome bryozoans:Testing a potential paleobathymetric tool[J]. Palaios,2007,22(2):220-224. doi: 10.2110/palo.2006.p06-064r
[5] VAN HINSBERGEN D J J,KOUWENHOVEN T J,VAN DER ZWAAN G J. Paleobathymetry in the backstripping procedure:Correction for oxygenation effects on depth estimates[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2005,221(3/4):245-265.
[6] MUTO T,STEEL R J. Role of autoretreat and A/S changes in the understanding of deltaic shoreline trajectory:a semi-quantitative approach[J]. Basin Research,2002,14(3):303-318. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2117.2002.00179.x
[7] HELLAND-HANSEN W,MARTINSEN O J. Shoreline trajectories and sequences:description of variable depositional-dip scenarios[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1996,66(4):670-688.
[8] HENRIKSEN S,HAMPSON G J,HELLAND-HANSEN W,et al. Shelf edge and shoreline trajectories,a dynamic approach to stratigraphic analysis[J]. Basin Research,2009,21(5):445-453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2009.00432.x
[9] 杨桥,漆家福,程秀申,等. 河南东濮凹陷古近系各组段的原始地层厚度分布及其构造古地理意义[J]. 古地理学报,2006,8(3):407-413. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2006.03.013
[10] 董刚,何幼斌. 根据地层厚度恢复古水深的研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版),2010,7(3):484-486.
[11] 龙祖烈,黄玉平,朱俊章,等. 南海珠江口盆地白云凹陷现今地温场与新生代构造-热演化特征[J]. 地质科学,2020,55(4):1266-1276. doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2020.075
[12] 胡杰,龙祖烈,黄玉平,等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷新生代构造-热演化模拟[J]. 地球物理学报,2021,64(5):1654-1665.
[13] HE L J,WANG K L,XIONG L P,et al. Heat flow and thermal history of the South China Sea[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,2001,126(3/4):211-220.
[14] 袁玉松,郑和荣,张功成,等. 南海北部深水区新生代热演化史[J]. 地质科学,2009,44(3):911-921. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.03.010
[15] 胡圣标,龙祖烈,朱俊章,等. 珠江口盆地地温场特征及构造-热演化[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(增刊):178-187.
[16] 龚再升, 李思田, 谢泰俊, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997.
[17] 吴时国,袁圣强. 世界深水油气勘探进展与我国南海深水油气前景[J]. 天然气地球科学,2005,16(6):693-699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2005.06.002
[18] 庞雄, 陈长民, 彭大钧, 等. 南海珠江深水扇系统及油气[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007.
[19] 朱伟林,钟锴,李友川,等. 南海北部深水区油气成藏与勘探[J]. 科学通报,2012,57(20):1833-1841.
[20] 陈长民, 施和生, 许仕策, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
[21] 张功成,杨海长,陈莹,等. 白云凹陷——珠江口盆地深水区一个巨大的富生气凹陷[J]. 天然气工业,2014,34(11):19-33.
[22] 米立军,柳保军,何敏,等. 南海北部陆缘白云深水区油气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气,2016,28(2):14-26.
[23] 龚再升. 中国近海盆地晚期断裂活动和油气成藏[J]. 中国石油勘探,2004,9(2):20-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2004.02.003
[24] 郭伟. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷东北部珠海组SQ5沉积体系分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.
[25] 徐少华. 南海北部白云凹陷SB23.8层序沉积体系研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.
[26] 郭雯,刘永涛,赵俊峰,等. 层拉平技术在地震解释中的深化应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2020,55(5):1110-1120.
[27] 刘永涛,刘池洋,周义军,等. 双界面地震层拉平的古地貌恢复技术及应用:以鄂尔多斯盆地天环坳陷为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2019,54(3):656-666.
[28] LIN C S, JIANG J, SHI H S, et al. Sequence architecture and depositional evolution of the northern continental slope of the South China Sea: responses to tectonic processes and changes in sea level. Basin Research, 2018, 30(1): 568-595.
[29] 林畅松,施和生,李浩,等. 南海北部珠江口盆地陆架边缘斜坡带层序结构和沉积演化及控制作用[J]. 地球科学,2018,43(10):3407-3422.
[30] 柳保军,庞雄,颜承志,等. 珠江口盆地白云深水区渐新世—中新世陆架坡折带演化及油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报,2011,32(2):234-242. doi: 10.7623/syxb201102007
[31] 王家豪,刘丽华,陈胜红,等. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷珠琼运动二幕的构造-沉积响应及区域构造意义[J]. 石油学报,2011,32(4):588-595. doi: 10.7623/syxb201104005
[32] 庞雄,陈长民,彭大钧,等. 南海珠江深水扇系统的层序地层学研究[J]. 地学前缘,2007,14(1):220-229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.01.021
[33] 李磊,王英民,徐强,等. 南海北部白云凹陷21Ma深水重力流沉积体系[J]. 石油学报,2012,33(5):798-806. doi: 10.7623/syxb201205008
[34] 李冬,徐强,王永凤,等. 南海珠江21Ma深水扇特征及控制因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2012,36(4):7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2012.04.002
[35] 徐少华, 王英民, 何敏, 等. 珠江口盆地陆坡类型及其对深水储层的控制[J]. 2016, 45(5): 982-992.
[36] 朱俊杰,张尚锋,朱锐,等. 珠江口盆地番禺低隆起A井区珠海组沉积研究[J]. 长江大学学报 (自然科学版),2011,8(2):20-22.
[37] 周家伟,王英民,何敏,等. 基于轨迹分析和数值模拟的陆架边缘沉积研究:以珠江口盆地13.8Ma陆架边缘三角洲为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(3):603-614.
[38] 柳保军,袁立忠,申俊,等. 南海北部陆坡古地貌特征与13.8Ma以来珠江深水扇[J]. 沉积学报,2006,24(4):476-482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.04.003
[39] 祝彦贺,朱伟林,徐强,等. 珠江口盆地13.8Ma陆架边缘三角洲与陆坡深水扇的“源−汇”关系[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2011,42(12):3827-3834.
[40] 易雪斐,张昌民,李少华,等. 珠江口盆地21Ma和13.8Ma陆架边缘三角洲对比[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2014,35(5):670-678. doi: 10.11743/ogg20140512
[41] 杨璐,王英民,何敏,等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷13.8Ma前后深水扇差异沉积过程及主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2018,39(4):791-800. doi: 10.11743/ogg20180416
[42] 姜静,张忠涛,李浩,等. 珠江口盆地东北陆架边缘斜坡带晚中新世—第四纪层序模式与单向迁移水道[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2019,40(4):864-874.
-




 下载:
下载: